Abstract
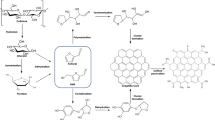
Seven composites of iron oxide nanoparticles embedded in organic microparticles mediated by Cu(II) were synthesized using yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) dry leaf extract as precipitant, capping agent, and dispersant medium, using different Cu/Fe molar ratios. A thorough characterization of the particles by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis-mass spectrometry (TGA-MS), Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR), and atomic absorption-spectrometry (AA) indicates that all materials have spheric-like morphology with nanoparticles composed by metal oxide phases embedded into organic microparticles. Interestingly, this organic matter is proposed to play an important role in the solids’ photocatalytic activity in a photo-Fenton reaction, in which iron photo-leaching was elucidated, and a mechanism through ligand-to-metal charge transfer processes was proposed. All materials showed catalytic activity in the methyl orange elimination, achieving discolorations up to 96% in 2 h under UV irradiation at 375 nm. An experimental correlation between all samples’ UV/Vis spectra and their performances for methyl orange discoloration was observed. This process opens a landscape very interesting for the use of agroindustrial residues for green synthesis of metal oxide nanomaterials and their use and understanding of organo-metallic systems participation in Fenton-based processes.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Ali I, Hasan N, Ahmad M, Khan Z (2018) Biosynthesis of iron nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract for photocatalytic methyl orange dye degradation and antibacterial applications. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 183:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.014
Almeida CL, Garcia-segura S, Arias C et al (2012) Electrochemical mineralization of the azo dye Acid Red 29 ( Chromotrope 2R ) by photoelectro-Fenton process. Chemosphere 89:751–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.07.007
Amaliyah S, Pangesti DP, Masruri M et al (2020) Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Piper retrofractum Vahl extract as bioreductor and capping agent. Heliyon 6:e04636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04636
Andreozzi R, Caprio V, Insola A, Marotta R (1999) Advanced oxidation processes ( AOP ) for water purification and recovery. Catal Today 53:51–59
Arzate S, Pfister S, Oberschelp C, Sánchez-Pérez JA (2019) Environmental impacts of an advanced oxidation process as tertiary treatment in a wastewater treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 694:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.378
Asghar MA, Zahir E, Shahid SM et al (2018) Iron, copper and silver nanoparticles: green synthesis using green and black tea leaves extracts and evaluation of antibacterial, antifungal and aflatoxin B1 adsorption activity. LWT - Food Sci Technol 90:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.12.009
Azadi F, Karimi-Jashni A, Zerafat MM (2018) Green synthesis and optimization of nano-magnetite using Persicaria bistorta root extract and its application for rosewater distillation wastewater treatment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.032
Azam A, Ahmed AS, Oves M et al (2012) Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of CuO nanoparticles against Gram-positive and -negative bacterial strains. Int J Nanomedicine 7:3527–3535. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S29020
Bhuiyan MSH, Miah MY, Paul SC et al (2020) Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticle using Carica papaya leaf extract: application for photocatalytic degradation of remazol yellow RR dye and antibacterial activity. Heliyon 6:e04603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04603
Bolong N, Ismail AF, Salim MR, Matsuura T (2009) A review of the effects of emerging contaminants in wastewater and options for their removal. Desalination 238:229–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.03.020
Bost N, Ammar MR, Bouchetou ML, Poirier J (2016) The catalytic effect of iron oxides on the formation of nano-carbon by the Boudouard reaction in refractories. J Eur Ceram Soc 36:2133–2142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.02.052
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review. Appl Catal B Environ 166–167:603–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.11.016
Carvalho SSF, Carvalho NMF (2017) Dye degradation by green heterogeneous Fenton catalysts prepared in presence of Camellia sinensis. J Environ Manage 187:82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.11.032
Chernyshova IV, Hochella MF, Madden AS (2007) Size-dependent structural transformations of hematite nanoparticles. 1. Phase Transition Phys Chem Chem Phys 9:1736–1750. https://doi.org/10.1039/b618790k
De la Cruz N, Giménez J, Esplugas S et al (2012) Degradation of 32 emergent contaminants by UV and neutral photo-fenton in domestic wastewater effluent previously treated by activated sludge. Water Res 46:1947–1957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.014
Dhand V, Soumya L, Bharadwaj S et al (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coffea arabica seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Mater Sci Eng 58:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.08.018
Donadelli JA, Carlos L, Arques A, GarcíaEinschlag FS (2018) Kinetic and mechanistic analysis of azo dyes decolorization by ZVI-assisted Fenton systems: pH-dependent shift in the contributions of reductive and oxidative transformation pathways. Appl Catal B Environ 231:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.02.057
García FE, Senn AM, Meichtry JM et al (2019) Iron-based nanoparticles prepared from yerba mate extract. Synthesis, characterization and use on chromium removal. J Environ Manage 235:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.002
Gordon-falconí C, Florencia M, Sara M et al (2020) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles with remediative potential using discarded yerba mate : an eco-friendly approach. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104425
Guimaraes IR, Giroto A, Oliveira LCA et al (2009) Synthesis and thermal treatment of cu-doped goethite: oxidation of quinoline through heterogeneous fenton process. Appl Catal B Environ 91:581–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.06.030
Haji S, Benstaali B, Al-Bastaki N (2011) Degradation of methyl orange by UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Chem Eng J 168:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.050
He D, Wu X, Chen Y et al (2018) In-situ growth of lepidocrocite on Bi2O3 rod: A perfect cycle coupling photocatalysis and heterogeneous fenton-like process by potential-level matching with advanced oxidation. Chemosphere 210:334–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.142
Hou L, Zhang Q, Jérôme F et al (2014) Shape-controlled nanostructured magnetite-type materials as highly efficient Fenton catalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 144:739–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.072
Hou X, Huang X, Jia F et al (2017) Hydroxylamine promoted goethite surface fenton degradation of organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 51:5118–5126. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05906
Huang X, Hou X, Zhao J, Zhang L (2016) Hematite facet confined ferrous ions as high efficient Fenton catalysts to degrade organic contaminants by lowering H2O2 decomposition energetic span. Appl Catal B Environ 181:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.06.061
Huang X, Hou X, Jia F et al (2017) Ascorbate-Promoted surface iron cycle for efficient heterogeneous fenton alachlor degradation with hematite nanocrystals. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:8751–8758. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b16600
Jain B, Singh AK, Kim H et al (2018) Treatment of organic pollutants by homogeneous and heterogeneous Fenton reaction processes. Environ Chem Lett 16:947–967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0738-3
Khalaj M, Kamali M, Costa MEV, Capela I (2020) Green synthesis of nanomaterials - a scientometric assessment. J Clean Prod 267:122036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122036
Khanna L, Gupta G, Tripathi SK (2019) Effect of size and silica coating on structural, magnetic as well as cytotoxicity properties of copper ferrite nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 97:552–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.12.051
Kuang Y, Wang Q, Chen Z et al (2013) Heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation of monochlorobenzene using green synthesis of iron nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 410:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.08.020
Kumar S, Ojha AK, Bhorolua D et al (2019) Facile synthesis of CuO nanowires and Cu 2 O nanospheres grown on rGO surface and exploiting its photocatalytic, antibacterial and supercapacitive properties. Phys B Condens Matter 558:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.01.040
Li Y, Zhang W, Niu J, Chen Y (2013) Surface-coating-dependent dissolution, aggregation, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation of silver nanoparticles under different irradiation conditions. Environ Sci Technol 47:10293–10301. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400945v
Lin ZR, Zhao L, Dong YH (2015) Quantitative characterization of hydroxyl radical generation in a goethite-catalyzed Fenton-like reaction. Chemosphere 141:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.066
Litter MI (2005) Introduction to photochemical advanced oxidation processes for water treatment. Environmental Photochemistry Part II. Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 325–366
Lorenzo D, Dominguez CM, Romero A, Santos A (2019) Wet peroxide oxidation of chlorobenzenes catalyzed by goethite and promoted by hydroxylamine. Catalysts 9:.https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9060553
Magnacca G, Allera A, Montoneri E et al (2014) Novel magnetite nanoparticles coated with waste sourced bio- based substances as sustainable and renewable adsorbing materials. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1518–1524. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500213j
Mahmoud AED, Al-Qahtani KM, Alflaij SO et al (2021) Green copper oxide nanoparticles for lead, nickel, and cadmium removal from contaminated water. Sci Rep 11:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91093-7
Manickam-Periyaraman P, Espinosa JC, Ferrer B et al (2020) Bimetallic iron-copper oxide nanoparticles supported on nanometric diamond as efficient and stable sunlight-assisted Fenton photocatalyst. Chem Eng J 393:124770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124770
Martínez-Pachón D, Espinosa-Barrera P, Rincón-Ortíz J, Moncayo-Lasso A (2019) Advanced oxidation of antihypertensives losartan and valsartan by photo-electro-Fenton at near-neutral pH using natural organic acids and a dimensional stable anode-gas diffusion electrode (DSA-GDE) system under light emission diode (LED) lighting. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:4426–4437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2645-3
Mazellier P, Sulzberger B (2001) Diuron degradation in irradiated, heterogeneous iron/oxalate systems : the rate-determining step. Enviromental, Sci Technol 35:3314–3320
Mercado DF, Weiss RG (2018) Polydimethylsiloxane as a matrix for the stabilization and immobilization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Applications to dehalogenation of environmentally deleterious molecules. J Braz Chem Soc 29:1427–1439. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20180006
Mercado DF, Magnacca G, Malandrino M et al (2014) Paramagnetic iron-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles with improved metal sorption properties. A bioorganic substrates- mediated synthesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:3937–3946. https://doi.org/10.1021/am405217j
Mercado DF, Rubert A, Magnacca G et al (2017) Versatile Fe-containing hydroxyapatite nanomaterials as efficient substrates for lead ions adsorption. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17:9081–9090. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2017.13870
Mercado DF, Caregnato P, Villata LS, Gonzalez MC (2018) Ilex paraguariensis extract-coated magnetite nanoparticles: a sustainable nano-adsorbent and antioxidant. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 28:519–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0757-8
Mercado DF, Cipollone M, González MC, Sánchez FH (2018) Yerba Mate applications: Magnetic response of powders and colloids of iron oxide nanoparticles coated with Ilex paraguariensis derivatives. J Magn Magn Mater 462:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.04.048
Minella M, Marchetti G, De Laurentiis E et al (2014) Photo-Fenton oxidation of phenol with magnetite as iron source. Appl Catal B Environ 154–155:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.02.006
Mondal P, Anweshan A, Purkait MK (2020) Green synthesis and environmental application of iron-based nanomaterials and nanocomposite: a review. Chemosphere 259:127509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127509
Monje DS, Chacon KM, Galindo IC et al (2021) Carbon dots from agroindustrial residues: a critical comparison of the effect of physicochemical properties on their performance as photocatalyst and emulsion stabilizer. Mater Today Chem 20:100445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2021.100445
Munoz M, de Pedro ZM, Casas JA, Rodriguez JJ (2015) Preparation of magnetite-based catalysts and their application in heterogeneous Fenton oxidation - a review. Appl Catal B Environ 176–177:249–265
Muthukumar H, Manickam M (2015) Amaranthus spinosus leaf extract mediated FeO nanoparticles : Physicochemical traits, photocatalytic and antioxidant activity. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:3149–3156. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00722
Nalbandian L, Patrikiadou E, Zaspalis V et al (2015) Magnetic nanoparticles in medical diagnostic applications: synthesis, characterization and proteins conjugation. Curr Nanosci 12:455–468. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573413712666151210230002
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003) A review of classic Fenton ’ s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J Hazard Mater 98:33–50
Önal ES, Yatkin T, Ergüt M, Özer A (2017) Green Synthesis of iron nanoparticles by aqueous extract of eriobotrya japonica leaves as a heterogenous Fenton-like Catalyst: degradation of basic red 46. Int J Chem Eng Appl 8:328–333. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijcea.2017.8.5.678
Ouyang Q, Kou F, Tsang PE et al (2019) Green synthesis of Fe-based material using tea polyphenols and its application as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of lincomycin. J Clean Prod 232:1492–1498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.043
Pal A (2001) Photochemical dissolution of gold nanoparticles by bromine containing trihalomethanes (THMs) in an aqueous triton X-100 medium and its analytical application. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 142:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(01)00465-8
Papoutsakis S, Pulgarin C, Oller I et al (2016) Enhancement of the Fenton and photo-Fenton processes by components found in wastewater from the industrial processing of natural products : the possibilities of cork boiling wastewater reuse. Chem Eng J 304:890–896
Pratiwi J, Lin JY, Mahasti NNN et al (2021) Fluidized-bed synthesis of iron-copper bimetallic catalyst (FeIIICuI@SiO2) for mineralization of benzoic acid in blue light-assisted Fenton process. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 119:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2021.02.007
Qin M, Lu B, Feng S et al (2019) Role of exposed facets and surface OH groups in the Fenton-like reactivity of lepidocrocite catalyst. Chemosphere 230:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.071
Quiroz MA, Bandala ER, Martinez-Huitle CA (2011) Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for removal of pesticides from aqueous media. In: Pesticides - Formulations, Effects, Fate. InTech, pp 685–730
Raffi M, Mehrwan S, Bhatti TM et al (2010) Investigations into the antibacterial behavior of copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 60:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0015-6
Rahimi S, Moattari RMM, Rajabi L et al (2015) Iron oxide/hydroxide (α, γ-FeOOH) nanoparticles as high potential adsorbents for lead removal from polluted aquatic media. J Ind Eng Chem 23:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.07.039
Ramirez JH, Maldonado-Hódar FJ, Pérez-Cadenas AF et al (2007) Azo-dye Orange II degradation by heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction using carbon-Fe catalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 75:312–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.05.003
Rangel AV, Becerra MG, Guerrero-Amaya H et al (2021) Sulfate radical anion activated agro-industrial residues for Cr(VI) adsorption: is this activation process technically and economically feasible? J Clean Prod 289:125793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125793
Rose AL, Waite TD (2003) Kinetics of iron complexation by dissolved natural organic matter in coastal waters. Mar Chem 84:85–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4203(03)00113-0
Saif S, Tahir A, Chen Y (2016) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their environmental applications and implications. Nanomaterials 6:1–26. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110209
Salgado P, Márquez K, Rubilar O et al (2019) The effect of phenolic compounds on the green synthesis of iron nanoparticles (Fe x O y -NPs) with photocatalytic activity. Appl Nanosci 9:371–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0931-5
Sánchez Pérez JA, Arzate S, Soriano-Molina P et al (2020) Neutral or acidic pH for the removal of contaminants of emerging concern in wastewater by solar photo-Fenton? A techno-economic assessment of continuous raceway pond reactors. Sci Total Environ 736:139681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139681
Santos A, Rodríguez S, Pardo F, Romero A (2015) Use of Fenton reagent combined with humic acids for the removal of PFOA from contaminated water. Sci Total Environ 563–564:657–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.044
Spuhler D, Andrés Rengifo-Herrera J, Pulgarin C (2010) The effect of Fe2+, Fe3+, H2O2 and the photo-Fenton reagent at near neutral pH on the solar disinfection (SODIS) at low temperatures of water containing Escherichia coli K12. Appl Catal B Environ 96:126–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.02.010
Starling MCVM, Souza PP, Le Person A, et al (2019) Intensification of UV-C treatment to remove emerging contaminants by UV-C/H 2 O 2 and UV-C/S 2 O 82− : Susceptibility to photolysis and investigation of acute toxicity. Chem Eng J 0–1.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.135
Sulzberger B, Laubscher H (2009) Photochemical reductive dissolution of lepidocrocite. 279–290. https://doi.org/10.1021/ba-1995-0244.ch014
Sun H, Xie G, He D, Zhang L (2020) Ascorbic acid promoted magnetite Fenton degradation of alachlor: mechanistic insights and kinetic modeling. Appl Catal B Environ 267:118383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118383
Tabbì G, Giuffrida A, Bonomo RP (2013) Determination of formal redox potentials in aqueous solution of copper(II) complexes with ligands having nitrogen and oxygen donor atoms and comparison with their EPR and UV-Vis spectral features. J Inorg Biochem 128:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2013.07.035
Thanh NTK, Maclean N, Mahiddine S (2014) Mechanisms of nucleation and growth of nanoparticles in solution. Chem Rev 114:7610–7630. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400544s
Thomas N, Dionysiou DD, Pillai SC (2021) Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts: a review of recent advances. J Hazard Mater 404:124082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124082
Veneranda M, Aramendia J, Bellot-Gurlet L et al (2018) FTIR spectroscopic semi-quantification of iron phases: a new method to evaluate the protection ability index (PAI) of archaeological artefacts corrosion systems. Corros Sci 133:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.01.016
Vidhu VK, Philip D (2014) Catalytic degradation of organic dyes using biosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Micron 56:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2013.10.006
Villegas-Guzman P, Giannakis S, Torres-Palma RA, Pulgarin C (2017) Remarkable enhancement of bacterial inactivation in wastewater through promotion of solar photo-Fenton at near-neutral pH by natural organic acids. Appl Catal B Environ 205:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.12.021
Vione D, Merlo F, Maurino V (2004) Effect of humic acids on the Fenton degradation of phenol. Enviromental Chem Lett 2:129–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-004-0086-3
Wang Y, Gao Y, Chen L, Zhang H (2015) Goethite as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the degradation of methyl orange. Catal Today 252:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2015.01.012
Wang Y, Zhao H, Zhao G (2015) Iron-copper bimetallic nanoparticles embedded within ordered mesoporous carbon as effective and stable heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the degradation of organic contaminants. Appl Catal B Environ 164:396–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.09.047
Wang J, Liu C, Hussain I et al (2016) Iron-copper bimetallic nanoparticles supported on hollow mesoporous silica spheres: the effect of Fe/Cu ratio on heterogeneous Fenton degradation of a dye. RSC Adv 6:54623–54635. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra08501f
Webster NAS, Loan MJ, Madsen IC et al (2012) An in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction investigation of lepidocrocite and ferrihydrite-seeded Al(OH) 3 crystallisation from supersaturated sodium aluminate liquor. J Cryst Growth 340:112–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2011.12.002
Wu H, Dou X, Deng D et al (2012) Decolourization of the azo dye Orange G in aqueous solution via a heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction catalysed by goethite. Environ Technol (united Kingdom) 33:1545–1552. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2011.635709
Wu Y, Zeng S, Wang F et al (2015) Heterogeneous Fenton-like oxidation of malachite green by iron-based nanoparticles synthesized by tea extract as a catalyst. Sep Purif Technol 154:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.09.022
Xu T, Zhu R, Shang H et al (2019) Photochemical behavior of ferrihydrite-oxalate system : Interfacial reaction mechanism and charge transfer process. Water Res 159:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.04.055
Yeh CKJ, Hsu CY, Chiu CH, Huang KL (2008) Reaction efficiencies and rate constants for the goethite-catalyzed Fenton-like reaction of NAPL-form aromatic hydrocarbons and chloroethylenes. J Hazard Mater 151:562–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.06.014
Yew YP, Shameli K, Miyake M et al (2016) Green Synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles using seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) extract. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:276. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1498-2
Zhou T, Wu X, Zhang Y et al (2013) Synergistic catalytic degradation of antibiotic sulfamethazine in a heterogeneous sonophotolytic goethite/oxalate Fenton-like system. Appl Catal B Environ 136–137:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.02.004
Zhu B, Xia P, Ho W, Yu J (2015) Isoelectric point and adsorption activity of porous g-C 3 N 4. Appl Surf Sci 344:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.086
Funding
DSM thank MinCiencias and the Universidad Nacional de Colombia for a Joven Investigador scholarship HERMES 43136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dany Santiago Monje: investigation, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing. Orlando Simón Ruiz: methodology, supervision. Gloria Cristina Valencia: methodology, investigation, supervision, and D. Fabio Mercado: term, conceptualization, methodology, investigation, supervision, writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo A. Torres-Palma
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monje, D.S., Ruiz, O.S., Valencia, G.C. et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles embedded in organic microparticles from Yerba Mate useful for remediation of textile wastewater through a photo-Fenton treatment: Ilex paraguariensis as a platform of environmental interest – Part 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 57127–57146 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19744-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19744-4