Abstract
Presently, the rapid pace in the discovery of emerging aquatic pollutants is increasing the demand for the remediation and treatment of our natural resources. Regarding this, nanotechnology is being considered the potential solution for contaminated water remediation with techniques such as filtration, adsorption, catalysis, and desalination. For this purpose, zerovalent iron (ZVI) is being widely used in the remediation of environmental pollutants due to its large specific surface area and high reactivity. However, ZVI is easy to agglomerate and oxidize, limiting its application in the real environment. Therefore, the present study was designed to discuss the preparation and characterization methods of ZVI composite materials, factors affecting adsorption, the removal effect, and adsorption mechanism of different pollutants by Fe–C materials because the optimization and modification of nano-zero-valent iron is a hot research topic nowadays in this field. Moreover, this paper does also analyze the possibility of the practical application prospects of the team’s technology for preparing iron-carbon materials. Thus, this information will be helpful for the development and application of Fe–C-based technologies for water and soil remediation and the prediction of the future research direction of Fe–C composite materials.
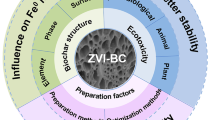
Graphical abstract
















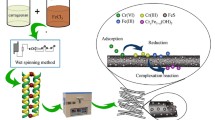
Adopted from Wu et al. (2015) with permission from Elsevier


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting this review is available within the main body and in its supplementary materials.
References
Ahmaruzzaman M (2010) A review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog Energy Combust Sci 36(3):327–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2009.11.003
Ai, YJ., Liu, Y., Lan, WY., Jin, JR., Xing, JL., Zou, YD., Zhao, CF., Wang, XK. (2018). The effect of pH on the U(VI) sorption on graphene oxide (GO): a theoretical study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 343(Vi), 460–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.027
Alexandratos, SD., Zhu, X. (2017). The effect of hydrogen bonding in enhancing the ionic affinities of immobilized monoprotic phosphate ligands. Materials, 10(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10080968
Arellano O, Flores M, Guerra J, Hidalgo A, Rojas D, Strubinger A (2016) Hydrothermal carbonization of corncob and characterization of the obtained hydrochar. Chem Eng Trans 50(June):235–240. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1650040
Benkhaya S, Harfi S, El S, El A (2017) Classifications, properties and applications of textile dyes A review. Appl J Environ Eng Sci 3:311–320. https://doi.org/10.48422/IMIST.PRSM/ajees-v3i3.9681
Cai Z, Sun Y, Liu W, Pan F, Sun P, Fu J (2017) An overview of nanomaterials applied for removing dyes from wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(19):15882–15904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9003-8
Chen SS, Hsu HD, Li CW (2004) A new method to produce nanoscale iron for nitrate removal. J Nanopart Res 6(6):639–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-004-6672-2
Crane RA, Scott TB (2012) Nanoscale zero-valent iron: future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J Hazard Mater 211–212:112–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.073
Crini G, Lichtfouse E (2019) Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 17(1):145–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0785-9
Cwiertny DM, Bransfield SJ, Livi KJT, Fairbrother DH, Roberts AL (2006) Exploring the influence of granular iron additives on 1,1,1-trichloroethane reduction. Environ Sci Technol 40(21):6837–6843. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060921v
Danks AE, Hall SR, Schnepp Z (2016) The evolution of “sol-gel” chemistry as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater Horiz 3(2):91–112. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5mh00260e
Daoud M, Benturki O, Girods P, Donnot A, Fontana S (2019) Adsorption ability of activated carbons from Phoenix dactylifera rachis and Ziziphus jujube stones for the removal of commercial dye and the treatment of dyestuff wastewater[J]. Microchem J 148:493–502
Deng, L., Du, P., Yu, W., Yuan, P., Annabi-Bergaya, F., Liu, D., Zhou, J. (2019). Novel hierarchically porous allophane/diatomite nanocomposite for benzene adsorption. Applied Clay Science, 168, 155–163. http://ir.gyig.ac.cn/handle/42920512-1/10540
Diraki A, Mackey HR, Mckay G, Abdala A (2019) Removal of emulsified and dissolved diesel oil from high salinity wastewater by adsorption onto graphene oxide. J Environ Chem Eng 7(3):103106. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2019.103106
Dong, H., Deng, J., Xie, Y., Zhang, C., Jiang, Z., Cheng, Y., Hou, K., & Zeng, G. (2017). Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. In Journal of Hazardous Materials (Vol. 332, Issue Vi). Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.03.002
Dong H, Guan X, Lo IMC (2012) Fate of As(V)-treated nano zero-valent iron: Determination of arsenic desorption potential under varying environmental conditions by phosphate extraction. Water Res 46(13):4071–4080. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2012.05.015
Dong H, Zhang C, Deng J, Jiang Z, Zhang L, Cheng Y, Hou K, Tang L, Zeng G (2018) Factors influencing degradation of trichloroethylene by sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous solution. Water Res 135:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.017
Doong RA, Chen KT, Tsai HC (2003) Reductive dechlorination of carbon tetrachloride and tetrachloroethylene by zerovalent silicon - iron reductants. Environ Sci Technol 37(11):2575–2581. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020978r
dos Santos JMN, Pereira CR, Foletto EL, Dotto GL (2019) Alternative synthesis for ZnFe2O4/chitosan magnetic particles to remove diclofenac from water by adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 131:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2019.03.079
Du Y, Dai M, Cao J, Liu J, Peng C (2019) Preparation of granular red mud supported zero-valent iron for Crystal Violet removal from aqueous solution. Desalination and Water Trreatment 158:353–363. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24230
Du, Y., Dai, M., Cao, J., Peng, C., Ali, I., Naz, I., Li, J. (2020). Efficient removal of acid orange 7 using a porous adsorbent-supported zero-valent iron as a synergistic catalyst in advanced oxidation process. In Chemosphere (Vol. 244). Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125522
Duan S, Wang Y, Liu X, Shao D, Hayat T, Alsaedi A, Li J (2017) Removal of U(VI) from aqueous solution by amino functionalized flake graphite prepared by plasma treatment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(5):4073–4085. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b00069
Fan D, Lan Y, Tratnyek PG, Johnson RL, Filip J, O’Carroll DM, Nunez Garcia A, Agrawal A (2017) Sulfidation of iron-based materials: a review of processes and implications for water treatment and remediation. Environ Sci Technol 51(22):13070–13085. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b04177
Fayazi M, Ghanei-Motlagh M, Taher MA (2015) The adsorption of basic dye (Alizarin red S) from aqueous solution onto activated carbon/γ-Fe2O3 nano-composite: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Mater Sci Semicond Process 40:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.06.044
Feng C, Ren P, Huo M, Dai Z, Liang D, Jin Y, Ren F (2020) Facile synthesis of trimethylammonium grafted cellulose foams with high capacity for selective adsorption of anionic dyes from water. Carbohyd Polym 241(April):116369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116369
Fu F, Dionysiou DD, Liu H (2014) The use of zero-valent iron for groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment : a review. J Hazard Mater 267:194–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.062
Fu R, Yang Y, Xu Z, Zhang X, Guo X, Bi D (2015) The removal of chromium (VI) and lead (II) from groundwater using sepiolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-NZVI). Chemosphere 138:726–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.051
Gillham, RW., O’Hannesin, SF. (1994). Enhanced degradation of halogenated aliphatics. In Groundwater (Vol. 32, Issue 6, pp. 958–967).
Glainmer K, Quiton N, Lu M, Huang Y (2021) Chemosphere Synthesis and catalytic utilization of bimetallic systems for wastewater remediation : a review. Chemosphere 262:128371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128371
Glavee GN, Klabunde KJ, Sorensen CM, Hadjipanayis GC (2002) Chemistry of borohydride reduction of iron(II) and iron(III) ions in aqueous and nonaqueous media. Formation of Nanoscale Fe, FeB, and Fe2B Powders. Inorganic Chem 34(1):28–35. https://doi.org/10.1021/IC00105A009
Gosavi, VD., Sharma, S. (2013). A general review on various treatment methods for textile wastewater. Journal of Environmental Science, Computer Science Engineering & Technology, 3(1), 29–039. www.jecet.org
Guan X, Du X, Liu M, Qin H, Qiao J, Sun Y (2020) Enhanced trichloroethylene dechlorination by carbon-modified zero-valent iron: revisiting the role of carbon additives. J Hazard Mater 394(January):122564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122564
Guan, X., Sun, Y., Qin, H., Li, J., Lo, I. M. C., He, D., Dong, H. (2015). The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: the development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994–2014). In Water Research (Vol. 75). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.034
Hassan Mohammad-M., Christopher M. (2022). Biomasderived porous carbonaceous materials and their composites as adsorbents for cationic and anionic dyes A review[J].https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129087
Han Z, Guo Y, Yang W, Tang R, Wang H, Wu S (2020) Removal of mercury from flue gases over iron modified activated carbon made by in situ ion exchange method. J Energy Inst 93(4):1411–1418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2020.01.003
Huang L, Liu G, Dong G, Wu X, Wang C, Liu Y (2017) Reaction mechanism of zero-valent iron coupling with microbe to degrade tetracycline in permeable reactive barrier (PRB). Chem Eng J 316:525–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.096
Huang S, Xu C, Shao Q, Wang Y, Zhang B, Gao B, Zhou W, Tratnyek PG (2018) Sulfide-modified zerovalent iron for enhanced antimonite sequestration: characterization, performance, and reaction mechanisms. Chem Eng J 338:539–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.033
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN (2014) Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol 7(2):60–72. https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2014-0009
Ji Y, Xu F, Wei W, Gao H, Zhang K, Zhang G, Xu Y, Zhang P (2021) Efficient and fast adsorption of methylene blue dye onto a nanosheet MFI zeolite. J Solid State Chem 295(October 2020):121917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2020.121917
Kalkan NA, Aksoy S, Ayse AE, Hasirci N (2012) Adsorption of Reactive Yellow 145 onto chitosan coated magnetite nanoparticles. J Appl Polym Sci 124(1):576–584. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.34986
Ken DS, Sinha A (2020) Recent developments in surface modification of nano zero-valent iron (nZVI): remediation, toxicity and environmental impacts. Environ Nanotechnol, Monitor Manag 14:100344. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENMM.2020.100344
Kim SA, Kamala-Kannan S, Lee KJ, Park YJ, Shea PJ, Lee WH, Kim HM, Oh BT (2013) Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by a zeolite-nanoscale zero-valent iron composite. Chem Eng J 217:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.097
Kunhikrishnan A, Shon HK, Bolan NS, El Saliby I, Vigneswaran S (2015) Sources, distribution, environmental fate, and ecological effects of nanomaterials in wastewater streams. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45(4):277–318. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2013.852407
Liang L, Xi F, Tan W, Meng X, Hu B, Wang X (2021) Review of organic and inorganic pollutants removal by biochar and biochar-based composites. Biochar 3:255–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-021-00101-6
Li F, Vipulanandan C, Mohanty KK (2003) Microemulsion and solution approaches to nanoparticle iron production for degradation of trichloroethylene. Colloids Surf, A 223(1–3):103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(03)00187-0
Li H, Qiu Y et al (2017) Biochar supported Ni/Fe Bimetallic nanoparticles to remove 1,1,1-trichloroethane under various reaction conditions. Chemosphere 169:534–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.117
Li L, Fan M, Brown RC, Leeuwen JHV, Wang J, Wang W (2006) Synthesis, properties, and environmental applications of nanoscale iron-based materials: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 36:405–431. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380600620387
Li, M., Liu, H., Chen, T., Chen, D., Wang, C., Wei, L., & Wang, L. (2019). Efficient U(VI) adsorption on iron/carbon composites derived from the coupling of cellulose with iron oxides: performance and mechanism. Science of the Total Environment, 703(xxxx), 135604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135604
Li, X., Zhao, Y., Xi, B., Meng, X., Gong, B., Li, R., Peng, X., Liu, H. (2017c). Decolorization of Methyl Orange by a new clay-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: Synergetic effect, efficiency optimization and mechanism. J Environ Sci, 52(Beidou Xi), 8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.03.022
Li Y, Cheng W, Sheng G, Li J, Dong H, Chen Y, Zhu L (2015) Synergetic effect of a pillared bentonite support on SE(VI) removal by nanoscale zero valent iron. Appl Catal B 174–175:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.03.025
Lien HL, Zhang WX (2007) Nanoscale Pd/Fe bimetallic particles: catalytic effects of palladium on hydrodechlorination. Appl Catal B 77(1–2):110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.07.014
Yang L, Jiang Zhihui, Jie Fu (2022) Iron-biochar production from oily sludge pyrolysis and its application for organic dyes removal[J]. Chemosphere 301:134803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134803
Liu J, Du Y, Sun W, Chang Q, Peng C (2019) Preparation of new adsorbent-supported Fe/Ni particles for the removal of crystal violet and methylene blue by a heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction. Royal Soc of Chem 9(1):22513–22522. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra04710g
Liu, J., Mwamulima, T., Wang, Y., Fang, Y., Song, S., Peng, C. (2017). Removal of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using the fly ash-based adsorbent material-supported zero-valent iron. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 243(Ii), 205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.004
Liu J, Wang Y, Fang Y, Mwamulima T, Song S, Peng C (2018) Removal of crystal violet and methylene blue from aqueous solutions using the fly ash-based adsorbent material-supported zero-valent iron. J Mol Liq 250:468–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.12.003
Liu J, Wang Y, Zhang X, Fang Y (2018) Preparation of Fe @ GAC and Fe @ GAR and their application for removal of crystal violet from wastewater. Water, Air, & Soil Pollut 229:38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3692-6
Liu X, Tian J, Li Y, Sun N, Mi S, Xie Y, Chen Z (2019) Enhanced dyes adsorption from wastewater via Fe3O4 nanoparticles functionalized activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 373:397–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2019.03.103
Lu H-J, Wang J-K, Ferguson S, Wang T, Bao Y, Hao H (2016) Mechanism, synthesis and modification of nano zerovalent iron in water treatment. Nanoscale 8:9962–9975. https://doi.org/10.1039/x0xx00000x
Ma C, Wu Y (2008) Dechlorination of perchloroethylene using zero-valent metal and microbial community. Environ Geol 55(1):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0963-8
Manavi N, Kazemi AS, Bonakdarpour B, Kazemi AS, Bonakdarpour B, Wastewater D (2016) The development of aerobic granules from conventional activated sludge under anaerobic-aerobic cycles and their adaptation for treatment of dyeing wastewater. Chem Eng J 312:336–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.154
Mansha M, Waheed A, Ahmad T, Kazi IW, Ullah N (2020) Synthesis of a novel polysuccinimide based resin for the ultrahigh removal of anionic azo dyes from aqueous solution. Environ Res 184:109337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109337
Matheson LJ, Tratnyek PG (1994) Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated methanes by iron metal. Environ Sci Technol 28(12):2045–2053. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00061a012
Meng F, Li M, Wang H, Xin L, Wu X, Liu X (2020) Encapsulating microscale zero valent iron-activated carbon into porous calcium alginate for the improvement on the nitrate removal rate and Fe 0 utilization factor. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 307(July):110522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110522
Mohseni-Bandpi A, Kakavandi B, Kalantary RR, Azari A, Keramati A (2015) Development of a novel magnetite-chitosan composite for the removal of fluoride from drinking water: adsorption modeling and optimization. RSC Adv 5(89):73279–73289. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra11294j
Mukherjee R, Kumar R, Sinha A, Lama Y, Saha AK (2016) A review on synthesis, characterization, and applications of nano zero valent iron (nZVI) for environmental remediation. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46(5):443–466. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2015.1103832
Nurmi JT, Tratnyek PG, Sarathy V, Baer DR, Amonette JE, Pecher K, Wang C, Linehan JC, Matson DW, Penn RL, Driessen MD (2005) Characterization and properties of metallic iron nanoparticles: spectroscopy, electrochemistry, and kinetics. Environ Sci Technol 39(5):1221–1230. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049190u
O’Carroll D, Sleep B, Krol M, Boparai H, Kocur C (2013) Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Adv Water Resour 51:104–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.02.005
Patanjali P, Mandal A, Chopra I, Singh R (2020) Adsorption of cationic dyes onto biopolymer-bentonite composites: kinetics and isotherm studies. Int J Environ Anal Chem 00(00):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1849660
Peng S, Deng S, Li D, Xie B, Yang X, Lai C, Sun S, Yao H (2020) Iron-carbon galvanic cells strengthened anaerobic/anoxic/oxic process (Fe/C-A2O) for high-nitrogen/phosphorus and low-carbon sewage treatment. Sci Total Environ 722:137657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137657
Quinn J, Geiger C, Clausen C, Brooks K, Coon C, O’Hara S, Krug T, Major D, Yoon WS, Gavaskar A, Holdsworth T (2005) Field demonstration of DNAPL dehalogenation using emulsified zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39(5):1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0490018
Ren G, Wang X, Huang P, Zhong B, Zhang Z, Yang L, Yang X (2017) Science of the Total Environment Chromium ( VI ) adsorption from wastewater using porous magnetite nanoparticles prepared from titanium residue by a novel solid-phase reduction method. Sci Total Environ 607–608:900–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.103
Riffat, R. (2012). Fundamentals of wastewater treatment and engineering. CRC Press. https://books.google.com/books?id=vXzMBQAAQBAJ&dq=regulations+towards+pollutants+in+wastewater&lr=
Senthil VKP, Dai K, Vo VN, Gokulakrishnan PSM, Crystal CV (2021) Enzyme - loaded nanoparticles for the degradation of wastewater contaminants : a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(0123456789):2331–2350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01158-8
Shan G, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY, Zhang TC (2009) Applications of nanomaterials in environmental science and engineering: review. Pract Period Hazard, Toxic, Radioactive Waste Manag 13(2):110–119. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-025X(2009)13:2(110)
Sheng G, Yang P, Tang Y, Hu Q, Li H, Ren X, Hu B, Wang X, Huang Y (2016) New insights into the primary roles of diatomite in the enhanced sequestration of UO22+ by zerovalent iron nanoparticles: an advanced approach utilizing XPS and EXAFS. Appl Catal B 193:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.035
Shivangi R, Richa S, Subhash C, ra. (2013) Microbial degradation of synthetic textile dyes: a cost effective and eco-friendly approach. African J Microbiol Res 7(24):2983–2989. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajmr12.1804
Stefaniuk, M., Oleszczuk, P., Ok, YS. (2015). Review on nano zerovalent iron ( nZVI ): from synthesis to environmental applications. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.11.046
Stjepanović M, Velić N, Galić A, Kosović I, Jakovljević T, Habuda-Stanić M (2021) From waste to biosorbent: removal of congo red from water by waste wood biomass. Water (Switzerland) 13:3. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030279
Su F, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Wang G (2016) Three-dimensional honeycomb-like structured zero-valent iron/chitosan composite foams for effective removal of inorganic arsenic in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 478:421–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.06.035
Su, Fan Y, Cheng Y, Ling Y, Hsin Y (2013) Removal of trichloroethylene by zerovalent iron/activated carbon derived from agricultural wastes. J Environ Manag 129:361–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.08.003
Suárez-Iglesias O, Collado S, Oulego P, Díaz M (2017) Graphene-family nanomaterials in wastewater treatment plants. Chem Eng J 313:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.022
Subramoney S (1998) Novel nanocarbons - structure, properties, and potential applications. Adv Mater 10(15):1157–1171. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-4095(199810)10:15%3c1157::AID-ADMA1157%3e3.0.CO;2-N
Sun YP, Li XQ, Zhang WX, Wang HP (2007) A method for the preparation of stable dispersion of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Colloids Surf, A 308(1–3):60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.05.029
Suryanarayana C (2001) Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog Mater Sci 46(1–2):1–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00010-9
Teshager Fitfety-M., Habtu Nigus-G., Mequanint Kibret. (2022). A systematic study of cellulose-reactive anionic dye removal using a sustainable bioadsorbent[J]. ECSN: 135024.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135024
Vakili B, Shahmoradi B, Maleki A, Safari M, Yang J, Pawar RR, Lee S (2019) Synthesis of immobilized cerium doped ZnO nanoparticles through the mild hydrothermal approach and their application in the photodegradation of synthetic wastewater. J Mol Liq 280:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.103
Wang Q, Kanel SR, Park H, Ryu A, Choi H (2009) Controllable synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of nanoscale zerovalent iron with specific high Brunauer-Emmett-Teller surface area. J Nanopart Res 11(3):749–755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9524-7
Wang S, Jin H, Deng Y, Xiao Y (2020) Comprehensive utilization status of red mud in China: a critical review. J Clean Prod 289:125136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125136
Wang J, Yao J, Wang L, Xue Q, Hu Z, Pan B (2020) Multivariate optimization ofthe pulse electrochemical oxidation for treating recalcitrant dye wastewater. Separ Purif Technol 230:115851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115851
Wang S, Gao B, Li Y, Creamer AE, He F (2017) Adsorptive removal of arsenate from aqueous solutions by biochar supported zero-valent iron nanocomposite: Batch and continuous flow tests. J Hazard Mater 322:172–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.052
Wang S, Zhao M, Zhou M, Li YC, Wang J, Gao B, Sato S, Feng K, Yin W, Igalavithana AD, Oleszczuk P, Wang X, Ok YS (2019) Biochar-supported nZVI (nZVI/BC) for contaminant removal from soil and water: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 373:820–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.080
Wang Y, Shao Q, Huang SS, Zhang B, Xu C (2018) High performance and simultaneous sequestration of Cr(VI) and Sb(III) by sulfidated zerovalent iron. J Clean Prod 191:436–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.217
Wen R, Tu B, Guo X, Hao X, Wu X, Tao H (2020) An ion release controlled Cr(VI) treatment agent: nano zero-valent iron/carbon/alginate composite gel. Int J Biol Macromol 146:692–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.168
Wilkin RT, Lee TR, Sexton MR, Acree SD, Puls RW, Blowes DW, Kalinowski C, Tilton JM, Woods LL (2019) Geochemical and isotope study of trichloroethene degradation in a zero-valent iron permeable reactive barrier: a twenty-two-year performance evaluation. Environ Sci Technol 53(1):296–306. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b04081
Wu J, Gao H, Yao S, Chen L, Gao Y, Zhang H (2015) Degradation of Crystal Violet by catalytic ozonation using Fe/activated carbon catalyst. Sep Purif Technol 147:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.04.022
Wu S, Li F, Wu Y, Xu R, Li G (2010) Preparation of novel poly(vinyl alcohol)/SiO2 composite nanofiber membranes with mesostructure and their application for removal of Cu2+ from waste water. Chem Commun 46(10):1694–1696. https://doi.org/10.1039/b925296g
Wu Y, Yang XT, Fang X, Cheng XR, Hu A, Lin LF, Yu CP (2020) Hydrothermal conversion of waste cartons into a magnetic carbon-iron composite for use as an efficient and recyclable dye adsorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 578:717–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.06.049
Xie Z, Wang C, Yin L (2017) Nickel-assisted iron oxide catalysts for the enhanced degradation of refractory DDT in heterogeneous Fenton-like system. J Catal 353:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2017.03.024
Xu P, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Feng CL, Hu S, Zhao MH, Lai C, Wei Z, Huang C, Xie GX, Liu ZF (2012) Use of iron oxide nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 424:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.023
Yao QS, Huang C, Wang MK, Xiong L, Chen XD (2020) Treatment of water hyacinth anaerobic fermentation wastewater by combining Fe-C micro-electrolysis with Fenton reaction. J Environ Chem Eng 8(5):104157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104157
Ye J, Yin H, Xie D, Peng H, Huang J, Liang W (2013) Copper biosorption and ions release by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in the presence of benzo[a]pyrene. Chem Eng J 219:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.093
Yin Z, Cui C, Chen H, Duoni Yu, X., Qian, W. (2020) The application of carbon nanotube/graphene-based nanomaterials in wastewater treatment. Small 16(15):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201902301
Zhan J, Zheng T, Piringer G, Day C, Mcpherson GL, Lu Y, Papadopoulos K, John VT (2008) Transport characteristics of nanoscale functional zerovalent iron/silica composites for in situ remediation of trichloroethylene. Environ Sci Technol 42(23):8871–8876. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800387p
Zhang S, Xue X, Liu X, Duan P, Yang H, Jiang T, Wang D, Liu R (2006) Current situation and comprehensive utilization of iron ore tailing resources. J Min Sci 4(42):403–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10913-006-0069-9
Zhang X, Li A, Jiang Z, Zhang Q (2006) Adsorption of dyes and phenol from water on resin adsorbents: effect of adsorbate size and pore size distribution. J Hazard Mater 137(2):1115–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2006.03.061
Zhu J, Zheng W, He B, Zhang J, Anpo M (2004) Characterization of Fe–TiO2 photocatalysts synthesized by hydrothermal method and their photocatalytic reactivity for photodegradation of XRG dye diluted in water. J Mol Catal a: Chem 216(1):35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLCATA.2004.01.008
Funding
This work was supported by the Guangdong University Innovation Team (2021KCXTD055) and the Guangdong College Students’ Innovative Project (pdjh2021b0538, X201910580158).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data collection and analysis were performed by Mr. Robinson Vega and Mr. Rong Rong. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mr. Robinson Vega, Mr. Rong Rong, and Dr. Min Dai. It was revised critically by Dr. Imran Ali and Dr. Iffat Naz. Finally, Prof. Changsheng Peng approved this review to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: George Z. Kyzas.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vega, R., Rong, R., Dai, M. et al. Fe–C-based materials: synthesis modulation for the remediation of environmental pollutants—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 64345–64369 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21849-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21849-9