Abstract
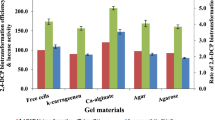
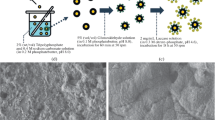
This pilot investigation aimed to evaluate the removal efficiency and the underlying biocatalytic pathways of immobilized fungal laccase during the oxidative biotransformation of a non-phenolic metabolite, 3,5-dichloroaniline (3,5-DCA) derived from dicarboximide fungicides. The maximum loading of laccase on the microporous support surfaces could reach 36.4 mg/g. The immobilized laccase on the microporous support surfaces exhibited excellent thermal stability, pH adaptability, storage stability, and reusability compared to free laccase. The ILMS assay indicated that the immobilized laccase efficiently removed studied 3,5-DCA (99–100%) in the aqueous medium, within 72 h in the presence of catechol. In this study, we identified three coupling reaction products during the removal of 3,5-DCA through an ILMS assay. Based on the identified coupling reaction products, we proposed the reaction pathway for the biotransformation of 3,5-DCA by immobilized laccase, which was shown to be potentially useful in the sustainable environmental remediation of aniline metabolite (i.e., 3,5-DCA) derived from dicarboximide fungicides.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arregui L, Ayala M, Gómez-Gil X, Gutiérrez-Soto G, Hernández-Luna CE, de Los H, Santos M, Levin L, Rojo-Domínguez A, Romero-Martínez D, Saparrat MC, Trujillo-Roldán MA (2019) Laccases: structure, function, and potential application in water bioremediation. Microb Cell Fact 18:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1248-0
Bansal M, Kumar D, Chauhan GS, Kaushik A (2018) Preparation, characterization and trifluralin degradation of laccase-modified cellulose nanofibers. Mater Sci Energy Technol 1:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2018.04.002
Bayramoglu G, Arica MY (2019) Biodegradation of methylene blue and carbaryl by Trametes versicolor laccase preparations in the presence of a mediator compound. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem 56:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2019.1565549
Bilal M, Ashraf SS, Cui J, Lou WY, Franco M, Mulla SI, Iqbal HM (2021) Harnessing the biocatalytic attributes and applied perspectives of nanoengineered laccases—a review. Int J Biol Macromol 166:352–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.195
Bilal M, Iqbal HMN, Barceló D (2019) Persistence of pesticides-based contaminants in the environment and their effective degradation using laccase-assisted biocatalytic systems. Sci Total Environ 695.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133896
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Canas AI, Camarero S (2010) Laccases and their natural mediators: biotechnological tools for sustainable eco-friendly processes. Biotechnol Adv 28(6):694–705
Cuprys A, Thomson P, Suresh G, Roussi T, Brar SK, Drogui P (2021) Potential of agro-industrial produced laccase to remove ciprofloxacin. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13578-2
Das A, Singh J, Yogalakshmi KN (2017) Laccase immobilized magnetic iron nanoparticles: fabrication and its performance evaluation in chlorpyrifos degradation. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 117:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.01.007
Derakhshani E, Naghizadeh A (2018) Optimization of humic acid removal by adsorption onto bentonite and montmorillonite nanoparticles. J Mol Liq 259:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.03.014
Dou RN, Wang JH, Chen YC, Hu YY (2018) The transformation of triclosan by laccase: effect of humic acid on the reaction kinetics, products and pathway. Environ Pollut 234:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.119
Guardado ALP, Druon-Bocquet S, Belleville MP, Sanchez-Marcano J (2021) A novel process for the covalent immobilization of laccases on silica gel and its application for the elimination of pharmaceutical micropollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:25579–25593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12394-y
Javadi S, Ghavami M, Zhao Q, Bate B (2017) Advection and retardation of non-polar contaminants in compacted clay barrier material with organoclay amendment. Appl Clay Sci 142:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.10.041
Jia Y, Chen Y, Luo J, Hu Y (2019) Immobilization of laccase onto meso-MIL-53(Al) via physical adsorption for the catalytic conversion of triclosan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184:109670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109670
Kong D, Xia Q, Liu G, Huang Q, Lu J (2013) Covalent bonding of chloroanilines to humic constituents: pathways, kinetics, and stability. Environ Pollut 180:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.05.018
Kupski L, Salcedo GM, Caldas SS, de Souza TD, Furlong EB, Primel EG (2019) Optimization of a laccase-mediator system with natural redox-mediating compounds for pesticide removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:5131–5139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4010-y
Kwak SY, Lee SH, Sarker A, Kim HY, Shin BG, Kim JE (2021) Uptake and carry-over of procymidone residues to non-target succeeding crop from applied on preceding crop. Kor J Environ Agril 40(3):203–210
Lassouane F, Aït-Amar H, Amrani S, Rodriguez-Couto S (2019) A promising laccase immobilization approach for bisphenol A removal from aqueous solutions. Bioresour Technol 271:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.129
Lee JB, Sohn HY, Shin KS, Kim JS, Jo MS, Jeon CP, Jang JO, Kim JE, Kwon GS (2008) Microbial biodegradation and toxicity of vinclozolin and its toxic metabolite 3, 5-dichloroaniline. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18(2):343–349
Li Z, Chen Z, Zhu Q, Song J, Li S, Liu X (2020) Improved performance of immobilized laccase on Fe3O4@C-Cu2+ nanoparticles and its application for biodegradation of dyes. J Hazard Mater 399:123088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123088
Liu Y, Zeng Z, Zeng G, Tang L, Pang Y, Li Z, Liu C, Lei X, Wu M, Ren P, Liu Z (2012) Immobilization of laccase on magnetic bimodal mesoporous carbon and the application in the removal of phenolic compounds. Bioresour Technol 115:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.015
Malhotra M, Suman SK (2021) Laccase-mediated delignification and detoxification of lignocellulosic biomass: removing obstacles in energy generation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:58929–58944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13283-0
Maryskova M, Linhartova L, Novotny V, Rysova M, Cajthaml T, Sevcu A (2021) Laccase and horseradish peroxidase for green treatment of phenolic micropollutants in real drinking water and wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:31566–31574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12910-0
Mehra R, Muschiol J, Meyer AS, Kepp KP (2018) A structural-chemical explanation of fungal laccase activity. Sci Rep 8:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35633-8
Morozova OV, Shumakovich GP, Shleev SV, Yaropolov YI (2007) Laccase-mediator systems and their applications: a review. Appl Biochem Microbiol 43:523–535. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683807050055
Qiu X, Wang S, Miao S, Suo H, Xu H, Hu Y (2021) Co-immobilization of laccase and ABTS onto amino-functionalized ionic liquid-modified magnetic chitosan nanoparticles for pollutants removal. J Hazard Mater 401.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123353
Racine CR, Ferguson T, Preston D, Ward D, Ball J, Anestis D, Valentovic M, Rankin, (2016) The role of biotransformation and oxidative stress in 3,5-dichloroaniline (3,5-DCA) induced nephrotoxicity in isolated renal cortical cells from male Fischer 344 rats. Toxicology 341–343:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2016.01.006
Sadeghzadeh S, Nejad ZG, Ghasemi S, Khafaji M, Borghei SM (2020) Removal of bisphenol A in aqueous solution using magnetic cross-linked laccase aggregates from Trametes hirsuta. Bioresour Technol 306:123169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123169
Salem S, Salem A (2017) A novel design for clean and economical manufacturing new nano-porous zeolite based adsorbent by alkali cement kiln dust for lead uptake from wastewater. J Clean Prod 143:440–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.091
Sarker A, Lee SH, Kwak SY, Nandi R, Kim JE (2020) Comparative catalytic degradation of a metabolite 3,5-dichloroaniline derived from dicarboximide fungicide by laccase and MnO2 mediators. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 196:110561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110561
Sarker A, Nandi R, Kim JE, Islam T (2021) Remediation of chemical pesticides from contaminated sites through potential microorganisms and their functional enzymes: prospects and challenges. Environ Technol Innov 23:101777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101777
Sathishkumar P, Kamala-Kannan S, Cho M, Kim JS, Hadibarata T, Salim MR, Oh BT (2014) Laccase immobilization on cellulose nanofiber: the catalytic efficiency and recyclic application for simulated dye effluent treatment. J Mol Catal B Enzym 100:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2013.12.008
Shao B, Liu Z, Zeng G, Liu Y, Yang X, Zhou C, Chen M, Liu Y, Jiang Y, Yan M (2019) Immobilization of laccase on hollow mesoporous carbon nanospheres: noteworthy immobilization, excellent stability and efficacious for antibiotic contaminants removal. J Hazard Mater 362:318–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.069
Sondhi S, Kaur R, Kaur S, Kaur PS (2018) Immobilization of laccase-ABTS system for the development of a continuous flow packed bed bioreactor for decolorization of textile effluent. Int J Biol Macromol 117:1093–1100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.007
Su J, Fu J, Wang Q, Silva C, Cavaco-Paulo A (2018) Laccase: a green catalyst for the biosynthesis of poly-phenols. Critic Rev Biotechnol 38(2):294–307
Taghizadeh T, Talebian-Kiakalaieh A, Jahandar H, Amin M, Tarighi S, Faramarzi MA (2020) Biodegradation of bisphenol A by the immobilized laccase on some synthesized and modified forms of zeolite Y. J Hazard Mater 386:121950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121950
Vasileiadis S, Puglisi E, Papadopoulou ES, Pertile G, Suciu N, Pappolla RA, Tourna M, Karas PA, Papadimitriou F, Kasiotakis A, Ipsilanti N (2018) Blame it on the metabolite: 3,5-dichloroaniline rather than the parent compound is responsible for the decreasing diversity and function of soil microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 84.https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01536-18
Vera M, Nyanhongo GS, Pellis A, Rivas BL, Guebitz GM (2019) Immobilization of Myceliophthora thermophila laccase on poly(glycidyl methacrylate) microspheres enhances the degradation of azinphos-methyl. J Appl Polym Sci 136:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47417
Vidal-Limon A, García Suárez PC, Arellano-García E, Contreras OE, Aguila SA (2018) Enhanced degradation of pesticide dichlorophen by laccase immobilized on nanoporous materials: a cytotoxic and molecular simulation investigation. Bioconjug Chem 29:1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00739
Wang D, Lou J, Xu J, Yuan J, Wang Q, Wang P, Fan X (2021) Degradation of octylphenol polyethoxylates with a long ethoxylate chain using the laccase-mediated systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:37781–37792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13400-z
Wen X, Zeng Z, Du C, Huang D, Zeng G, Xiao R, Lai C, Xu P, Zhang C, Wan J, Hu L (2019) Immobilized laccase on bentonite-derived mesoporous materials for removal of tetracycline. Chemosphere 222:865–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.020
Wu W, Shi C, Bian X, Bai Y (2017) Microwave radiation hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of micro- and mesoporous composite molecular sieve Y/SBA-15. Arab J Chem 10:S2773–S2777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.10.027
Yang H, Sun H, Zhang S, Wu B, Pan B (2015) Potential of acetylacetone as a mediator for Trametes versicolor laccase in enzymatic transformation of organic pollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10882–10889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4312-2
Yang Y, Xu Y, Yang Y, Yang H, Yuan H, Huang Y, Liu X (2016) Laccase immobilized on mesoporous SiO2 and its use for degradation of chlorophenol pesticides. Russ J Phys Chem A 90:2044–2054. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024416100307
Zeng S, Qin X, Xia L (2017) Degradation of the herbicide isoproturon by laccase-mediator systems. Biochem Eng J 119:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2016.12.016
Zubrod JP, Bundschuh M, Arts G, Brühl CA, Imfeld G, Knäbel A, Payraudeau S, Rasmussen JJ, Rohr J, Scharmüller A, Smalling K (2019) Fungicides: an overlooked pesticide class? Environ Sci Technol 53:3347–3365. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b04392
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea for proofreading, plagiarism checking, and other technical supports throughout the writing period of the paper.
Funding
This research work was supported by the 2021 research fund of Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Aniruddha Sarker, Tofazzal Islam, Jang-Eok Kim, and Muhammad Bilal. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Aniruddha Sarker, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarker, A., Islam, T., Bilal, M. et al. A pilot study for enhanced transformation of a metabolite 3,5-dichloroaniline derived from dicarboximide fungicides through immobilized laccase mediator system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 52857–52872 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19645-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19645-6