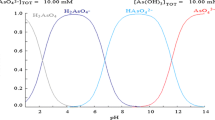
Abstract
Accessibility to clean drinking water often remains a crucial task at times. Among other water pollutants, arsenic is considered a more lethal contaminant and has become a serious threat to human life globally. This review discussed the sources, chemistry, distribution, and toxicity of arsenic and various conventional technologies that are in option for its removal from the water system. Nowadays, biosorbents are considered the best option for arsenic-contaminated water treatment. We have mainly focused on the need and potential of biosorbents especially the role of chitosan-based composites for arsenic removal. The chitosan-based sorbents are economically more efficient in terms of their, low toxicity, cost-effectiveness, biodegradability, eco-friendly nature, and reusability. The role of various modification techniques, such as physical and chemical, has also been evaluated to improve the physicochemical properties of biosorbent. The importance of adsorption kinetic and isotherm models and the role of solution pH and pHPZC for arsenic uptake from the polluted water have also been investigated. Some other potential applications of chitosan-based biosorbents have also been discussed along with its sustainability aspect. Finally, some suggestions have been highlighted for further improvements in this field.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abd El-Monaem EM, Eltaweil AS, Elshishini HM, Hosny M, Abou Alsoaud MM, Attia NF, El-Subruiti GM, Omer AM (2022) Sustainable adsorptive removal of antibiotic residues by chitosan composites: an insight into current developments and future recommendations. Arab J Chem 103743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.103743
Abdellaoui Y, El Ibrahimi B, Abou Oualid H, Kassab Z, Quintal-Franco C, Giácoman-Vallejos G, Gamero-Melo P (2021) Iron-zirconium microwave-assisted modification of small-pore zeolite W and its alginate composites for enhanced aqueous removal of As(V) ions: experimental and theoretical studies. Chem Eng J 421:129909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129909
Abdul Mubarak NS, Bahrudin N, Jawad AH, Hameed B, Sabar S (2021) Microwave enhanced synthesis of sulfonated chitosan-montmorillonite for effective removal of methylene blue. J Polym Environ 29:4027–4039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02172-9
Abdulhameed AS, Mohammad A, Jawad AH (2019) Modeling and mechanism of reactive orange 16 dye adsorption by chitosan-glyoxal/TiO2 nanocomposite: application of response surface methodology. Desalin Water Treat 164:346–360. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24384
Afshin S, Rashtbari Y, Vosough M, Dargahi A, Fazlzadeh M, Behzad A, Yousefi M (2021) Application of Box–Behnken design for optimizing parameters of hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions using Fe3O4 loaded on activated carbon prepared from alga: kinetics and equilibrium study. J Water Process Eng https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102113
Ahmad K, Naseem HA, Parveen S, Shah SSA, Shaheen S, Ashfaq A, Jamil J, Ahmad MM, Ashfaq M (2019) Synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of medicinal azo derivatives and metal complexes of Indandion. J Mol Struct 1198:126885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.126885
Ahmad K, Nazir MA, Qureshi AK, Hussain E, Najam T, Javed MS, Shah SSA, Tufail MK, Hussain S, Khan NA (2020) Engineering of Zirconium based metal-organic frameworks (Zr-MOFs) as efficient adsorbents. Mater Sci Eng B 262:114766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114766
Ahmad K, Ashfaq M, Nawaz H (2021a) Removal of decidedly lethal metal arsenic from water using metal organic frameworks: a critical review. Rev Inorg Chem. https://doi.org/10.1515/revic-2021a-0005
Ahmad K, Ashfaq M, Shah SSA, Hussain E, Naseem HA, Parveen S, Ayub A (2021b) Effect of metal atom in zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIF-8 & 67) for removal of Pb2+ & Hg2+ from water. Food Chem Food Chem Toxicol 149:112008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112008
Ahmad K, H-u-R S, Ashfaq A, Ashfaq M, Kashif M, Naseem HA, Aziz T, Parveen S, Nazir I (2021c) Synthesis of new series of phenyldiazene based metal complexes for designing most active antibacterial and antifungal agents. J Chem Soc Pak 43:578–586. https://doi.org/10.52568/000599/JCSP/43.05.2021
Ahmad K, Shah H-U-R, Nasim HA, Ayub A, Ashfaq M, Rauf A, Shah SSA, Ahmad MM, Nawaz H, Hussain E (2021d) Synthesis and characterization of water stable polymeric metallo organic composite (PMOC) for the removal of arsenic and lead from brackish water. Toxin Rev. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2021d.1919902
Ahmadi M, Niari MH, Kakavandi B (2017) Development of maghemite nanoparticles supported on cross-linked chitosan (γ-Fe2O3@ CS) as a recoverable mesoporous magnetic composite for effective heavy metals removal. J Mol Liq 248:184–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.10.014
Ali N, Khan A, Bilal M, Malik S, Badshah S, Iqbal H (2020) Chitosan-based bio-composite modified with thiocarbamate moiety for decontamination of cations from the aqueous media. Molecules 25:226. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010226
Alka S, Shahir S, Ibrahim N, Ndejiko MJ, Vo D-VN, Abd Manan F (2021) Arsenic removal technologies and future trends: a mini review. J Clean Prod 278:123805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123805
Altowayti WAH, Almoalemi H, Shahir S, Othman N (2020a) Comparison of culture-independent and dependent approaches for identification of native arsenic-resistant bacteria and their potential use for arsenic bioremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 205:111267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111267
Altowayti WAH, Haris SA, Almoalemi H, Shahir S, Zakaria Z, Ibrahim S (2020b) The removal of arsenic species from aqueous solution by indigenous microbes: batch bioadsorption and artificial neural network model. Environ Technol Innov 19:100830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100830
Alves HJ, Gasparrini LJ, Silva FEB, Caciano L, de Muniz GIB, Ballester ELC, Cremonez PA, Arantes MK (2021) Alternative methods for the pilot-scale production and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:10977–10987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11343-5
Amen R, Bashir H, Bibi I, Shaheen SM, Niazi NK, Shahid M, Hussain MM, Antoniadis V, Shakoor MB, Al-Solaimani SG (2020) A critical review on arsenic removal from water using biochar-based sorbents: the significance of modification and redox reactions. Chem Eng J 396:125195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125195
Aramesh N, Bagheri AR, Bilal M (2021) Chitosan-composite/hybrid biomaterials for adsorptive removal of dyes and underlying interaction mechanisms. Int J Biol Macromol 183:399–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.158
Araujo SF, Caldeira CL, Ciminelli VS, Borba RP, Rodrigues JP, Simões GF (2022) Basic oxygen furnace sludge to treat industrial arsenic-and sulfate-rich acid mine drainage. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18120-y
Ayele A, Haile S, Alemu D, Kamaraj M (2021) Comparative utilization of dead and live fungal biomass for the removal of heavy metal: a concise review. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5588111
Ayub A, Raza ZA, Majeed MI, Tariq MR, Irfan A (2020) Development of sustainable magnetic chitosan biosorbent beads for kinetic remediation of arsenic contaminated water. Int J Bio Macromol 163:603–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.287
Ayub A, Raza ZA (2021) Arsenic removal approaches: a focus on chitosan biosorption to conserve the water sources. Int J Biol Macromol 192:1196–1216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.050
Ayub A, Irfan A, Raza ZA, Abbas M, Muhammad A, Ahmad K, Munwar A (2022) Development of poly (1-vinylimidazole)-chitosan composite sorbent under microwave irradiation for enhanced uptake of Cd (II) ions from aqueous media. Polym Bull 79:807–827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03523
Bahrudin N, Nawi M, Jawad AH, Sabar S (2020) Adsorption characteristics and mechanistic study of immobilized chitosan-montmorillonite composite for methyl orange removal. J Polym Environ 28:1901–1913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01734-7
Bajpai A (2019) Facile preparation of ionotropically crosslinked chitosan-alginate nanosorbents by water-in-oil (W/O) microemulsion technique: optimization and study of arsenic (V) removal. J Water Process 32(100920):100920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100920
Battampara P, Sathish TN, Reddy R, Guna V, Nagananda G, Reddy N, Ramesha B, Maharaddi V, Rao AP, Ravikumar H (2020) Properties of chitin and chitosan extracted from silkworm pupae and egg shells. Int J Biol Macromol 161:1296–1304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.161
Begum S, Yuhana NY, Saleh NM, Kamarudin NN, Sulong AB (2021) Review of chitosan composite as a heavy metal adsorbent: material preparation and properties. Carbohydr Polym 259:117613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117613
Bertin PN, Crognale S, Plewniak F, Battaglia-Brunet F, Rossetti S, Mench M (2021) Water and soil contaminated by arsenic: the use of microorganisms and plants in bioremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17817-4
Bisaria K, Wadhwa S, Mathur A, Roy S, Dixit A, Singh R (2022) New bismuth oxyiodide/chitosan nanocomposite for ultrasonic waves expedited adsorptive removal of amoxicillin from aqueous medium: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic investigations. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 1-17 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17546-8
Bruckmann FdS, Rossato Viana A, Tonel MZ, Fagan SB, Garcia WJdS, Oliveira AHd, Dorneles LS, Roberto Mortari S, Silva WLd, Silva IZd (2022) Influence of magnetite incorporation into chitosan on the adsorption of the methotrexate and in vitro cytotoxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20786-x
Çermikli E, Şen F, Altıok E, Wolska J, Cyganowski P, Kabay N, Bryjak M, Arda M, Yüksel M (2020) Performances of novel chelating ion exchange resins for boron and arsenic removal from saline geothermal water using adsorption-membrane filtration hybrid process. Desalination 491:114504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114504
Chauhan D, Dwivedi J, Sankararamakrishnan N (2014) Novel chitosan/PVA/zerovalent iron biopolymeric nanofibers with enhanced arsenic removal applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9430–9442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2864-12
Choi J-S, Lingamdinne LP, Yang J-K, Chang Y-Y, Koduru JR (2020) Fabrication of chitosan/graphene oxide-gadolinium nanorods as a novel nanocomposite for arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. J Mol Liq 320(114410):114410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114410
Corroto C, Iriel A, Cirelli AF, Carrera AP (2019) Constructed wetlands as an alternative for arsenic removal from reverse osmosis effluent. Sci Total Environ 691:1242–1250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.234
Coyte RM, Vengosh A (2020) Factors controlling the risks of co-occurrence of the redox-sensitive elements of arsenic, chromium, vanadium, and uranium in groundwater from the eastern United States. Environ Sci Technol 54:4367–4375. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06471
Darvishi Cheshmeh Soltani R, Safari M, Maleki A, Rezaee R, Shahmoradi B, Shahmohammadi S, Ghahramani E (2017) Decontamination of arsenic (V)-contained liquid phase utilizing Fe3O4/bone char nanocomposite encapsulated in chitosan biopolymer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:15157–15166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9128-9
de Vargas BG, de Andrade JR, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2020) Removal of toxic metals from water using chitosan-based magnetic adsorbents. A Review Environ Chem Lett 18:1145–1168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01003-y
Dev VV, Baburaj G, Antony S, Arun V, Krishnan KA (2020) Zwitterion-chitosan bed for the simultaneous immobilization of Zn (II), Cd (II), Pb (II) and Cu (II) from multi-metal aqueous systems. J Clean Prod 255:120309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120309
Dhoble RM, Maddigapu PR, Rayalu SS, Bhole A, Dhoble AS, Dhoble SR (2017) Removal of arsenic (III) from water by magnetic binary oxide particles (MBOP): experimental studies on fixed bed column. J Hazard Mater 322:469–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.075
Dima JB, Sequeiros C, Zaritzky N (2017) Chitosan from marine crustaceans: production, characterization and applications, In: E A Shalaby (ed) Biological activities and application of marine polysaccharides. IntechOpen, London, pp 39–56 https://doi.org/10.5772/65258
Ding W, Wan X, Zheng H, Wu Y, Muhammad S (2021) Sulfite-assisted oxidation/adsorption coupled with a TiO2 supported CuO composite for rapid arsenic removal: performance and mechanistic studies. J Hazard Mater 413:125449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125449
Elkady M, Salama E, Amer WA, Ebeid E-ZM, Ayad MM, Shokry H (2020) Novel eco-friendly electrospun nanomagnetic zinc oxide hybridized PVA/alginate/chitosan nanofibers for enhanced phenol decontamination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:43077–43092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10247-8
Faniband SM, Vidyasagar C, Jimenez V, Shridhar A (2022) Mechanistic insight into the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant and electrochemical behavior of modified MWCNTs/Cu-Co3O4 nanocomposite. React Chem Eng 01-26. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RE00117A
Fekry M, Elmesallamy SM, El-Rahman NRA, Bekhit M, Elsaied HA (2022) Eco-friendly adsorbents based on abietic acid, boswellic acid, and chitosan/magnetite for removing waste oil from the surface of the water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20169-2
Ferrah N, Merghache D, Meftah S, Benbellil S (2022) A new alternative of a green polymeric matrix chitosan/alginate-polyethyleniminemethylene phosphonic acid for pharmaceutical residues adsorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:13675–13687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16599-z
Gabris MA, Rezania S, Rafieizonooz M, Khankhaje E, Devanesan S, AlSalhi MS, Aljaafreh MJ, Shadravan A (2022) Chitosan magnetic graphene grafted polyaniline doped with cobalt oxide for removal of arsenic (V) from water. Environ Res 207:112209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112209
Gao Z, Jiang C, Lyu R, Yang Z, Zhang T (2020) Optimization of the preparation of fungal-algal pellets for use in the remediation of arsenic-contaminated water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:36789–36798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09757-2
García-García JJ, Gómez-Espinosa RM, Rangel RN, Romero RR, Morales GR (2022) New material for arsenic (V) removal based on chitosan supported onto modified polypropylene membrane. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:1909–1916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15725-1
Ghiasi F, Solaimany Nazar AR, Farhadian M, Tangestaninejad S, Emami N (2022) Synthesis of aqueous media stable MIL101-OH/chitosan for diphenhydramine and metronidazole adsorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:24286–24297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17739-1
Gonçalves JO, da Silva KA, Rios EC, Crispim MM, Dotto GL, de Almeida Pinto LA (2020) Chitosan hydrogel scaffold modified with carbon nanotubes and its application for food dyes removal in single and binary aqueous systems. Int J Biol Macromol 142:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.074
Gopinath KP, Madhav NV, Krishnan A, Malolan R, Rangarajan G (2020) Present applications of titanium dioxide for the photocatalytic removal of pollutants from water: a review. J Environ Manage 270:110906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110906
Guo J, Cheng J, Wang J, Hu S (2021) Simultaneous removal of trivalent arsenic and nitrate using microbial fuel cells. Processes 9:673. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040673
Han C, Yang T, Liu H, Yang L, Luo Y (2019) Characterizations and mechanisms for synthesis of chitosan-coated Na–X zeolite from fly ash and As (V) adsorption study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:10106–10116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04466-x
Hannachi Y, Hafidh A (2020) Biosorption potential of Sargassum muticum algal biomass for methylene blue and lead removal from aqueous medium. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:3875–3890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02742-9
Heidarzadeh-Samani M, Behzad T, Mehrabani-Zeinabad A (2021) Development of a continuous fixed–bed column to eliminate cadmium (II) ions by starch-g-poly (acrylic acid)/cellulose nanofiber bio-nanocomposite hydrogel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:57902–57917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14567-1
Heydaripour J, Gazi M, Oladipo AA, Gulcan HO (2019) Porous magnetic resin-g-chitosan beads for adsorptive removal of phenolic compounds. Int J Biol Macromol 123:1125–1131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.168
Hu W, Niu Y, Zhu H, Dong K, Wang D, Liu F (2021) Remediation of zinc-contaminated soils by using the two-step washing with citric acid and water-soluble chitosan. Chemosphere 282:131092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131092
Humelnicu D, Lazar MM, Ignat M, Dinu IA, Dragan ES, Dinu MV (2020) Removal of heavy metal ions from multi-component aqueous solutions by eco-friendly and low-cost composite sorbents with anisotropic pores. J Hazard Mater 381:120980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120980
Jawad AH, Nawi M (2012) Fabrication, optimization and application of an immobilized layer-by-layer TiO 2/Chitosan system for the removal of phenol and its intermediates under 45-W fluorescent lamp. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 106:49–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-011-0396-y
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Facile synthesis of crosslinked chitosan-tripolyphosphate/kaolin clay composite for decolourization and COD reduction of remazol brilliant blue R dye: optimization by using response surface methodology. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 605:125329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125329
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Abd Malek NN, ALOthman ZA, (2020) Statistical optimization and modeling for color removal and COD reduction of reactive blue 19 dye by mesoporous chitosan-epichlorohydrin/kaolin clay composite. Int J Biol Macromol 164:4218–4230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.201
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Kashi E, Yaseen ZM, ALOthman ZA, Khan MR, (2022) Cross-linked chitosan-glyoxal/kaolin clay composite: parametric optimization for color removal and COD reduction of remazol brilliant blue R dye. J Polym Environ 30:164–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02188-1
Joseph SM, Krishnamoorthy S, Paranthaman R, Moses J, Anandharamakrishnan C (2021) A review on source-specific chemistry, functionality, and applications of chitin and chitosan. Carbohydr Polym Technol Appl 2:100036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2021.100036
Kabir F, Chowdhury S (2017) Arsenic removal methods for drinking water in the developing countries: technological developments and research needs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24102–24120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0240-7
Kalaitzidou K, Zouboulis A, Mitrakas M (2020) Cost evaluation for Se (IV) removal, by applying common drinking water treatment processes: coagulation/precipitation or adsorption. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104209
Kamari A, Pulford I, Hargreaves J (2011) Chitosan as a potential amendment to remediate metal contaminated soil—A characterisation study. Colloids Surf B 82:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.08.019
Kim N, Seo JH, Yun Y-S, Park D (2020) New insight into continuous recirculation-process for treating arsenate using bacterial biosorbent. Bioresour Technol 316:123961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123961
Kloster GA, Valiente M, Marcovich NE, Mosiewicki MA (2020) Adsorption of arsenic onto films based on chitosan and chitosan/nano-iron oxide. Int J Biol Macromol 165:1286–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.244
Kluczka J (2020) Removal of Boron and Manganese Ions from Wet-Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater by Hybrid Chitosan-Zirconium Sorbent. Polymers 12:635. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030635
Kuczajowska-Zadrożna M, Filipkowska U, Jóźwiak T (2020) Adsorption of Cu (II) and Cd (II) from aqueous solutions by chitosan immobilized in alginate beads. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103878
Kumar I, Quaff A (2019) Comparative study on the effectiveness of natural coagulant aids and commercial coagulant: removal of arsenic from water. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:5989–5994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1980-
Kumararaja P, Manjaiah K, Datta S, Shabeer TA, Sarkar B (2018) Chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid)-bentonite composite: a potential immobilizing agent of heavy metals in soil. Cellulose 25:3985–3999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1828-x
Kwok K, Koong LF, Al Ansari T, McKay G (2018) Adsorption/desorption of arsenite and arsenate on chitosan and nanochitosan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:14734–14742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1501-9
Kyzas GZ, Siafaka PI, Pavlidou EG, Chrissafis KJ, Bikiaris DN (2015) Synthesis and adsorption application of succinyl-grafted chitosan for the simultaneous removal of zinc and cationic dye from binary hazardous mixtures. Chem Eng J 259:438–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.019
Lei C, Wang C, Chen W, He M, Huang B (2020) Polyaniline@ magnetic chitosan nanomaterials for highly efficient simultaneous adsorption and in-situ chemical reduction of hexavalent chromium: removal efficacy and mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 733:139316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139316
Leichner C, Jelkmann M, Prüfert F, Laffleur F, Bernkop-Schnürch A (2019) Intestinal enzyme delivery: Chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles providing a targeted release behind the mucus gel barrier. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 144:125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.09.012
Li H, Ji H, Cui X, Che X, Zhang Q, Zhong J, Jin R, Wang L, Luo Y (2021) Kinetics, thermodynamics, and equilibrium of As (III), Cd (II), Cu (II) and Pb (II) adsorption using porous chitosan bead-supported MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Int J Min Sci Technol 31:1107–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.10.004
Liang X, Li Y, Tang S, Shi X, Zhou N, Liu K, Ma J, Yu F, Li Y (2022) Mechanism underlying how a chitosan-based phosphorus adsorbent alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Bidens pilosa L. and its impact on soil microbial communities: a field study. Chemosphere 295:133943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133943
Liu J, Liu W, Wang Y, Xu M, Wang B (2016) A novel reusable nanocomposite adsorbent, xanthated Fe3O4-chitosan grafted onto graphene oxide, for removing Cu (II) from aqueous solutions. Appl Surf Sci 367:327–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.176
Liu Y, Jia J, Zhang H, Sun S (2022) Enhanced Cr (VI) stabilization in soil by chitosan/bentonite composites. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 238:113573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113573
Lobo C, Castellari J, Lerner JC, Bertola N, Zaritzky N (2020) Functional iron chitosan microspheres synthesized by ionotropic gelation for the removal of arsenic (V) from water. Int J Biol Macromol 164:1575–1583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020
Lou S, Liu B, Qin Y, Zeng Y, Zhang W, Zhang L (2021) Enhanced removal of As (III) and As (V) from water by a novel zirconium-chitosan modified spherical sodium alginate composite. Int J Biol Macromol 176:304–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021
Lu H, Wang J, Stoller M, Wang T, Bao Y, Hao H (2016) An overview of nanomaterials for water and wastewater treatment. Advances in Mater Sci Eng 2016:4964828. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4964828
Luo J, Fan C, Xiao Z, Sun T, Zhou X (2019) Novel graphene oxide/carboxymethyl chitosan aerogels via vacuum-assisted self-assembly for heavy metal adsorption capacity. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 578:123584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123584
Md Rasid H, Aziz N, Abdul Ghani FS, Abdullah N (2020): Removal of Lead (II) and Chromium (III) from aqueous solution by using organic-functionalized MCM-41. Sci. Lett. J. 14, 23–33 https://doi.org/10.24191/sl.v14i1.7898
Meng F, Yang B, Wang B, Duan S, Chen Z, Ma W (2017) Novel dendrimerlike magnetic biosorbent based on modified orange peel waste: adsorption–reduction behavior of arsenic. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:9692–9700. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b01273
Moghaddam MH, Nabizadeh R, Dehghani MH, Akbarpour B, Azari A, Yousefi M (2019) Performance investigation of Zeolitic Imidazolate framework–8 (ZIF-8) in the removal of trichloroethylene from aqueous solutions. Microchem J 150:104185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104185
Mora BP, Bellu S, Mangiameli MF, Frascaroli MI, González JC (2019) Response surface methodology and optimization of arsenic continuous sorption process from contaminated water using chitosan. J Water Process 32:100913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100913
Morin-Crini N, Winterton P, Fourmentin S, Wilson LD, Fenyvesi E, Crini G (2018) Water-insoluble β-cyclodextrin–epichlorohydrin polymers for removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions by sorption processes using batch studies: a review of inclusion mechanisms. Prog Polym Sci 78:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.07.004
Mu C, Zhang L, Zhang X, Zhong L, Li Y (2020) Selective adsorption of Ag (I) from aqueous solutions using Chitosan/polydopamine@ C@ magnetic fly ash adsorbent beads. J Hazard Mater 381:120943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120943
Mukhopadhyay M, Lakhotia SR, Ghosh A, Bindal R (2019) Removal of arsenic from aqueous media using zeolite/chitosan nanocomposite membrane. Sep Sci Technol 54:282–288. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1459704
Naga Babu A, Raja Sree T, Srinivasa Reddy D, Suresh Kumar G, Krishna Mohan G (2021) Experimental and statistical analysis of As (III) adsorption from contaminated water using activated red mud doped calcium-alginate beads. Environ Technol 42:1810–1825. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1681520
Nicomel NR, Leus K, Folens K, Van Der Voort P, Du Laing G (2016) Technologies for arsenic removal from water: current status and future perspectives. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13:62. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13010062
Nina M, Fathana H, Iqhrammullah M (2022) Preparation and characterization of new magnetic chitosan-glycine-PEGDE (Fe3O4/Ch-GP) beads for aqueous Cd (II) removal. J Water Process 45:102493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102493
Ociński D (2019) Optimization of hybrid polymer preparation by ex situ embedding of waste Fe/Mn oxides into chitosan matrix as an effective As (III) and As (V) sorbent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:26026–26038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05856-x
Oladoye PO (2022) Natural, low-cost adsorbents for toxic Pb (II) ion sequestration from (waste) water: a state-of-the-art review. Chemosphere 287:132130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132130
Pan C, Qian J, Zhao C, Yang H, Zhao X, Guo H (2020) Study on the relationship between crosslinking degree and properties of TPP crosslinked chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 241:116349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116349
Pandey N, Shukla S, Singh N (2017) Water purification by polymer nanocomposites: an overview. Nanocomposites 3:47–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/20550324.2017.1329983
Pérez-Calderón J, Scian A, Ducos M, Santos V, Zaritzky N (2021) Performance of oxalic acid-chitosan/alumina ceramic biocomposite for the adsorption of a reactive anionic azo dye. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:67032–67052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15123-7
Pincus LN, Petrović PV, Gonzalez IS, Stavitski E, Fishman ZS, Rudel HE, Anastas PT, Zimmerman JB (2021) Selective adsorption of arsenic over phosphate by transition metal cross-linked chitosan. Chem Eng J 412(128582):128582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128582
Pompeu LD, Muraro PCL, Chuy G, Vizzotto BS, Pavoski G, Espinosa DCR, da Silva Fernandes L, da Silva WL (2022) Adsorption for rhodamine b dye and biological activity of nano-porous chitosan from shrimp shells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19259-y
Pramod L, Gandhimathi R, Lavanya A, Ramesh S, Nidheesh P (2020) Heterogeneous Fenton process coupled with microfiltration for the treatment of water with higher arsenic content. Chem Eng Commun 207:1646–1657. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2019.1674814
Priya VN, Rajkumar M, Magesh G, Mobika J, Sibi SL (2020) Chitosan assisted Fe-Al double layered hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide composites for As (V) removal. Mater Chem Phys 251:123108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123108
Qu B, Luo Y (2020) Chitosan-based hydrogel beads: preparations, modifications and applications in food and agriculture sectors–A review. Int J Biol Macromol 152:437–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.240
Raval NP, Mukherjee S, Shah NK, Gikas P, Kumar M (2020) Hexametaphosphate cross-linked chitosan beads for the eco-efficient removal of organic dyes: tackling water quality. J Environ Manage 280:111680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111680
Rawat S, Maiti A (2021) Facile preparation of iron oxyhydroxide–biopolymer (Chitosan/Alginate) beads and their comparative insights into arsenic removal. Sep Purif Technol 272:118983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118983
Raza ZA, Khalil S, Ayub A, Banat IM (2020) Recent developments in chitosan encapsulation of various active ingredients for multifunctional applications. Carbohydr Res 492:108004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2020.108004
Raza ZA, Munim S, Ayub A (2021) Recent developments in polysaccharide-based electrospun nanofibers for environmental applications. Carbohydr Res 510:108443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2021.108443
Reghioua A, Barkat D, Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Rangabhashiyam S, Khan MR, ALOthman ZA, (2021) Magnetic chitosan-glutaraldehyde/zinc oxide/Fe3O4 nanocomposite: optimization and adsorptive mechanism of remazol brilliant blue R dye removal. J Polym Environ 29:3932–3947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02160-z
Ribeiro ICA, Vasques ICF, Teodoro JC, Guerra MBB, da Silva Carneiro JS, Melo LCA, Guilherme LRG (2021) Fast and effective arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by a novel low-cost eggshell byproduct. Sci Total Environ 783:147022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147022
Saeed RM, Dmour I, Taha MO (2020) Stable chitosan-based nanoparticles using polyphosphoric acid or hexametaphosphate for tandem ionotropic/covalent crosslinking and subsequent investigation as novel vehicles for drug delivery. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00004
Safie N, Zahrim A (2021) Recovery of nutrients from sewage using zeolite-chitosan-biochar adsorbent: current practices and perspectives. J Water Process 40:101845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101845
Saha S, Sarkar P (2016) Arsenic mitigation by chitosan-based porous magnesia-impregnated alumina: performance evaluation in continuous packed bed column. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:243–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0806-1
Saleh S, Mohammadnejad S, Khorgooei H, Otadi M (2021) Photooxidation/adsorption of arsenic (III) in aqueous solution over Bentonite/Chitosan/TiO2 heterostructured catalyst. Chemosphere 280:130583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130583
Salehi E, Daraei P, Shamsabadi AA (2016) A review on chitosan-based adsorptive membranes. Carbohyd Polym 152:419–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.033
Salih SS, Mahdi A, Kadhom M, Ghosh TK (2019) Competitive adsorption of As (III) and As (V) onto chitosan/diatomaceous earth adsorbent. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103407
Sanakousar F, Vidyasagar C, Jiménez-Pérez V, Prakash K (2022) Recent progress on visible-light-driven metal and non-metal doped ZnO nanostructures for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Mater Sci Semicond Process 140:106390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2021.106390
Sanakousar M, Vidyasagar CC, Jiménez-Pérez VM, Jayanna B, Shridhar A, Prakash K (2021) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet dye and electrochemical performance of modified MWCNTs/Cd-ZnO nanoparticles with quantum chemical calculations. J Hazard Mater Adv 2:100004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2021.100004
Saravanan A, Karishma S, Kumar PS, Varjani S, Yaashikaa P, Jeevanantham S, Ramamurthy R, Reshma B (2021) Simultaneous removal of Cu (II) and reactive green 6 dye from wastewater using immobilized mixed fungal biomass and its recovery. Chemosphere 271:129519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129519
Sawood GM, Mishra A, Gupta S (2021) Optimization of arsenate adsorption over aluminum-impregnated tea waste biochar using RSM–central composite design and adsorption mechanism. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 25:04020075. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000581
Schiffer S, Matyssek A, Hartinger M, Bolduan P, Mund P, Kulozik U (2021) Effects of selective layer properties of ceramic multi-channel microfiltration membranes on the milk protein fractionation. Sep Purif Technol 259:118050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118050
Şenol ZM (2021) A chitosan-based composite for absorption of uranyl ions; mechanism, isothems, kinetics and thermodynamics. Int J Biol Macromol 183:1640–1648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.130
Shakoor MB, Niazi NK, Bibi I, Shahid M, Saqib ZA, Nawaz MF, Shaheen SM, Wang H, Tsang DC, Bundschuh J (2019) Exploring the arsenic removal potential of various biosorbents from water. Environ Int 123:567–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.049
Shan H, Peng S, Zhao C, Zhan H, Zeng C (2020) Highly efficient removal of As (III) from aqueous solutions using goethite/graphene oxide/chitosan nanocomposite. Int J Biol Macromol 164:13–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.108
Sherlala A, Raman A, Bello MM, Buthiyappan A (2019) Adsorption of arsenic using chitosan magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite. J Environ Manage 246:547–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.117
Sheth Y, Dharaskar S, Khalid M, Sonawane S (2021) An environment friendly approach for heavy metal removal from industrial wastewater using chitosan based biosorbent: a review. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 43:100951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2020.100951
Shi Q-X, Li Y, Wang L, Wang J, Cao Y-L (2020) Preparation of supported chitosan adsorbent with high adsorption capacity for Titan Yellow removal. Int J Biol Macromol 152:449–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.265
Siddiqui SI, Chaudhry SA (2017) Arsenic removal from water using nanocomposites: a review. Curr Environ Eng 4:81–102. https://doi.org/10.2174/2212717804666161214143715
Sirajudheen P, Karthikeyan P, Ramkumar K, Meenakshi S (2020) Effective removal of organic pollutants by adsorption onto chitosan supported graphene oxide-hydroxyapatite composite: a novel reusable adsorbent. J Mol Liq 318:114200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114200
Son E-B, Poo K-M, Chang J-S, Chae K-J (2018) Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions using engineered magnetic biochars derived from waste marine macro-algal biomass. Sci Total Environ 615:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.171
Su F, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Wang G (2016) Three-dimensional honeycomb-like structured zero-valent iron/chitosan composite foams for effective removal of inorganic arsenic in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 478:421–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.06.03
Su H, Ye Z, Hmidi N (2017) High-performance iron oxide–graphene oxide nanocomposite adsorbents for arsenic removal. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 522:161–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.02.065
Surgutskaia NS, Di Martino A, Zednik J, Ozaltin K, Lovecká L, Bergerová ED, Kimmer D, Svoboda J, Sedlarik V (2020) Efficient Cu2+, Pb2+ and Ni2+ ion removal from wastewater using electrospun DTPA-modified chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers. Sep Purif Technol 247:116914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116914
Sutirman ZA, Rahim EA, Sanagi MM, Abd Karim KJ, Ibrahim WAW (2020) New efficient chitosan derivative for Cu (II) ions removal: characterization and adsorption performance. Int J Biol Macromol 153:513–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.015
Talukder ME, Pervez MN, Jianming W, Gao Z, Stylios GK, Hassan MM, Song H, Naddeo V (2021) Chitosan-functionalized sodium alginate-based electrospun nanofiber membrane for As (III) removal from aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106693
Tang S, Yang J, Lin L, Peng K, Chen Y, Jin S, Yao W (2020) Construction of physically crosslinked chitosan/sodium alginate/calcium ion double-network hydrogel and its application to heavy metal ions removal. Chem Eng J 393:124728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124728
Tanvi DA, Pratam K, Lohit R, Vijayalakshmi B, Devaraja T, Vasudha M, Ramesh A, Chakra PS, Gayathri D (2020) Biosorption of heavy metal arsenic from Industrial Sewage of Davangere District, Karnataka, India, using indigenous fungal isolates. SN Appl Sci 2:1860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03622-0
Tapouk FA, Nabizadeh R, Nasseri S, Mesdaghinia A, Khorsandi H, Yousefi M, Alimohammadi M, Khoobi M (2020) Embedding of L-Arginine into graphene oxide (GO) for endotoxin removal from water: modeling and optimization approach. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 607:125491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125491
Tariq MR, Raza ZA, Majeed MI, Ayub A, Khubaib MA (2022) Bioreactor scale co-production of poly (hydroxyalkanoate) and rhamnolipids with distinct nitrogen sources. Biologia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01014-w
Thiruselvi D, Kumar PS, Kumar MA, Lay C-H, Aathika S, Mani Y, Jagadiswary D, Dhanasekaran A, Shanmugam P, Sivanesan S (2021) A critical review on global trends in biogas scenario with its up-gradation techniques for fuel cell and future perspectives. Int J Hydrog Energy 46:16734–16750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.10.023
Upadhyay U, Sreedhar I, Singh SA, Patel CM, Anitha K (2020) Recent advances in heavy metal removal by chitosan based adsorbents. Carbohydr Polym 251:117000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117000
Upadhyay U, Sreedhar I, Singh SA, Patel CM, Anitha K (2021) Recent advances in heavy metal removal by chitosan based adsorbents. Carbohydr Polym 251:117000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117000
Usman M, Katsoyiannis I, Rodrigues JH, Ernst M (2021) Arsenate removal from drinking water using by-products from conventional iron oxyhydroxides production as adsorbents coupled with submerged microfiltration unit. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:59063–59075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08327-w
Vakili M, Deng S, Li T, Wang W, Wang W, Yu G (2018) Novel crosslinked chitosan for enhanced adsorption of hexavalent chromium in acidic solution. Chem Eng J 347:782–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.181
Vasilieva S, Lobakova E, Grigoriev T, Selyakh I, Semenova L, Chivkunova O, Gotovtsev P, Antipova C, Zagoskin Y, Scherbakov P (2021) Bio-inspired materials for nutrient biocapture from wastewater: microalgal cells immobilized on chitosan-based carriers. J Water Process 40:101774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101774
Vedula SS, Yadav GD (2021) Chitosan-based membranes preparation and applications: challenges and opportunities. J Indian Chem Soc 98:100017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jics.2021.100017
Vijayasri K, Tiwari A (2021) Detoxification of arsenic from contaminated water using chitosan and radiation-induced grafted chitosan: a comparative study. Chem Ecol 37:323–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2021.1886280
Wang D, Root RA, Chorover J (2021a) Biochar-templated surface precipitation and inner-sphere complexation effectively removes arsenic from acid mine drainage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:45519–45533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13869-8
Wang S, Lu Y, Ouyang X-k, Liang XX, Yu D, Yang L-Y, Huang F (2019) Fabrication of chitosan-based MCS/ZnO@ Alg gel microspheres for efficient adsorption of As (V). Int J Biol Macromol 139:886–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.070
Wang X, Liu Y, Zheng J (2016) Removal of As (III) and As (V) from water by chitosan and chitosan derivatives: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:13789–13801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6602-8
Wang Z, Liao P, He X, Wan P, Hua B, Deng B (2021b) Enhanced arsenic removal from water by mass re-equilibrium: kinetics and performance evaluation in a binary-adsorbent system. Water Res 190:116676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116676
Wei Y, Yu X, Liu C, Ma J, Wei S, Chen T, Yin K, Liu H, Luo S (2019) Enhanced arsenite removal from water by radially porous Fe-chitosan beads: adsorption and H2O2 catalytic oxidation. J Hazard Mater 373:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.070
Wen J, Yang C, Chen X, Qiu M, Fan Y (2021) Effective and efficient fabrication of high-flux tight ZrO2 ultrafiltration membranes using a nanocrystalline precursor. J Membr Sci 634:119378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119378
Xue Q, Ran Y, Tan Y, Peacock CL, Du H (2019) Arsenite and arsenate binding to ferrihydrite organo-mineral coprecipitate: implications for arsenic mobility and fate in natural environments. Chemosphere 224:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.118
Yadav P, Yadav A, Labhasetwar PK (2022) Sustainable adsorptive removal of antibiotics from aqueous streams using Fe3O4-functionalized MIL101 (Fe) chitosan composite beads. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18385-3
Ye Y, Zhang T, Lv L, Chen Y, Tang W, Tang S (2021) Functionalization of chitosan by grafting sulfhydryl groups to intensify the adsorption of arsenite from water. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 622:126601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126601
Yi L, Yang J, Fang X, Xia Y, Zhao L, Wu H, Guo S (2020) Facile fabrication of wood-inspired aerogel from chitosan for efficient removal of oil from Water. J Hazard Mater 385:121507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121507
Yousefi M, Gholami M, Oskoei V, Mohammadi AA, Baziar M, Esrafili A (2021) Comparison of LSSVM and RSM in simulating the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions using magnetization of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes: process optimization using GA and RSM techniques. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105677. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2021.105677
Yuan D, Zhang W, Cui J, He L, Wang J, Yan C, Kou Y, Li J (2020) Facile fabrication of magnetic phosphorylated chitosan for the removal of Co (II) in water treatment: separation properties and adsorption mechanisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:2588–2598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07026-5
Yusof MSM, Othman MHD, Wahab RA, Jumbri K, Razak FIA, Kurniawan TA, Samah RA, Mustafa A, Rahman MA, Jaafar J (2020) Arsenic adsorption mechanism on palm oil fuel ash (POFA) powder suspension. J Hazard Mater 383:121214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121214J.Hazard.Mater.383,121214
Yusuf A, Sodiq A, Giwa A, Eke J, Pikuda O, De Luca G, Di Salvo JL, Chakraborty S (2020) A review of emerging trends in membrane science and technology for sustainable water treatment. J Clean Prod 266:121867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121867
Yuvaraja G, Zheng N-C, Pang Y, Su M, Chen D-Y, Kong L-J, Mehmood S, Subbaiah MV, Wen J-C (2020) Removal of U (VI) from aqueous and polluted water solutions using magnetic Arachis hypogaea leaves powder impregnated into chitosan macromolecule. Int J Biol Macromol 148:887–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.042
Zakeri H, Yousefi M, Mohammadi A, Baziar M, Mojiri S, Salehnia S, Hosseinzadeh A (2021) Chemical coagulation-electro fenton as a superior combination process for treatment of dairy wastewater: performance and modelling. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18:3929–3942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03149-w
Zavareh S, Zarei M, Darvishi F, Azizi H (2015) As (III) adsorption and antimicrobial properties of Cu–chitosan/alumina nanocomposite. Chem Eng J 273:610–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03149-w
Zeng H, Wang F, Xu K, Zhang J, Li D (2020a) Optimization and regeneration of chitosan-alginate hybrid adsorbent embedding iron-manganese sludge for arsenic removal. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 607:125500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125500
Zeng H, Yu Y, Wang F, Zhang J, Li D (2020b) Arsenic (V) removal by granular adsorbents made from water treatment residuals materials and chitosan. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 585:124036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124036
Zeng H, Xu K, Wang F, Sun S, Li D, Zhang J (2021a) Adsorption of As (III) from aqueous solutions using MnO2 strengthened WTRs-chitosan beads made by homogenous method with freeze-drying. React Funct Polym 167:105016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2021.105016
Zeng H, Xu K, Wang F, Sun S, Li D, Zhang J (2021b) Preparation of adsorbent based on water treatment residuals and chitosan by homogeneous method with freeze-drying and its As (V) removal performance. Int J Biol Macromol 184:313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.032
Zeng H, Sun S, Xu K, Zhao W, Hao R, Zhang J, Li D (2022): Adsorption of As (V) by magnetic alginate-chitosan porous beads based on iron sludge. J Clean Prod 132117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132117
Zeng J, Qi P, Shi J, Pichler T, Wang F, Wang Y, Sui K (2020c) Chitosan functionalized iron nanosheet for enhanced removal of As (III) and Sb (III): Synergistic effect and mechanism. Chem Eng J 382:122999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122999
Zhang C, Zhang H, Li R, Xing Y (2017) Morphology and adsorption properties of chitosan sulfate salt microspheres prepared by a microwave-assisted method. RSC Adv 7:48189–48198. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA09867G
Zhao L, Guan X, Yu B, Ding N, Liu X, Ma Q, Yang S, Yilihamu A, Yang S-T (2019) Carboxylated graphene oxide-chitosan spheres immobilize Cu2+ in soil and reduce its bioaccumulation in wheat plants. Environ Int 133:105208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105208
Zhao Z, Xiong Y, Cheng X, Hou X, Yang Y, Tian Y, You J, Xu L (2020) Adsorptive removal of trace thallium (I) from wastewater: a review and new perspectives. J Hazard Mater 393:122378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122378
Zhixiang G, Changjin J, Rongtao L, Yang Z, Zhang T (2020) Optimization of the preparation of fungal-algal pellets for use in the remediation of arsenic-contaminated water. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:36789–36798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09757-2
Zhou H, Liu G, Zhang L, Zhou C, Mian MM, Cheema AI (2021) Strategies for arsenic pollution control from copper pyrometallurgy based on the study of arsenic sources, emission pathways and speciation characterization in copper flash smelting systems. Environ Pollut 270:116203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116203
Zhu N, Qiao J, Yan T (2019) Arsenic immobilization through regulated ferrolysis in paddy field amendment with bismuth impregnated biochar. Sci Total Environ 648:993–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Asif Ayub: conceptualization, writing—original draft, review, and editing. Khaysy Srithilat: conceptualization, critical analysis, validation. Irum Fatima: conceptualization, critical analysis, resources. Nadia Masaya Panduro-Tenazoa: literature search and data analysis, visualization. Iqbal Ahmed: literature search, visualization. Muhammad Usman Akhtar: formal analysis. Waqas Shabbir: formal analysis. Khalil Ahmad: conceptualization, data analysis. Ali Muhammad: formal analysis, visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayub, A., Srithilat, K., Fatima, I. et al. Arsenic in drinking water: overview of removal strategies and role of chitosan biosorbent for its remediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 64312–64344 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21988-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21988-z