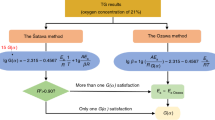
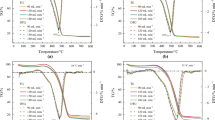
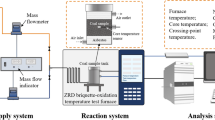
Abstract
Oxygen plays a crucial role in coal spontaneous combustion (CSC), and the magnitude of oxygen concentration determines the oxidation reaction intensity of CSC. This work is aiming to investigate the contribution of oxygen concentration to CSC and to predict the spontaneous combustion stage of coal at different oxygen concentrations. Firstly, experiments on the spontaneous combustion of coal samples at six oxygen concentrations (6%, 9%, 12%, 15%, 18%, and 21%) were carried out combined with a temperature-programmed system. Then, the gas products at different temperature stages were extracted to provide detailed classification and assessment of the indicator gasses for coal spontaneous combustion at different oxygen concentrations. The results show that the oxygen concentration and the crossing point temperature (CPT) are inversely proportional. The higher the oxygen concentration, the more intense the coal-oxygen complex reaction and the greater the gas product concentration. The critical temperature of some stages in high oxygen concentration environment is lower than that in low oxygen concentration environment. The oxidation process can be slowed down by reducing the oxygen concentration as much as possible. Indicator gasses are different for different oxygen concentration environments and should be selected reasonably and optimally to match the specific environment for judging natural coal fires in order to effectively prevent coal spontaneous combustion fire disasters.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Alipour M, Alizadeh B, Jahangard AA, GandomiSani AR (2021) Wildfire events at the Triassic–Jurassic boundary of the Tabas Basin, Central Iran. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8(5):897–907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-021-00436-2
Arisoy A, Beamish B (2015) Mutual effects of pyrite and moisture on coal self-heating rates and reaction rate data for pyrite oxidation. Fuel 139:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.08.036
Baris K, Kizgut S, Didari V (2012) Low-temperature oxidation of some Turkish coals. Fuel 93:423–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.08.066
Chao J, Yang H, Wu Y et al (2016) The investigation of the coal ignition temperature and ignition characteristics in an oxygen-enriched FBR. Fuel 183:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.06.089
Choi H, Thiruppathiraja C, Kim S et al (2011) Moisture readsorption and low temperature oxidation characteristics of upgraded low rank coal. Fuel Process Technol 92(10):2005–2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.05.025
Deng J, Ren L, Ma L et al (2018) Effect of oxygen concentration on low-temperature exothermic oxidation of pulverized coal. Thermochim Acta 667:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2018.07.012
Deng J, Ren SJ, Xiao Y et al (2019) Thermophysical properties of coal during low temperature oxidation under different oxygen concentrations. Thermochim Acta 676:186–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2019.05.003
Deng J, Xiao Y, Li Q et al (2015) Experimental studies of spontaneous combustion and anaerobic cooling of coal. Fuel 157:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.04.063
Dong X, Wen Z, Wang F, Meng Y (2019) Law of gas production during coal heating oxidation. Int J Min Sci Technol 29(4):617–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2019.06.011
Duan Y, Wang S, Wang W, Zheng K (2020) Atmospheric disturbance on the gas explosion in closed fire zone. Int J Coal Sci Technol 7(4):752–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-020-00295-3
Hu X, Yang S, Zhou X et al (2015) Coal spontaneous combustion prediction in gob using chaos analysis on gas indicators from upper tunnel. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 26:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2015.06.047
Jia X, Wu J, Lian C et al (2021) Investigating the effect of coal particle size on spontaneous combustion and oxidation characteristics of coal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(11):16113–16122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16929-1
Küçük A, Kadioǧlu Y, Gülaboǧlu MŞ (2003) A study of spontaneous combustion characteristics of a Turkish lignite: particle size, moisture of coal, humidity of air. Combust Flame 133(3):255–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-2180(02)00553-9
Liang Y, Zhang J, Wang L et al (2019) Forecasting spontaneous combustion of coal in underground coal mines by index gases: a review. J Loss Prev Process Ind 57:208–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2018.12.003
Liang Z, Wang JR (2011) The technology of forecasting and predicting the hidden danger of underground coal spontaneous combustion. Procedia Eng 26:2301–2305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.2438
Liu Y, Wang C, Che D (2012) Ignition and kinetics analysis of coal combustion in low oxygen concentration. Energy Sources, Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 34(9):810–819. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567031003645585
Lü HF, Deng J, Li DJ et al (2021) Effect of oxidation temperature and oxygen concentration on macro characteristics of pre-oxidised coal spontaneous combustion process. Energy 227:120431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120431
Lü HF, Xiao Y, Deng J et al (2019) Inhibiting effects of 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazole tetrafluoroborate on coal spontaneous combustion under different oxygen concentrations. Energy 186:115907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.115907
Lu P, Liao GX, Sun JH, Li PD (2004) Experimental research on index gas of the coal spontaneous at low-temperature stage. J Loss Prev Process Ind 17(3):243–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2004.03.002
Lu W, Li J, Li J et al (2021) Oxidative kinetic characteristics of dried soaked coal and its related spontaneous combustion mechanism. Fuel 305:121626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121626
Nádudvari Á, Abramowicz A, Fabiańska M et al (2021) Classification of fires in coal waste dumps based on Landsat, Aster thermal bands and thermal camera in Polish and Ukrainian mining regions. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8(3):441–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-020-00375-4
Pan R, Fu D, Xiao Z, Chen L (2018) The inducement of coal spontaneous combustion disaster and control technology in a wide range of coal mine closed area. Environ Earth Sci 77(10):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7540-1
Pan R, Ma J, Zheng L, Wang J (2020) Experimental study on the effects of chemical composite additive on the microscopic characteristics of spontaneous combustion coal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(5):5606–5619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07340-y
Perdochova M, Derychova K, Veznikova H et al (2015) The influence of oxygen concentration on the composition of gaseous products occurring during the self-heating of coal and wood sawdust. Process Saf Environ Prot 94:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.10.006
Qi G, Wang D, Zheng K et al (2015) Kinetics characteristics of coal low-temperature oxidation in oxygen-depleted air. J Loss Prev Process Ind 35:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2015.05.011
Shi X, Zhang Y, Chen X, Zhang Y (2021) Effects of thermal boundary conditions on spontaneous combustion of coal under temperature-programmed conditions. Fuel 295:120591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120591
Singh AK, Singh RVK, Singh MP et al (2007) Mine fire gas indices and their application to Indian underground coal mine fires. Int J Coal Geol 69(3):192–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2006.04.004
Szkudlarek Z, Janas S (2021) Active protection of work area against explosion of dust–gas mixture. Int J Coal Sci Technol 8(4):674–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-020-00387-0
Tan B, Liu H, Xu B, Wang T (2020) Comparative study of the explosion pressure characteristics of micro- and nano-sized coal dust and methane–coal dust mixtures in a pipe. Int J Coal Sci Technol 7(1):68–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-019-00289-w
Wang D (2008) Mine Fire Science. rsity Min Technol Xuzhou, China
Wang H, Dlugogorski BZ, Kennedy EM (2003) Coal oxidation at low temperatures: oxygen consumption, oxidation products, reaction mechanism and kinetic modelling. Prog Energy Combust Sci 29(6):487–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1285(03)00042-X
Wang J, Zhang Y, Xue S et al (2018) Assessment of spontaneous combustion status of coal based on relationships between oxygen consumption and gaseous product emissions. Fuel Process Technol 179:60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.06.015
Wang K, He Y, Fan H, Shang B (2021) Study of the coal secondary spontaneous combustion behavior under different pre-heating oxygen concentrations. J Therm Anal Calorim 146(2):681–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10036-y
Wen H, Yu Z, Fan S et al (2017) Prediction of spontaneous combustion potential of coal in the gob area using co extreme concentration: a case study. Combust Sci Technol 189(10):1713–1727. https://doi.org/10.1080/00102202.2017.1327430
Xiao Y, Li DJ, Lü HF et al (2019) Effects of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate and the oxygen concentration on the spontaneous combustion of coal. J Therm Anal Calorim 138(5):3445–3454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08331-4
Xie J, Xue S, Cheng W, Wang G (2011) Early detection of spontaneous combustion of coal in underground coal mines with development of an ethylene enriching system. Int J Coal Geol 85(1):123–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2010.10.007
Xu Y, Li Z, Liu H et al (2020) A model for assessing the compound risk represented by spontaneous coal combustion and methane emission in a gob. J Clean Prod 273:122925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122925
Yuan L, Smith AC (2011) CO and CO2 emissions from spontaneous heating of coal under different ventilation rates. Int J Coal Geol 88(1):24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2011.07.004
Zhang Y, Li Y, Huang Y et al (2018) Characteristics of mass, heat and gaseous products during coal spontaneous combustion using TG/DSC–FTIR technology. J Therm Anal Calorim 131(3):2963–2974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6738-x
Zhu H, Liu X (2012) Investigation into spontaneous combustion hazard and numerical simulation of nitrogen injection fire prevention effects in the roof coal. Meitan Xuebao/Journal China Coal Soc 37(6):1015–1020
Funding
The research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. cstc2020jcyj-msxmX1013); Chongqing Safety Production (Coal Development) Special project “Research on Gas Recovery Technology of Underground Drilling Foam Drainage in Coal Mine” (Project No. 2020B182[5985]20015511).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaoliang Jia: methodology, experiment, validation, writing – original and editing
Jiaokun Wu: methodology, software, writing – review draft
Changjun Lian: supervision, resources
Jilai Rao: supervision
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Shimin Liu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, X., Wu, J., Lian, C. et al. Assessment of coal spontaneous combustion index gas under different oxygen concentration environment: an experimental study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 87257–87267 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21920-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21920-5