Abstract
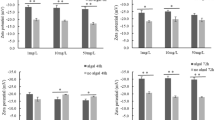
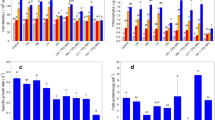
The extensive application of cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs), a type of rare earth nanomaterial, led to pollution into aquatic environments. Cyanobacteria, a significant component of freshwater ecosystems, can interact with CeO2 NPs. However, little attention has been paid as to whether CeO2 NPs will have adverse effects on cyanobacteria. In the present study, Microcystis aeruginosa (FACHB-942) was exposed to different concentrations (0, 1, 10, and 50 mg/L) of CeO2 NPs. Results showed 50 mg/L CeO2 NPs inhibited algal growth (11.48% ± 5.76%), suppressed photosynthesis and induced the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) after 72 h exposure. The toxicity mechanism is the adsorption of CeO2 NPs on cell surface, the ROS formation and the intracellular Ce. Additionally, the intracellular microcystins (MCs) content was significantly induced (11.84% ± 1.47%) by 50 mg/L CeO2 NPs, while no significance was found in 1 and 10 mg/L CeO2 NP treatments. Results indicated high concentrations of CeO2 NPs could be toxic to algae through the adverse effects on algal growth and photosynthesis. Moreover, the promoted MCs production could also pose a threat to freshwater ecosystems due to the possible release into the environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Angel BM, Vallotton P, Apte SC (2015) On the mechanism of nanoparticulate CeO2 toxicity to freshwater algae. Aquat Toxicol 168:90–97
Auffan M, Rose J, Orsiere T, De Meo M, Thill A, Zeyons O, Proux O, Masion A, Chaurand P, Spalla O, Botta A, Wiesner MR, Bottero J (2009) CeO2 nanoparticles induce DNA damage towards human dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Nanotoxicology 3(2):161–171
Bennett SW, Keller AA (2011) Comparative photoactivity of CeO2, γ-Fe2O3, TiO2 and ZnO in various aqueous systems. Appl Catal B-Environ 102(3–4):600–607
Booth A, Storseth T, Altin D, Fornara A, Ahniyaz A, Jungnickel H, Laux P, Luch A, Sorensen L (2015) Freshwater dispersion stability of PAA-stabilised cerium oxide nanoparticles and toxicity towards Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Sci Total Environ 505:596–605
Bour A, Mouchet F, Cadarsi S, Silvestre J, Baqué D, Gauthier L, Pinelli E (2017) CeO2 nanoparticle fate in environmental conditions and toxicity on a freshwater predator species: a microcosm study. Environ Sci Pollut R 24(20):17081–17089
Chen S, Zhang L, Chen H, Chen Z, Wen Y (2019) Enantioselective toxicity of chiral herbicide metolachlor to Microcystis aeruginosa. J Agric Food Chem 67(6):1631–1637
Chen W, Liu H, Zhang Q, Dai S (2010) Effect of nitrite on growth and microcystins production of Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. J Appl Phycol 23(4):665–671
Deng XY, Cheng J, Hu XL, Wang L, Li D, Gao K (2017) Biological effects of TiO2 and CeO2 nanoparticles on the growth, photosynthetic activity, and cellular components of a marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Sci Total Environ 575:87–96
Dhall A, Self W (2018) Cerium oxide nanoparticles: a brief review of their synthesis methods and biomedical applications. Antioxidants (Basel) 7(8).
Hou J, Yang Y, Wang P, Wang C, Miao L, Wang X, Lv B, You G, Liu Z (2017) Effects of CeO2, CuO, and ZnO nanoparticles on physiological features of Microcystis aeruginosa and the production and composition of extracellular polymeric substances. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(1):226–235
Huang W, Bi Y, Hu Z (2014) Effects of fertilizer-urea on growth, photosynthetic activity and microcystins production of Microcystis aeruginosa isolated from Dianchi Lake. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92(5):514–519
Keller AA, McFerran S, Lazareva A, Suh S (2013) Global life cycle releases of engineered nanomaterials. J Nanopart Res 15(6).
Koehle-Divo V, Cossu-Leguille C, Pain-Devin S, Simonin C, Bertrand C, Sohm B, Mouneyrac C, Devin S, Giamberini L (2018) Genotoxicity and physiological effects of CeO2 NPs on a freshwater bivalve (Corbicula fluminea). Aquat Toxicol 198:141–148
Kosak Nee Rohder LA, Brandt T, Sigg L, Behra R (2018) Uptake and effects of cerium(III) and cerium oxide nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat Toxicol 197:41–46
Krishnamoorthy K, Veerapandian M, Zhang LH, Yun K, Kim SJ (2014) Surface chemistry of cerium oxide nanocubes: toxicity against pathogenic bacteria and their mechanistic study. J Ind Eng Chem 20(5):3513–3517
Lee WM, An YJ (2013) Effects of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on green algae under visible, UVA, and UVB irradiations: no evidence of enhanced algal toxicity under UV pre-irradiation. Chemosphere 91(4):536–544
Leung YH, Yung MM, Ng AM, Ma AP, Wong SW, Chan CM, Ng YH, Djurisic AB, Guo M, Wong MT, Leung FC, Chan WK, Leung KM, Lee HK (2015) Toxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles - the effect of nanoparticle properties. J Photochem Photobiol B 145:48–59
Lin D, Ji J, Long Z, Yang K, Wu F (2012) The influence of dissolved and surface-bound humic acid on the toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to Chlorella sp. Water Res 46(14):4477–4487
Liu Y, Chen S, Zhang J, Li X, Gao B (2017) Stimulation effects of ciprofloxacin and sulphamethoxazole in Microcystis aeruginosa and isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation-based screening of antibiotic targets. Mol Ecol 26(2):689–701
Manier N, Bado-Nilles A, Delalain P, Aguerre-Chariol O, Pandard P (2013) Ecotoxicity of non-aged and aged CeO2 nanomaterials towards freshwater microalgae. Environ Pollut 180:63–70
Manier N, Garaud M, Delalain P, Aguerre-Chariol O, Pandard P (2011) Behaviour of ceria nanoparticles in standardized test media – influence on the results of ecotoxicological tests. J Phys Conf Ser 304.
Miroshnikova EP, Kosyan DB, Arizhanov AE, Sizova EA, Kalashnikov VV (2016) Assessment of general toxicity and prooxidant effects of CeO2 and SiO2 nanoparticles on Danio rerio. Agr Biol 51(6):921–928
Montini T, Melchionna M, Monai M, Fornasiero P (2016) Fundamentals and catalytic applications of CeO2-based materials. Chem Rev 116(10):5987–6041
Mukherjee K, Acharya K (2018) Toxicological effect of metal oxide nanoparticles on soil and aquatic habitats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 75(2):175–186
Otto M, Zilliges Y, Kehr JC, Meissner S, Ishida K, Mikkat S, Hagemann M, Kaplan A, Börner T, Dittmann E (2011) The cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin binds to proteins and increases the fitness of Microcystis under oxidative stress conditions. PLoS ONE 6(3).
Paerl HW, Otten TG (2013) Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: causes, consequences, and controls. Microb Ecol 65(4):995–1010
Paerl HW, Xu H, McCarthy MJ, Zhu G, Qin B, Li Y, Gardner WS (2011) Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res 45(5):1973–1983
Park EJ, Choi J, Park YK, Park K (2008) Oxidative stress induced by cerium oxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicology 245(1–2):90–100
Peng G, Martin RM, Dearth SP, Sun X, Boyer GL, Campagna SR, Lin S, Wilhelm SW (2018) Seasonally relevant cool temperatures interact with N chemistry to increase microcystins produced in lab cultures of Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843. Environ Sci Technol 52(7):4127–4136
Rodea-Palomares I, Boltes K, Fernandez-Pinas F, Leganes F, Garcia-Calvo E, Santiago J, Rosal R (2011) Physicochemical characterization and ecotoxicological assessment of CeO2 nanoparticles using two aquatic microorganisms. Toxicol Sci 119(1):135–145
Rodea-Palomares I, Gonzalo S, Santiago-Morales J, Leganes F, Garcia-Calvo E, Rosal R, Fernandez-Pinas F (2012) An insight into the mechanisms of nanoceria toxicity in aquatic photosynthetic organisms. Aquat Toxicol 122–123:133–143
Rogers NJ, Franklin NM, Apte SC, Batley GE, Angel BM, Lead JR, Baalousha M (2010) Physico-chemical behaviour and algal toxicity of nanoparticulate CeO2 in freshwater. Environ Chem 7(1).
Rohder LA, Brandt T, Sigg L, Behra R (2014) Influence of agglomeration of cerium oxide nanoparticles and speciation of cerium(III) on short term effects to the green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat Toxicol 152:121–130
Saison C, Perreault F, Daigle JC, Fortin C, Claverie J, Morin M, Popovic R (2010) Effect of core-shell copper oxide nanoparticles on cell culture morphology and photosynthesis (photosystem II energy distribution) in the green alga Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii. Aquat Toxicol 96(2):109–114
Sendra M, Blasco J, Araújo CVM (2018) Is the cell wall of marine phytoplankton a protective barrier or a nanoparticle interaction site? Toxicological responses of Chlorella autotrophica and Dunaliella salina to Ag and CeO2 nanoparticles. Ecol Indic 95:1053–1067
Sendra M, Moreno-Garrido I, Blasco J, Araujo CVM (2018) Effect of erythromycin and modulating effect of CeO2 NPs on the toxicity exerted by the antibiotic on the microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Environ Pollut 242(Pt A):357–366
Sendra M, Yeste PM, Moreno-Garrido I, Gatica JM, Blasco J (2017) CeO2 NPs, toxic or protective to phytoplankton? Charge of nanoparticles and cell wall as factors which cause changes in cell complexity. Sci Total Environ 590–591:304–315
Suman TY, Radhika Rajasree SR, Kirubagaran R (2015) Evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles toxicity on marine algae Chlorella vulgaris through flow cytometric, cytotoxicity and oxidative stress analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:23–30
Tai P, Zhao Q, Su D, Li P, Stagnitti F (2010) Biological toxicity of lanthanide elements on algae. Chemosphere 80(9):1031–1035
Tang Y, Tian J, Li S, Xue C, Xue Z, Yin D, Yu S (2015) Combined effects of graphene oxide and Cd on the photosynthetic capacity and survival of Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci Total Environ 532:154–161
Wan J, Guo P, Zhang S (2014) Response of the cyanobacterium Microcystis flos-aquae to levofloxacin. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21(5):3858–3865
Wan L, Wu Y, Zhang B, Yang W, Ding H, Zhang W (2020) Effects of moxifloxacin and gatifloxacin stress on growth, photosynthesis, antioxidant responses, and microcystin release in Microcystis aeruginosa. J Hazard Mater 124518.
Wang S, Wang Y, Ma X, Xu Z (2016) Effects of garlic and diallyl trisulfide on the growth, photosynthesis, and alkaline phosphatase activity of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(6):5712–5720
Wang X, Lin Y, Liu D, Xu H, Liu T, Zhao F (2012) Cerium toxicity, uptake and translocation in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. J Rare Earth 30(6):579–585
Wang Y, Li J, LÜ Y, Jin H, Deng S, Zeng Y (2012) Effects of cerium on growth and physiological characteristics of Anabaena flosaquae. J Rare Earth 30(12):1287–1292
Wang Z, Chen Q, Hu L, Wang M (2018) Combined effects of binary antibiotic mixture on growth, microcystin production, and extracellular release of Microcystis aeruginosa: application of response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(1):736–748
Wang Z, Cui F, An Q, Chen M, Wu B, Guan X (2004) Study on influence of pH on the advance of eutrophication in reservoir. Water Wastewater Engineering 30(5):37–41
Wu J, Kong Q, Yang L, Xiao L, Sun C (2009) Effect of the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa on the pH value and the nitrogen transformation in the medium. J Lake Sci 21(1):123–127
Wu Y, Wan L, Zhang W, Ding H, Yang W (2020) Resistance of cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa to erythromycin with multiple exposure. Chemosphere 249:126147
Xie C, Ma Y, Zhang P, Zhang J, Li X, Zheng K, Li A, Wu W, Pang Q, He X, Zhang Z (2021) Elucidating the origin of the toxicity of nano-CeO2 to Chlorella pyrenoidosa: the role of specific surface area and chemical composition. Environ Sci-Nano 8(3).
Zhang M, Wang X, Tao J, Li S, Hao S, Zhu X, Hong Y (2018) PAHs would alter cyanobacterial blooms by affecting the microcystin production and physiological characteristics of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:134–142
Zhang Q, Song Q, Wang C, Zhou C, Lu C, Zhao M (2017) Effects of glufosinate on the growth of and microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa at environmentally relevant concentrations. Sci Total Environ 575:513–518
Zhao G, Wu D, Cao S, Du W, Yin Y, Guo H (2020) Effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on Microcystis aeruginosa growth and microcystin production. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 104(6):834–839
Zheng X, Yuan Y, Li Y, Liu X, Wang X, Fan Z (2021) Polystyrene nanoplastics affect growth and microcystin production of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28(11):13394–13403
Funding
This study was supported by the Department of Ecology and Environment of Jiangsu Province of China (TH2019403) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20161404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Di Wu: formal analysis, writing—original draft. Juanjuan Zhang: analysis, investigation. Wenchao Du: data curation. Ying Yin: conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Hongyan Guo: resources, supervision, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The reported studies did not involve human participants and human data.
Consent for publication
This does not involve any individual’s data.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vitor Vasconcelos.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, D., Zhang, J., Du, W. et al. Toxicity mechanism of cerium oxide nanoparticles on cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and their ecological risks. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 34010–34018 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18090-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18090-1