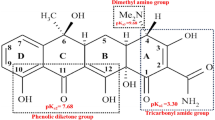
Abstract
Erythromycin (ERY), designated as a risk-prioritized macrolide antibiotic on the 2015 European Union watch list, is the third most commonly used antibiotic, most likely due to its ability to inhibit the protein. ERY has revealed record-high aquatic concentrations threatening the entire ecosystem and hence demands priority remedial measures. The inefficiency of various conventional ERY degradation methodologies opened up a gateway to advanced technologies. The conventional approach comprising of a chemically formulated, single photocatalyst has a major drawback of creating multiple environmental stresses. In this context, photocatalysis is grabbing tremendous attention as an efficient and cost-effective antibiotic treatment approach. Several studies have ascertained that ZnO, TiO2, Fe3O4, and rGO nanoparticles possess remarkable pollution minimizing operational capabilities. Additionally, composites are found much more effective in antibiotic removal than single nanoparticles. In this review, an attempt has been made to provide a comprehensive baseline for efficient reactive radical production by a phyto-mediated composite kept under a certain source of irradiation. Considerable efforts have been directed towards the in-depth investigation of rGO-embedded, phyto-mediated ZnO/TiO2/Fe3O4 photocatalyst fabrication for efficient ERY degradation, undergoing green photocatalysis. This detailed review provides photocatalytic nanocomposite individualities along with a hypothetical ERY degradation mechanism. It is assumed that derived information presented here will provoke innovative ideas for water purification incorporating green photocatalysis, initiating the construction of high-performance biogenic hierarchical nanocatalysts.















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Information was obtained by searching literature and article from peer-reviewed journals using the scientific databases and various search engines including Web of Science, Google Scholar, Science Direct, NCBI, and other major publishers.
References
Ahmad W, Jaiswal KK, Soni S (2020) Green synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles by using Mentha arvensis leaves extract and its antimicrobial properties. Inorganic and Nano-Metal Chemistry, 50(10), 1032-1038. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1732419
Ahmed S, Saifullah AM et al (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica aqueous leaf extract. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 9:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.06.006
Ahmed S, Annu CSA, Ikram S (2017) A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and microbes: a prospect towards green chemistry. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 166:272–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.12.011
Ai M, Zhang JW, Wu YW, Pan L, Shi C, Zou JJ (2020) Role of vacancies in photocatalysis: a review of recent progress. Chem an Asian J 15:3599–3619. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.202000889
Albornoz LL, Bortolozzi JP, Banús ED, Brussino P, da Silva SW, Bernardes AM, Ulla MA (2021) Synthesis and characterization of immobilized titanium-zirconium Sn-doped oxides onto metallic meshes and their photocatalytic activity for erythromycin mineralization. Chem Eng J 414:128891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128891
Alvarino T, Torregrosa N, Omil F, Lema JM, Suarez S (2017) Assessing the feasibility of two hybrid MBR systems using PAC for removing macro and micropollutants. J Environ Manage 203:831–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.03.023
Ambrosetti Barbara, Campanella Luigi, Palmisano Raffaella (2015) Degradation of antibiotics in aqueous solution by photocatalytic process: comparing the efficiency in the use of ZnO or TiO2. J Environ Sci Eng A 4:273–281. https://doi.org/10.17265/2162-5298/2015.06.001
Amina SX, Wu K et al (2018) Synergistic effects and mechanisms of hydroxyl radical-mediated oxidative degradation of sulfamethoxazole by Fe(II)-EDTA catalyzed calcium peroxide: Implications for remediation of antibiotic-contaminated water. Chem Eng J 353:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.078
Arenas-Alatorre J, Silva-Velazquez Y, Alva Medina A, Rivera M (2010) Advantages and limitations of OM, SEM, TEM and AFM in the study of ancient decorated pottery. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 98:617–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-009-5451-4
Arif M, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ahmed R, Irshad S, Ashraf A, ... & Rashid MS (2021) Synthesis, characteristics and mechanistic insight into the clays and clay minerals biochar surface interactions for contaminants removal-A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 310, 127548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127548
Ashraf A, Liu G, Yousaf B et al (2021) Science of the Total Environment Recent trends in advanced oxidation process-based degradation of erythromycin : pollution status, eco-toxicity and degradation mechanism in aquatic ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 772:145389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145389
Ateia M, Alalm MG, Awfa D, Johnson MS, Yoshimura C (2020) Modeling the degradation and disinfection of water pollutants by photocatalysts and composites: A critical review. Science of The Total Environment, 698, 134197.
Aydin S, Aydin ME, Beduk F, Ulvi A (2019) Removal of antibiotics from aqueous solution by using magnetic Fe 3 O 4 /red mud-nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 670:539–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.205
Babić S, Ćurković L, Ljubas D, Čizmić M (2017) TiO2 assisted photocatalytic degradation of macrolide antibiotics. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 6:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2017.05.004
Bagheri S, Termehyousefi A, Do TO (2017) Photocatalytic pathway toward degradation of environmental pharmaceutical pollutants: structure, kinetics and mechanism approach. Catal Sci Technol 7:4548–4569. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cy00468k
Basheer AA (2018) New generation nano-adsorbents for the removal of emerging contaminants in water. J Mol Liq 261:583–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.021
Bayrami A, Ghorbani E, Rahim S, Habibi-yangjeh A (2019) Ultrasonics - Sonochemistry Enriched zinc oxide nanoparticles by Nasturtium o ffi cinale leaf extract : Joint ultrasound-microwave-facilitated synthesis, characterization, and implementation for diabetes control and bacterial inhibition. Ultrason - Sonochemistry 58:104613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104613
Bazin DC, Sayers DA, Rehr JJ (1997) Comparison between X-ray absorption spectroscopy, anomalous wide angle X-ray scattering, anomalous small angle X-ray scattering, and diffraction anomalous fine structure techniques applied to nanometer-scale metallic clusters. J Phys Chem B 101:11040–11050. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9721311
Besha AT, Gebreyohannes AY, Tufa RA, Bekele DN, Curcio E, Giorno L (2017) Removal of emerging micropollutants by activated sludge process and membrane bioreactors and the effects of micropollutants on membrane fouling: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2395–2414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.04.027
Bhattacharya G, Sas S, Wadhwa S et al (2017) Aloe vera assisted facile green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical and dye removal applications. RSC Adv 7:26680–26688. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra02828h
Bilal M, Mehmood S, Rasheed T, Iqbal HMN (2019) Antibiotics traces in the aquatic environment: persistence and adverse environmental impact. Curr Opin Environ Sci Heal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2019.11.005
Blaney L (2014) Ozone treatment of antibiotics in water. In Water reclamation and sustainability (pp. 265-316). Elsevier.
Bolade OP, Williams AB, Benson NU (2020) Environmental nanotechnology, monitoring & management green synthesis of iron-based nanomaterials for environmental remediation : A review. Environ Nanotechnology, Monit Manag 13:100279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2019.100279
Bottoni, P., Caroli, S., & Caracciolo, A. B. (2010). Pharmaceuticals as priority water contaminants. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 92(3), 549-565. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772241003614320
Cai W, Weng X, Chen Z (2019) Highly efficient removal of antibiotic rifampicin from aqueous solution using green synthesis of recyclable nano-Fe3O4. Environ Pollut 247:839–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.108
Calvete MJF, Piccirillo G, Vinagreiro CS, Pereira MM (2019) Hybrid Materials for Heterogeneous Photocatalytic Degradation of Antibiotics 395:63–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.05.004
Cowan AJ, Durrant JR (2013) Long-lived charge separated states in nanostructured semiconductor photoelectrodes for the production of solar fuels. Chem Soc Rev 42:2281–2293. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35305a
Cuerda-Correa EM, Alexandre-Franco MF, & Fernández-González C (2020) Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of antibiotics from water. An overview. Water, 12(1), 102.
da Silva SW, Welter JB, Albornoz LL, Heberle ANA, Ferreira JZ, Bernardes AM (2021) Advanced electrochemical oxidation processes in the treatment of pharmaceutical containing water and wastewater: a review. Curr Pollut Reports 7:146–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-021-00176-6
Das M, Chatterjee S (2019) Green synthesis of metal/metal oxide nanoparticles toward biomedical applications: Boon or bane. In Green synthesis, characterization and applications of nanoparticles (pp. 265-301). Elsevier.
Dash SP, Dixit S, Sahoo, S (2017) Phytochemical and biochemical characterizations from leaf extracts from Azadirachta Indica: an important medicinal plant. Biochem Anal Biochem, 6(323), 2161-1009. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-1009.1000323
Dehghan S, Jafari AJ, FarzadKia M et al (2019) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of Metalaxyl by reduced graphene oxide/Fe 3 O 4 /ZnO ternary nanohybrid: influential factors, mechanism and toxicity bioassay. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 375:280–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.01.024
Demirezen DA, Yıldız YŞ, Yılmaz DD (2019) Amoxicillin degradation using green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles: Kinetics and mechanism analysis. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2019.100219
Devi TB, Ahmaruzzaman M (2017) Bio-inspired facile and green fabrication of Au@Ag@AgCl core–double shells nanoparticles and their potential applications for elimination of toxic emerging pollutants: a green and efficient approach for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 317:726–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.082
Dhanemozhi AC, Rajeswari V, Sathyajothi S (2017) ScienceDirect green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle using green tea leaf extract for supercapacitor application. Mater Today Proc 4:660–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.01.070
Dhifi W, Bellili S, Jazi S, Nasr SB, El Beyrouthy M, & Mnif W (2018) Phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of Tunisian Laurus nobilis. Pakistan journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 31(6), 2397-2402.
Di Salvo A, della Rocca G, Cagnardi P, Pellegrino RM (2013) Pharmacokinetics and residue depletion of erythromycin in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 36:1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12074
Divya S, Nampoori VPN, Radhakrishnan P, & Mujeeb A (2014) Electronic and optical properties of TiO2 and its polymorphs by Z-scan method. Chinese Physics B, 23(8), 084203. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/23/8/084203
Doll TE, Frimmel FH (2005) Removal of selected persistent organic pollutants by heterogeneous photocatalysis in water. Catal Today 101:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2005.03.005
Dong S, Sun J, Li Y et al (2014) Applied Catalysis B : Environmental ZnSnO 3 hollow nanospheres / reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites as high-performance photocatalysts for degradation of metronidazole. "Applied Catal B. Environ 144:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.043
Fakhri A, Rashidi S, Tyagi I et al (2016) Photodegradation of Erythromycin antibiotic by γ-Fe2O3/SiO2 nanocomposite: response surface methodology modeling and optimization. J Mol Liq 214:378–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.11.037
Farbod M, Jafarpoor E (2012) Fabrication of different ZnO nanostructures and investigation of morphology dependence of their photocatalytic properties. Mater Lett 85:47–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.06.080
Feng K, Zhang H, Gao J, Xu J, Dong Y, Kang Z, & Zhong J (2020) Single atoms or not? The limitation of EXAFS. Applied Physics Letters, 116(19), 191903. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0008748
Fernández L, Gamallo M, González-Gómez MA et al (2019) Insight into antibiotics removal: exploring the photocatalytic performance of a Fe 3 O 4 /ZnO nanocomposite in a novel magnetic sequential batch reactor. J Environ Manage 237:595–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.089
Foo C, Li Y, Lebedev K, Chen T, Day S, Tang C, Tsang SCE (2021) Characterisation of oxygen defects and nitrogen impurities in TiO2 photocatalysts using variable-temperature X-ray powder diffraction. Nat Commun 12:661. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-20977-z
Franzen Ramos L, da Silva SW, Schneider DE, Rodrigues MAS, Bernardes AM (2020) Mineralization of erythromycin by UV-based and electro-oxidation processes. J Water Process Eng 33:101039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101039
Franzen Ramos L, da Silva SW, Schneider DE, Rodrigues MAS, Bernardes AM (2020) Mineralization of erythromycin by UV-based and electro-oxidation processes. J Water Process Eng. 33:101039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101039
Ganesh M, Lee SG, Jayaprakash J et al (2019) Hydnocarpus alpina Wt extract mediated green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticle and screening of its anti-microbial, free radical scavenging, and photocatalytic activity. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 19:101129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101129
Gholami A, Hajiani M, Hossein M, Anari S (2019) ARTICLE ORIGINAL investigation of photocatalytic degradation of clindamycin by TiO 2(4):139–146. https://doi.org/10.22090/jwent.2019.02.005
Gnanasekaran L, Hemamalini R, Rajendran S, Qin J, Yola ML, Atar N, Gracia F (2019) Nanosized Fe3O4 incorporated on a TiO2 surface for the enhanced photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 287, 110967.
Göbel A, McArdell CS, Joss A et al (2007) Fate of sulfonamides, macrolides, and trimethoprim in different wastewater treatment technologies. Sci Total Environ 372:361–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.07.039
Gole JL, Stout JD, Burda C, Lou Y, & Chen X (2004) Highly efficient formation of visible light tunable TiO2-x N x photocatalysts and their transformation at the nanoscale. The journal of physical chemistry B, 108(4), 1230-1240. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp030843n
Gudikandula K, Charya Maringanti S (2016) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by chemical and biological methods and their antimicrobial properties. J Exp Nanosci 11:714–721. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2016.1139196
Guo MT, Bin YQ, Yang J (2013) Ultraviolet reduction of erythromycin and tetracycline resistant heterotrophic bacteria and their resistance genes in municipal wastewater. Chemosphere 93:2864–2868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.068
Hashemi S, Asrar Z, Pourseyedi S, Nadernejad N (2016) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Olive (Olea europaea). IET nanobiotechnology, 10(6), 400-404. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2015.0117
Hassan SS, El Azab WI, Ali HR, Mansour MS (2015) Green synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of anthracene. Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 6(4), 045012. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/6/4/045012
He X, Yang DP, Zhang X et al (2019) Waste eggshell membrane-templated CuO-ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced adsorption, catalysis and antibacterial properties for water purification. Chem Eng J 369:621–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.047
Heberle ANA, Alves MEP, da Silva SW, Klauck CR, Rodrigues MAS, Bernardes AM (2019) Phytotoxicity and genotoxicity evaluation of 2,4,6-tribromophenol solution treated by UV-based oxidation processes. Environ Pollut 249:354–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.057
Hirsch R, Ternes T, Haberer K, Kratz KL (1999) Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 225:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00337-4
Huo P, Guan J, Zhou M, Ma C, Liu X, Yan Y & Yuan S (2017) Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Carbon quantum dots modi fi ed CdSe loaded reduced graphene oxide for enhancing photocatalytic activity. J Ind Eng Chem 50:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.02.008
Hussain A, Oves M, Alajmi MF, Hussain I, Amir S, Ahmed J, ... & Ali I (2019) Biogenesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pandanus odorifer leaf extract: anticancer and antimicrobial activities. RSC advances, 9(27), 15357–15369. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra01659g
Islas-Espinoza M, Aydin S, de Heraslas A et al (2018) Sustainable bioremediation of antibacterials, metals and pathogenic DNA in water. J Clean Prod 183:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.068
Jessick AM (2010) Detection, fate, and bioavailability of erythromycin in environmental matrices. Iowa state university
Jin X, Li N, Weng X et al (2018). Accepted Manuscript. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.199
Jin X, Zhou X, Sun P, Lin S, Cao W, Li Z, Liu W (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of norfloxacin using N-doped TiO2: optimization, mechanism, identification of intermediates and toxicity evaluation. Chemosphere 237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124433
Jo WK, Tonda S (2019) Novel CoAl-LDH/g-C3N4/RGO ternary heterojunction with notable 2D/2D/2D configuration for highly efficient visible-light-induced photocatalytic elimination of dye and antibiotic pollutants. J Hazard Mater 368:778–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.114
Jonidi-Jafari A, Shirzad-Siboni M, Yang JK et al (2015) Photocatalytic degradation of diazinon with illuminated ZnO-TiO2 composite. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 50:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.12.020
Kanfer I, Skinner MF, Walker RB (1998) Analysis of macrolide antibiotics. J Chromatogr A 812:255–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00276-3
Karaköse E, Çolak H (2018) Structural, electrical, and antimicrobial characterization of green synthesized ZnO nanorods from aqueous Mentha extract. MRS Commun 8:577–585. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.31
Karnan T, Selvakumar SAS (2016) Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using rambutan (Nephelium lappaceumL.) peel extract and their photocatalytic activity on methyl orange dye. Journal of molecular Structure, 1125, 358-365.
Karnan T, Selvakumar SAS (2016) Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using rambutan (Nephelium lappaceumL.) peel extract and their photocatalytic activity on methyl orange dye. J Mol Struct 1125:358–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.07.029
Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Dinsdale RM, Guwy AJ (2009) The removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Water Res 43:363–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.10.047
Kanmani SS, Ramachandran K (2012) Synthesis and characterization of TiO2/ZnO core/shell nanomaterials for solar cell applications. Renewable Energy, 43, 149-156.
Khalafi T, Buazar F, Ghanemi K (2019) Phycosynthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles toward organosulfur pollutants. Sci Rep 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43368-3
Khan ZUH, Sadiq HM, Shah NS et al (2019) Greener synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Trianthema portulacastrum extract and evaluation of its photocatalytic and biological applications. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 192:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.01.013
Kim BS (2017). Biological Reduction of Graphene Oxide Using Plant Leaf Extracts Biological Reduction of Graphene Oxide Using Plant Leaf Extracts. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.1862
Kim YH, Heinze TM, Beger R et al (2004) A kinetic study on the degradation of erythromycin A in aqueous solution. Int J Pharm 271:63–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2003.10.023
Kovalova L, Siegrist H, Von GuntenEugster UJ, Hagenbuch M, Wittmer A, Moser R, McArdell CS (2013) Elimination of micropollutants during post-treatment of hospital wastewater with powdered activated carbon, ozone, and UV. Environ Sci Technol 47:7899–7908. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400708w
Kumar S, Lalit C (2017) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Calotropis gigantea : characterization and its evaluation on tree seedling growth in nursery stage. Appl Nanosci 7:501–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0586-7
Kumar A, Pandey G (2017) A Review on the Factors Affecting the Photocatalytic Degradation of Hazardous Materials. Mater Sci Eng Int J 1:1–10. https://doi.org/10.15406/mseij.2017.01.00018
Kuppusamy P, Yusoff MM, Maniam GP, Govindan N (2016) Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications – An updated report. Saudi Pharm J 24:473–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2014.11.013
Labbe M (2008) Photocatalytic Degradation of Select Drinking Water Pollutants Using NANO-TiO2 Catalyst (Doctoral dissertation, University of Windsor).
Lazar MA, Varghese S, Nair SS (2012) Photocatalytic water treatment by titanium dioxide: Recent updates. Catalysts 2:572–601. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal2040572
Lendzion-Bieluń Z, Wojciechowska A, Grzechulska-Damszel J et al (2020) Effective processes of phenol degradation on Fe3O4–TiO2 nanostructured magnetic photocatalyst. J Phys Chem Solids 136:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.109178
Li XZ, Liu H, Cheng LF, Tong HJ (2003) Photocatalytic oxidation using a new catalyst - TiO2 microsphere -for water and wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Technol 37:3989–3994. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0262941
Li W, Shi Y, Gao L et al (2012) Chemosphere Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 89:1307–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.079
Li G, Wang B, Zhang J et al (2019) Rational construction of a direct Z-scheme g-C 3 N 4 /CdS photocatalyst with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity and degradation of erythromycin and tetracycline. Appl Surf Sci 478:1056–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.035
Li Y, Fu Y, Zhu M (2020) Green synthesis of 3D tripyramid TiO2 architectures with assistance of aloe extracts for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 260, 118149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118149
Lin AYC, Lin CF, Chiou JM, Hong PKA (2009) O3 and O3/H2O2 treatment of sulfonamide and macrolide antibiotics in wastewater. J Hazard Mater 171:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.031
Lin L, Wang H, Xu P (2017) Immobilized TiO 2 -reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites on optical fibers as high performance photocatalysts for degradation of pharmaceuticals. Chem Eng J 310:389–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.024
Lin L, Yu Z, Wang X (2019) Crystalline Carbon Nitride Semiconductors for Photocatalytic Water Splitting. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 58:6164–6175. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201809897
Liu Y, Jiao Y, Yin B et al (2013) Hierarchical semiconductor oxide photocatalyst: A case of the SnO2 microflower. Nano-Micro Lett 5:234–241. https://doi.org/10.5101/nml.v5i4.p234-241
Liu J, Lu G, Ding J et al (2014) Tissue distribution, bioconcentration, metabolism, and effects of erythromycin in crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Sci Total Environ 490:914–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.055
Liu M, Zhang D, Han J, Liu C, Ding Y, Wang Z, Wang A (2020) Adsorption enhanced photocatalytic degradation sulfadiazine antibiotic using porous carbon nitride nanosheets with carbon vacancies. Chem Eng J, 382, 123017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123017
Louvet JN, Giammarino C, Potier O, Pons MN (2010) Adverse effects of erythromycin on the structure and chemistry of activated sludge. Environ Pollut 158:688–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.10.021
Luo J, Wang Z, Jiang H, Liu S, Xiong FQ, Ma J (2020) Localized building titania-graphene charge transfer interfaces for enhanced photocatalytic performance. Langmuir 36:4637–4644. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c00297
Lyu J, Shao J, Wang Y et al (2018). Construction of a Porous Core-Shell Homojunction for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Antibiotics Abstract. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.085
Madhubala V, Kalaivani T (2018) Phyto and hydrothermal synthesis of Fe 3 O 4 @ZnO core-shell nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica and its cytotoxicity studies. Appl Surf Sci 449:584–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.105
Mahdavi M, Namvar F, Ahmad MB, Mohamad R (2013) Green biosynthesis and characterization of magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using seaweed (Sargassum muticum) aqueous extract. Molecules, 18(5), 5954-5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18055954
Malesic-Eleftheriadou N, Evgenidou E, Kyzas GZ et al (2019) Removal of antibiotics in aqueous media by using new synthesized bio-based poly(ethylene terephthalate)-TiO2 photocatalysts. Chemosphere 234:746–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.239
Maletić M, Vukčević M, Kalijadis A et al (2016) Hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2/carbon composites and their application for removal of organic pollutants. Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.06.020
Matinise N, Fuku XG, Kaviyarasu K et al (2017) Applied Surface Science ZnO nanoparticles via Moringa oleifera green synthesis : physical properties & mechanism of formation. Appl Surf Sci 406:339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.219
Miao X, Bishay F, Chen M, Metcalfe CD (2004) Occurrence of Antimicrobials in the Final Effluents of Wastewater Treatment Plants in Canada 38:3533–3541
Michiels JA, Kevers C, Pincemail J et al (2012) Extraction conditions can greatly influence antioxidant capacity assays in plant food matrices. Food Chem 130:986–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.117
Minale M, Gu Z, Guadie A et al (2020) Application of graphene-based materials for removal of tetracyclines using adsorption and photocatalytic-degradation : a review. J Environ Manage 276:111310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111310
Mohamad NAN, Arham NA, Jai J, Hadi A (2014) Plant extract as reducing agent in synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: a review. Adv Mater Res 832:350–355. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.832.350
Mourdikoudis S, Pallares RM, Thanh NTK (2018) Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 10:12871–12934. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr02278j
Nardi G, Manet I, Monti S, Miranda MA, Lhiaubet-Vallet V (2014) Scope and limitations of the TEMPO/EPR method for singlet oxygen detection: the misleading role of electron transfer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 77:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.08.020
Naseer M, Aslam U, Khalid B, Chen B (2020) Green route to synthesize zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci Rep, 10(1),1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65949-3
Nithya K, Kalyanasundharam S (2019) Effect of chemically synthesis compared to biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles using aqueous extract of C. halicacabum and their antibacterial activity. OpenNano, 4, 100024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onano.2018.10.001
Nnadozie EC, Ajibade PA (2020) Green synthesis and characterization of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using Chromolaena odorata root extract for smart nanocomposite. Mater Lett, 263, 127145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.127145
Omri K, Alonizan N (2019) Effects of ZnO/Mn concentration on the micro-structure and optical properties of ZnO/Mn–TiO2 nano-composite for applications in photo-catalysis. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 29:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0979-4
Padhi DK, Panigrahi TK, Parida K et al (2017) Green synthesis of Fe3O4/RGO nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic performance for Cr(VI) reduction, phenol degradation, and antibacterial activity. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:10551–10562. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02548
Pai S, HS, Varadavenkatesan T, et al (2019) Photocatalytic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesis using Peltophorum pterocarpum leaf extract and their characterization. Optik (stuttg) 185:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.03.101
Pala-Ozkok I, Orhon D (2013) Chronic effect of erythromycin on substrate biodegradation kinetics of activated sludge. Biochem Eng J 81:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.10.002
Parthasarathy G, Saroja M, Venkatachalam M, Evanjelene VK (2017a) Characterization and antibacterial activity of green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles from Ocimum basilicum leaf extract. Adv. Biores, 8, 29-35. https://doi.org/10.15515/abr.0976-4585.8.3.2935
Parthasarathy G, Saroja M, Venkatachalam M (2017b) Bio-synthesized nano formulation of zinc oxide-Aloe vera and to study their characterization and antibacterial activities against multiple pathogens. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 8(2), 900. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.8(2).900-07
Pavithra NS, Lingaraju K, Raghu GK, Nagaraju G (2017) Citrus maxima (Pomelo) juice mediated eco-friendly synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: applications to photocatalytic, electrochemical sensor and antibacterial activities. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 185:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.05.032
Perdigo A, Petre A, Rosal R et al (2010) Occurrence of Emerging Pollutants in Urban Wastewater and Their Removal through Biological Treatment Followed by Ozonation 44:578–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.07.004
Pérez T, Sirés I, Brillas E, Nava JL (2017) Solar photoelectro-Fenton flow plant modeling for the degradation of the antibiotic erythromycin in sulfate medium. Electrochim Acta 228:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.01.047
Radjenovic J, Petrovic M, Barceló D (2007) Analysis of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and removal using a membrane bioreactor. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1365–1377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0883-6
Raizada P, Kumari J, Shandilya P et al (2017) Magnetically retrievable Bi 2 WO 6 /Fe 3 O 4 immobilized on graphene sand composite for investigation of photocatalytic mineralization of oxytetracycline and ampicillin. Process Saf Environ Prot 106:104–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.12.012
Raja A, Ashokkumar S, Marthandam RP et al (2018) The present work reports the green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles ( ZnO NPs ). J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.02.011
Ramesh M, Anbuvannan M, Viruthagiri G (2014) Spectrochimica Acta Part A : Molecular and biomolecular spectroscopy green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Spectrochim ACTA PART A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.09.105
Ramesh M, Anbuvannan M, Viruthagiri G (2015) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 136:864–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.09.105
Ramos PG, Flores E, Luyo C et al (2019) Fabrication of ZnO-RGO nanorods by electrospinning assisted hydrothermal method with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater Today Commun 19:407–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.03.010
Rao KG, Ashok CH, Rao KV, Chakra CS, Tambur P (2015). Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using Aloe vera extract. Int. J. Adv. Res. Phys. Sci, 2(1A), 28-34.
Rao TN, Riyazuddin BP et al (2019) Green synthesis and structural classification of Acacia nilotica mediated-silver doped titanium oxide (Ag/TiO2) spherical nanoparticles: Assessment of its antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Saudi J Biol Sci 26:1385–1391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.09.005
Rasli NI, Basri H, Harun Z (2020) Heliyon Zinc oxide from aloe vera extract : two-level factorial screening of biosynthesis parameters. Heliyon 6:e03156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03156
Ratanatawanate C, Bui A, Vu K, Balkus KJ (2011) Low-Temperature synthesis of copper(II) sulfide quantum dot decorated TiO2 nanotubes and their photocatalytic properties. J Phys Chem C 115:6175–6180. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp109716q
Reddy SB, Mandal BK (2017) Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Eucalyptus globulus and their photocatalytic and antioxidant activity. Adv Powder Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.11.026
Roberts DJ (2014) Erythromycin Encycl Toxicol Third Ed 2:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-386454-3.00727-2
Rodrigues S, Antunes SC, Correia AT, Nunes B (2016) Acute and chronic effects of erythromycin exposure on oxidative stress and genotoxicity parameters of Oncorhynchus mykiss. Sci Total Environ 545–546:591–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.138
Kanagasubbulakshmi S, Kadirvelu K (2017) Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Lagenaria siceraria and evaluation of its antimicrobial activity. Defence Life Science Journal, 2(4), 422-427. https://doi.org/10.14429/dlsj.2.12277
Sadhukhan P, Kundu M, Rana S, Kumar R, Das J, Sil PC (2019) Microwave induced synthesis of ZnO nanorods and their efficacy as a drug carrier with profound anticancer and antibacterial properties. Toxicol Reports 6:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.01.006
Sahar E, David I, Gelman Y, Chikurel H, Aharoni A, Messalem R, Brenner A (2011) The use of RO to remove emerging micropollutants following CAS/UF or MBR treatment of municipal wastewater. Desalination 273:142–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.004
Sahaya P, Kumar M, Francis AP, Devasena T (2014) Biosynthesized and chemically synthesized titania nanoparticles: comparative analysis of antibacterial activity. J Environ Nanotechnol 3:73–81. https://doi.org/10.13074/jent.2014.09.143098
Sangeetha G, Rajeshwari S, Venckatesh R (2011) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract : structure and optical properties. Mater Res Bull 46:2560–2566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.07.046
Santhoshkumar J, Kumar SV, Rajeshkumar S (2017) Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant leaf extract against urinary tract infection pathogen. Resource-Efficient Technologies, 3(4), 459-465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reffit.2017.05.001
Santiago MR, Salvo LM (2018) Effects of the neem extract (Azadirachta indica) on mammalian reproduction. Journal of Analytical & Pharmaceutical Research, 7(2):203-204. https://doi.org/10.15406/japlr.2018.07.00227
Sayadi MH, Sobhani S, Shekari H (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of azithromycin using GO@Fe3O4/ ZnO/ SnO2 nanocomposites. J Clean Prod 232:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.338
Schafhauser BH, Kristofco LA, de Oliveira CMR, Brooks BW (2018) Global review and analysis of erythromycin in the environment: occurrence, bioaccumulation and antibiotic resistance hazards. Environ Pollut 238:440–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.052
Seebauer EG, Kratzer MC (2006) Charged point defects in semiconductors. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Reports 55:57–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2006.01.002
Selim YA, Azb MA, Ragab I, HM Abd El-Azim M (2020) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Deverra tortuosa and their cytotoxic activities. Scientific reports, 10(1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60541-1
Serrano D, Suárez S, Lema JM, Omil F (2011) Removal of persistent pharmaceutical micropollutants from sewage by addition of PAC in a sequential membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 45:5323–5333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.07.037
Si, X., Wu, K., Si, Y., & Yousaf, B. (2020). Mechanistic insights into the reactive radicals- assisted degradation of sulfamethoxazole via calcium peroxide activation by manganese-incorporated iron oxide–graphene nanocomposite: formation of radicals and degradation pathway. Chemical Engineering Journal, 384, 123360.
Sher Shah MSA, Park AR, Zhang K, Park JH, Yoo PJ (2012) Green synthesis of biphasic TiO2–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with highly enhanced photocatalytic activity. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 4(8), 3893-3901.
Sharma G, Kumar A, Sharma S et al (2020) Fe 3 O 4 / ZnO / Si 3 N 4 nanocomposite based photocatalyst for the degradation of dyes from aqueous solution. Mater Lett 278:128359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128359
Shi Y, Huang J, Zeng G et al (2019) Photocatalytic membrane in water purification: is it stepping closer to be driven by visible light? J Memb Sci 584:364–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.04.078
Singer AC, Järhult JD, Grabic R, Khan GA, Lindberg RH, Fedorova G, Söderström H (2014) Intraand inter-pandemic variations of antiviral, antibiotics and decongestants in wastewater treatment plants and receiving rivers. PLoS One, 9(9), e108621. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108621
Singh P, Kim YJ, Zhang D, Yang DC (2016) Biological synthesis of nanoparticles from plants and microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol 34:588–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.02.006
Singh KK, Senapati KK, Sarma KC (2017) Synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with green tea polyphenols and their use for removal of dye pollutant from aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2214–2221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.04.022
Singh J, Dutta T, Kim KH et al (2018) “Green” synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: applications for environmental remediation. J Nanobiotechnology 16:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0408-4
Song J, Wu X, Zhang M, Liu C, Yu J, Sun G, ... & Ding B (2020) Highly flexible, core-shell heterostructured, and visible-light-driven titania-based nanofibrous membranes for antibiotic removal and E. coil inactivation. ChemEng J, 379, 122269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122269
Srinivasan M, Venkatesan M, Arumugam V, Natesan G, Saravanan N, Murugesan S, ... & Pugazhendhi A (2019) Green synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) using Sesbania grandiflora and evaluation of toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Process Biochemistry, 80, 197-202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.02.010
Stan M, Lung I, Soran ML et al (2017) Removal of antibiotics from aqueous solutions by green synthesized magnetite nanoparticles with selected agro-waste extracts. Process Saf Environ Prot 107:357–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.03.003
Suresh D, Shobharani RM, Nethravathi PC et al (2015) Artocarpus gomezianus aided green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles : luminescence, photocatalytic and antioxidant properties. Spectrochim ACTA PART A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.01.048
Tiwari JN, Tiwari RN, Kim KS (2012) Zero-dimensional, one-dimensional, two-dimensional and three-dimensional nanostructured materials for advanced electrochemical energy devices. Prog Mater Sci 57:724–803
Vahidi A, Vaghari H, Najian Y, Najian MJ, & Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H (2019) Evaluation of three different green fabrication methods for the synthesis of crystalline ZnO nanoparticles using Pelargonium zonale leaf extract. Green Processing and Synthesis, 8(1), 302-308.
Varadavenkatesan T, Lyubchik E, Pai S et al (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B by zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the leaf extract of Cyanometra ramiflora. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 199:111621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111621
Vignesh K, Rajarajan M, Suganthi A (2014) Photocatalytic degradation of erythromycin under visible light by zinc phthalocyanine-modified titania nanoparticles. Mater Sci Semicond Process 23:98–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.02.050
Voigt M, Jaeger M (2017) On the photodegradation of azithromycin, erythromycin and tylosin and their transformation products – a kinetic study. Sustain Chem Pharm 5:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2016.12.001
Waiser MJ, Swerhone GDW, Roy J et al (2016) Effects of erythromycin, trimethoprim and clindamycin on attached microbial communities from an effluent dominated prairie stream. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 132:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.05.026
Wang J, Zhuan R (2020) Degradation of antibiotics by advanced oxidation processes: an overview. Sci Total Environ 701:135023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135023
Wang X, Yin R, Zeng L, Zhu M (2019) A review of graphene-based nanomaterials for removal of antibiotics from aqueous environments. Environ Pollut 253:100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.067
Wang X, Dou X, Wu J, Meng F (2021) Attenuation pathways of erythromycin and biochemical responses related to algal growth and lipid synthesis in a microalga-effluent system. Environ. Res. 195:110873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110873
Weldegebrieal GK (2020) Synthesis method, antibacterial and photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles for azo dyes in wastewater treatment: A review. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 120, 108140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2020.108140
Welter JB, da Silva SW, Schneider DE, Rodrigues MAS, Ferreira JZ (2020) Performance of Nb/BDD material for the electrochemical advanced oxidation of prednisone in different water matrix. Chemosphere 248:126062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126062
Wohlmuth da Silva S, Arenhart Heberle AN, Pereira Santos A, Siqueira Rodrigues MA, Pérez-Herranz V, Moura Bernardes A (2019) Antibiotics mineralization by electrochemical and UV-based hybrid processes: evaluation of the synergistic effect. Environ Technol (united Kingdom) 40:3456–3466. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1478453
Wu S, Hu YH (2021) A comprehensive review on catalysts for electrocatalytic and photoelectrocatalytic degradation of antibiotics. Chem Eng J 409:127739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127739
Xekoukoulotakis NP, Xinidis N, Chroni M et al (2010) UV-A/TiO2 photocatalytic decomposition of erythromycin in water: factors affecting mineralization and antibiotic activity. Catal Today 151:29–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2010.01.040
Xu W, Zhang G, Li X et al (2007) Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), South China. Water Res 41:4526–4534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.023
Xu Y, Li H, Sun B et al (2020) Surface oxygen vacancy defect-promoted electron-hole separation for porous defective ZnO hexagonal plates and enhanced solar-driven photocatalytic performance. Chem Eng J 379:122295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122295
Xu Z, Cao J, Chen X, Shi L, Bian Z (2021) Enhancing photocatalytic performance of NH2-UIO66 by defective structural engineering. Trans Tianjin Univ 27:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-020-00278-0
Yamada N (2015) Kinetic energy discrimination in collision/reaction cell ICP-MS: Theoretical review of principles and limitations. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At Spectrosc. 110:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2015.05.008
Yang X, Flowers RC, Weinberg HS, Singer PC (2011) Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in an advanced wastewater reclamation plant. Water Res 45:5218–5228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.07.026
Yao W, Li Y, Yan D et al (2013) Fabrication and photocatalysis of TiO2-graphene sandwich nanosheets with smooth surface and controlled thickness. Chem Eng J 229:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.027
Zhang Y, Liu H, Xin Y et al (2019) Erythromycin degradation and ERY-resistant gene inactivation in erythromycin mycelial dreg by heat-activated persulfate oxidation. Chem Eng J 358:1446–1453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.157
Zhang S, Wang Y, Cao Z et al (2020) Simultaneous enhancements of light-harvesting and charge transfer in UiO- 67 / CdS / rGO composites toward ofloxacin photo-degradation. Chem Eng J 381:122771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122771
Zhang Y, Jiao Z, Hu Y, Lv S, Fan H, Zeng Y, ... & Wang M (2017) Removal of tetracycline and oxytetracycline from water by magnetic Fe3O4@ graphene. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(3), 2987-2995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7964-7
Zhao C, Yang Y, Luo L, Shao S, Yiji Zhou, Shao Y, Zhan F, Yang J, Yaoyu Zhou (2020) γ-ray induced formation of oxygen vacancies and Ti3+ defects in anatase TiO2 for efficient photocatalytic organic pollutant degradation. Sci Total Environ. 747:141533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141533
Zhou LJ, Ying GG, Liu S, Zhao JL, Yang B, Chen ZF, Lai HJ (2013) Occurrence and fate of eleven classes of antibiotics in two typical wastewater treatment plants in South China. Sci Total Environ. 452–453:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.03.010
Zoppas FM, da Silva SW, Beltrame TF, Marchesini FA, Bernardes AM, & Miro E (2020) Mineralization of formic acid from catalytic nitrate reduction effluent by UV based and electrochemical processes. J Environ Chem Eng, 8(5), 104127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104127
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 41173032) and the Key Program for Science and Technology Development of Anhui Province (No. 1804b06020358).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aniqa Ashraf: Writing—original draft, visualization; Guijian Liu: Resources, supervision, funding acquisition; Balal Yousaf: Conceptualization; Muhammad Arif: writing, data compilation; Rafay Ahmed: Visualization, data compilation; Audil Rashid: Revision and editing; Luqman Riaz: Table formulation and editing; Muhammad Saqib Rashid: Visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors ensure that principles of ethical and professional conduct have been followed, information regarding sources of funding, potential conflicts of interest (financial or non-financial) are disclosed. And no human or animal participation is involved in this work.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Sami Rtimi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashraf, A., Liu, G., Yousaf, B. et al. Phyto-mediated photocatalysis: a critical review of in-depth base to reactive radical generation for erythromycin degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 32513–32544 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19119-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19119-9