Abstract
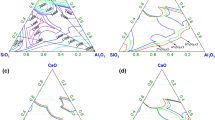
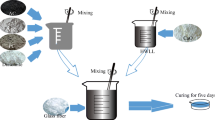
In order to give full play to the alkaline neutralization value of carbide slag and reduce the environmental hazards of carbide slag, it is of great practical significance to study the resource utilization of carbide slag. The adsorption of sulfur compounds on carbide slag was studied in the laboratory, and the process parameters of carbide slag desulfurization were explored and optimized. The specific surface area, pore distribution, and other physicochemical parameters were analyzed by XRD and SEM, which explained the changes of products and carbide slag before and after desulfurization. The test results show that carbide slag and limestone have almost the same desulfurization effect. The kinetics of carbide slag desulfurization process conforms to pseudo-first-order kinetics, and the sulfur content of calcium carbide slag reaches to 1000 mgSO2·g−1. A project demonstration was carried out in the gold smelting Tielu Plant of Zhenyuan Huashuo Precious Metals Development Co., Ltd., in Yunnan. The results of the 2-year demonstration project showed that the desulphurization efficiency of the four-stage series desulphurization tower exceeds 95%. The concentration of sulfur dioxide in the discharged flue gas is reduced to less than 20 mg·m−3, which meets the requirements of ultra-low emission standard in China. Therefore, whether from theoretical research or engineering practice analysis, it is feasible to replace limestone with calcium carbide slag for flue gas desulfurization. The paper also discusses the problems existing in the demonstration project, and provides a new idea of “using waste to treat waste” in order to solve the problem of carbide slag disposal.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmad AA, Hameed BH, Aziz N (2007) Adsorption of direct dye on palm ash: kinetic and equilibrium modeling. J Hazard Mater 141(1):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.06.094
Basinas P, Wu Y, Grammelis P, Anthony EJ, Grace JR, Jim Lim C (2014) Effect of pressure and gas concentration on CO2 and SO2 capture performance of limestones. Fuel 122:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.01.038
Bravo RV, Camacho RF, Moya VM, Garcia LAI (2002) Desulphurization of SO2-N2 mixtures by limestone slurries. Chem Eng Sci 57:2047–2058. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(02)00095-7
Chen L, Ramsier C, Bigham J, Slater B, Kost D, Lee YB, Dick WA (2009) Oxidation of FGD-CaSO3 and effect on soil chemical properties when applied to the soil surface. Fuel 88:1167–1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2008.07.015
Cui P (2012) Reasons and control measures of high content of calcium sulfite in desulphurization system. Electric Saf Technol 14:50–52. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-6226.2012.10.017
Feng Z, Wang L, Zhang Y (2006) The influence of pH value in assimilateive liquid to desulfurized efficiency by limestone-gypsum method to decarbolize in soot. Opencast Mining Technol 6:45–47. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-9816.2006.06.019
Fu H (2013) Phase transformation and crystallization of calcium sulfite and calcium sulfate in calcium chloride solution. Dissertation, Zhejiang University
Guan B, Shen Z, Wu Z, Yang L, Ma X (2010) Effect of pH on the preparation of α-calcium sulfate hemihydrate from FGD gypsum with the hydrothermal method. J Am Ceram Soc 91:3835–3840. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02729.x
Guan B, Yang L, Fu H, Kong B, Li T, Yang L (2011) α-calcium sulfate hemihydrate preparation from FGD gypsum in recycling mixed salt solutions. Chem Eng J 174:296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.09.033
Huang Z, Long J, Deng L, Che D (2019) Feasibility study of using carbide slag as in-bed desulfurizer in circulating fluidized bed boiler. Appl Sci 9:4517. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214517
Jiang Z (2019) Experiment and application analysis on carbide slag-gypsum wet method of flue gas desulfurization technology for coal fired power plant. Boiler Technol 50:10–14. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-4763.2019.04.002
Li R, Wang B, Jia L, Gao J, Liu C, Liu T, Ning P, Wang F (2021) Dry catalytic purification of NO by modified calcium carbide slag. Chin J Environ Eng 15:1599–1605. https://doi.org/10.12030/j.cjee.202004069
Liu P, Yang L, Sun L (2021) Multi-objective economic model predictive control of wet limestone flue gas desulfurisation system. Process Saf Environ Prot 150:269–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.04.012
Ma X, Kaneko T, Tashimo T, Yoshida T, Kato K (2000) Use of limestone for SO2 removal from flue gas in the semidry FGD process with a powder-particle spouted bed. Chem Eng Sci 55:4643–4652. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(00)00090-7
Ma L, Xiang G, Zhao X, Yao Q (2006) Experimental study on additive enhanced limestone wet flue gas desulfurization. Res Environ Sci 19(1):39–42. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2006.01.010
Mahuli S (1996) Pore structure optimization of calcium carbonate sorbents for enhanced SO2 capture. Fuel Energy Abstracts 38:272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6701(97)85237-X
Mchabe D, Everson RC, Ramachandran PA, Neomagus HWJP, Branken DJ (2021) Development of an integrated model for absorption of sulphur dioxide in limestone slurry. Chem Eng Sci 229:116050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2020.116050
Niu S, Liu M, Lu C, Hui L (2014) Thermogravimetric analysis of carbide slag. J Therm Anal Calorim 115:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-013-3268-z
Pimentel Lages V, de Campos VF, Bentes Carvalho R, Da Cunha ALC, Dweck J (2018) A new thermogravimetric method to quantify SO2 absorption capacity by limestone. Thermochim Acta 667:140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2018.07.024
Sofrá F, Boger DV (2002) Environmental rheology for waste minimisation in the minerals industry. Chem Eng J 86:319–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-8947(01)00225-X
Sun L, Li K, Tang L, Liu N, Ning P, Sun X, Zhang X (2017) Research progress of common metal oxides for flue gas desulfurization. Chem Indus Eng Prog 36(181):188. https://doi.org/10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2017.01.023
Wang X, Li Y, Shi J, Zhao J, Wang Z, Liu H, Zhou X (2018a) Simultaneous SO2/NO removal performance of carbide slag pellets by bagasse templating in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor. Fuel Process Technol 180:75–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.08.007
Wang Y, Chen M, Cui S, Ma X (2018b) Desulfurization and denitrification performance of rice husk ash-carbide slag composite absorbent. Mater Rev 32:3995–3999
Wang X, Li Y, Zhang W, Zhao J, Wang Z (2020) Simultaneous SO2 and NO removal by pellets made of carbide slag and coal char in a bubbling fluidized-bed reactor. Process Saf Environ Prot 134:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.11.022
Wang X, Wu K, Wu D, Zhang Q, Dong Y (2021) Progress in application of calcium carbide slag in desulfurization process of coal-fired power plant. Chem Indus Eng Prog 40(z2):140–148. https://doi.org/10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2021-0523
Wang X (2019) Simultaneous removal of SO2/NO from calcium carbide slag pellets during fluidization. Dissertation, Shandong University
Wu C, Lv W, Mei Y, Yu B (2015) Application and running economic analysis of wet flue gas desulfurization technology. Chem Indus Eng Prog 34(12):4368–4374. https://doi.org/10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2015.12.039
Xu Z, Hu M, Sun J (2012) Analyses on the reasons of high moisture content of gypsum and some suggestions of control measures. Indus Saf Environ Protect 38:28–30. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2012.09.009
Xu H, Li H, Sun S, Jin J, Wang M, Pan W (2015) Effects of organic acid additives on enhancement of carbide slag flue gas desulfurization. J Chin Soc Power Eng 35:659–665. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-7607.2015.08.009
Xu J, Cao Z, Zhang Y, Yuan Z, Lou Z, Xu X, Wang X (2018) A review of functionalized carbon nanotubes and graphene for heavy metal adsorption from water: preparation, application, and mechanism. Chemosphere 195:351–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.061
Xu R, Zhang Z, Zhang G, Chen L, Lu H, Guan F, Liu R (2019) Application of calcium carbide slag instead of limestone as desulfurizer in Yuanyanghu Power Plant. Ningxia Electric Power 6:61–64. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-3643.2019.06.013
Yang H, Cao J, Wang Z, Chen H, Gong X (2014) Discovery of impurities existing state in carbide slag by chemical dissociation. Int J Miner Process 130:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2014.05.003
Yang J, Liu S, Ma L, Zhao S, Liu H, Dai Q, Yang Y, Xu C, Xin X, Zhang X, Liu J (2021) Mechanism analysis of carbide slag capture of CO2 via a gas-liquid-solid three-phase fluidization system. J Clean Prod 279:123712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123712
Zacharczuk W, Andruszkiewicz A, Tatarek A, Alahmer A, Alsaqoor S (2021) Effect of Ca-based additives on the capture of SO2 during combustion of pulverized lignite. Energy 231:120988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120988
Zhang T, Wu C, Li B, Wang J, Ravat R, Chen X, Wei J, Yu Q (2019b) Linking the SO2 emission of cement plants to the sulfur characteristics of their limestones: a study of 80 NSP cement lines in China. J Clean Prod 220:200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.133
Zhang Y, Qian W, Zhou P, Liu Y, Lei X, Li B, Ning P (2021) Research on red mud-limestone modified desulfurization mechanism and engineering application. Sep Purif Technol 272:118867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118867
Zhang H, Ma L, Zhan N, Bai J (2019a) Application of calcium carbide slag as desulfurizer in clinker production line. Cement 9:24–25. https://doi.org/10.13739/j.cnki.cn11-1899/tq.2019.09.007
Zhao Y, Zhan J, Liu G, Zheng M, Jin R, Yang L, Hao L, Wu X, Zhang X, Wang P (2017) Evaluation of dioxins and dioxin-like compounds from a cement plant using carbide slag from chlor-alkali industry as the major raw material. J Hazard Mater 330:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.02.018
Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Gao W, Baleta J, Liu C, Li W, Weng W, Dai H, Zheng C, Gao X (2021) Simulation of SO2 absorption and performance enhancement of wet flue gas desulfurization system. Process Saf Environ Prot 150:453–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.04.032
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFC0214400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jiamin Qi: data curation, formal analysis, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft. Bin Li: supervision, resources, writing—review and editing. PengXiang Zhou: methodology, conceptualization, investigation, supervision. Di Yang: conceptualization, data curation. Zixuan Wang: writing—review and editing. The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval was not required for this research.
Consent for publication
All authors are informed and agree to the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, J., Zhou, P., Yang, D. et al. Desulphurization mechanism and engineering practice of carbide slag. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 88519–88530 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21894-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21894-4