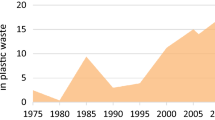
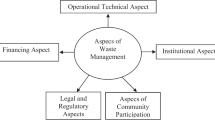
Abstract
The growing interest of policy-makers, environmental stakeholders, and academics in rural domestic waste treatment has made it a recent focus of research in the field of rural human settlements. Many studies have been conducted to understand the related factors; however, their results are inconsistent. Therefore, different from previous studies, the study systematically analyzed and summarized empirical studies on rural domestic waste treatment and explored the key factors that fostered and impeded it. It also examined the reasons for differences in research level and trends in key factors over time. A random-effects meta-analysis of 24 studies revealed that education, political status, perceived value, behavioral attitude, subjective norm, garbage collection facilities and services, environmental knowledge and propaganda, and government policy and regulation had a significant positive correlation with rural domestic waste treatment; perceived value had the highest impact, followed by behavioral attitude. All of the variables had significant heterogeneity. Some of the heterogeneity can be explained by differences in research methods, sample size, and variable measurement methods. An increasing trend was observed in the effects of perceived value, behavioral attitude, and subjective norm. Finally, based on these results, the study provided suggestions on policy and academic aspects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajzen I (1991) The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 50:172–211
Atinkut HB, Yan TW, Arega Y, Raza MH (2020) Farmers’ willingness-to-pay for eco-friendly agricultural waste management in Ethiopia: a contingent valuation. J Cleaner Product 261:121211
Abrahamse W, Steg L (2013) Social influence approaches to encourage resource conservation: a meta-analysis. Global Environ Change 23:1773–1785
Bax L, Yu LM, Ikeda N, Moons KGM (2007) A systematic comparison of software dedicated to meta-analysis of causal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 7(40):1–9
Bel G, Fageda X, Warner ME (2010) Is private production of public services cheaper than public production? A meta-regression analysis of solid waste and water services. J Policy Analysis Manag 29(03):553–577
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT (2010) A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res Synthesis Methods 1(02):97–111
Chae Y, An YJ (2018) Current research trends on plastic pollution and ecological impacts on the soil ecosystem: a review. Environ Pollut 240:387–395
Chen H, Manning AK, Dupuis J (2012) A method of moments estimator for random effect multivariate meta-analysis. Biometrics 68(04):1278–1284
Dang YF (2019) Research on the influence of social capitals on behavior of peasants’ protecting environment - based on the national survey data from 3844 farmers in 263 villages. J Shanxi Agric Univ(Social Science Edition) 18(06):62–69 (in Chinese)
Duval S, Tweedie R (2000) Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56(2):455–463
Field AP, Gillett R (2010) How to do a meta-analysis. British J Mathematical Stat Psychol 63(03):665–694
Geiger JL, Steg L, Werff EVD, Unal AB (2019) A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. J Environ Psychol 64:78–97
Gong WJ (2020) Changes in urban domestic waste management policies-Based on the analysis of urban domestic waste treatment policies from 1949 to 2019. Study Exploration 02:28–35 (in Chinese)
Gu HB, Dang GY (2019) Analysis of farmers’ willingness to pay for domestic waste treatment and its influencing factors:a case study of Yaodu District, Linfen City. Shanxi Province. Hubei Agric Sci 58(09):182–187 (in Chinese)
Guagnano GA, Stern PC, Dietz T (1995) Influences on Attitude-Behavior relationships: a natural experiment with curbside recycling. Environ Behav 27:699–718
Han ZY, Zeng D, Li QB, Cheng C, Shi GZ, Mou ZS (2019) Public willingness to pay and participate in domestic waste management in rural areas of China. Resour Conserv Recycl 140:166–174
He HQ, Chen K (2006) Methods for measuring heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Chinese Journal of Health. Statistics (06):486-487+490 (in Chinese)
Huang KX, Wang JX, Bai JF, Qiu HG (2013) Domestic solid waste discharge: volume, structure and determinants in rural China. Chinese Acad Sci 5(04):512–525
Hunter JE (2006) Methods of meta-analysis. BMS: Bull Sociol Methodol (91)
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21(11):1539–1558
Jackson D, White IR, Riley RD (2012) Quantifying the impact of between-study heterogeneity in multivariate meta-analyses. Stat Med 31(29):3805–3820
Jia YJ, Zhao MJ (2019) The influence of environmental concern and institutional trust on farmers’ willingness to participate in rural domestic waste treatment. Resour Sci 41(08):1500–1512 (in Chinese)
Jia YJ, Zhao MJ, Xia XL, Yao LY (2019) Mode of classified treatment of rural domestic wastes and suggestions. Resour Sci 41(02):338–351 (in Chinese)
Jiang LN, Zhao X (2020) Classified treatment management of rural domestic waste: model comparison and policy enlightenment based on a case study of four ecological conservation areas in Beijing. China Rural Survey 02:16–33 (in Chinese)
Kamarehie B, Jafari A, Ghaderpoori M, Azimi F, Faridan M, Sharafi K, Ahmadi F, Karami MA (2020) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of municipal solid waste in Iran for implementation of best waste management practice : a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:37514–37526
Li DQ, Hou LL, Min S, Huang JK (2021) The effects of rural living environment improvement programs: evidence from a household survey in 7 provinces of China. Manag World 37(10):182-195+249-251 (in Chinese)
Li GC (2015) Introduction to cumulative meta-analysis and application of CMA software. J Evidence-Based Med 15(04):247–251 (in Chinese)
Li H, Li SP, Nan L, Li XQ (2018) A Meta-analysis of farmers’ environment-friendly pesticide application behavior in China. Resour Sci 40(01):74–88 (in Chinese)
Li XR, Bi F, Han ZD, Qin Y, Wang HS, Wu WX (2019) Garbage source classification performance, impact factor, and management strategy in rural areas of China: a case study in Hangzhou. Waste Manag 89:313–321
Liang ZF, Xiao XC, Ni QP (2014) Analysis of the influential factors of farmers’ willingness to pay for rural household waste disposal in Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ Pollut Control 36(09):100-105+110 (in Chinese)
Liu R, Wang Y (2019) Farmers’ household waste disposal behavior and its influence factors in developing countries: evidence from Jiangsu, China. Appl Ecol Environ Res 17(4):8737–8748
Macaskill P, Walter SD, Irwig L (2001) A comparison of methods to detect publication bias in meta-analysis. Stat Med 20(4):641–654
Michie S, Abraham C, Whittington C (2009) Effective techniques in healthy eating and physical activity interventions: a meta-regression. Health Psychol 28(06):690–701
Ma Y, Wang HL, Kong R (2020) The effect of policy instruments on rural households’ solid waste separation behavior and the mediation of perceived value using SEM. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:19398–19409
Meng XY (2019) Analysis on residents’ behavior of domestic solid waste source separation based on structural equation. Resour Sci 41(06):1111–1119 (in Chinese)
Ostrom E (2010) Background on the Institutional Analysis and Development Framework. Policy Stud J 39(01):7–27
Pigott TD (2006) Methods of meta-analysis: correcting error and bias in research findings. Evaluation and Program Planning (3)
Peng YC, Gu LL (2014) Meta-regression analysis in economics. Economic Trends 02:126–131
Qiu CM, Yu PH, Cao SW (2019) The willingness to pay and determinants of rural residents for household garbage management. J Hunan Univ Finance Econ 35(01):49–57 (in Chinese)
Schanes K, Dobernig K, Gozet B (2018) Food waste matters-a systematic review of household food waste practices and their policy implications. J Cleaner Production 182:978–991
Shi CY (2018) A study on household waste governance in Metropolitan Community: a case study of Meilong Sancun Community. J East China Univ Sci Technol (Social Sci Edition) (04):68–75+92 (in Chinese)
Spigolon LMG, Giannott M, Larocca AP, Russo MAT, Souza ND (2018) Landfill siting based on optimisation, multiple decision analysis, and geographic information system analyses. Waste Manag Res 36(07):606–615
Stanley TD, Doucouliagos C, Jarrell SB (2006) Meta-regression analysis as the socio-economics of economics research. J Socio-Econ (1)
Stern PC (2000) Towards a coherent theory of environmentally significant behavior. J Soc Issues 56:407–424
Schwartz SH, Howard JA (1981) A normative decision-making model of altruism
Taghipour H, Amjad Z, Aslani H, Armanfar F, Dehghanzadeh R (2016) Characterizing and quantifying solid waste of rural communities. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 18(04):790–797
Tang L, Luo XF, Zhang JB (2019) Social supervision, group identity and farmers’ domestic waste centralized disposal behavior: an analysis based on mediation effect and regulation effect of the face concept. China Rural Survey 02:18–33 (in Chinese)
Tang X, Zhang Y, Fang XM (2018) Cost and willingness to pay for the rural household waste collection: based on a survey of five provinces. J China Agric Univ 23(08):204–211 (in Chinese)
Varotto A, Spagnolli A (2017) Psychological strategies to promote household recycling. A systematic review with meta-analysis of validated field interventions. J Environ Psychol 51:168–188
Wang AQ, Gao QF, Shi YJ, Liu CF, Zhang LX (2016) The situation of rural solid waste management and determination: empirical analysis based on field surveys of 101 villages in 5 provinces. Issues in Agricultural Economy (04): 30-38+111 (in Chinese)
Wang JM (2013) The influence of resource conservation consciousness on resource conservation behavior: a model of interaction effect and moderation effect in the context of Chinese culture. Manag World (08):77–90+100 (in Chinese)
Wang SW, Wen XN, Qin L (2014) Construction of public participation in management and government regulation interactive model of urban living garbage 24(04):142-148 (in Chinese)
Wu R, Shi GQ (2019) Research on the process and mechanism of rural environmental cooperative governance-based on the case of S village. Rural Econ 03:113–121 (in Chinese)
Winterton R, Warburton J, Keating N, Petersen M, Berg T, Wilson J (2016) Understanding the influence of community characteristics on wellness for rural older adults: a meta-synthesis. J Rural Stud 45:320–327
Xu L, Ling ML, Lu YJ (2017) Key determinants of urban household solid waste recycling behavior. Journal of. Public Manag 14(01):142–153+160 (in Chinese)
Xu ZW, Yao SB, Miao SS (2016) The paradox between willingness and behavior: factors influencing the house-holds’ willingness to pay and real payment behavior on rural domestic garbage centralized treatment. J Arid Land Resour Environ 30(02):1–6 (in Chinese)
Yang Y, Lan X, Jones TE (2019) Tourism-enhancing effect of World Heritage Sites: Panacea or placebo? A meta-analysis. Annals Tourism Res 75:29–41
Zhao JW, Zhao R, He YF, Wang S, An QQ (2014) Rural domestic garbage processing pattern based on the principle of 3R. China Population, Resour Environ 24(S2):263–266 (in Chinese)
Zheng LY, Liu Q, Qian WR (2018) An empirical analysis of farmers’ willingness to pay for household waste management: Evidence from the rural areas of Shandong, Anhui and Chongqing. Res Agric Moderniz 39(05):828–835 (in Chinese)
Zheng LY, Yang F, Hong MY (2019) The willingness to pay and for rural household domestic waste governance its determinants: empirical evidence from three provinces in China. J Arid Land Resour Environ 33(05):14–18 (in Chinese)
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
The research was financially supported by the Shaanxi Provincial Social Science fund, grant numbers 2019D012. We appreciate all the participants for their cooperation and completion of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Donghui Zheng: formal analysis and writing. Jing Shen, Rong Li, Bei Jian, Jihong Zeng, and Yongliang Mao: literature selection and data selection. Pradipta Halder: review and editing. Mei Qu and Xiaoning Zhang: conceptualization and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This manuscript has not been published or presented elsewhere in part or in entirety and is not under consideration by another journal. The study design was approved by the appropriate ethics review board. We have read and understood your journal’s policies, and we believe that neither the manuscript nor the study violates any of these.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(XLSX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, D., Shen, J., Li, R. et al. Understanding the key factors determining rural domestic waste treatment behavior in China: a meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 11076–11090 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17999-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17999-x