Abstract
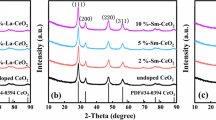
Tuning morphology and doping additional rare earth (RE) cations are potential techniques to promote the photocatalytic performance of ceria (CeO2), evaluating the collaborative effects of morphology and RE dopants is significant for producing high active ceria-based catalysts. So in this work, cubic, polyhedral and rod-like nanoceria doped with 10 mol % La (lanthanum), Y (yttrium), or Sm (samarium) were synthesized by a facile template-free hydrothermal method. Phases, morphologies, oxygen vacancies (OVs) concentration, energy band structure, photo-carriers separation/recombination, and photodegradation ratio toward methylene blue (MB) dye of as prepared ceria were studied. Results show that doped CeO2 maintains a similar morphology structure with un-doped sample and the band gap narrows slightly. Y-doped nanoceria, with an improved separation and a reduced recombination of photo-excited electrons (e−) and holes (h+), owns a higher MB photodegradation ratio than that of samples doping with La or Sm, which is measured as 79.04, 84.43, and 85.59% for Y-doped cubic, polyhedral, and rod-like CeO2. The collaborative influence of morphology tuning and RE (La, Y, and Sm) doping on photocatalytic performance of nanoceria includes the effects of doped elements and the formation of OVs. The elevation of OVs concentration as well as the separation efficiency of photo-generated e−/h+ are suggested to further enhance the photocatalytic performance of ceria.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Authors can confirm that all relevant data are included in the article and/or its supplementary information files.
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The manuscript does not involve the use of any animal or human data or tissue.
Consent for publication.
Not applicable, this paper does not contain data from any individual person.
References
Aboutaleb WA, El-Salamony RA (2019) Effect of Fe2O3-CeO2 nanocomposite synthesis method on the Congo red dye photodegradation under visible light irradiation. Mater Chem Phys 236:121724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121724
Amalric Popescu D, Herrmann J-M, Ensuque A, Bozon-Verduraz F (2001) Nanosized tin dioxide: spectroscopic (UV–VIS, NIR, EPR) and electrical conductivity studies. Phys Chem Chem Phys 3:2522–2530. https://doi.org/10.1039/b100553g
Amani H, Habibey R, Hajmiresmail SJ, Latifi S, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Akhavan O (2017) Antioxidant nanomaterials in advanced diagnoses and treatments of ischemia reperfusion injuries. J Mater Chem B 5:9452–9476. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb01689a
Ansari SA, Khan MM, Kalathil S, Nisar A, Lee J, Cho MH (2013) Oxygen vacancy induced band gap narrowing of ZnO nanostructures by an electrochemically active biofilm. Nanoscale 5:9238–9246. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr02678g
Bakkiyaraj R, Balakrishnan M, Bharath G, Ponpandian N (2017) Facile synthesis, structural characterization, photocatalytic and antimicrobial activities of Zr doped CeO2 nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 724:555–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.07.049
Bi H, Zhang LX, Xing Y, Zhang P, Chen JJ, Yin J, Bie LJ (2021) Morphology-controlled synthesis of CeO2 nanocrystals and their facet-dependent gas sensing properties. Sens Actuators, B 330:129374–129384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129374
Borchert H, Frolova YV, Kaichev VV, Prosvirin IP, Alikina GM, Lukashevich AI, Zaikovskii VI, Moroz EM, Trukhan SN, Ivanov VP, Paukshtis EA, Bukhtiyarov VI, Sadykov VA (2005) Electronic and chemical properties of nanostructured cerium dioxide doped with praseodymium. J Phys Chem B 109:5728–5738. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp045828c
Choudhury B, Chetri P, Choudhury A (2014) Oxygen defects and formation of Ce3+affecting the photocatalytic performance of CeO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv 4:4663–4671. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra44603d
Dong B, Li LY, Dong ZF, Xu R, Wu Y (2018) Fabrication of CeO2 nanorods for enhanced solar photocatalysts. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:5275–5282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.10.061
Du HW, Wang Y, Arandiyan H, Scott J, Wan T, Chu DW (2018) Correlating morphology and doping effects with the carbon monoxide catalytic activity of Zn doped CeO2 nanocrystals. Catal Sci Technol 8:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cy01999h
Fandi Z, Ameur N, Brahimi FT, Bedrane S, Bachir R (2020) Photocatalytic and corrosion inhibitor performances of CeO2 nanoparticles decorated by noble metals: Au, Ag. Pt J Environ Chem Eng 8:104346–104355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104346
Huang YC, Wu SH, Hsiao CH, Lee AT, Huang MH (2020) Mild synthesis of size-tunable CeO2 octahedra for band gap variation. Chem Mater 32:2631–2638. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c00318
Irshad MS, Aziz MH, Fatima M, Rehman SU, Idrees M, Rana S, Shaheen F, Ahmed A, Javed MQ, Huang Q (2019) Green synthesis, cytotoxicity, antioxidant and photocatalytic activity of CeO2 nanoparticles mediated via orange peel extract (OPE). Mater Res Express 2053-1591. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab3326
Islam MJ, Reddy DA, Choi J, Kim TK (2016) Surface oxygen vacancy assisted electron transfer and shuttling for enhanced photocatalytic activity of a Z-scheme CeO2-AgI nanocomposite. RSC Adv 6:19341–19350. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra27533d
Issarapanacheewin S, Wetchakun K, Phanichphant S, Kangwansupamonkon W, Wetchakun N (2015) A novel CeO2/Bi2WO6 composite with highly enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater Lett 156:28–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.04.139
Jiang D, Wang WZ, Zhang L, Zheng YL, Wang Z (2015) Insights into the surface-defect dependence of photoreactivity over CeO2 nanocrystals with well-defined crystal facets. ACS Catal 5:4851–4858. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b01128
Lan YP, Sohn HY (2018a) Effect of oxygen vacancies and phases on catalytic properties of hydrogen-treated nanoceria particles. Mater Res Express 5:035501–035511. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaaff4
Lan YP, Sohn HY (2018b) Nanoceria synthesis in molten KOH-NaOH mixture: characterization and oxygen vacancy formation. Ceram Int 44:3847–3855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.172
Lan YP, Sohn HY, Mohassab Y, Liu Q, Xu B (2017) Nanoceria synthesis in the KCl-LiCl salt system: Crystal formation and properties. J Am Ceram Soc 100:1863–1875. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.14747
Lan Y, Xia X, Li J, Mao X, Chen C, Ning D, Chu Z, Zhang J, Liu F (2021) Insight into the contributions of surface oxygen vacancies on the promoted photocatalytic property of nanoceria. Nanomaterials 2079-4991. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051168
Lee Y, He G, Akey AJ, Si R, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M, Herman IP (2011) Raman analysis of mode softening in nanoparticle CeO2-δ and Au-CeO2-δ during CO oxidation. J Am Ceram Soc 133:12952–12955. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja204479j
Liu BS, Zhao XJ, Terashima C, Fujishima A, Nakata K (2014) Thermodynamic and kinetic analysis of heterogeneous photocatalysis for semiconductor systems. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:8751–8760. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp55317e
Liyanage AD, Perera SD, Tan K, Chabal Y, Balkus KJ (2014) Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activity of Y-doped CeO2 nanorods. ACS Catal 4:577–584. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400889y
Lucid AK, Keating PRL, Allen JP, Watson GW (2016) Structure and reducibility of CeO2 doped with trivalent cations. J Phys Chem C 120:23430–23440. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b08118
Mai HX, Sun LD, Zhang YW, Si R, Feng W, Zhang H, Liu H, Yan C (2005) Shape-selective synthesis and oxygen storage behavior of ceria nanopolyhedra, nanorods, and nanocubes. J Phys Chem B 109:24380–24385. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp055584b
Majeed Khan MA, Khan W, Naziruddin Khan M, Alhazaa AN (2019) Enhanced visible light-driven photocatalytic performance of Zr doped CeO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron 30:8291–8300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01147-w
Mao X, Xia X, Li J, Chen C, Zhang J, Ning D, Lan Y-P (2021) Homogenously rare-earth-ion-doped nanoceria synthesis in KOH-NaOH molten flux: characterization and photocatalytic property. J Mater Eng Perform 30:3795–3805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05683-7
Melchionna M, Fornasiero P (2014) The role of ceria-based nanostructured materials in energy applications. Mater Today 17:349–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2014.05.005
Mitchell KJ, Abboud KA, Christou G (2017) Atomically-precise colloidal nanoparticles of cerium dioxide. Nat Commun 8:1445–1451. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01672-4
Monsef R, Ghiyasiyan-Arani M, Salavati-Niasari M (2021) Design of magnetically recyclable ternary Fe2O3/EuVO4/g-C3N4 nanocomposites for photocatalytic and electrochemical hydrogen storage. ACS Applied Energy Materials 4:680–695. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.0c02557
Mori T, Drennan J, Lee JH, Li JG, Ikegami T (2002) Oxide ionic conductivity and microstructures of Sm- or La-doped CeO2-based systems. Solid State Ionics 154–155:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00483-6
Murali A, Lan YP, Sohn HY (2019) Effect of oxygen vacancies in non-stoichiometric ceria on its photocatalytic properties. Nano-Struct Nano-Objects 18:100257–100270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2019.100257
Nolan M, Grigoleit S, Sayle DC, Parker SC, Watson GW (2005) Density functional theory studies of the structure and electronic structure of pure and defective low index surfaces of ceria. Surf Sci 576:217–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2004.12.016
Normand FL, Fallah JE, Hilaire L, Légaré P, Kotani A, Parlebas JC (1989) Photoemission on 3d core levels of cerium: an experimental and theoretical investigation of the reduction of cerium dioxide. Solid State Commun 7:885–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-1098(89)90555-3
Peng SS, Yang JX, Guo L, Wang JJ, Zhao JC, Xu JL, Li ZQ (2020) Shape-dependent CeO2@BiOI for degradation of aqueous Cr(VI). Adv Mater Interfaces 7:1901879–1901887. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201901879
Prathap Kumar M, Suganya Josephine GA, Sivasamy A (2017) Oxidation of organic dye using nanocrystalline rare earth metal ion doped CeO2 under UV and visible light irradiations. J Mol Liq 242:789–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.07.082
Qiao ZA, Wu ZL, Dai S (2013) Shape-controlled ceria-based nanostructures for catalysis applications. Chemsuschem 6:1821–1833. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201300428
Qin Y, Liu X, Zhu T, Zhu T (2019) Catalytic oxidation of ethyl acetate over silver catalysts supported on CeO2 with different morphologies. Mater Chem Phys 229:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.02.065
Sakar M, Rubini R, Tripathy S, Balakumar S (2012) Effect of Gd dopant concentration on the defect engineering in ceria nanostructures. Mater Res Bull 47:4340–4346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.09.007
Si R, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M (2008) Shape and crystal-plane effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au-CeO2 catalysts for the water–gas shift reaction. Angew Chem 120:2926–2929. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja204479j
Singh K, Kumar K, Srivastava S, Chowdhury A (2017) Effect of rare-earth doping in CeO2 matrix: correlations with structure, catalytic and visible light photocatalytic properties. Ceram Int 43:17041–17047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.116
Singhania A (2017) High surface area M (M = La, Pr, Nd, and Pm)-doped ceria nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and activity comparison for CO oxidation. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:13594–13601. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b03143
Thill AS, Lobato FO, Vaz MO, Fernandes WP, Carvalho VE, Soares EA, Poletto F, Teixeira SR, Bernardi F (2020) Shifting the band gap from UV to visible region in cerium oxide nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 528:146860–146866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146860
Wang ZJ, Gao YZ, Chabal YJ, Balkus KJ (2017) Oxidative dehydrogenation of cyclohexane and cyclohexene over Y-doped CeO2 nanorods. Catal Lett 147:738–744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-017-1974-z
Wang J, Fu W, Xu W, Wu M, Sun Y, Dai Y (2021) Oxide nanofibers as catalysts toward energy conversion and environmental protection. Chem Res Chin Univ 37:366–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-021-1110-x
Wang M, Shen M, Jin X, Tian J, Shao Y, Zhang L, Li Y, Shi J (2022) Exploring the enhancement effects of hetero-metal doping in CeO2 on CO2 photocatalytic reduction performance. Chem Eng J 130987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130987
Wetchakun N, Chaiwichain S, Inceesungvorn B, Pingmuang K, Phanichphant S, Minett AI, Chen J (2012) BiVO4/CeO2 nanocomposites with high visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:3718–3723. https://doi.org/10.1021/am300812n
Xia XW, Li JQ, Chen CY, Lan YP, Mao XS, Bai FS (2021) Optimal rare-earth (La, Y and Sm) doping conditions and enhanced mechanism for photocatalytic application of ceria nanorods. Nanotechnology 32:195708–195722. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/abdf90
Xiao Y, Tan S, Wang D, Wu J, Jia T, Liu Q, Qi Y, Qi X, He P, Zhou M (2020) CeO2/BiOIO3 heterojunction with oxygen vacancies and Ce4+/Ce3+ redox centers synergistically enhanced photocatalytic removal heavy metal. Appl Surf Sci 530:147116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147116
Xie SL, Wang ZL, Cheng FL, Zhang P, Mai WJ, Tong YX (2017) Ceria and ceria-based nanostructured materials for photoenergy applications. Nano Energy 34:313–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.02.029
Xu B, Zhang QT, Yuan SS, Zhang M, Ohno T (2015) Morphology control and photocatalytic characterization of yttrium-doped hedgehog-like CeO2. Appl Catal B 164:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.07.045
Xu B, Yang H, Zhang QT, Yuan SS, Xie A, Zhang M, Ohno T (2020) Design and synthesis of Sm, Y, La and Nd-doped CeO2 with a broom-like hierarchical structure: a photocatalyst with enhanced oxidation performance. ChemCatChem 12:2638–2646. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201902309
Yang C, Yu X, Plessow PN, Heissler S, Weidler PG, Nefedov A, Studt F, Wang Y, Woll C (2017) Rendering photoreactivity to ceria: the role of defects. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56:14301–14305. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201707965
Yang H, Xu B, Yuan SS, Zhang QT, Zhang M, Ohno T (2019) Synthesis of Y-doped CeO2/PCN nanocomposited photocatalyst with promoted photoredox performance. Appl Catal B 243:513–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.057
Yang XJ, Liu Y, Li J, Zhang YL (2019b) Effects of calcination temperature on morphology and structure of CeO2 nanofibers and their photocatalytic activity. Mater Lett 241:76–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.01.006
Yang C, Yang J, Duan X, Hu G, Liu QC, Ren S, Li JL, Kong M (2020) Roles of photo-generated holes and oxygen vacancies in enhancing photocatalytic performance over CeO2 prepared by molten salt method. Adv Powder Technol 31:4072–4081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.08.017
Younis A, Chu DW, Kaneti YV, Li S (2016) Tuning the surface oxygen concentration of 111 surrounded ceria nanocrystals for enhanced photocatalytic activities. Nanoscale 8:378–387. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr06588g
Yue L, Zhang XM (2009) Structural characterization and photocatalytic behaviors of doped CeO2 nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 475:702–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.07.096
Zhang KJ, Gu SW, Wu Y, Fan QW, Zhu C (2020a) Preparation of pyramidal SnO/CeO2 nano-heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic activity for degradation of tetracycline. Nanotechnology 31:123522–123539. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab73b4
Zhang Q, Zhao X, Duan L, Shen H, Liu R (2020) Controlling oxygen vacancies and enhanced visible light photocatalysis of CeO2/ZnO nanocomposites. J Photochem Photobiol A 392:112156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112156
Zhong MH, Wang ZD, Dai D, Yang BZ, Zuo SX, Yao C, Wu FQ, Li XZ (2021) Upconversion hollow nanospheres CeF3 co-doped with Yb3+ and Tm3+ for photocatalytic nitrogen fixation. J Rare Earths. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2021.03.004
Zinatloo-Ajabshir S, Mortazavi-Derazkola S, Salavati-Niasari M (2018) Nd2O3-SiO2 nanocomposites: a simple sonochemical preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity. Ultrason Sonochem 42:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.11.026
Funding
This study received financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 52164025, 51804088, 52164017, U1812402, 52074096, and 51774102, Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Projects under the Grant No. [2017]5788, [2018]5781, [2020]1Y219, and [2019]1082, and the Doctor Funding of Guizhou University with Grant No. (2017)04.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception, literature, analysis, and writing. Prof. Yuan-Pei Lan, Prof. Junqi Li, and Prof. Chaoyi Chen put forward the research ideas and finally approved the whole content. Deyang Ning, Zhiyao Chu, and Xisong Mao did the experiments and characterizations. Associate Xuewen Xia directed the research data, analyzed the results, and organized the writing framework. Junshan Zhang and Fengyuan Liu discussed the characterization results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, X., Li, J., Chen, C. et al. Collaborative influence of morphology tuning and RE (La, Y, and Sm) doping on photocatalytic performance of nanoceria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 88866–88881 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21787-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21787-6