Abstract
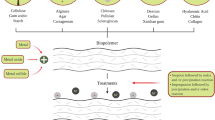
Efficient sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes (SR-AOPs) are important for treating organic contaminants of industrial wastewater. To achieve this goal, tannic acid (TA)–modified skin collagen fibers (CFs) were prepared for the enhanced immobilization of Fe3+ based on multiple complexation interactions, resulting in a heterogeneous catalyst with more catalytic sites (defined as TA-Fe-CFs) for activating peroxymonosulfate (PMS). During the removal of an organic dye (rhodamine B, RhB) from water, the hierarchical TA-Fe-CFs exhibited excellent adsorption capacity at the early stage before the introduction of PMS, which can be ascribed to the π-π interaction between TA and aromatic RhB. Such improved mass transfer of target contaminants into the catalytic support was proved to be beneficial for improving the utilization efficiency of sulfate radicals in subsequent SR-AOPs. After introducing PMS, the reductive TA moieties of the heterogeneous catalyst were able to accelerate the redox cycle of Fe3+/Fe2+ in Fenton reactions, facilitating the activation of PMS to generate sulfate radicals for the degradation of organic RhB.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alvarez PJJ, Chan CK, Elimelech M, Halas NJ, Villagrán D (2018) Emerging opportunities for nanotechnology to enhance water security. Nat Nanotechnol 13:634–641. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0203-2
Ao XW, Eloranta J, Huang C, Santoro D, Sun W, Lu Z, Li C (2021) Peracetic acid-based advanced oxidation processes for decontamination and disinfection of water: a review. Water Res 188:116479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116479
Chen Y, Zhang G, Liu H, Qu J (2019) Ultrafast Fenton-like process in interspacing of MoS2 membrane enabled by confining sufficient free-radicals in close vicinity to contaminants. Angew Chem Int Ed 131:8218–8222. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201903531
Ejima H, Richardson JJ, Liang K, Best JP, Koeverden MPV, Such GK, Cui J, Caruso F (2013) One-Step assembly of coordination complexes for versatile film and particle engineering. Science 341:154–157. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1237265
Fan J, Gu L, Wu D, Liu Z (2018) Mackinawite (FeS) activation of persulfate for the degradation of p-chloroaniline: surface reaction mechanism and sulfur-mediated cycling of iron species. Chem Eng J 333:657–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.175
Gan P, Li SFY (2013) Efficient removal of rhodamine B using a rice hull-based silica supported iron catalyst by Fenton-like process. Chem Eng J 229:351–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.020
Guo X, Meng Q, Wang D, Zha F, Tang X, Tian H (2021) S-doped NiFe-based catalyst for fast degradation of methylene blue by heterogeneous photo-Fenton reaction. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:36112–36121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13212-1
Lan T, An R, Liu Z, Li K, Xiang J, Liu G (2018) Facile fabrication of a biomass-based film with interwoven fibrous network structure as heterogeneous catalysis platform. J Colloid Interface Sci 532:331–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.07.133
Li H, Zheng W, Xiao H, Hao B, Wang Y, Huang X, Shi B (2021) Collagen fiber membrane-derived chemically and mechanically durable superhydrophobic membrane for high-performance emulsion separation. J Leather Sci Eng 3:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42825-021-00060-5
Liu G, Yu R, Lan T, Liu Z, Zhang P, Liang R (2019) Gallic acid-functionalized graphene hydrogel as adsorbent for removal of chromium (III) and organic dye pollutants from tannery wastewater. RSC Adv 9:27060–27068. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA05664E
Liu G, Jiang J, Yu R, Yan H, Liang R (2020) Silver nanoparticle-incorporated porous renewable film as low-cost bactericidal and antifouling filter for point-of-use water disinfection. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:10857–10867. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c00157
Liu WJ, Yang H, Park YK, Kwon E, Huang CW, Thanh BX, Khiem TC, You S, Ghanbari F, Lin KYA (2022) Enhanced degradation of ultra-violet stabilizer Bis(4-hydroxy) benzophenone using oxone catalyzed by hexagonal nanoplate-assembled CoS 3-dimensional cluster. Chemosphere 288:132427
Liu Y, Wei J, Zhao Y, Guang Z, Wen Z (2017) Enhanced catalytic degradation of methylene blue by α-Fe2O3/graphene oxide via heterogeneous photo-Fenton reactions. Appl Catal B-Environ 206:642–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.01.075
Lu J, Chen Q, Zhao Q, Liu X, Zhou J (2021) Catalytic activity comparison of natural ferrous minerals in photo-Fenton oxidation for tertiary treatment of dyeing wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:30373–30383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14042-x
Ma W, Ding Y, Zhang M, Gao S, Li Y, Huang C, Fu G (2020) Nature-inspired chemistry toward hierarchical superhydrophobic, antibacterial and biocompatible nanofibrous membranes for effective UV-shielding, self-cleaning and oil-water separation. J Hazard Mater 384:121476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121476
Pignatello JJ, Oliveros E, MacKay A (2006) Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. Cri Rev Environ Sci Technol 36:1–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380500326564
Sileika TS, Barrett DG, Zhang R, Lau KHA, Messersmith PB (2013) Colorless multifunctional coatings inspired by polyphenols found in tea, chocolate, and wine. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201304922
Madihi-Bidgoli S, Asadnezhad S, Yaghoot-Nezhad A, Hassani A (2021) Azurobine degradation using Fe2O3@multi-walled carbon nanotube activated peroxymonosulfate (PMS) under UVA-LED irradiation: performance, mechanism and environmental application. J Environ Chem Eng 6:106660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106660
Thomas N, Dionysiou DD, Pillai SC (2021) Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts: a review of recent advances. J Hazard Mater 404:124082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124082
Tran NH, Reinhard M, Gin KYH (2018) Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plants from different geographical regions-a review. Water Res 133:182–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.029
Wang J, Li B, Li Y, Fan X, Zhang F, Zhang G, Peng W (2021) Facile synthesis of atomic Fe-N-C materials and dual roles investigation of Fe-N4 sites in Fenton-like reactions. Adv Sci 22:2101824. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202101824
Wu H, Wu C, He Q, Liao X, Shi B (2010) Collagen fiber with surface-grafted polyphenol as a novel support for Pd(0) nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and catalytic application. Mater Sci and Eng C 30:770–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2010.03.013
Wu S, Lin Y, Hu Y (2021) Strategies of tuning catalysts for efficient photodegradation of antibiotics in water environments: a review. J Mater Chem A 9:2592–2611. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA09173A
Xia Q, Yang L, Hu K, Li K, Xiang J, Liu G, Wang Y (2019) Chromium cross-linking based immobilization of silver nanoparticle coating on leather surface with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and durability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:2352–2363. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b17061
Xiao S, Cheng M, Zhong H, Liu Z, Liu Y, Yang X, Liang Q (2018) Iron-mediated activation of persulfate and peroxymonosulfate in both homogeneous and heterogeneous ways: a review. Chem Eng J 384:123265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123265
Xie A, Cui J, Yang J, Chen Y, Dai J, Lang J, Li CX, Yan Y (2019) Photo-Fenton self-cleaning membranes with robust flux recovery for an efficient oil/water emulsion separation. J Mater Chem A 7:8491–8502. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA00521H
Xu H, Zheng X, Feng Z, Lu Z, Cui Y (2021) Organic wastewater treatment by a single-atom catalyst and electrolytically produced H2O2. Nat Sustain 4:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-020-00635-w
Yu R, Lan T, Jiang J, Peng H, Liang R, Liu G (2020) Facile fabrication of functional cellulose paper with high-capacity immobilization of Ag nanoparticles for catalytic applications for tannery wastewater. J Leather Sci Eng 2:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42825-020-00019-y
Zhang L, Liu Z, Liu L, Ju X, Wang W, Xie R, Chu L (2017) Novel smart microreactors equipped with responsive catalytic nanoparticles on microchannels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:33137–33148. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b09939
Zhang S, Hedtke T, Zhu Q, Sun M, Weon S, Zhao Y, Stavitski E, Elimelech M, Kim JH (2021) Membrane-confined iron oxychloride nanocatalysts for highly efficient heterogeneous Fenton water treatment. Environ Sci Technol 55:9266–9275. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c01391
Zhao Y, Kang S, Qin L, Wang W, Zhang T, Song S, Komarneni S (2020) Self-assembled gels of Fe-chitosan/montmorillonite nanosheets: dye degradation by the synergistic effect of adsorption and photo-Fenton reaction. Chem Eng J 379:122322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122322
Zhou H, Zhang H, He Y, Huang B, Zhou C, Yao G, Lai B (2021) Critical review of reductant-enhanced peroxide activation processes: trade-off between accelerated Fe3+/Fe2+ cycle and quenching reactions. Appl Catal B 286:119900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119900
Acknowledgements
The authors would also like to thank Dr. Zhonghui Wang for her great help in the using of UV-vis spectrophotometer Hitachi U-3900.
Funding
The research was financially supported by the Key Technology Support Program of Sichuan Province (2021YFG0241); the Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Leather Chemistry and Engineering, Sichuan University, Ministry of Education (SCU2021D005), and the Program of Sichuan University featured research groups in engineering disciplines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gongyan Liu conceived the idea and designed the study. Rui Wang carried out materials preparation and performed the experiments. Rui Wang and Ruiquan Yu analyzed the experiments data. Gongyan Liu and Rui Wang drafted the manuscript. Junchao Wang, Jun Xiang, Chaojian Chen, and Xuepin Liao reviewed and corrected the manuscript. All authors read and approved this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo A. Torres-Palma
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Yu, R., Wang, J. et al. Hierarchical collagen fibers complexed with tannic acid and Fe3+ as a heterogeneous catalyst for enhancing sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 58675–58684 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19907-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19907-3