Abstract
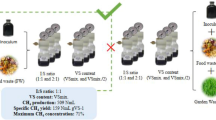
Toilet revolution is driven by the urgent need for solutions to improve sanitation and access to high-quality organic fertilizer for rural areas, which is tagged “resource recovery from human waste.” This study provides a possible solution via semi-solid anaerobic co-digestion (Aco-D) of source-separated fecal slag (SFS) and food waste (FW) (3:1). A comprehensive investigation of Aco-D at different inoculum/substrate ratios (ISR) was conducted. Results revealed that the reactor with ISR of 1:4 reached the highest methane yield (255.05 mL/gVS), which enhanced Methanosaetaceae, Methanomicrobiales, and Syntrophomonas. Additionally, the reactor with low feedstock (ISR of 1:2) showed higher removal efficiency of antibiotics (74.75%). The ecological risk of digestate decreased to an insignificant hazard quotient level, and the contents of nutrients and heavy metals were in line with the standard requirement for fertilizer. This study could serve as an alternative technology to support further research in SFS management and digestate utilization as fertilizer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript and its supplementary information files.
References
Abudi ZN, Hu Z, Abood AR, Liu D, Gao A (2020) Effects of alkali pre-treatment, total solid content, substrate to inoculum ratio, and pH on biogas production from AD of mango leaves. Waste Biomass Valori 11:887–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0437-0
Ajayi-Banji AA, Rahman S (2021) Efficacy of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles for enhancing solid-state anaerobic co-digestion: focus on reactor performance and retention time. Bioresour Technol 324:124670. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2021.124670
APHA (2012) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) and Water Environment Federation (WEF), Washington, DC
Belete YZ, Mau V, Yahav Spitzer R, Posmanik R, Jassby D, Iddya A, Kassem N, Tester JW, Gross A (2021) Hydrothermal carbonization of anaerobic digestate and manure from a dairy farm on energy recovery and the fate of nutrients. Bioresour Technol 333:125164. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2021.125164
Blau K, Jacquiod S, Sørensen SJ, Su JQ, Zhu YG, Smalla K, Jechalke S (2019) Manure and doxycycline affect the bacterial community and its resistome in lettuce rhizosphere and bulk soil. Front Microbiol 10:725. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00725
Boleas S, Alonso C, Pro J, Fernández C, Carbonell G, Tarazona JV (2005) Toxicity of the antimicrobial oxytetracycline to soil organisms in a multi-species-soil system (MS·3) and influence of manure co-addition. J Hazard Mater 122:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2005.03.003
BSI (2014) PAS 110: 2014 Specification for whole digestate, separated liquor and separated fibre derived from the AD of source-segregated biodegradable materials. Br Stand Inst Ltd., London, p 46
Cheng S, Li Z, Uddin SMN, Mang HP, Zhou X, Zhang J, Zheng L, Zhang L (2018) Toilet revolution in China. J Environ Manage 216:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.09.043
Chessa L, Pusino A, Garau G, Mangia NP, Pinna MV (2016) Soil microbial response to tetracycline in two different soils amended with cow manure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:5807–5817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5789-4
Córdoba V, Fernández M, Santalla E (2016) The effect of substrate/inoculum ratio on the kinetics of methane production in swine wastewater AD. Adv Environ Biotechnol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0039-6
Cristina G, Camelin E, Pugliese M, Tommasi T, Fino D (2019) Evaluation of anaerobic digestates from sewage sludge as a potential solution for improvement of soil fertility. Waste Manag 99:122–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2019.08.018
Farhat A, Miladi B, Hamdi M, Bouallagui H (2018) Fermentative hydrogen and methane co-production from anaerobic co-digestion of organic wastes at high loading rate coupling continuously and sequencing batch digesters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:27945–27958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2796-2
Gao M, Zhang L, Liu Y (2020) High-loading food waste and blackwater anaerobic co-digestion: maximizing bioenergy recovery. Chem Eng J 394:124911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124911
Gurmessa B, Pedretti EF, Cocco S, Cardelli V, Corti G (2020) Manure AD effects and the role of pre- and post-treatments on veterinary antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes removal efficiency. Sci Total Environ 721:137532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137532
Harder R, Wielemaker R, Larsen TA, Zeeman G, Öberg G (2019) Recycling nutrients contained in human excreta to agriculture: pathways, processes, and products. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 49:695–743. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2018.1558889
Hashemi S, Han M (2018) Optimizing source-separated feces degradation and fertility using nitrifying microorganisms. J Environ Manage 206:540–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2017.10.074
Hashimoto AG (1989) Effect of inoculum/substrate ratio on methane yield and production rate from straw. Biological Wastes 28(4):247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7483(89)90108-0
Hobbs SR, Landis AE, Rittmann BE, Young MN, Parameswaran P (2018) Enhancing AD of food waste through biochemical methane potential assays at different substrate: inoculum ratios. Waste Manag 71:612–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2017.06.029
Huang X, Ye ZL, Cai J, Lin L (2021) Quantification of DOM effects on tetracyclines transport during struvite recovery from swine wastewater. Water Res 206:117756. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2021.117756
Jiang Y, Xie SH, Dennehy C, Lawlor PG, Hu ZH, Wu GX, Zhan XM, Gardiner GE (2020) Inactivation of pathogens in AD systems for converting biowastes to bioenergy: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 120:109654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109654
Kataki S, Hazarika S, Baruah DC (2017) Assessment of by-products of bioenergy systems (AD and gasification) as potential crop nutrient. Waste Manag 59:102–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.10.018
Legros S, Levard C, Marcato-Romain CE, Guiresse M, Doelsch E (2017) AD alters copper and zinc speciation. Environ Sci Technol 51:10326–10334. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.7B01662/SUPPL_FILE/ES7B01662_SI_001.PDF
Liu F, Ying GG, Tao R, Zhao JL, Yang JF, Zhao LF (2009) Effects of six selected antibiotics on plant growth and soil microbial and enzymatic activities. Environ Pollut 157:1636–1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2008.12.021
Lorine D, Céline D, Caroline LM, Frédéric B, Lorette H, Julie B, Laure M, Christine Z, Typhaine P, Sandra R, Emmanuelle H, Rabab SZ, Jeanne C, Anne-Marie P (2021) Influence of operating conditions on the persistence of E. coli, enterococci, Clostridium perfringens and Clostridioides difficile in semi-continuous mesophilic anaerobic reactors. Waste Manag 134:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2021.08.003
Lou Y, Ye X, Ye ZL, Chiang PC, Chen S (2018) Occurrence and ecological risks of veterinary antibiotics in struvite recovered from swine wastewater. J Clean Prod 201:678–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.012
Lv N, Zhao L, Wang R, Ning J, Pan X, Li C, Cai G, Zhu G (2020a) Novel strategy for relieving acid accumulation by enriching syntrophic associations of syntrophic fatty acid-oxidation bacteria and H2/formate-scavenging methanogens in AD. Bioresour Technol 313:123702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123702
Lv Y, Xu J, Xu K, Liu X, Guo X, Lu S, Xi B (2020b) Accumulation characteristics and biological response of ginger to sulfamethoxazole and ofloxacin. Environ Pollut 262:114203. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2020.114203
Ma X, Jiang T, Chang J, Tang Q, Luo T, Cui Z (2019) Effect of substrate to inoculum ratio on biogas production and microbial community during hemi-solid-state batch anaerobic co-digestion of rape straw and dairy manure. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 189:884–902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03035-9
Mahon JM, Knappe J, Gill LW (2022) Sludge accumulation rates in septic tanks used as part of the on-site treatment of domestic wastewater in a northern maritime temperate climate. J Environ Manage 304:114199. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2021.114199
Meng L, Xie L, Kinh CT, Suenaga T, Hori T, Riya S, Terada A, Hosomi M (2018) Influence of feedstock-to-inoculum ratio on performance and microbial community succession during solid-state thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of pig urine and rice straw. Bioresour Technol 252:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2017.12.099
Momayez F, Karimi K, Taherzadeh MJ (2019) Energy recovery from industrial crop wastes by dry anaerobic digestion: A review. Ind Crop Prod 129:673–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.12.051
Moset V, Al-zohairi N, Møller HB (2015) The impact of inoculum source, inoculum to substrate ratio and sample preservation on methane potential from different substrates. Biomass Bioenerg 83:474–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOMBIOE.2015.10.018
MOA (2015) Report on agricultural resources, environment protection and rural energy development. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Ministry of Agriculture of PRC (2012) Limits values organic fertilizer of China (NY525, 2012). China
Nkoa R (2014) Agricultural benefits and environmental risks of soil fertilization with anaerobic digestates: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 34:473–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-013-0196-z
Owamah HI, Dahunsi SO, Oranusi US, Alfa MI (2014) Fertilizer and sanitary quality of digestate biofertilizer from the co-digestion of food waste and human excreta. Waste Manag 34:747–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.01.017
Pan X, Angelidaki I, Alvarado-Morales M, Liu H, Liu Y, Huang X, Zhu G (2016) Methane production from formate, acetate and H2/CO2; focusing on kinetics and microbial characterization. Bioresour Technol 218:796–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2016.07.032
Pan X, Zhao L, Li C, Angelidaki I, Lv N, Ning J, Cai G, Zhu G (2021) Deep insights into the network of acetate metabolism in AD: focusing on syntrophic acetate oxidation and homoacetogenesis. Water Res 190:116774. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2020.116774
Peter PO, Rashid A, Hou L, Nkinahamira F, Kiki Claude, Sun Qian, Yu C-P, Hu A (2020) Elemental contaminants in surface sediments from jiulong river estuary, china: pollution level and ecotoxicological risk assessment. Water 12(6):1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061640
Pezzolla D, Di Maria F, Zadra C, Massaccesi L, Sordi A, Gigliotti G (2017) Optimization of solid-state AD through the percolate recirculation. Biomass Bioenerg 96:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2016.11.012
Rajagopal R, Massé DI, Singh G (2013) A critical review on inhibition of AD process by excess ammonia. Bioresour Technol 143:632–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.030
Riggio S, Torrijos M, Debord R, Esposito G, van Hullebusch ED, Steyer JP, Escudié R (2017) Mesophilic AD of several types of spent livestock bedding in a batch leach-bed reactor: substrate characterization and process performance. Waste Manag 59:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.10.027
Riungu J, Ronteltap M, van Lier JB (2018) Build-up and impact of volatile fatty acids on E. coli and A. lumbricoides during co-digestion of urine diverting dehydrating toilet (UDDT-F) faeces. J Environ Manage 215:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2018.02.076
Rocamora I, Wagland ST, Villa R, Simpson EW, Fernández O, Bajón-Fernández Y (2020) Dry AD of organic waste: a review of operational parameters and their impact on process performance. Bioresour Technol 299:122681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122681
Rose C, Parker A, Jefferson B, Cartmell E (2015) The characterization of feces and urine: a review of the literature to inform advanced treatment technology. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:1827–1879. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2014.1000761
Schmidt O, Hink L, Horn MA, Drake HL (2016) Peat: home to novel syntrophic species that feed acetate- and hydrogen-scavenging methanogens. ISME J 10:1954–1966. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.256
Slepetiene A, Volungevicius J, Jurgutis L, Liaudanskiene I, Amaleviciute-Volunge K, Slepetys J, Ceseviciene J (2020) The potential of digestate as a biofertilizer in eroded soils of Lithuania. Waste Manag 102:441–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2019.11.008
Sui Q, Meng X, Wang R, Zhang J, Yu D, Chen M, Wang Y, Wei Y (2018) Effects of endogenous inhibitors on the evolution of antibiotic resistance genes during high solid AD of swine manure. Bioresour Technol 270:328–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.043
Thiele-Bruhn S, Beck IC (2005) Effects of sulfonamide and tetracycline antibiotics on soil microbial activity and microbial biomass. Chemosphere 59:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2005.01.023
Torrisi B, Allegra M, Amenta M, Gentile F, Rapisarda P, Fabroni S, Ferlito F (2021) Physico-chemical and multielemental traits of anaerobic digestate from Mediterranean agro-industrial wastes and assessment as fertilizer for citrus nurseries. Waste Manag 131:201–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2021.06.007
UN Habitat, WHO (2021) Progress on wastewater treatment - global status and acceleration needs for SDG indicator 6.3.1, United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat) and World Healtth Organization (WHO). Geneva
Union E (2019) Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 laying down rules on the making available on the market of EU fertilising products and amending Regulations (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009 and repealing Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003. Off J Eur Union L 170:1–114
US-EPA (1994) EPA: a plain English guide to the EPA part 503 biosolids rule. Excellence in compliance through original technical solutions, Epa-832/R-93/003. US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Wastewater Management
US-EPA (2007) Method 3051A (SW-846): Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, and oils. In: environmental sampling and analytical methods (ESAM) program, Revision 1. Washington, DC
Visca A, Rauseo J, Spataro F, Patrolecco L, Grenni P, Massini G, Mazzurco Miritana V, Barra Caracciolo A (2022) Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in anaerobic digesters and predicted concentrations in agroecosystems. J Environ Manage 301:113891. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2021.113891
Wang H, Zhu S, Qu B, Zhang Y, Fan B (2018) Anaerobic treatment of source-separated domestic bio-wastes with an improved upflow solid reactor at a short HRT. J Environ Sci 66:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.05.014
Wang H, Li Z, Zhou X, Wang X, Zuo S (2020a) Anaerobic co-digestion of kitchen waste and blackwater for different practical application scenarios in decentralized scale: from wastes to energy recovery. Water 12:2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092556
Wang Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Jia S, Song Y, Sun Y, Zheng Z, Yu J, Cui Z, Han Y, Hao J, Li G (2020b) Methane production from the co-digestion of pig manure and corn stover with the addition of cucumber residue: role of the total solids content and feedstock-to-inoculum ratio. Bioresour Technol 306:123172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123172
Wang Z, Jiang Y, Wang S, Zhang Y, Hu Y, Hu ZH, Wu G, Zhan X (2020c) Impact of total solids content on anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and food waste: insights into shifting of the methanogenic pathway. Waste Manag 114:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.06.048
Wang Z, Wang S, Xie S, Jiang Y, Meng J, Wu G, Hu Y, Zhan X (2022) Stimulatory effects of biochar addition on dry anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and food waste under mesophilic conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:19212–19223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17129-7
Xiao MY, An J, Ji ZH, Cui S, Li P (2014) Toxic effects of six typical antibiotics on seed germination and physiological characteristics of chinese cabbage. Chin J Ecol 33:2775–2781
Ye ZL, Deng Y, Lou Y, Ye X, Zhang J, Chen S (2017) Adsorption behavior of tetracyclines by struvite particles in the process of phosphorus recovery from synthetic swine wastewater. Chem Eng J 313:1633–1638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.062
Zhang L, Guo B, Zhang Q, Florentino A, Xu R, Zhang Y, Liu Y (2019) Co-digestion of blackwater with kitchen organic waste: effects of mixing ratios and insights into microbial community. J Clean Prod 236:117703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117703
Zhou X, Wang J, Lu C, Liao Q, Gudda FO, Ling W (2020) Antibiotics in animal manure and manure-based fertilizers: occurrence and ecological risk assessment. Chemosphere 255:127006. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2020.127006
Zhu TT, Su ZX, Lai WX, Zhang YB, Liu YW (2021) Insights into the fate and removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes using biological wastewater treatment technology. Sci Total Environ 776:145906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145906
Acknowledgements
We are also grateful to all Wastewater Treatment and Nutrient Recovery Research Group members for their support during the research period. We also thank Consolata Nanjala, Nan Lv, Ruming Wang, Junjie Li, and Yanlin Li for their valuable support and suggestions.
Funding
The authors received financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Contract No. 2018YFC1903205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hamza Hassan Yusuf and Zhi-Long Ye were responsible for the study’s conceptualization and design. Hamza Hassan Yusuf, Xiaofang Pan, Guanjing Cai, Jiasheng Cai, Xuewei Huang, and Zhi-Long Ye performed material preparation, data collection, data analysis, and data validation. Hamza Hassan Yusuf wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors commented on the previous version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Zhi-Long Ye was in charge of supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yusuf, H.H., Pan, X., Cai, G. et al. Semi-solid anaerobic co-digestion of source-separated fecal slag and food waste: focusing on methane production, ecological risk assessment, and quality evaluation as fertilizer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 66578–66590 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20249-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20249-3