Abstract
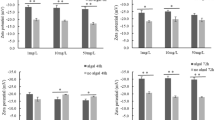
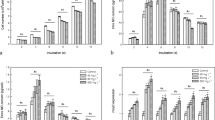
Nanoparticles (NPs) are becoming more widely produced, used, and released into the aquatic environment. In aquatic ecosystems, these NPs affect different populations of photosynthesizing organisms, such as cyanobacteria. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of titanium dioxide (TiO2) NPs (48 mg l−1) combined with low (0.04 mM) and high (9 mM) concentrations of urea and nitrate on Microcystis aeruginosa. Microcystins (MCs) production and release were monitored in the cyanobacterium. The results showed that high urea concentration (9 mM) combined with TiO2 NPs inhibited growth, pigment, and malondialdehyde (MDA) content by 82%, 63%, and 47%, respectively. The treatment also increased the reactive oxygen species (ROS) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) activity by 40.7% and 67.7%, respectively. Similarly, low nitrate (0.04 mM) combined with TiO2 NPs inhibited growth by 40.3% and GST activity by 36.3% but stimulated pigment production and ROS concentration in M. aeruginosa. These responses suggest that high urea combined with TiO2.NPs and high nitrate combined with TiO2 NPs induced oxidative stress in cyanobacteria. The peroxidase (POD) activity of M. aeruginosa decreased by 17.7% with increasing urea concentrations. Our findings suggest that TiO2 NPs combined with changing nutrient (urea and nitrate) concentrations may adversely affect cyanobacterial development and antioxidant defense enzymes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The corresponding author will provide the datasets produced and analyzed during the current work upon request.
References
Arabia S (2010) Differential responses of epiphytic and planktonic toxic cyanobacteria to allelopathic substances of the submerged macrophyte Stratiotes aloides. Int Rev Hydrobiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.200911219
Aruoja V, Dubourguier HC, Kasemets K, Kahru A (2009) Toxicity of nanoparticles of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 to microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Sci Total Environ 407(4):1461–1468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.053
Brêda-Alves F, de Oliveira Fernandes V, Cordeiro-Araújo MK, Chia MA (2021) The combined effect of clethodim (herbicide) and nitrogen variation on allelopathic interactions between Microcystis aeruginosa and Raphidiopsis raciborskii. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(9):11528–11539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11367-x
Bremner JM, Keeney DR (1965) Steam distillation methods for determination of ammonium, nitrate and nitrite. Anal Chimica Acta 32:485–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88973-4
Chaffin JD, Bridgeman TB (2014) Organic and inorganic nitrogen utilization by nitrogen-stressed cyanobacteria during bloom conditions. J Appl Phycol 26(1):299–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-0118-0
Chaudhary I, Singh V (2020) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles and its impact on growth, biomass and yield of agricultural crops under environmental stress: a review. Res J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjnn.2020.1.8
Chen W, Liu HL, Zhang Q, Dai S (2010) Effect of nitrite on growth and Microcystins production of 30 Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. J Appl Phycol 23:665–671
Chen H, Chen J, Guo Y, Wen Y, Liu J, Liu W (2012) Evaluation of the role of the glutathione redox cycle in Cu ( II ) toxicity to green algae by a chiral perturbation approach. Aquat Toxicol 120–121:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.04.011
Chen Q, Wang M, Zhang J, Shi W, Mynett AE, Yan H, Hu L (2019) Physiological effects of nitrate, ammonium, and urea on the growth and microcystins contamination of Microcystis aeruginosa: implication for nitrogen mitigation. Water Res 163:114890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.114890
Cherchi C, Gu AZ (2010) Impact of titanium dioxide nanomaterials on nitrogen fixation rate and intracellular nitrogen storage in Anabaena variabilis. Environ Sci Technol 44(21):8302–8307. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101658p
Cherchi C, Lin Y, Gu AZ (2021) Nano-titanium dioxide exposure impacts nitrogen metabolism pathways in cyanobacteria. Environ Eng Sci 38(6):469–480. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2020.0150
Chia MA, Jankowiak JG, Kramer BJ, Goleski JA, Huang IS, Zimba PV, do Carmo Bittencourt-Oliveira M, Gobler CJ (2018) Succession and toxicity of Microcystis and Anabaena (Dolichospermum) blooms are controlled by nutrient-dependent allelopathic interactions. Harmful Algae 74:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2018.03.002
Clément L, Hurel C, Marmier N (2013) Toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to cladocerans, algae, rotifers and plants—effects of size and crystalline structure. Chemosphere 90(3):1083–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.09.013
Collos Y, Harrison PJ (2014) Acclimation and toxicity of high ammonium concentrations to unicellular algae. Mar Pollut Bull 80(1–2):8–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.01.006
Dai GZ, Shang JL, Qiu BS (2012) Ammonia may play an important role in the succession of cyanobacterial blooms and the distribution of common algal species in shallow freshwater lakes. Glob Change Biol 18(5):1571–1581. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2012.02638.x
Dai R, Wang P, Jia P, Zhang Y, Chu X, Wang Y (2016) A review of factors affecting microcystins production by algae in aquatic environments. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-2003-2
Das P, Metcalfe CD, Xenopoulos MA (2014) Interactive effects of silver nanoparticles and phosphorus on phytoplankton growth in natural waters. Environ Sci Technol 48(8):4573–4580
Dauda S, Chia MA, Bako SP (2017) Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to Chlorella vulgaris beyerinck (beijerinck) 1890 (trebouxiophyceae, chlorophyta) under changing nitrogen conditions. Aquat Toxicol 187:108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.03.020
Dauda S, Gabriel AM, Idris OF, Chia MA (2020) Combined nanoTiO2 and nitrogen effects on phytoplankton: a mesocosm approach. J Appl Phycol 32(5):3123–3132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02187-0
Deng XY, Cheng J, Hu XL, Wang L, Li D, Gao K (2017) Biological effects of TiO2 and CeO2 nanoparticles on the growth, photosynthetic activity, and cellular components of a marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Sci Total Environ 575:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.003
Donald DB, Bogard MJ, Finlay K, Leavitt PR (2011) Comparative effects of urea, ammonium, and nitrate on phytoplankton abundance, community composition, and toxicity in hypereutrophic freshwaters. Limnol Oceanogr 56(3):2161–2175. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2011.56.6.2161
Elser JJ, Andersen T, Baron JS, Bergström AK, Jansson M, Kyle M, Nydick KR, Steger L, Hessen DO (2009) Shifts in lake N: P stoichiometry and nutrient limitation driven by atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Science 326(5954):835–837. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1176199
Erratt KJ, Creed IF, Trick CG (2018) Comparative effects of ammonium, nitrate and urea on growth and photosynthetic efficiency of three bloom-forming cyanobacteria. Freshw Biol 63(7):626–638. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13099
Finlay K, Patoine A, Donald DB, Bogard MJ, Leavitt PR (2010) Experimental evidence that pollution with urea can degrade water quality in phosphorus-rich lakes of the Northern Great Plains. Limnol Oceanogr 55(3):1213–1230. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2010.55.3.1213
Glibert PM, Wilkerson FP, Dugdale RC, Raven JA, Dupont CL, Leavitt PR, Parker AE, Burkholder JM, Kana TM (2016) Pluses and minuses of ammonium and nitrate uptake and assimilation by phytoplankton and implications for productivity and community composition, with emphasis on nitrogen-enriched conditions. Limnol Oceanogr 61(1):165–197. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10203
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hampel JJ, McCarthy MJ, Neudeck M, Bullerjahn GS, McKay RML, Newell SE (2019) Ammonium recycling supports toxic planktothrix blooms in sandusky bay, lake erie: evidence from stable isotope and metatranscriptome data. Harmful Algae 81:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2018.11.011
Harke MJ, Gobler CJ (2013) Global transcriptional responses of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to nitrogen stress, phosphorus stress, and growth on organic matter. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069834
Harke MJ, Davis TW, Watson SB, Gobler CJ (2016) Nutrient-controlled niche differentiation of western lake erie cyanobacterial populations revealed via metatranscriptomic surveys. Environ Sci Technol 50(2):604–615. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03931
Hartmann NB, Von der Kammer F, Hofmann T, Baalousha M, Ottofuelling S, Baun A (2010) Algal testing of titanium dioxide nanoparticles—testing considerations, inhibitory effects and modification of cadmium bioavailability. Toxicology 269(2–3):190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.08.008
Heath L, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch biochem Biophys 125(1):189–198
Hu H (2006) Nitrate and phosphate supplementation to increase toxin production by the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Mar Pollut Bull 52:756–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.11.005
Huang B, Wei ZB, Yang LY, Pan K, Miao AJ (2019) Combined toxicity of silver nanoparticles with hematite or plastic nanoparticles toward two freshwater algae. Environ Sci Technol 53(7):3871–3879. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b07001
Illona V (2008) Aquatic ecotoxicity tests of some nanomaterials. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(9):1942–1947
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1982) Glycolate metabolism of three submersed aquatic angiosperms during ageing. Aquat Botany 12:345–354
Ju-Nam Y, Lead JR (2008) Manufactured nanoparticles: an overview of their chemistry, interactions and potential environmental implications. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.06.042
Keller AA, Wang H, Zhou D, Lenihan HS, Cherr G, Cardinale BJ, Robert M, Ji Z (2010) Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. Environ Sci Technol 44(6):1962–1967
Kulacki KJ, Cardinale BJ (2012) Effects of nano-titanium dioxide on freshwater algal population dynamics. PloSOne. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047130
Li F, Liang Z, Zheng X, Zhao W, Wu M, Wang Z (2015) Toxicity of nano-TiO 2 on algae and the site of reactive oxygen species production. Aquat Toxicol 158:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.10.014
Li J, Zhang J, Huang W, Kong F, Li Y, Xi M, Zheng Z (2016) Comparative bioavailability of ammonium, nitrate, nitrite and urea to typically harmful cyanobacterium microcystis aeruginosa. Mar Pollut Bull 110(1):93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.077
Li R, Li T, Zhou Q (2020) Impact of titanium dioxide (TiO 2) modification on its application to pollution treatment—a review. Catalysts 10(7):804
Liang F, Wen X, Geng Y, Ouyang Z, Luo L, Li Y (2013) Growth rate and biomass productivity of Chlorella as affected by culture depth and cell density in an open circular photobioreactor. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(4):539–544. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1209.09047
Liang X, Cui S, Li H, Abdelhady A, Wang H (2019) Removal effect on stormwater runoff pollution of porous concrete treated with nanometer titanium dioxide. Transp Res Part D 73:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2019.06.001
Ma S, Zhou K, Yang K, Lin D (2014) Hetero-agglomeration of oxide nanoparticles with algal cells: effects of particle type, ionic strength and pH. Environ Sci Technol 49(2):932–939. https://doi.org/10.1021/es504730k
Mahler GJ, Esch MB, Tako E, Southard TL, Archer SD, Glahn RP, Shuler ML (2012) Oral exposure to polystyrene nanoparticles affects iron absorption. Nat Nanotechnol 7:264–271. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2012.3
Melegari SP, Perreault F, Costa RHR, Popovic R, Matias WG (2013) Evaluation of toxicity and oxidative stress induced by copper oxide nanoparticles in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat Toxicol 142:431–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.09.015
Pejić S, Todorović A, Stojiljković V, Kasapović J, Pajović SB (2009) Antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in endometrium of patients with polyps, myoma, hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 7:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-7-149
Peng G, Martin RM, Dearth SP, Sun X, Boyer GL, Campagna SR, Lin S, Wilhelm SW (2018) Seasonally relevant cool temperatures interact with N chemistry to increase microcystins produced in lab cultures of microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843. Environ Sci Technol 52(7):4127–4136. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06532
Perreault F, Bogdan N, Morin M, Claverie J, Popovic R (2012) Interaction of gold nanoglycodendrimers with algal cells (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii) and their effect on physiological processes. Nanotoxicology 6(2):109–120. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2011.562325
Pimentel JSM, Giani A, Pimentel JSM, Giani A (2014) Microcystin production and regulation under nutrient stress conditions in toxic Microcystis Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(18):5836–5843. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01009-14
Piotrowska-Niczyporuk A, Bajguz A, Zambrzycka E, Godlewska-Z̈yłkiewicz B (2012) Phytohormones as regulators of heavy metal biosorption and toxicity in green alga Chlorella vulgaris (Chlorophyceae). Plant Physiol Biochem 52:52–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2011.11.009
Planchon M, Jittawuttipoka T, Cassier-chauvat C, Guyot F, Gelabert A, Benedetti MF, Chauvat F, Spalla O (2013) Exopolysaccharides protect Synechocystis against the deleterious effects of Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in natural and artificial waters. J Colloid Interface Sci 405:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.05.061
Reddy JK, Suga T, Mannaerts GP, Lazarow PB, Subramani S (eds) (1996) Peroxisomes: biology and role in toxicology and disease. Annals of the New York academy of sciences, vol 804. New York Academy of Sciences, New York, pp 1–795
Reynolds CS (2006) Ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ritchie RJ (2006) Consistent sets of spectrophotometric chlorophyll equations for acetone, methanol and ethanol solvents. Photosynth Res 89:27–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-006-9065-9
Sadiq IM, Dalai S, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2011) Ecotoxicity study of titania (TiO2) NPs on two microalgae species: Scenedesmus sp. and Chlorella sp. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 74(5):1180–1187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.03.006
Song G, Gao Y, Wu H, Hou W, Zhang C, Ma H (2012) Physiological effect of anatase TiO2 nanoparticles on Lemna minor. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(9):2147–2152. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.1933
Tang Y, Li S, Qiao J, Wang H, Li L (2013) Synergistic effects of nano-sized titanium dioxide and zinc on the photosynthetic capacity and survival of Anabaena sp. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140714395
Tripathi DK, Gaur S, Singh S, Singh S, Pandey R, Singh VP, Sharma NC, Prasad SM, Dubey NK, Chauhan DK (2016) An overview on manufactured nanoparticles in plants: uptake, translocation, accumulation and phytotoxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.07.030
Turner AD, Dhanji-rapkova M, Neill AO, Coates L, Lewis A, Lewis K (2018) Analysis of microcystins in cyanobacterial blooms from freshwater bodies in England. Toxins 10(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010039
Wagner ND, Quach E, Buscho S, Ricciardelli A, Kannan A, Naung SW, Phillip G, Sheppard B, Ferguson L, Allen A, Sharon C, Duke JR, Taylor RB, Austin BJ, Stovall JK, Haggard BE, Chambliss CK, Brooks BW, Scott JT (2021) Nitrogen form, concentration, and micronutrient availability affect microcystin production in cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 103:102002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2021.102002
Wang Z, Chen Q, Hu L, Wang M (2017) Combined effects of binary antibiotic mixture on growth, microcystin production, and extracellular release of Microcystis aeruginosa: application of response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:736–748
Wiench K, Wohlleben W, Hisgen V, Radke K, Salinas E, Zok S, Landsiedel R (2009) Chemosphere acute and chronic effects of nano- and non-nano-scale TiO 2 and ZnO particles on mobility and reproduction of the freshwater invertebrate Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 76(10):1356–1365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.06.025
Wu X, Yan Y, Wang P, Ni L, Gao J, Dai R (2015) Bioresource Technology Effect of urea on growth and Microcystins production of Microcystis aeruginosa. Biores Technol 181:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.035
Wu D, Yang S, Du W, Yin Y, Zhang J, Guo H (2019) Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on Microcystis aeruginosa and Microcystins production and release. J Hazard Mater 377:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.013
Xia B, Chen B, Sun X, Qu K, Ma F, Du M (2014) Science of the Total Environment Interaction of TiO 2 nanoparticles with the marine microalga nitzschia closterium: growth inhibition, oxidative stress and internalization. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.11.066
Xiao B, Zhang Y, Wang X, Chen M, Sun B (2019) Occurrence and trophic transfer of nanoparticulate Ag and Ti in the natural aquatic food web of Taihu Lake China. Environ Sci Nano. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en00797k
Xu K, Li Z, Juneau P, Xiao F, Lian Y, Zhang W, Shu L, Jiang H, Zhang K, Wang C, Wang S, Yan Q, He Z (2021) Toxic and protective mechanisms of cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. in response to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environl Pollut 274:116508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116508
Zhang M, Wang X, Tao J, Li S, Hao S, Zhu X, Hong Y (2018a) PAHs would alter cyanobacterial blooms by affecting the microcystin production and physiological characteristics of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.052
Zhang Q, Qu Q, Lu T, Ke M, Zhu Y, Zhang M, Zhang Z, Du B, Pan X, Sun L, Qian H (2018b) The combined toxicity effect of nanoplastics and glyphosate on microcystis aeruginosa growth. Environ Pollut 243:1106–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.073
Zhang J, Jiang L, Wu D, Yin Y, Guo H (2020) Effects of environmental factors on the growth and microcystin production of microcystis aeruginosa under TiO2 nanoparticles stress. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139443
Zheng L, Hong F, Lu S, Liu C (2005) Effect of nano-TiO2 on strength of naturally aged seeds and growth of spinach. Biol Trace Elem Res 104:83–91
Funding
No specific grant was provided for this research by funding organizations in the public, private, or nonprofit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SSA collected data and wrote the main manuscript text, and MAC and SD performed data analysis and prepared all the Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4. WNY, MAC, WSJ, and JH supervised the project and revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no known competing financial interests or personal ties that could be perceived as having influenced the work described in this study.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Samuel, S.A., Chia, M.A., Yusufu, W.N. et al. Nitrogen forms and concentration influence the impact of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the biomass and antioxidant enzyme activities of Microcystis aeruginosa. Arch Microbiol 205, 177 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03500-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03500-4