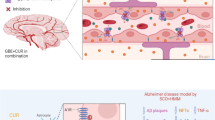
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a slowly progressive brain degenerative disorder which gradually impairs memory, thinking, and ability to perform easy routine tasks. This degenerative disorder mainly targets the elderly people and has imposed an endemic burden on society. Hence, there is a crucial need to investigate the efficacious herbal pharmacotherapies that can effectively mitigate and prevent the pathological hallmarks of AD. The current study aims to explore the potential efficacy of curcuminoid-rich extract (CRE) and its ternary complex (TC). Experimental rodents were administered with AlCl3 (300 mg/kg) to induce AD and treated with rivastigmine, curcuminoid crude extract, CRE, and TC orally for three consecutive weeks. Neurobehavioral, biochemical, and histopathological studies were performed from the last week of the study period. The mRNA expression of different pathological biomarkers was estimated by RT-qPCR analysis. The results of the study suggested that CRE and TC significantly improved the behavioral, biochemical parameters and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity in treatment groups. Histological analysis was also carried out indicating that the neurodegenerative changes and neuronal loss were stabilized by CRE and TC supplementation. CRE and TC supplementation remarkably downregulated the interleukin-1α, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, acetylcholinesterase, and β-secretase pathological gene expression. Hence, it was concluded that CRE and TC may act as promising candidates in the prevention of AD via numerous underlying signaling pathways.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated and/or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abuelezz NZ, Nasr FE, AbdulKader MA, Bassiouny AR, Zaky A (2021) MicroRNAs as potential orchestrators of Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies: insights on current status and future possibilities. Front Aging Neurosci 13:743573. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.743573
Ahsan H, Parveen N, Khan NU, Hadi S (1999) Pro-oxidant, anti-oxidant and cleavage activities on DNA of curcumin and its derivatives demethoxycurcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin. Chem Biol Interact 121:161–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2797(99)00096-4
Amalraj A, Pius A, Gopi S, Gopi S (2017) Biological activities of curcuminoids, other biomolecules from turmeric and their derivatives–a review. J Tradit Complement Med 7:205–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2016.05.005
Arya A et al (2021) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory potential of various sesquiterpene analogues for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Biomolecules 11:350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11030350
Bertram L, Tanzi RE (2008) Thirty years of Alzheimer's disease genetics: the implications of systematic meta-analyses. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:768–778. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2494
Bhattacharjee S, Zhao Y, Hill JM, Percy ME, Lukiw WJ (2014) Aluminum and its potential contribution to Alzheimer's disease (AD). Front Aging Neurosci 6:62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00062
Bondy SC (2014) Prolonged exposure to low levels of aluminum leads to changes associated with brain aging and neurodegeneration. Toxicology 315:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2013.10.008
Butterfield DA, Reed T, Newman SF, Sultana R (2007) Roles of amyloid β-peptide-associated oxidative stress and brain protein modifications in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Free Radic Biol Med 43:658–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.05.037
Chauhdary Z, Saleem U, Ahmad B, Shah S, Shah MA (2019) Neuroprotective evaluation of Tribulus terrestris L. in aluminum chloride induced Alzheimer's disease. Pak J Pharm Sci 32:805–816
Cheignon C, Tomas M, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Faller P, Hureau C, Collin F (2018) Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biol 14:450–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.10.014
Cheng X-j et al (2019) Tacrine–hydrogen sulfide donor hybrid ameliorates cognitive impairment in the aluminum chloride mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:3500–3509. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00120
Chiroma SM, Moklas MAM, Taib CNM, Baharuldin MTH, Amon Z (2018) D-galactose and aluminium chloride induced rat model with cognitive impairments. Biomed Pharmacother 103:1602–1608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.152
Chiroma SM, Baharuldin MTH, Taib CNM, Amom Z, Jagadeesan S, Adenan MI, Moklas MAM (2019) Protective effect of Centella asiatica against D-galactose and aluminium chloride induced rats: behavioral and ultrastructural approaches. Biomed Pharmacother 109:853–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.111
D’Hooge R, De Deyn PP (2001) Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res Rev 36:60–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0173(01)00067-4
Di Martino RMC et al (2016) Versatility of the curcumin scaffold: discovery of potent and balanced dual BACE-1 and GSK-3β inhibitors. J Med Chem 59:531–544. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00894
Galeano P et al (2014) Longitudinal analysis of the behavioral phenotype in a novel transgenic rat model of early stages of Alzheimer's disease. Front Behav Neurosci 8:321. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00321
Grewal AK et al (2021) Mechanistic insights and perspectives involved in neuroprotective action of quercetin. Biomed Pharmacother 140:111729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111729
Haider S et al (2015) Pretreatment with curcumin attenuates anxiety while strengthens memory performance after one short stress experience in male rats. Brain Res Bull 115:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.04.001
Haque RU, Levey AI (2019) Alzheimer's disease: a clinical perspective and future nonhuman primate research opportunities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:26224–26229. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1912954116
Hatcher H, Planalp R, Cho J, Torti F, Torti S (2008) Curcumin: from ancient medicine to current clinical trials. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1631–1652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-7452-4
Hesari A et al (2019) Effect of curcumin on glioblastoma cells. J Cell Physiol 234:10281–10288. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27933
Hossain MF et al (2019) Melatonin in Alzheimer's disease: a latent endogenous regulator of neurogenesis to mitigate Alzheimer's neuropathology. Mol Neurobiol 56:8255–8276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01660-3
Justin Thenmozhi A, Dhivyabharathi M, William Raja TR, Manivasagam T, Essa MM (2016) Tannoid principles of Emblica officinalis renovate cognitive deficits and attenuate amyloid pathologies against aluminum chloride induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Nutr Neurosci 19:269–278. https://doi.org/10.1179/1476830515Y.0000000016
Kabir M et al (2021a) Potential role of curcumin and its nanoformulations to treat various types of cancers. Biomolecules 11:392. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11030392
Kabir M et al (2021b) Anti-Alzheimer’s molecules derived from marine life: understanding molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Marine Drugs 19:251. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050251
Kimura R, Ohno M (2009) Impairments in remote memory stabilization precede hippocampal synaptic and cognitive failures in 5XFAD Alzheimer mouse model. Neurobiol Dis 33:229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2008.10.006
Lakshmi BV, Sudhakar M, Prakash KS (2015) Protective effect of selenium against aluminum chloride-induced Alzheimer's disease: behavioral and biochemical alterations in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 165:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0229-3
Lateh L, Yuenyongsawad S, Chen H, Panichayupakaranant P (2019) A green method for preparation of curcuminoid-rich Curcuma longa extract and evaluation of its anticancer activity. Pharmacogn Mag 15:730. https://doi.org/10.4103/pm.pm_162_19
Lateh L, Kaewnopparat N, Yuenyongsawad S, Panichayupakaranant P (2022) Enhancing the water-solubility of curcuminoids-rich extract using a ternary inclusion complex system: preparation, characterization, and anti-cancer activity. Food Chem 368:130827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130827
Li W et al (2009) Structure elucidation and NMR assignments for curcuminoids from the rhizomes of Curcuma longa. Magn Reson Chem 47:902–908. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrc.2478
Liaquat L, Sadir S, Batool Z, Tabassum S, Shahzad S, Afzal A, Haider S (2019) Acute aluminum chloride toxicity revisited: study on DNA damage and histopathological, biochemical and neurochemical alterations in rat brain. Life Sci 217:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.12.009
Mathiyazahan DB, Thenmozhi AJ, Manivasagam T (2015) Protective effect of black tea extract against aluminium chloride-induced Alzheimer's disease in rats: a behavioural, biochemical and molecular approach. J Funct Foods 16:423–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2015.05.001
Naert A, Callaerts-Vegh Z, D’Hooge R (2011) Nocturnal hyperactivity, increased social novelty preference and delayed extinction of fear responses in post-weaning socially isolated mice. Brain Res Bull 85:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.03.027
Noorafshan A, Asadi-Golshan R, Karbalay-Doust S, Abdollahifar MA, Rashidiani-Rashidabadi A (2013) Curcumin, the main part of turmeric, prevents learning and memory changes induced by sodium metabisulfite, a preservative agent, in rats. Exp Neurobiol 22:23. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2013.22.1.23
Petrasek T et al (2018) The McGill transgenic rat model of Alzheimer's disease displays cognitive and motor impairments, changes in anxiety and social behavior, and altered circadian activity. Front Aging Neurosci 10:250. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00250
Popa-Wagner A, Mitran S, Sivanesan S, Chang E, Buga A-M (2013) ROS and brain diseases: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:963520. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/963520
Priyadarsini KI (2014) The chemistry of curcumin: from extraction to therapeutic agent. Molecules 19:20091–20112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220091
Rui P, Sheng Q, Lu D-x, Jun D (2008) Curcumin improves learning and memory ability and its neuroprotective mechanism in mice. Chin Med J 121:832–839. https://doi.org/10.1097/00029330-200805010-00015
Salehi B et al (2020) Curcumin's nanomedicine formulations for therapeutic application in neurological diseases. J Clin Med 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020430
Salter MW, Stevens B (2017) Microglia emerge as central players in brain disease. Nat Med 23:1018–1027. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4397
Shaftel SS, Griffin WST, O'Banion MK (2008) The role of interleukin-1 in neuroinflammation and Alzheimer disease: an evolving perspective. J Neuroinflammation 5:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-5-7
Sharma VK et al (2021) Dysbiosis and Alzheimer’s disease: a role for chronic stress? Biomolecules 11:678. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050678
Shi X et al (2015) Curcumin inhibits Aβ-induced microglial inflammatory responses in vitro: involvement of ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways. Neurosci Lett 594:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.03.045
Silva MVF, Loures CMG, Alves LCV, de Souza LC, Borges KBG, Carvalho MDG (2019) Alzheimer's disease: risk factors and potentially protective measures. J Biomed Sci 26:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-019-0524-y
Somparn P, Phisalaphong C, Nakornchai S, Unchern S, Morales NP (2007) Comparative antioxidant activities of curcumin and its demethoxy and hydrogenated derivatives. Biol Pharm Bull 30:74–78. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.30.74
Sultana R, Butterfield DA (2008) Redox proteomics studies of in vivo amyloid beta-peptide animal models of Alzheimer's disease: insight into the role of oxidative stress. PROTEOMICS–Clinical Applications 2:685–696. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.200780024
Tan Q, Li Y, Wu J, Mei H, Zhao C, Zhang J (2012) An optimized molecular inclusion complex of diferuloylmethane: enhanced physical properties and biological activity. Int J Nanomedicine 5:5385–5393. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S36404
Thenmozhi AJ, Raja TRW, Janakiraman U, Manivasagam T (2015) Neuroprotective effect of hesperidin on aluminium chloride induced Alzheimer’s disease in Wistar rats. Neurochem Res 40:767–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1525-1
Tillerson JL, Miller GW (2003) Grid performance test to measure behavioral impairment in the MPTP-treated-mouse model of parkinsonism. J Neurosci Methods 123:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0270(02)00360-6
Tokaç M et al (2013) Protective effects of curcumin against oxidative stress parameters and DNA damage in the livers and kidneys of rats with biliary obstruction. Food Chem Toxicol 61:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.01.015
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1:848–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.116
Walton J (2012) Cognitive deterioration and associated pathology induced by chronic low-level aluminum ingestion in a translational rat model provides an explanation of Alzheimer's disease, tests for susceptibility and avenues for treatment. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/914947
Wang L, Hu J, Zhao Y, Lu X, Zhang Q, Niu Q (2014a) Effects of aluminium on β-amyloid (1–42) and secretases (APP-cleaving enzymes) in rat brain. Neurochem Res 39:1338–1345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1317-z
Wang X, Wang W, Li L, Perry G, Lee H-g, Zhu X (2014b) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Di 1842:1240–1247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.10.015
Zerrouki K, Djebli N, Ozkan EE, Ozsoy N, Gul O, Mat A (2016) Hypericum perforatum improve memory and learning in Alzheimer’s model: (experimental study in mice). Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 8:49–57
Zetterberg BKDLM (2006) H. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 368:387. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69113-7
Zhao Y, Zhao B (2013) Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:316523. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/316523
Zheng K et al (2017) Curcumin ameliorates memory decline via inhibiting BACE1 expression and β-amyloid pathology in 5× FAD transgenic mice. Mol Neurobiol 54:1967–1977. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9802-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS: literature search, data curation, experimental analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, and validation. KR: investigation, conceptualization, writing—final draft, and editing. MSHA: project administration, supervision, conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, and editing. MA and ZC: data curation. PP and MAS prepared and standardized the extracts.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was ethically approved from the Institutional Review Board (GCUF/ERC/2196) of Government College University Faisalabad (GCUF).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shabbir, A., Rehman, K., Akash, M.S.H. et al. Differential neuroprotective effect of curcuminoid formulations in aluminum chloride–induced Alzheimer’s disease. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 67981–67996 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20593-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20593-4