Abstract
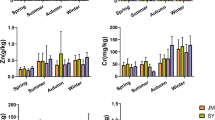
To analyze the impact of particle sizes on sources and related health risks for heavy metals, road dust samples in Beijing were collected and sifted into five particle sizes. The positive matrix factorization (PMF), human health risk assessment model (HHRA), and Monte Carlo simulation were used in the health risk assessment and source apportionment. Results showed that mass of particles < 74 μm occupied about 50% of the total particles, while only 8.48% of the particles were > 500 μm. Mass distribution and concentrations of heavy metals in each particle size changed in temporal. Over 85.00% of carcinogenic risks (CR) were from particles <74 μm, whereas CR from particles >250 μm were ignorable. Sources for health risks in each particle size were traffic exhaust, fuel combustion, construction, and use of pesticides and fertilizers. Proportions of sources to CR differed among particle sizes. Traffic exhaust and fuel combustion contributed over 90% to CR in particles <74 μm, whereas construction contributed the highest (31.68–54.14%) among all sources in particles 74–250 μm. Furthermore, the difference between health risks based on sifted road dust and that based on unsifted road dust was quantitatively analyzed. Source-specific health risk apportionment based on unsifted road dust was not presentative to all particle sizes, and true value of health risks could be over 2.5 times of the estimated value based on unsifted road dust, emphasized the importance of sifting of road dust.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainalis D, Ducarne L, Kaufmann O, Tshibangu J-P, Verlinden O, Kouroussis G (2018) Improved analysis of ground vibrations produced by man-made sources. Sci Total Environ 616-617:517–530
Amato F, Alastuey A, Karanasiou A, Lucarelli F, Querol X (2016a) AIRUSE-LIFE+: A harmonized PM speciation and source apportionment in five southern European cities. Atmos Chem Phys 16:23989–24039
Amato F, Zandveld P, Keuken M, Jonkers S, Querol X, Reche C, Gon HACD vd, Schaap M (2016b) Improving the modeling of road dust levels for Barcelona at urban scale and street level. Atmos Environ 125:231–242
Aryal R, Beecham S, Sarkar B, Chong MN, Kinsela A, Kandasamy J, Vigneswaran S (2016) Readily wash-off road dust and associated heavy metals on motorways. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:1
August A, Junjun D, Ke D, Mei Z, Caiqing Y, Martin SL, Örjan G (2015) Regionally-varying combustion sources of the January 2013 severe haze events over eastern China. Environ Sci Technol 49:2038–2043
Bai Y, Laenen A, Haufroid V, Nawrot TS, Nemery B (2019) Urinary lead in relation to combustion-derived air pollution in urban environments. A longitudinal study of an international panel. Environ Int 125:75–81
Bari MA, Kindzierski WB (2016) Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Edmonton, Canada: source apportionment and potential risk for human health. Environ Pollut 218:219–229
Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics (2021) The main data of the seventh national census in Beijing. http://www.beijing.gov.cn/gongkai/shuju/sjjd/202105/t20210519_2392877.html
Bi X, Liang S, Li X (2013) A novel in situ method for sampling urban soil dust: particle size distribution, trace metal concentrations, and stable lead isotopes. Environ Pollut 177:48–57
Bi X-Y, Li Z-G, Wang S-X, Zhang L, Xu R, Liu J-L, Yang H-M, Guo M-Z (2017) Lead isotopic compositions of selected coals, Pb/Zn ores and fuels in China and the application for source tracing. Environ Sci Technol 51:13502–13508
Bourliva A, Kantiranis N, Papadopoulou L, Aidona E, Christophoridis C, Kollias P, Evgenakis M, Fytianos K (2018) Seasonal and spatial variations of magnetic susceptibility and potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in road dusts of Thessaloniki city, Greece: a one-year monitoring period. Sci Total Environ 639:417–427
Cao Z, Xu F, Li W, Sun J, Shen M, Su X, Feng J, Yu G, Covaci A (2015) Seasonal and particle size-dependent variations of hexabromocyclododecanes in settled dust: implications for sampling. Environ Sci Technol 49:11151–11157
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512-513:143–153
Chen T, Chang Q, Liu J, Clevers J, Kooistra L (2016) Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: a case study in northwest China. Sci Total Environ 565:155–164
Chen G, Wang X, Wang R, Liu G (2019) Health risk assessment of potentially harmful elements in subsidence water bodies using a Monte Carlo approach: an example from the Huainan coal mining area, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:737–745
Conte M, Contini D (2019) Size-resolved particle emission factors of vehicular traffic derived from urban eddy covariance measurements. Environ Pollut 251:830–838
Dehghani S, Moore F, Keshavarzi B, Hale BA (2017) Health risk implications of potentially toxic metals in street dust and surface soil of Tehran. Iran Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 136:92–103
Dietrich M, Wolfe A, Burke M, Krekeler MP (2019) The first pollution investigation of road sediment in Gary, Indiana: anthropogenic metals and possible health implications for a socioeconomically disadvantaged area. Environ Int 128:175–192
Gonzalez-Grijalva B, Meza-Figueroa D, Romero FM, Robles-Morua A, Meza-Montenegro M, Garcia-Rico L, Ochoa-Contreras R (2019) The role of soil mineralogy on oral bioaccessibility of lead: Implications for land use and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 657:1468–1479
Gu Y-G, Gao Y-P, Lin Q (2016) Contamination, bioaccessibility and human health risk of heavy metals in exposed-lawn soils from 28 urban parks in southern China's largest city, Guangzhou. Appl Geochem 67:52–58
Guo GH, Wang YT, Zhang DG, Lei M (2021) Source-specific ecological and health risks of potentially toxicelements in agricultural soils in Southern Yunnan Province and associated uncertainty analysis. J Hazard Mater 417:126144
He X, Shen S, Miao S, Dou J, Zhang Y (2015) Quantitative detection of urban climate resources and the establishment of an urban climate map (UCMap) system in Beijing. Build Environ 92:668–678
Ho K-F, Wu K-C, Niu X, Wu Y, Zhu C-S, Wu F, Cao J-J, Shen Z-X, Hsiao T-C, Chuang K-J (2019) Contributions of local pollution emissions to particle bioreactivity in downwind cities in China during Asian dust periods. Environ Pollut 245:675–683
Hongbo F, Jun L, Guangfeng S, Wenbo D, Grassian VH, Carmichael GR, Yan L, Jianmin C (2012) Solubility of iron from combustion source particles in acidic media linked to iron speciation. Environ Sci Technol 46:11119–11127
Hu X, Zhang Y, Luo J, Wang T, Lian H, Ding Z (2011) Bioaccessibility and health risk of arsenic, mercury and other metals in urban street dusts from a mega-city, Nanjing, China. Environ Pollut 159:1215–1221
Huang Y, Li T, Wu C, He Z, Japenga J, Deng M, Yang X (2015) An integrated approach to assess heavy metal source apportionment in peri-urban agricultural soils. J Hazard Mater 299:540–549
Huang RJ, Cheng R, Jing M, Yang L, Cao JJ (2018) Source-specific health risk analysis on particulate trace elements: coal combustion and traffic emission as major contributors in wintertime Beijing. Environ Sci Technol 52:acs.est.8b02091
Ikegami M, Yoneda M, Tsuji T, Bannai O, Morisawa S (2014) Effect of particle size on risk assessment of direct soil ingestion and metals adhered to children's hands at playgrounds. Risk Anal 34:1677
Jayarathne A, Egodawatta P, Ayoko GA, Goonetilleke A (2017) Geochemical phase and particle size relationships of metals in urban road dust. Environ Pollut 230:218–226
Jayarathne A, Mummullage S, Gunawardana C, Egodawatta P, Ayoko GA, Goonetilleke A (2019) Influence of physicochemical properties of road dust on the build-up of hydrocarbons. Sci Total Environ 694:133812
Jeong GY, Kim JY, Seo J, Kim GM, Jin HC, Chun Y (2014) Long-range transport of giant particles in Asian dust identified by physical, mineralogical, and meteorological analysis. Atmos Chem Phys 14:505–521
Ji X, Xie R, Hao Y, Lu J (2017) Quantitative identification of nitrate pollution sources and uncertainty analysis based on dual isotope approach in an agricultural watershed. Environ Pollut 229:586–594
Jiang Y, Chao S, Liu J, Yang Y, Chen Y, Zhang A, Cao H (2016) Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 168:1658–1668
Jin C, Feng X, Wang X (2014) An exploratory study on the seasonal pattern of tourism in China - Taking Beijing, Shanghai, Yunnan, Sichuan, Fujian and Hainan as examples. Shanghai management science in Chinese 36:63–68
Joshi N, Gupta D, Suryavanshi S, Adamowski J, Madramootoo CA (2016) Analysis of trends and dominant periodicities in drought variables in India: a wavelet transform based approach. Atmos Res 182:200–220
Karlsson HL, Johanna G, Pontus C, Lennart ML (2009) Size-dependent toxicity of metal oxide particles--a comparison between nano- and micrometer size. Toxicol Lett 188:112–118
Khan MF, Latif MT, Lim CH, Amil N, Jaafar SA, Dominick D, Nadzir MSM, Sahani M, Tahir NM (2015) Seasonal effect and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM 2.5. Atmos Environ 106:178–190
Kumar P, Morawska L, Martani C, Biskos G, Neophytou M, Sabatino SD, Bell M, Norford L, Britter R (2015) The rise of low-cost sensing for managing air pollution in cities. Environ Int 75:199–205
Lan Y, Lingxiao Y, Qi Y, Chao Y, Can D, Chuanping M, Xiao S, Fei Y, Yaling L, Wenxing W (2016) Sources apportionment of PM2.5 in a background site in the North China Plain. Sci Total Environ 541:590–598
Lanzerstorfer C, Logiewa A (2019) The upper size limit of the dust samples in road dust heavy metal studies: benefits of a combined sieving and air classification sample preparation procedure. Environ Pollut 245:1079–1085
Ledda C, Fiore M, Santarelli L, Bracci M, Mascali G, D'Agati MG, Busà A, Ferrante M, Rapisarda V (2015) Gestational hypertension and organophosphorus pesticide exposure: a cross-sectional study. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–5
Lemieux CL, Long AS, Lambert IB, Lundstedt S, Tysklind M, White PA (2015) Cancer risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soils determined using bioassay-derived levels of benzo [a] pyrene equivalents. Environ Sci Technol 49:1797–1805
Li F, Zhang J, Huang J, Huang D, Yang J, Song Y, Zeng G (2016) Heavy metals in road dust from Xiandao District, Changsha City, China: characteristics, health risk assessment, and integrated source identification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:13100–13113
Li J, He J, Li Y, Liu Y, Li W, Wu N, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Niu Z (2019) Assessing the threats of organophosphate esters (flame retardants and plasticizers) to drinking water safety based on USEPA oral reference dose (RfD) and oral cancer slope factor (SFO). Water Res 154:84–93
Li Z, Liang T, Li K, Wang P (2020) Exposure of children to light rare earth elements through ingestion of various size fractions of road dust in REEs mining areas. Sci Total Environ 743:140432
Libraries M (2015) Temporal assessment of copper speciation, bioavailability and toxicity in UK freshwaters using chemical equilibrium and biotic ligand models: implications for compliance with copper environmental quality standards. Sci Total Environ 538:385–401
Liu A, Liu L, Li D, Guan Y (2015) Characterizing heavy metal build-up on urban road surfaces: Implication for stormwater reuse. Sci Total Environ 515-516:20–29
Liu R, Men C, Yu W, Xu F, Wang Q, Shen Z (2017) Uncertainty in positive matrix factorization solutions for PAHs in surface sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary in different seasons. Chemosphere 191:S004565351731651X
Liu A, Ma Y, Gunawardena JMA, Egodawatta P, Ayoko GA, Goonetilleke A (2018a) Heavy metals transport pathways: the importance of atmospheric pollution contributing to stormwater pollution. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:696–703
Liu A, Mummullage S, Ma Y, Egodawatta P, Ayoko GA, Goonetilleke A (2018b) Linking source characterisation and human health risk assessment of metals to rainfall characteristics. Environ Pollut 238:866–873
Liu T, Tian Y, Xue Q, Wei Z, Qian Y, Feng Y (2018c) An advanced three-way factor analysis model (SDABB model) for size-resolved PM source apportionment constrained by size distribution of chemical species in source profiles. Environ Pollut 242:1606–1615
Lu H, Yu S (2018) Spatio-temporal variational characteristics analysis of heavy metals pollution in water of the typical northern rivers, China. J Hydrol 559:S002216941830163X
Massadeh A, Jaradat Q, Obiedat M (2007) Chemical speciation of lead and cadmium in different size fractions of dust samples from two busy roads in Irbid City, Jordan. Soil Sediment Contam 16:371–382
Men C, Liu R, Wang Q, Guo L, Shen Z (2018a) The impact of seasonal varied human activity on characteristics and sources of heavy metals in metropolitan road dusts. Sci Total Environ 637:844–854
Men C, Liu R, Xu F, Wang Q, Guo L, Shen Z (2018b) Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 612:138–147
Men C, Liu R, Wang Q, Guo L, Miao Y, Shen Z (2019) Uncertainty analysis in source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust based on positive matrix factorization model and geographic information system. Sci Total Environ 652:27–39
Men C, Wang Y, Liu R, Wang Q, Miao Y, Jiao L, Shoaib M, Shen Z (2020) Temporal variations of levels and sources of health risk associated with heavy metals in road dust in Beijing from May 2016 to April 2018. Chemosphere 270:129434
Meng F, Liu G, Hu Y, Su M, Yang Z (2018) Urban carbon flow and structure analysis in a multi-scales economy. Energy Policy 121:553–564
Michie T, Jun Y, Atsushi T (2006) Influence of paint chips on lead concentration in the soil of public playgrounds in Tokyo. J Environ Monit Jem 8:393–398
Miller TR, Bartlett SL, Weirich CA, Hernandez J (2019) Automated subdaily sampling of cyanobacterial toxins on a buoy reveals new temporal patterns in Toxin dynamics. Environ Sci Technol 53:5661–5670
Mullan-Boudreau G, Belland R, Devito K, Noernberg T, Pelletier R, Shotyk W (2017) Sphagnum moss as an indicator of contemporary rates of atmospheric dust deposition in the Athabasca bituminous sands region. Environ Sci Technol 51:7422–7431
Naghmeh S, Behnam K, Farid M, Tahereh T, Ahmad Reza L, Nemat J, Maryam K (2015) Ecological and human health hazards of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Isfahan metropolis, Iran. Sci Total Environ 505:712–723
O'Connor D, Hou D, Ye J, Zhang Y, Ok YS, Song Y, Coulon F, Peng T, Tian L (2018) Lead-based paint remains a major public health concern: a critical review of global production, trade, use, exposure, health risk, and implications. Environ Int 121:85–101
Olson LH, Misenheimer JC, Nelson CM, Bradham KD, Richardson CJ (2017) Influences of coal ash leachates and emergent macrophytes on water quality in wetland microcosms. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:344
Overgaard HJ, Ekbom B, Suwonkerd W, Takagi M (2003) Effect of landscape structure on anopheline mosquito density and diversity in northern Thailand: implications for malaria transmission and control. Landsc Ecol 18:605
Padoan E, Romè C, Ajmone-Marsan F (2017) Bioaccessibility and size distribution of metals in road dust and roadside soils along a peri-urban transect. Sci Total Environ 601–602:89–98
Padoan E, Ajmone-Marsan F, Querol X, Amato F (2018) An empirical model to predict road dust emissions based on pavement and traffic characteristics. Environ Pollut 237:713–720
Pan H, Lu X, Lei K (2017a) A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi'an, China: contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 609:1361
Pan X, Zhang J, Huang Y, Liu Y (2017b) Construction of metallurgical interface with high strength between immiscible Cu and Nb by direct bonding method. J Alloys Compd 723:1053–1061
Paraskevopoulou D, Bougiatioti A, Stavroulas I, Fang T, Lianou M, Liakakou E, Gerasopoulos E, Weber R, Nenes A, Mihalopoulos N (2019) Yearlong variability of oxidative potential of particulate matter in an urban Mediterranean environment. Atmos Environ 206:183–196
Peng H, Chen Y, Weng L, Ma J, Ma Y, Li Y, Islam MS (2019) Comparisons of heavy metal input inventory in agricultural soils in North and South China: A review. Sci Total Environ 660:776–786
Perkins J, Suh S (2019) Uncertainty implications of hybrid approach in LCA: precision versus accuracy. Environ Sci Technol 53:3681–3688
Ranmar DO, Matveev V, Dayan U, Peleg M, Kaplan J, Gertler AW, Luria M, Kallos G, Katsafados P, Mahrer Y (2002) Impact of coastal transportation emissions on inland air pollution over Israel: utilizing numerical simulations, airborne measurements, and synoptic analyses. J Geophys Res 107:4331
Ratynskaia S, Vignitchouk L, Tolias P, Bykov I, Bergsåker H, Litnovsky A, den Harder N, Lazzaro E (2013) Migration of tungsten dust in tokamaks: role of dust–wall collisions. Nuclear Fusion 53:123002
Safiur Rahman M, Khan MDH, Jolly YN, Kabir J, Akter S, Salam A (2019) Assessing risk to human health for heavy metal contamination through street dust in the Southeast Asian Megacity: Dhaka, Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 660:1610–1622
Sapkota M, Young J, Slaughter L, Acosta-Martínez V, Coldren C (2021) Soil microbial biomass and composition from urban landscapes in a semiarid climate. Appl Soil Ecol 158:103810
Shi JP, Mark D, Harrison RM (2000) Characterization of particles from a current technology heavy-duty diesel engine. Environ Sci Technol 34:748–755
Shi G, Chen Z, Bi C, Li W, Teng J, Li Y, Xu S (2011) A comparative study of health risk of potentially toxic metals in urban and suburban road dust in the most populated city of China. Atmos Environ 45:764–771
Silva SD, Ball AS, Huynh T, Reichman SM (2015) Metal accumulation in roadside soil in Melbourne, Australia: effect ofroad age, traffic density and vehicular speed. Environ Pollut 208:102–109
Sun L, Cai Y, Yang W, Yi Y, Yang Z (2019) Climatic variations within the dry valleys in southwestern China and the influences of artificial reservoirs
Sun Z-b, Wang H, Guo C, Wu J, Cheng T, Li Z-m (2019c) Barrier effect of terrain on cold air and return flow of dust air masses. Atmos Res 220:81–91
Tang L, Tang XY, Zhu YG, Zheng MH, Miao QL (2005) Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environ Int 31:822–828
Tanner PA, Hoi-Ling M, Yu PKN (2013) Fingerprinting metals in urban street dust of Beijing, Shanghai, and Hong Kong. Environ Sci Technol 42:7111–7117
Thiruvengadam A, Besch MC, Yoon S, Collins J, Kappanna H, Carder DK, Ayala A, Herner J, Gautam M (2014) Characterization of particulate matter emissions from a current technology natural gas engine. Environ Sci Technol 48:8235–8242
Trujillo-González JM, Torres-Mora MA, Keesstra S, Brevik EC, Jiménez-Ballesta R (2016) Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Sci Total Environ 553:636–642
Wang J, Li S, Cui X, Li H, Qian X, Wang C, Sun Y (2016) Bioaccessibility, sources and health risk assessment of trace metals in urban park dust in Nanjing, Southeast China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 128:161–170
Wang J, Feng J, Yan Z (2018) Impact of extensive urbanization on summertime rainfall in the Beijing region and the role of local precipitation recycling. J Geophys Res Atmospheres 123
Wang P, Chen H, Kopittke PM, Zhao F-J (2019a) Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ Pollut 249:1038–1048
Wang S, Cai LM, Wen HH, Luo J, Wang QS, Liu X (2019b) Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci Total Environ 655:92–101
Wang Z, Zhou J, Zhang C, Qu L, Mei K, Dahlgren RA, Zhang M, Xia F (2019d) A comprehensive risk assessment of metals in riverine surface sediments across the rural-urban interface of a rapidly developing watershed. Environ Pollut 245:1022–1030
Wang SY, Wang LQ, Huan YZ, Wang R, Liang T (2022) Concentrations, spatial distribution, sources and environmental health risks of potentially toxic elements in urban road dust across China. Sci Total Environ 805:150266
Wei X, Gao B, Wang P, Zhou H, Lu J (2015) Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dusts from different functional areas in Beijing, China ☆. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:186–192
Wiseman CL, Niu J, Levesque C, Chénier M, Rasmussen PE (2018) An assessment of the inhalation bioaccessibility of platinum group elements in road dust using a simulated lung fluid. Environ Pollut 241:1009–1017
Xu X, Zhang H, Chen J, Li Q, Wang X, Wang W, Zhang Q, Xue L, Ding A, Mellouki A (2018) Six sources mainly contributing to the haze episodes and health risk assessment of PM2.5 at Beijing suburb in winter 2016. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:146–156
Yamamoto N, Takahashi Y, Yoshinaga J, Tanaka A, Shibata Y (2006) Size distributions of soil particles adhered to children’s hands. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:157–163
Yan L, Ma Y, Qiu X, Ran L, Fang Y, Wang J, Zhu Y, Di H (2015) Sources, transformation, and health implications of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their nitrated, hydroxylated, and oxygenated derivatives in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Beijing. J Geophys Res-Atmos 120:7219–7228
Yang S, Liu J, Bi X, Ning Y, Qiao S, Yu Q, Zhang J (2020) Risks related to heavy metal pollution in urban construction dust fall of fast-developing Chinese cities. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110628
Yao Y, He C, Li S, Ma W, Li S, Yu Q, Mi N, Yu J, Wang W, Yin L, Zhang Y (2019) Properties of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants in Shandong, China: daily fluctuation, influencing factors, and spatiotemporal distribution. Sci Total Environ 660:384–394
Yue Z-B, Zhang M-L, Sheng G-P, Liu R-H, Long Y, Xiang B-R, Wang J, Yu H-Q (2010) Determination of main components and anaerobic rumen digestibility of aquatic plants in vitro using near-infrared-reflectance spectroscopy. Water Res 44:2229–2234
Yu W, Liu R, Wang J, Xu F, Shen Z (2015) Source apportionment of PAHs in surface sediments using positive matrix factorization combined with GIS for the estuarine area of the Yangtze River, China. Chemosphere 134:263–271
Yu X, Lv Q, Zhang L, Wang X, Meng X, Zong H (2020) Study of thermal performance of air-source heat-pump heating for suburban residential buildings in Beijing. Sci Technol Built Environ 26(7):975–986
Yu T, Song X, Zhang Y, Han D, Ai L, Zhao T, Wang Y (2017) Using stable isotopes to understand seasonal and inter-annual dynamics in moisture sources and atmospheric circulation in precipitation. Hydrol Process 31:4682–4692
Zhang H, Wang S, Hao J, Wang X, Wang S, Chai F, Li M (2016) Air pollution and control action in Beijing. J Clean Prod 112:1519–1527
Zhang J, Wu J, Hua P, Zhao Z, Wu L, Fan G, Bai Y, Kaeseberg T, Krebs P (2017) The influence of land use on source apportionment and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in road-deposited sediment. Environ Pollut 229:705–714
Zhang J, Li R, Zhang X, Bai Y, Cao P, Hua P (2019a) Vehicular contribution of PAHs in size dependent road dust: a source apportionment by PCA-MLR, PMF, and Unmix receptor models. Sci Total Environ 649:1314–1322
Zhang J, Li R, Zhang X, Ding C, Hua P (2019b) Traffic contribution to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in road dust: a source apportionment analysis under different antecedent dry-weather periods. Sci Total Environ 658:996–1005
Zhang Y, Li S, Lai Y, Wang L, Wang F, Chen Z (2019c) Predicting future contents of soil heavy metals and related health risks by combining the models of source apportionment, soil metal accumulation and industrial economic theory. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:211–221
Zhang Y, Zheng H, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Xing X, Qi S (2019d) Fine particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) at an urban site of Wuhan, central China: Characteristics, potential sources and cancer risks apportionment. Environ Pollut 246:319–327
Zhao PS, Feng YC, Jin J, Han B, Bi XH, Zhu T, Zhang XL (2009) Characteristics and control indicators of fugitive dust from building construction sites. Acta Sci Circumst 29:1618–1623
Zhao H, Shao Y, Yin C, Jiang Y, Li X (2016) An index for estimating the potential metal pollution contribution to atmospheric particulate matter from road dust in Beijing. Sci Total Environ 550:167–175
Zhou Q, Zheng N, Liu J, Wang Y, Sun C, Liu Q, Wang H, Zhang J (2015) Residents health risk of Pb, Cd and Cu exposure to street dust based on different particle sizes around zinc smelting plant, Northeast of China. Environ Geochem Health 37:207–220
Zhu T, Wang X, Lin H, Ren J, Wang C, Gong P (2020) Accumulation of pollutants in proglacial lake sediments: impacts of glacial meltwater and anthropogenic activities. Environ Sci Technol 54:7901–7910
Zhuo S, Shen G, Zhu Y, Du W, Pan X, Li T, Han Y, Li B, Liu J, Cheng H, Xing B, Tao S (2017) Source-oriented risk assessment of inhalation exposure to ambient polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and contributions of non-priority isomers in urban Nanjing, a megacity located in Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ Pollut 224:796–809
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions on this paper.
Availability of data and materials
All the data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Funding
The research was funded by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (41530635) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0605001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cong Men: conceptualization, methodology, software, writing — original draft. Ruimin Liu: conceptualization, supervision, writing — review and editing. Yifang Wang: data curation, software, validation. Leiping Cao: analysis with constructive discussions. Lijun Jiao: investigation, data curation. Lin Li: investigation, visualization. Yue Wang: software, visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 22 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Men, C., Liu, R., Wang, Y. et al. Impact of particle sizes on health risks and source-specific health risks for heavy metals in road dust. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 75471–75486 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21060-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21060-w