Abstract
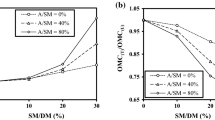
Metakaolin, fly ash, and mostly granulated blast furnace slag (GBFS) are traditionally used in the production of geopolymer. This study, adding to the knowledge base on geopolymer concretes as an alternative to cement mixtures, explored an experimental approach that investigates the use of ceramic dust (CD) and rice husk ash (RHA) with high SiO content instead of GBFS in the production of geopolymers. For this purpose, instead of GBFS, RHA at proportions of 0, 5%, 10%, and 15% and CD at proportions of 0, 10%, 20%, and 30% were used in the production of geopolymer concrete. In addition, groups were determined with a Taguchi L16 matrix with NaOH (an important material in geopolymer production) at 12, 14, 16, and 18 molality. Varying combinations of flow diameter, density, porosity, and water absorption rate were used, and their performance under high temperatures in terms of compressive strength was evaluated. The use of RHA in geopolymer concretes produced using CD and RHA had a negative effect on the flow and water absorption rates. However, the use of CD had a positive effect, and geopolymer concretes with high density and porosity were obtained. In addition, it was determined that strengths > 70 MPa could only be obtained if 5–20% CD were used at 14–16 molality. The resistance of geopolymer concretes to high temperatures is lower than normal concretes. However, when comparing RHA and CD, it was determined that the use of CD would be more effective on geopolymer materials, and special measures should be taken at temperatures > 450 °C.
Graphıcal abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abbasi SM, Ahmadi H, Khalaj G, Ghasemi B (2016) Microstructure and mechanical properties of a metakaolinite-based geopolymer nanocomposite reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Ceram Int 42:15171–15176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.080
Abdel-ghani NT, Elsayed HA, Abdelmoied S (2018) Geopolymer synthesis by the alkali-activation of blastfurnace steel slag and its fire-resistance. HBRC J 14:159–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbrcj.2016.06.001
Abdullah, Hussin, Zakaria M (2006) Pofa : a potential partial cement replacement material in aerated concrete. 6th Asia Pacific Struct Eng Constr (APSEC 2006) 5–6
Adesanya DA, Raheem AA (2009) Development of corn cob ash blended cement. Constr Build Mater 23:347–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.11.013
Akbar A, Farooq F, Shafique M et al (2021) Sugarcane bagasse ash-based engineered geopolymer mortar incorporating propylene fibers. J Build Eng 33:101492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101492
Albidah AS (2021) Effect of partial replacement of geopolymer binder materials on the fresh and mechanical properties: a review. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.127
Alnkaa A, Yaprak H, Memis S, Kaplan G (2018) Effect of different cure conditions on the shrinkage of geopolymer mortar. Int J Eng Res Dev 14:51–55
Alsubari B, Shafigh P, Jumaat MZ (2016) Utilization of high-volume treated palm oil fuel ash to produce sustainable self-compacting concrete. J Clean Prod 137:982–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.07.133
Altoubat S, Badran D, Junaid MT, Leblouba M (2016) Restrained shrinkage behavior of self-compacting concrete containing ground-granulated blast-furnace slag. Constr Build Mater 129:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.10.115
Ambedkar B, Alex J, Dhanalakshmi J (2017) Enhancement of mechanical properties and durability of the cement concrete by RHA as cement replacement: experiments and modeling. Constr Build Mater 148:167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.022
Ameri F, Shoaei P, Alireza S, Behforouz B (2019) Geopolymers vs. alkali-activated materials ( AAMs ): a comparative study on durability, microstructure, and resistance to elevated temperatures of lightweight mortars. Constr Build Mater 222:49–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.079
American Concrete Institute Building Code (2014) 318-14: Building code requirements for structural concrete and commentary
Amran M, Debbarma S, Ozbakkaloglu T (2021) Fly ash-based eco-friendly geopolymer concrete : a critical review of the long-term durability properties. Constr Build Mater 270:121857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121857
Annakoa MAI, Memis S, Kaplan G, Yaprak H (2019) Effect of Adding glass powder in geopolymer concrete. In: International Congress on Engineering and Life Science, ICELIS. pp 480–484
Arnold MC, de Vargas AS, Bianchini L (2017) Study of electric-arc furnace dust (EAFD) in fly ash and rice husk ash-based geopolymers. Adv Powder Technol 28:2023–2034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.05.007
Assi LN, Eddie Deaver E, Ziehl P (2018) Effect of source and particle size distribution on the mechanical and microstructural properties of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Constr Build Mater 167:372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.01.193
(2004) ASTM C1585–04, Standard Test method for measurement of rate of absorption of water by hydraulic-cement concretes,
ASTM C 136 / C136M-19 (2014) Standard test method for sieve analysis of fine and coarse aggregates. ASTM Int
ASTM C1437–20 (2020) Standard test method for flow of hydraulic cement mortar. ASTM Int
ASTM C642 (1997) Standard Test method for density , absorption , and voids in hardened concrete 1. 1–3
(2017) ASTM E2748–12a, Standard Guide for fire-resistance experiments,
ASTM E831 (2014) Standard test method for linear thermal expansion of solid materials by thermomechanical analysis,
Bagheri A, Nazari A (2014) Compressive strength of high strength class C fly ash-based geopolymers with reactive granulated blast furnace slag aggregates designed by Taguchi method. Mater Des 54:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.035
Bernal SA, Rodríguez ED, de Gutiérrez R et al (2011) Mechanical and thermal characterisation of geopolymers based on silicate-activated metakaolin/slag blends. J Mater Sci 46:5477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5490-z
Cannio M, Billong N (2017) Substitution of sodium silicate with rice husk ash-NaOH solution in metakaolin based geopolymer cement concerning reduction in global warming. J Clean Prod 142:3050–3060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.164
Charkhtab S, Madandoust R, Jamshidi M, Nikbin IM (2021) Mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete with crumb rubber and steel fiber under ambient and sulfuric acid conditions. Constr Build Mater 281:122571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122571
Cheah CB, Ramli M (2011) The implementation of wood waste ash as a partial cement replacement material in the production of structural grade concrete and mortar: an overview. Resour Conserv Recycl 55:669–685
Corinaldesi V, Fava G, Ruello ML (2010) Paper mill sludge ash as supplementary cementitious material. In: 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies. American Society of Civil Engineers, pp 85–94
Cristina M, De VAS, Bianchini L (2017) Study of electric-arc furnace dust ( EAFD ) in fly ash and rice husk ash-based geopolymers. Adv Powder Technol 28:2023–2034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.05.007
Dadsetan S, Siad H, Lachemi M, Sahmaran M (2021) Evaluation of the tridymite formation as a technique for enhancing geopolymer binders based on glass waste. J Clean Prod 278:123983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123983
Darsanasiri AGND, Matalkah F, Ramli S et al (2018) Ternary alkali aluminosilicate cement based on rice husk ash, slag and coal fly ash. J Build Eng 19:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2018.04.020
Dave SV, Bhogayata A (2020) The strength oriented mix design for geopolymer concrete using Taguchi method and Indian concrete mix design code. Constr Build Mater 262:120853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120853
Deepika S, Anand G, Bahurudeen A, Santhanam M (2017) Construction products with sugarcane bagasse ash binder. J Mater Civ Eng 29:04017189. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0001999
El-Dieb AS, Kanaan DM (2018) Ceramic waste powder an alternative cement replacement – characterization and evaluation. Sustain Mater Technol 17:e00063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2018.e00063
El-Gamal SMA, El-Hosiny FI, Amin MS, Sayed DG (2017) Ceramic waste as an efficient material for enhancing the fire resistance and mechanical properties of hardened Portland cement pastes. Constr Build Mater 154:1062–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.040
Elyamany HE, Abd Elmoaty AEM, Elshaboury AM (2018) Setting time and 7-day strength of geopolymer mortar with various binders. Constr Build Mater 187:974–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.025
BS EN 196–1 (2005) British standard methods of testing cement —. 3:
(2016) TS EN 196–1. Methods of testing cement - Part 1: Determination of strength. 35
(2020) TS EN 1015–11; Methods of test for mortar for masonry - Part 11: determination of flexural and compressive strength of hardened mortar. 18
Ganesan K, Rajagopal K, Thangavel K (2007) Evaluation of bagasse ash as supplementary cementitious material. Cem Concr Compos 29:515–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2007.03.001
Ghafoor MT, Khan QS, Qazi AU et al (2021) Influence of alkaline activators on the mechanical properties of fly ash based geopolymer concrete cured at ambient temperature. Constr Build Mater 273:121752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121752
Gielen D, Bennaceur K, Kerr T, et al (2007) IEA, Tracking ındustrial energy efficiency and co2 emissions
Görhan G, Kürklü G (2014) The influence of the NaOH solution on the properties of the fly ash-based geopolymer mortar cured at different temperatures. Compos Part B Eng 58:371–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.10.082
Habert G, D’Espinose De Lacaillerie JB, Roussel N (2011) An environmental evaluation of geopolymer based concrete production: reviewing current research trends. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.03.012
Hadi MNS, Farhan NA, Sheikh MN (2017) Design of geopolymer concrete with GGBFS at ambient curing condition using Taguchi method. Constr Build Mater 140:424–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.131
Heath A, Paine K, Mcmanus M (2014) Minimising the global warming potential of clay based geopolymers. J Clean Prod 78:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.04.046
Hu M, Zhu X, Long F (2009) Alkali-activated fly ash-based geopolymers with zeolite or bentonite as additives. Cem Concr Compos. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2009.07.006
Huseien GF, Sam ARM, Mirza J et al (2018) Waste ceramic powder incorporated alkali activated mortars exposed to elevated temperatures: performance evaluation. Constr Build Mater 187:307–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.226
Hwang C, Huynh T (2015) Effect of alkali-activator and rice husk ash content on strength development of fly ash and residual rice husk ash-based geopolymers. Constr Build Mater 101:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.10.025
IEA (2020) Cement, IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/cement
Jithendra C, Elavenil S (2020) Influences of parameters on slump flow and compressive strength properties of aluminosilicate based flowable geopolymer concrete using Taguchi method. SILICON 12:595–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00166-w
Kamseu E, Rizzuti A, Leonelli C, Perera D (2010) Enhanced thermal stability in K 2 O-metakaolin-based geopolymer concretes by Al 2 O 3 and SiO 2 fillers addition. 1715–1724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4108-1
Kamseu E, Beleuk à Moungam LM, Cannio M, et al (2017) Substitution of sodium silicate with rice husk ash-NaOH solution in metakaolin based geopolymer cement concerning reduction in global warming. J Clean Prod 142:3050–3060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.164
Kaplan G, Yaprak H, Memiş S, Alnkaa A (2019) Artificial neural network estimation of the effect of varying curing conditions and cement type on hardened concrete properties. Buildings 9:. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9010010
Kaur K, Singh J, Kaur M (2018) Compressive strength of rice husk ash based geopolymer: The effect of alkaline activator. Constr Build Mater 169:188–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.02.200
Khalaj G, Hassani SES, Khezrloo A, Haratifar EAD (2014) Split tensile strength of OPC-based geopolymers: application of doE method in evaluating the effect of production parameters and their optimum condition. Ceram Int 40:10945–10952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.03.094
Kishore K, Gupta N (2021) Materials today : proceedings mechanical characterization and assessment of composite geopolymer concrete. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.319
Komnitsas KA (2011) Potential of geopolymer technology towards green buildings and sustainable cities. Procedia Eng 21:1023–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.2108
Kumar M, Kumar S, Singh NB (2019) Influence of some additives on the properties of fly ash based geopolymer cement mortars. SN Appl Sci 1:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0506-4
Liang X, Wu C, Su Y, et al (2018) Development of ultra-high performance concrete with high fire resistance. Constr Build Mater 400–412
Masi G, Rickard WDA, Vickers L et al (2014) A comparison between different foaming methods for the synthesis of light weight geopolymers. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.05.108
Mayhoub OA, Nasr EAR, Ali Y, Kohail M (2020) Properties of slag based geopolymer reactive powder concrete. Ain Shams Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.08.013
Memis S, Kaplan G, Yildizel SA (2017a) Investigation of usability potential geopolimer concrete at animal barns. Turkish J Agric - Food Sci Technol 5:1365–1370
Memis S, Sahin S, Sirin U (2017b) Some properties of prefabricated building materials produced from ground diatomite and hydrophone clay. Pamukkale Univ J Eng Sci 23:245–249. https://doi.org/10.5505/pajes.2016.34467
Memis S, Kaplan G, Yaprak H, et al (2018) Some durability properties of alkali activated materials (AAM) produced with ceramic powder and micro calcite. Ceram - Silikaty 62:342–354. https://doi.org/10.13168/cs.2018.0030
Nath P, Sarker PK (2017) Flexural strength and elastic modulus of ambient-cured blended low-calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete. Constr Build Mater 130:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.11.034
Nazari A, Sanjayan JG (2015) Hybrid effects of alumina and silica nanoparticles on water absorption of geopolymers: application of Taguchi approach. Meas J Int Meas Confed 60:240–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2014.10.004
Nimwinya E, Arjharn W, Horpibulsuk S et al (2016) A sustainable calcined water treatment sludge and rice husk ash geopolymer. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.060
Nuaklong P, Jongvivatsakul P, Pothisiri T et al (2020) Influence of rice husk ash on mechanical properties and fire resistance of recycled aggregate high-calcium fly ash geopolymer concrete. J Clean Prod 252:119797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119797
Nuruddin MFB, Bayuji R (2009) Optimum Mix proportioning of mirha foamed concrete using taguchi ’ s approach. Apsec-Eacef 694–700
Nuruddin MF, Azmee NM, Yung CK (2014) Effect of fire flame exposure on ductile self-compacting concrete (DSCC) blended with MIRHA and fly ash. Constr Build Mater 50:388–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.09.038
Olivia M, Nikraz H (2012) Properties of fly ash geopolymer concrete designed by Taguchi method. Mater Des 36:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.10.036
Omer SA, Demirboga R, Khushefati WH (2015) Relationship between compressive strength and UPV of GGBFS based geopolymer mortars exposed to elevated temperatures. Constr Build Mater 94:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.07.006
Onoue K, Iwamoto T, Sagawa Y (2019) Optimization of the design parameters of fly ash-based geopolymer using the dynamic approach of the Taguchi method. Constr Build Mater 219:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.05.177
Perera DS, Vance ER, Finnie KS, et al (2006) Disposition of water in metakaolinite based geopolymers. In: Ceramic Transactions
Rajamane NP, Nataraja MC, Lakshmanan N (2011) An introduction to geopolymer concrete. Indian Concr J 85:25–28
Rashad AM (2013) A comprehensive overview about the influence of different additives on the properties of alkali-activated slag - A guide for civil engineer. Constr Build Mater 47:29–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.04.011
Riahi S, Nazari A, Zaarei D et al (2012) Compressive strength of ash-based geopolymers at early ages designed by Taguchi method. Mater Des 37:443–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.01.030
Rodier L, Bilba K, Onésippe C, Arsène MA (2017) Study of pozzolanic activity of bamboo stem ashes for use as partial replacement of cement. Mater Struct Constr 50:. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-016-0958-6
Roy RK (1990) A Primer on the Taguchi Method. Society of Manufacturing Engineers
Şahin S, Kocaman B, Örüng I, Memiş S (2006) Replacing cattle manure ash as cement into concrete. J Appl Sci 6:. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2006.2840.2842
Sanjayan JG, Nazari A, Pouraliakbar H (2015) FEA modelling of fracture toughness of steel fibre-reinforced geopolymer composites. Mater Des 76:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.03.029
Sarkar M, Dana K (2021) Partial replacement of metakaolin with red ceramic waste in geopolymer. Ceram Int 47:3473–3483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.191
Shoaei P, Musaeei HR, Mirlohi F, et al (2019) Waste ceramic powder-based geopolymer mortars: Effect of curing temperature and alkaline solution-to-binder ratio. Construction and Building Materials 227:116686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116686
Siyal AA, Azizli KA, Man Z, Ullah H (2016) Effects of Parameters on the setting time of fly ash based geopolymers using Taguchi method. Procedia Eng 148:302–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.624
Sua-Iam G, Makul N (2013) Use of increasing amounts of bagasse ash waste to produce self-compacting concrete by adding limestone powder waste. J Clean Prod 57:308–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.06.009
Suhendro B (2014) Toward green concrete for better sustainable environment. Procedia Eng 95:305–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.190
Suksiripattanapong C, Kua TA, Arulrajah A et al (2017) Strength and microstructure properties of spent coffee grounds stabilized with rice husk ash and slag geopolymers. Constr Build Mater 146:312–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.103
Tahwia (2017) Performance of ultra-high performance fiber reinforced concrete at high temperatures. Int J Eng Innov Technol 1–7
Temuujin J, Rickard W, Lee M, Van RA (2011) Preparation and thermal properties of fi re resistant metakaolin-based geopolymer-type coatings. J Non Cryst Solids 357:1399–1404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2010.09.063
Thomas BS, Kumar S, Arel HS (2017) Sustainable concrete containing palm oil fuel ash as a supplementary cementitious material – a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 80:550–561
Vald J, Rodrigue C, Giogetti J, et al (2021) Evaluation of performances of volcanic-ash-laterite based blended geopolymer concretes : mechanical properties and durability. 34:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101935
Villaquirán-Caicedo MA, de Gutiérrez RM (2018) Synthesis of ceramic materials from ecofriendly geopolymer precursors. Mater Lett 230:300–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.07.128
Yang T, Wu Q, Zhu H, Zhang Z (2017) Geopolymer with improved thermal stability by incorporating high-magnesium nickel slag. Constr Build Mater 155:475–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.081
Yaprak H, Memis S, Kaplan G (2017) Effect of ındustrial wastes as replacement of fine aggregate on properties of concrete. J Sci Eng Res 4:228–235
Yaprak H, Alnkaa A, Memis S, Kaplan G (2018a) The effects of steam curing time on the geopolymer mortar. In: International Congress on Engineering and Life Science, ICELIS. pp 13–16
Yaprak H, Memis S, Kaplan G, et al (2018b) Effects on compressive strenght of accelerated curing methods in alkali activated mortars. Int J Sci Technol Res 4:
Yaprak H, Alnkaa A, Memis S, Kaplan G (2019) Effects of different curing conditions on the properties of geopolymeric mortar. MOJ Civ Eng 5:45–50. https://doi.org/10.15406/mojce.2019.05.00148
Yasaswini K, Rao AV (2020) Materials today : proceedings behaviour of geopolymer concrete at elevated temperature. Mater Today Proc 33:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.833
Yildizay H, Gören R, Yanik G (2014) Use ofalunite as a starting materia l of geopolymer. AKU J Sci Eng 14:219–224
Zareei SA, Ameri F, Shoaei P, Bahrami N (2019) Recycled ceramic waste high strength concrete containing wollastonite particles and micro-silica: A comprehensive experimental study. Constr Build Mater 201:11–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.161
Zawrah MF, Sawan SEA, Khattab RM, Abdel-shafi AA (2020) Effect of nano sand on the properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer : study on its low rate sintering. Constr Build Mater 246:118486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118486
Zhao R, Yuan Y, Cheng Z et al (2019) Freeze-thaw resistance of Class F fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Constr Build Mater 222:474–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.166
Zhou S, Chen X (2012) Pozzolanic activity of feedlot biomass ( cattle manure ) ash. Constr Build Mater 28:493–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.09.003
Zhou S, Tang W, Xu P, Chen X (2015) Effect of cattle manure ash on strength, workability and water permeability of concrete. Constr Build Mater 84:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.03.062
Zhou W, Yan C, Duan P et al (2016) A comparative study of high- and low-Al2O3fly ash based-geopolymers: the role of mix proportion factors and curing temperature. Mater Des. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.01.084
Zhu W, Rao XH, Liu Y, Yang EH (2018) Lightweight aerated metakaolin-based geopolymer incorporating municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash as gas-forming agent. J Clean Prod 177:775–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.267
Živica V, Palou MT, Križma M (2015) Geopolymer cements and their properties: a review. Build Res J 61:85–100. https://doi.org/10.2478/brj-2014-0007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Selçuk Memiş contributed to writing of article and literature review. Mohamed Ahmed Mohamed BILAL performed the experiments and anayzed the results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: by Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Memiş, S., Bılal, M.A.M. Taguchi optimization of geopolymer concrete produced with rice husk ash and ceramic dust. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 15876–15895 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16869-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16869-w