Abstract
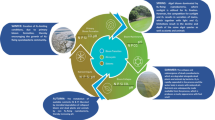
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) are a worldwide problem with substantial adverse effects on the aquatic environment as well as human health, which have prompted researchers to study measures to stem and control them. Meanwhile, it is key to research and develop monitoring methods to establish early warning HABs. However, both the current monitoring methods and control methods have some shortcomings, making the field application limited. Thus, we need to improve current approaches for monitoring and controlling HABs efficiently. Based on the freshwater system features in China, we review various monitoring and control methods of HABs, summarize and discuss the problems with these methods, and propose the future development direction of monitoring and control HABs. Finally, we envision that it can combine physical, chemical, and biological methods to inhibit HAB expansion in the future, complementing each other with advantages. Further, we promise to establish a long-term strategy of controlling HABs with various algicidal bacteria co-cultivate for field applications in China. Efforts in studying algicidal bacteria must be increased to better control HABs and mitigate the risks of aquatic ecosystems and human health in China.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Alamri SA, Mohamed ZA (2013) Selective inhibition of toxic cyanobacteria by beta-carboline-containing bacterium Bacillus flexus isolated from Saudi freshwaters. Saudi J Biol Sci 20(4):357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2013.04.002
Bishop WM, Willis BE, Richardson RJ, Cope WG (2018) The presence of algae mitigates the toxicity of copper-based algaecides to a nontarget organism. Environ Toxicol Chem 37(8):2132–2142. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4166
Bullerjahn GS, McKay RM, Davis TW, Baker DB, Boyer GL, D'Anglada LV, Doucette GJ et al (2016) Global solutions to regional problems: collecting global expertise to address the problem of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. A Lake Erie case study. Harmful Algae 54:223–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2016.01.003
Busch JA, Andree KB, Diogene J, Fernandez-Tejedor M, Toebe K, John U, Krock B, Tillmann U, Cembella AD (2016) Toxigenic algae and associated phycotoxins in two coastal embayments in the Ebro Delta (NW Mediterranean). Harmful Algae 55:191–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2016.02.012
Chen C, Pan G, Shi W, Xu F, Techtmann SM, Pfiffner SM, Hazen TC (2018) Clay flocculation effect on microbial community composition in water and sediment. Front Environ Sci 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2018.00060
Chen G, Ding X, Zhou W (2019) Study on ultrasonic treatment for degradation of microcystins (MCs). Ultrason Sonochem 63:104900–104900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104900
Chen L, Men X, Ma M, Li P, Jiao Q, Lu S, Kong F, Wu S (2010) Polysaccharide release by Aphanothece halophytica inhibits cyanobacteria/clay flocculation. J Phycol 46(3):417–423. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2010.00826.x
Chen S, Zheng T, Ye C, Huannixi W, Yakefu Z, Meng Y, Peng X, Tian Z, Wang J, Ma Y, Yang Y, Ma Z, Zuo Z (2018b) Algicidal properties of extracts from Cinnamomum camphora fresh leaves and their main compounds. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:594–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.115
Coffer MM, Schaeffer BA, Darling JA, Urquhart EA, Salls WB (2020) Quantifying national and regional cyanobacterial occurrence in US lakes using satellite remote sensing. Ecol Indic 111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105976
Daguer H, Hoff RB, Molognoni L, Kleemann CR, Felizardo LV (2018) Outbreaks, oxicology, and analytical methods of marine toxins in seafood. Curr Opin Food Sci 24:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2018.10.006
de Bakker DM, van Duyl FC, Bak RPM, Nugues MM, Nieuwland G, Meesters EH (2017) 40 years of benthic community change on the Caribbean reefs of Curacao and Bonaire: the rise of slimy cyanobacterial mats. Coral Reefs 36(2):355–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-016-1534-9
Dia S, Alameddine I, El-Fadel M (2019) Quantifying the efficacy of diquat dibromide in controlling Microcystis aeruginosa and Aphanizomenon flos-aquae in comparison to copper sulfate and potassium permanganate. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 5(1):140–151. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ew00532j
Duan W, Takara K, He B, Luo P, Nover D, Yamashiki Y (2013) Spatial and temporal trends in estimates of nutrient and suspended sediment loads in the Ishikari River, Japan, 1985 to 2010. Sci Total Environ 461:499–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.022
Fan F, Shi X, Zhang M, Liu C, Chen K (2019) Comparison of algal harvest and hydrogen peroxide treatment in mitigating cyanobacterial blooms via an in situ mesocosm experiment. Sci Total Environ 694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133721
Feng T, Wang C, Hou J, Wang PF, Liu Y, Dai QS, Yang YY, You GX (2018) Effect of inter-basin water transfer on water quality in an urban lake: a combined water quality index algorithm and biophysical modelling approach. Ecol Indic 92:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.06.044
Feng WY, Yang F, Zhang C, Liu J, Song FH, Chen HY, Zhu YR, Liu SS, Giesy JP (2020) Composition characterization and biotransformation of dissolved, particulate and algae organic phosphorus in eutrophic lakes. Environ Pollut 265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114838
Gallardo-Rodriguez JJ, Astuya-Villalon A, Llanos-Rivera A, Avello-Fontalba V, Ulloa-Jofre V (2019) A critical review on control methods for harmful algal blooms. Rev Aquac 11(3):661–684. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12251
Galluzzi L, Penna A, Bertozzini E, Vila M, Garces E, Magnani M (2004) Development of a real-time PCR assay for rapid detection and quantification of Alexandrium minutum (a Dinoflagellate). Appl Environ Microbiol 70(2):1199–1206. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.2.1199-1206.2004
Geer TD, Kinley CM, Iwinski KJ, Calomeni AJ, Rodgers JH (2016) Comparative toxicity of sodium carbonate peroxyhydrate to freshwater organisms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 132:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.05.037
Gholizadeh MH, Melesse AM, Reddi L (2016) A comprehensive review on water quality parameters estimation using remote sensing techniques. Sensors (Basel) 16(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081298
Gobler CJ (2020) Climate change and harmful algal blooms: insights and perspective. Harmful Algae 91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.101731
Gold AC, Thompson SP, Piehler MF (2017) Coastal stormwater wet pond sediment nitrogen dynamics. Sci Total Environ 609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.213
Gorham T, Jia Y, Shum CK, Lee J (2017) Ten-year survey of cyanobacterial blooms in Ohio’s waterbodies using satellite remote sensing. Harmful Algae 66:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2017.04.013
Greenfield DI, Duquette A, Goodson A, Keppler CJ, Williams SH, Brock LM, Stackley KD, White D, Wilde SB (2014) The effects of three chemical algaecides on cell numbers and toxin content of the cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaenopsis sp. Environ Manag 54(5):1110–1120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-014-0339-2
Gu N, Gao J, Wang K, Li B, Dong W, Ma Y (2016) Microcystis aeruginosa inhibition by Zn–Fe–LDHs as photocatalyst under visible light. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 64:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.04.016
Guo H, Chen L, Song X (2017) A kind of non-traditional biomanipulation model with constant releasing fish. Math Meth Appl Sci 40(13):4727–4737. https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.4340
Guo L, Wang Q, Xie P, Tao M, Zhang J, Niu Y, Ma Z (2015a) A non-classical biomanipulation experiment in Gonghu Bay of Lake Taihu: control of Microcystis blooms using silver and bighead carp. Aquac Res 46(9):2211–2224. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12375
Guo X, Liu X, Pan J, Yang H (2015b) Synergistic algicidal effect and mechanism of two diketopiperazines produced by Chryseobacterium sp strain GLY-1106 on the harmful bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci Rep 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14720
Guo X, Liu X, Wu L, Pan J, Yang H (2016) The algicidal activity of Aeromonas sp strain GLY-2107 against bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa is regulated by N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. Environ Microbiol 18(11):3867–3883. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13346
Hennon GMM, Dyhrman ST (2020) Progress and promise of omics for predicting the impacts of climate change on harmful algal blooms. Harmful Algae 91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.03.005
Herrera-Sepulveda A, Hernandez-Saavedra NY, Medlin LK, West N (2013) Capillary electrophoresis finger print technique (CE-SSCP): an alternative tool for the monitoring activities of HAB species in Baja California Sur Costal. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(10):6863–6871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1033-7
Ho JC, Michalak AM, Pahlevan N (2019) Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 574(7780):667-+. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1648-7
Hu W, Li CH, Ye C, Wang J, Wei WW, Deng Y (2019) Research progress on ecological models in the field of water eutrophication: CiteSpace analysis based on data from the ISI web of science database. Ecol Model 410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2019.108779
Huang Y-R, Li H-Z, Wei X-M, Wang D-H, Liu Y-T, Li L (2020) The effect of low frequency ultrasonic treatment on the release of extracellular organic matter of Microcystis aeruginosa. Chem Eng J 383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123141
Huisman J, Codd GA, Paerl HW, Ibelings BW, Verspagen JMH, Visser PM (2018) Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat Rev Microbiol 16(8):471–483. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0040-1
Huser BJ, Egemose S, Harper H, Hupfer M, Jensen H, Pilgrim KM, Reitzel K, Rydin E, Futter M (2016) Longevity and effectiveness of aluminum addition to reduce sediment phosphorus release and restore lake water quality. Water Res 97:122–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.06.051
Joo J-H, Wang P, Park BS, Byun J-H, Choi HJ, Kim SH, Han M-S (2017) Improvement of cyanobacterial-killing biologically derived substances (BDSs) using an ecologically safe and cost-effective naphthoquinone derivative. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 141:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.02.006
Kansole M, Lin T-F (2017) Impacts of hydrogen peroxide and copper sulfate on the control of Microcystis aeruginosa and MC-LR and the inhibition of MC-LR degrading bacterium Bacillus sp. Water 9(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/w9040255
Kong Y, Peng Y, Zhang Z, Zhang M, Zhou Y, Duan Z (2019) Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa by ultrasound: Inactivation mechanism and release of algal organic matter. Ultrason Sonochem 56:447–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.04.017
Landsberg, J.H., Hendrickson, J., Tabuchi, M., Kiryu, Y., Williams, B.J. and Tomlinson, M.C (2020) A large-scale sustained fish kill in the St. Johns River, Florida: a complex consequence of cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae 92. 10.1016/j.hal.2020.101771
Laporte D, Rodriguez F, Gonzalez A, Zuniga A, Castro-Nallar E, Saez CA, Moenne A (2020) Copper-induced concomitant increases in photosynthesis, respiration, and C, N and S assimilation revealed by transcriptomic analyses in Ulva compressa (Chlorophyta). BMC Plant Biol 20(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2229-5
Lee HW, Park BS, Joo JH, Patidar SK, Choi HJ, Jin E, Han MS (2018) Cyanobacteria-specific algicidal mechanism of bioinspired naphthoquinone derivative, NQ 2-0. Sci Rep 8(1):11595. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29976-5
Lee S, Thio SK, Park S-Y, Bae S (2019) An automated 3D-printed smartphone platform integrated with optoelectrowetting (OEW) microfluidic chip for on-site monitoring of viable algae in water. Harmful Algae 88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.101638
Leon-Munoz J, Urbina MA, Garreaud R, Luis Iriarte J (2018) Hydroclimatic conditions trigger record harmful algal bloom in western Patagonia (summer 2016). Sci Rep 8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19461-4
Li DX, Zhang H, Chen XH, Xie ZX, Zhang Y, Zhang SF, Lin L, Chen F, Wang DZ (2018a) Metaproteomics reveals major microbial players and their metabolic activities during the blooming period of a marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense. Environ Microbiol 20(2):632–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13986
Li L, Pan G (2013) A universal method for flocculating harmful algal blooms in marine and fresh waters using modified sand. Environ Sci Technol 47(9):4555–4562. https://doi.org/10.1021/es305234d
Li Q, Lin F, Yang C, Wang J, Lin Y, Shen M, Park MS, Li T, Zhao J (2018b) A large-scale comparative metagenomic study reveals the functional interactions in six bloom-forming Microcystis-epibiont communities. Front Microbiol 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00746
Li Y, Shi X, Zhang Z, Peng Y (2019) Enhanced coagulation by high-frequency ultrasound in Microcystis aeruginosa-laden water: Strategies and mechanisms. Ultrason Sonochem 55:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.01.022
Li Y, Zhu H, Lei X, Zhang H, Cai G, Chen Z, Fu L, Xu H, Zheng T (2015) The death mechanism of the harmful algal bloom species Alexandrium tamarense induced by algicidal bacterium Deinococcus sp Y35. Front Microbiol 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00992
Li Z, Lin S, Liu X, Tan J, Pan J, Yang H (2014) A freshwater bacterial strain, Shewanella sp. Lzh-2, isolated from Lake Taihu and its two algicidal active substances, hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione and 2, 3-indolinedione. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(10):4737–4748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5602-1
Liao C, Liu X (2014) High-cell-density cultivation and algicidal activity assays of a novel algicidal bacterium to control algal bloom caused by water eutrophication. Water Air Soil Pollut 225(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2120-9
Lin S, Geng M, Liu X, Tan J, Yang H (2015) On the control of Microcystis aeruginosa and Synechococccus species using an algicidal bacterium, Stenotrophomonas F6, and its algicidal compounds cyclo-(Gly-Pro) and hydroquinone. J Appl Phycol 28(1):345–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0549-x
Lin S, Pan J, Li Z, Liu X, Tan J, Yang H (2014) Characterization of an algicidal bacterium Brevundimonas J4 and chemical defense of Synechococcus sp BN60 against bacterium J4. Harmful Algae 37:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2014.05.002
Loreau M, Ullah H, Nagelkerken I, Goldenberg SU, Fordham DA (2018) Climate change could drive marine food web collapse through altered trophic flows and cyanobacterial proliferation. PLoS Biol 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2003446
Majsterek I, Sicinska P, Tarczynska M, Zalewski M, Walter Z (2004) Toxicity of microcystin from cyanobacteria growing in a source of drinking water. Comparative Biochem Physiol Part C 139(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2004.10.007
Maranon E (2015) Cell size as a key determinant of phytoplankton metabolism and community structure. Annu Rev Mar Sci 7:241–264. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-015955
Mucci M, Douglas G, Lurling M (2020) Lanthanum modified bentonite behaviour and efficiency in adsorbing phosphate in saline waters. Chemosphere 249:126131–126131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126131
Newell SE, Davis TW, Johengen TH, Gossiaux D, Burtner A, Palladino D, McCarthy MJ (2019) Reduced forms of nitrogen are a driver of non-nitrogen-fixing harmful cyanobacterial blooms and toxicity in Lake Erie. Harmful Algae 81:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2018.11.003
Nishu SD, Kang Y, Han I, Jung TY, Lee TK (2019) Nutritional status regulates algicidal activity of Aeromonas sp. L23 against cyanobacteria and green algae. PLoS One 14(3). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213370
Noyma NP, de Magalhaes L, Furtado LL, Mucci M, van Oosterhout F, Huszar VLM, Marinho MM, Lurling M (2016) Controlling cyanobacterial blooms through effective flocculation and sedimentation with combined use of flocculants and phosphorus adsorbing natural soil and modified clay. Water Res 97:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.057
Paerl HW, Otten TG (2013) Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: causes, consequences, and controls. Microb Ecol 65(4):995–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0159-y
Pahlevan N, Smith B, Schalles J, Binding C, Cao Z, Ma R, Alikas K, Kangro K, Gurlin D et al (2020) Seamless retrievals of chlorophyll-a from Sentinel-2 (MSI) and Sentinel-3 (OLCI) in inland and coastal waters: a machine-learning approach. Remote Sens Environ 240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111604
Pan G, Miao X, Bi L, Zhang H, Wang L, Wang L, Wang Z, Chen J, Ali J, Pan M, Zhang J, Yue B, Lyu T (2019) Modified local soil (MLS) technology for harmful algal bloom control, sediment remediation, and ecological restoration. Water 11(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061123
Pan G, Yang B, Wang D, Chen H, Tian BH, Zhang ML, Yuan XZ, Chen JA (2011) In-lake algal bloom removal and submerged vegetation restoration using modified local soils. Ecol Eng 37(2):302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.11.019
Pirasteh S, Mollaee S, Fatholahi SN, Li J (2020) Estimation of phytoplankton chlorophyll-a concentrations in the western basin of Lake Erie using Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 data. Can J Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1080/07038992.2020.1823825
Qin B, Zhou J, Elser JJ, Gardner WS, Deng J, Brookes JD (2020) Water depth underpins the relative role and fates of nitrogen and phosphorus in lakes. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05858
Ren L, Wang P, Wang C, Paerl HW, Wang H (2020) Effects of phosphorus availability and phosphorus utilization behavior of Microcystis aeruginosa on its adaptation capability to ultraviolet radiation. Environ Pollut 256:113441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113441
Rodriguez-Benito CV, Navarro G, Caballero I (2020) Using Copernicus Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 data to monitor harmful algal blooms in Southern Chile during the COVID-19 lockdown. Mar Pollut Bull 161(Pt A):111722–111722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111722
Rousso BZ, Bertone E, Stewart R, Hamilton DP (2020) A systematic literature review of forecasting and predictive models for cyanobacteria blooms in freshwater lakes. Water Res 182:115959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115959
Schaefer AM, Yrastorza L, Stockley N, Harvey K, Harris N, Grady R, Sullivan J, McFarland M, Reif JS (2020) Exposure to microcystin among coastal residents during a cyanobacteria bloom in Florida. Harmful Algae 92:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2020.101769
Schaeffer BA, Schaeffer KG, Keith D, Lunetta RS, Conmy R, Gould RW (2013) Barriers to adopting satellite remote sensing for water quality management. Int J Remote Sens 34(21):7534–7544. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2013.823524
Segura AM, Piccini C, Nogueira L, Alcantara I, Calliari D, Kruk C (2017) Increased sampled volume improves Microcystis aeruginosa complex (MAC) colonies detection and prediction using Random Forests. Ecol Indic 79:347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.04.047
Shen X, Zhang HT, He XL, Shi HL, Stephan C, Jiang H, Wan CH, Eichholz T (2019) Evaluating the treatment effectiveness of copper-based algaecides on toxic algae Microcystis aeruginosa using single cell-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(21):5531–5543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01933-9
Shi K, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li N, Qin B, Zhu G, Zhou Y (2019) Phenology of phytoplankton blooms in a trophic lake observed from long-term MODIS data. Environ Sci Technol 53(5):2324–2331. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b06887
Shi W, Tan W, Wang L, Pan G (2016) Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa using cationic starch modified soils. Water Res 97:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.06.029
Sildever S, Kawakami Y, Kanno N, Kasai H, Shiomoto A, Katakura S, Nagai S (2019) Toxic HAB species from the Sea of Okhotsk detected by a metagenetic approach, seasonality and environmental drivers. Harmful Algae 87:101631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.101631
Sinha AK, Romano N, Shrivastava J, Monico J, Bishop WM (2020) Oxidative stress, histopathological alterations and anti-oxidant capacity in different tissues of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) exposed to a newly developed sodium carbonate peroxyhydrate granular algaecide formulated with hydrogen peroxide. Aquat Toxicol 218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105348
Song W, Xu Q, Fu X, Zhang P, Pang Y, Song D (2018) Research on the relationship between water diversion and water quality of Xuanwu Lake, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061262
Soria-Perpinya X, Vicente E, Urrego P, Pereira-Sandoval M, Ruiz-Verdu A, Delegido J, Miguel Soria J, Moreno J (2020) Remote sensing of cyanobacterial blooms in a hypertrophic lagoon (Albufera of Valencia, Eastern Iberian Peninsula) using multitemporal Sentinel-2 images. Sci Total Environ 698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134305
Srivastava A, Singh S, Ahn CY, Oh HM, Asthana RK (2013) Monitoring approaches for a toxic cyanobacterial bloom. Environ Sci Technol 47(16):8999–9013. https://doi.org/10.1021/es401245k
Sun P, Esquivel-Elizondo S, Zhao Y, Wu Y (2017) Glucose triggers the cytotoxicity of Citrobacter sp. R1 against Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci Total Environ 603-604:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.056
Sun P, Hui C, Bai N, Yang S, Wan L, Zhang Q, Zhao Y (2015) Revealing the characteristics of a novel bioflocculant and its flocculation performance in Microcystis aeruginosa removal. Sci Rep 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17465
Tan X, Shu X, Guo J, Parajuli K, Zhang X, Duan Z (2018) Effects of low-frequency ultrasound on Microcystis aeruginosa from cell inactivation to disruption. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101(1):117–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2348-y
Tekile A, Kim I, Lee J-Y (2017) 200 kHz Sonication of mixed-algae suspension from a eutrophic lake: the effect on the caution vs. outbreak bloom alert levels. Water 9(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120915
Toldra A, Alcaraz C, Andree KB, Fernandez-Tejedor M, Diogene J, Katakis I, O'Sullivan CK, Campas M (2019) Colorimetric DNA-based assay for the specific detection and quantification of Ostreopsis cf. ovata and Ostreopsis cf. siamensis in the marine environment. Harmful Algae 84:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.02.003
Toldra A, O'Sullivan CK, Diogene J, Campas M (2020) Detecting harmful algal blooms with nucleic acid amplification-based biotechnological tools. Sci Total Environ 749:141605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141605
Toming K, Kutser T, Laas A, Sepp M, Paavel B, Nõges T (2016) First experiences in mapping lake water quality parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI imagery. Remote Sens 8(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080640
Trainer VL, Moore SK, Hallegraeff G, Kudela RM, Clement A, Mardones JI, Cochlan WP (2020) Pelagic harmful algal blooms and climate change: lessons from nature’s experiments with extremes. Harmful Algae 91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.03.009
Umphres GD, Roelke DL, Netherland MD (2012) A chemical approach for the mitigation of Prymnesium parvum blooms. Toxicon 60(7):1235–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2012.08.006
Wang BL, Song QY, Long JJ, Song GF, Mi WJ, Bi YH (2019a) Optimization method for Microcystis bloom mitigation by hydrogen peroxide and its stimulative effects on growth of chlorophytes. Chemosphere 228:503–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.138
Wang J-H, Yang C, He L-Q-S, Dao G-H, Du J-S, Han Y-P, Wu G-X, Wu Q-Y, Hu H-Y (2019b) Meteorological factors and water quality changes of Plateau Lake Dianchi in China (1990–2015) and their joint influences on cyanobacterial blooms. Sci Total Environ 665:406–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.010
Wang Y, Gu X, Zeng Q, Mao Z, Wang W (2016) Contrasting response of a plankton community to two filter-feeding fish and their feces: an in situ enclosure experiment. Aquaculture 465:330–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.08.014
Wang Y, Li S, Liu G, Li X, Yang Q, Xu Y, Hu Z, Chen CY, Chang JS (2020) Continuous production of algicidal compounds against Akashiwo sanguinea via a Vibrio sp. co-culture. Bioresour Technol 295:122246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122246
Wang Y, Liu Q, Wei Z, Liu N, Li Y, Li D, Jin Z, Xu X (2018) Thiazole amides, a novel class of algaecides against freshwater harmful algae. Sci Rep 8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26911-6
Wells ML, Karlson B, Wulff A, Kudela R, Trick C, Asnaghi V, Berdalet E, Cochlan W et al (2020) Future HAB science: directions and challenges in a changing climate. Harmful Algae 91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.101632
Wu L, Guo X, Liu X, Yang H (2017) NprR-NprX quorum-sensing system regulates the algicidal activity of Bacillus sp. strain S51107 against bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Front Microbiol 8, 1968. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01968
Xie M, Ren M, Yang C, Yi H, Li Z, Li T, Zhao J (2016) Metagenomic analysis reveals symbiotic relationship among bacteria in Microcystis-dominated community. Front Microbiol 7:56. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00056
Yamamoto K, King PM, Wu X, Mason TJ, Joyce EM (2015) Effect of ultrasonic frequency and power on the disruption of algal cells. Ultrason Sonochem 24:165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.11.002
Yan ZH, Yang HH, Dong HK, Ma BN, Sun HW, Pan T, Jiang RR, Zhou RR, Shen J, Liu JC, Lu GH (2018) Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of organic micropollutants in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China: a case study of water diversion. Environ Pollut 239:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.023
Yang C, Yang P, Geng J, Yin H, Chen K (2020) Sediment internal nutrient loading in the most polluted area of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Chaohu, China) and its contribution to lake eutrophication. Environ Pollut 262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114292
Yang J, Holbach A, Wilhelms A, Qin Y, Zheng B, Zou H, Qin B, Zhu G, Norra S (2019) Highly time-resolved analysis of seasonal water dynamics and algal kinetics based on in-situ multi-sensor-system monitoring data in Lake Taihu, China. Sci Total Environ 660:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.044
Yang K, Chen Q, Zhang D, Zhang H, Lei X, Chen Z, Li Y, Hong Y, Ma X, Zheng W, Tian Y, Zheng T, Xu H (2017) The algicidal mechanism of prodigiosin from Hahella sp KA22 against Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci Rep 7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08132-5
Ye L, Cai QH, Zhang M, Tan L (2014) Real-time observation, early warning and forecasting phytoplankton blooms by integrating in situ automated online sondes and hybrid evolutionary algorithms. Ecol Inform 22:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2014.04.001
Yi C, Guo L, Ni L, Luo C (2016) Silver carp exhibited an enhanced ability of biomanipulation to control cyanobacteria bloom compared to bighead carp in hypereutrophic Lake Taihu mesocosms. Ecol Eng 89:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.01.022
Yi Y-L, Lei Y, Yin Y-B, Zhang H-Y, Wang G-X (2011) The antialgal activity of 40 medicinal plants against Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 24(4):847–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9703-2
Yi YL, Yu XB, Zhang C, Wang GX (2015) Growth inhibition and microcystin degradation effects of Acinetobacter guillouiae A2 on Microcystis aeruginosa. Res Microbiol 166(2):93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2014.12.013
Yoon J-E, Lim J-H, Son S, Youn S-H, Oh H-J, Hwang J-D, Kwon J-I, Kim S-S, Kim I-N (2019) Assessment of satellite-based chlorophyll-a algorithms in eutrophic Korean coastal waters: Jinhae Bay case study. Front Mar Sci 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2019.00359
Yu M-L, Hong G-X, Xu H, Zhu G-W, Zhu M-Y, Quan Q-M (2019a) Effects of cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic lakes on water quality of connected rivers. Environmental. Science 40(2):603–613. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201804047
Yu M-L, Hong G-X, Zhu G-W, Quan Q-M, Xu H, Zhu M-Y, Ding W-H, Li W, Wu T-F (2019) Wind field influences on the spatial distribution of cyanobacterial blooms and nutrients in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu. China Environ Sci 40(8):3519–3529. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201901184
Yu S, Li C, Xu C, Effiong K, Xiao X (2019c) Understanding the inhibitory mechanism of antialgal allelochemical flavonoids from genetic variations: photosynthesis, toxin synthesis and nutrient utility. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 177:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.097
Yu Y, Zeng Y, Li J, Yang C, Zhang X, Luo F, Dai X (2019e) An algicidal Streptomyces amritsarensis strain against Microcystis aeruginosa strongly inhibits microcystin synthesis simultaneously. Sci Total Environ 650:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.433
Yu Z, Song X, Cao X, Liu Y (2017) Mitigation of harmful algal blooms using modified clays: theory, mechanisms, and applications. Harmful Algae 69:48–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2017.09.004
Zamor RM, Glenn KL, Hambright KD (2012) Incorporating molecular tools into routine HAB monitoring programs: using qPCR to track invasive Prymnesium. Harmful Algae 15:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2011.10.028
Zamyadi A, Choo F, Newcombe G, Stuetz R, Henderson RK (2016) A review of monitoring technologies for real-time management of cyanobacteria: recent advances and future direction. Trac-Trends Anal Chem 85:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.06.023
Zhang H, Liu J, He Y, Xie Z, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Lin L, Liu S, Wang D (2019) Quantitative proteomics reveals the key molecular events occurring at different cell cycle phases of the in situ blooming dinoflagellate cells. Sci Total Environ 676:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.216
Zhang, H., Wang, H., Zheng, W., Yao, Z., Peng, Y., Zhang, S., Hu, Z., Tao, Z. and Zheng, T (2017) Toxic effects of prodigiosin secreted by Hahella sp. KA22 on harmful alga Phaeocystis globosa. Frontiers in Microbiology 8. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00999
Zhang MX, Dolatshah A, Zhu WL, Yu GL (2018) Case study on water quality improvement in Xihu Lake through diversion and water distribution. Water 10(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030333
Zhang S, Zheng W, Wang H (2020) Physiological response and morphological changes of Heterosigma akashiwo to an algicidal compound prodigiosin. J Hazard Mater 385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121530
Zhang T, Zeng WH, Wang SR, Ni ZK (2014) Temporal and spatial changes of water quality and management strategies of Dianchi Lake in southwest China. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 18(4):1493–1502. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-18-1493-2014
Zhang X, Xie P, Huang XP (2008) A review of nontraditional biomanipulation. Sci World J 8:1184–1196. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2008.144
Zhao S, Yuan S, Wang H (2020) Threshold behavior in a stochastic algal growth model with stoichiometric constraints and seasonal variation. J Differ Equ 268(9):5113–5139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jde.2019.11.004
Zheng H, Sun C, Hou X, Wu M, Yao Y, Li F (2018) Pyrolysis of Arundo donax L. to produce pyrolytic vinegar and its effect on the growth of dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. Bioresour Technol 247:273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.049
Zhong J-C, You B-S, Fan C-X, Li B, Zhang L, Ding S-M (2008) Influence of sediment dredging on chemical forms and release of phosphorus. Pedosphere 18(1):34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60100-3
Zhou J, Zhang BY, Yu K, Du XP, Zhu JM, Zeng YH, Cai ZH (2020) Functional profiles of phycospheric microorganisms during a marine dinoflagellate bloom. Water Res 173:115554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115554
Zhou Y, Feng J, Feng L, Xie D, Peng H, Cai M, He H (2019) Synthesis and activity of 1,2,3-triazole aminopyrimidines against cyanobacteria as PDHc-E1 competitive inhibitors. J Agric Food Chem 67(45):12538–12546. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02878
Zhu JN, Yu ZM, He LY, Cao XH, Liu SY, Son XX (2018) Molecular mechanism of modified clay controlling the brown tide organism Aureococcus anophagefferens revealed by transcriptome analysis. Environ Sci Technol 52(12):7006–7014. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05172
Zhuohua MEI, Zhehai Z, Chunxia Z, Min XU, Min LI (2010) Dynamics of phytoplankton and water quality with control of cyanobacterial bloom in Lake Xuanwu. Nanjing Scientia Limnologica Sinica 22(1):44–48
Acknowledgements
The authors would also like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was financed by the Knowledge Innovation Program of Shenzhen (JSGG20180718115204691) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21377061, 81270041, 41907150).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shengjun Xu, Ping Lyu, Xiaoxu Zheng, Haijun Yang, Bing Xia, and Hui Li have written the manuscript. Hao Zhang and Shuanglong Ma helped in the critical revision. Shengjun Xu, Ping Lyu, and Xiaoxu Zheng have conceived the study and edited the manuscript. Ping Lyu has performed the literature search and data analysis. The authors have read and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vitor Vasconcelos
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, S., Lyu, P., Zheng, X. et al. Monitoring and control methods of harmful algal blooms in Chinese freshwater system: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 56908–56927 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21382-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21382-9