Abstract
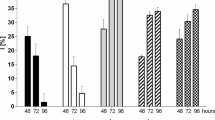
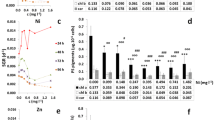
One of the most common pollutants in natural ecosystems is heavy metals. Algae are sensitive to the action of heavy metals. This allows to use algae to assess the toxicity of heavy metals, bioindication, and during phycoremediation. This study examines the effect of different Zn and Mn concentrations (1.0, 5.0, 25.0, 50.0, 500.0, 1000.0 mg L−1) on green algae Bracteacoccus minor and Lobosphaera incisa in a chronic bioassay. The results of this study showed that the toxic effect of Zn and Mn on B. minor and L. incisa begins to manifest itself at the lowest of the studied metal concentrations—1 mg L−1. The critical concentration of Zn, which leads to the complete death of B. minor and L. incisa, is 50.0 and 500.0 mg L−1, and Mn is 1000.0 mg L−1 and 500.0 mg L−1, respectively. It was found that principal component (PC) 1 accounts for 60.47% of the total variance and reflects changes associated with low concentrations of heavy metals (up to 5.0 mg L−1). PC2 accounts for 27.95% of the total variance. PC2 is mostly associated with high concentrations of ions of heavy metals. Thus, the effect of Zn and Mn concentrations up to 5 mg L−1and above 50 mg L−1on B. minor and L. incisa has a different character. At the same time, the response of the studied algae species to the action of Zn and Mn has individual differences. In general, B. minor is more resistant to Mn, while L. incisa is more resistant to Zn.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alho LOG, Gebara RC, Paina KA, Sarmento H, Melao MGG (2019) Responses of Raphidocelis subcapitata exposed to Cd and Pb: mechanisms of toxicity assessed by multiple endpoints. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 169:950–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2018.11.087
Andersson B, Godhe A, Filipsson HL, Rengefors K, Berglund O (2020) Differences in metal tolerance among strains, populations, and species of marine diatoms – importance of exponential growth for quantification. Aquat Toxicol 226:105551. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQUATOX.2020.105551
Azevedo JAM, Barros AB, Miranda PRB, Costa JG, Nascimento VX (2019) Biomonitoring of heavy metals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Mn, Cd and Cr) in oysters: Crassostrea rhizophorae of mangrove areas of Alagoas (Brazil). Braz Arch Biol Technol 62:19180211. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4324-2019180211
Balali-Mood M, Naseri K, Tahergorabi Z, Khazdair MR (2021) Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Front Pharmacol 12:643972. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPHAR.2021.643972
Baraud F, Zaiter A, Porée S, Leleyter L (2020) New approach for determination of Cd, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb, and Zn in sewage sludges, fired brick, and sediments using two analytical methods by microwave-induced plasma optical spectrometry and induced coupled plasma optical spectrometry. SN Appl Sci 2:1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03220-0
Battah M, El-Ayoty Y, Abomohra AEF, El-Ghany SA, Esmael A (2015) Effect of Mn2+, Co2+ and H2O2 on biomass and lipids of the green microalga Chlorella vulgaris as a potential candidate for biodiesel production. Ann Microbiol 65:155–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0846-7
Bhatt NC, Panwar A, Bisht TS, Tamta S (2014) Coupling of algal biofuel production with wastewater. Sci World J 210504:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/210504
ATT Bioquest Inc (2020) Quest Graph TM LC50 Calculator. http://www.aatbio.com/tools/lc50-calculator. Accessed 12 April 2021
Bischoff HW, Bold HC (1963) Phycological studies IV. Some soil algae from Enchanted Rock and related algal species. University of Texas Publication 6318:95
Cabala J, Rahmonov O, Jablonska M, Teper E (2011) Soil algal colonization and its ecological role in an environment polluted by past Zn-Pb mining and smelting activity. Water Air Soil Pollut 215:339–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0482-1
Cameron H, Mata MT, Riquelme C (2018) The effect of heavy metals on the viability of Tetraselmis marina AC16-MESO and an evaluation of the potential use of this microalga in bioremediation. PeerJ 6:e5295. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5295
Chakraborty S, Bhattacharya T, Singh G, Maity JP (2014) Benthic macroalgae as biological indicators of heavy metal pollution in the marine environments: a biomonitoring approach for pollution assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 100:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.12.003
Chekroun KB, Baghour M (2013) The role of algae in phytoremediation of heavy metals: a review. J Mater Environ Sci 4(6):873–880
Chen M, Tang H, Ma H, Holland TC, Ng KY, Salley SO (2011) Effect of nutrients on growth and lipid accumulation in the green algae Dunaliella tertiolecta. Bioresour Technol 102(2):1649–1655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.062
Chen HYH, Biswas SR, Sobey TM, Brassard BW, Bartels SF (2017) Reclamation strategies for mined forest soils and overstorey drive understorey vegetation. J Appl Ecol 55:926–936. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.13018
Chernikova AA, Tsoglin LN, Markelova AG, Zorin SN, Mazo VK, Pronina NA (2006) Capacity of Spirulina platensis to accumulate manganese and its distribution in cell. Russ J Pl Physiol 53:800–806. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443706060112
Dao LHT, Beardall J (2016) Effects of lead on two green microalgae Chlorella and Scenedesmus: photosystem II activity and heterogeneity. Algal Res 16:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.03.006
Dinesh KS, Santhanam P, Ananth S, Devi AS, Nandakumar R, Prasath BB, Jeyanthi S, Jayalakshmi S, Ananthi P (2014) Effect of different dosages of zinc on the growth and biomass in five marine microalgae. Int J Fish Aquac 6(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJFA2013.0393
Duffus JH (2002) “Heavy metals” a meaningless term? (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl Chem 74:793–807. https://doi.org/10.1351/PAC200274050793
Expósito N, Carafa R, Kumar V, Sierra J, Schuhmacher M, Papiol GG (2021) Performance of Chlorella vulgaris exposed to heavy metal mixtures: linking measured endpoints and mechanisms. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH18031037
Figueroa-Torresa GM, Mahmooda WMAW, Pittmanb JK, Theodoropoulosa C (2019) Microalgal biomass as a biorefinery platform for biobutanol and biodiesel production. Biochem Eng J 153:107396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107396
Fontanetti CS, Nogarol LR, de Souza RB, Perez DG, Maziviero GT (2011) Bioindicators and biomarkers in the assessment of soil toxicity. In: Pascucci S (ed) Soil contamination Intechopen, Rijeka, pp 143–168. https://doi.org/10.5772/25042
Gani P, Sunar NM, Peralta HM, Latiff AAA, Parjo UK, Razak ARA (2015) Phycoremediation of wastewaters and potential hydrocarbon from microalgae: a review. Adv Environ Biol 9(20):1–8
Gao B, Huang L, Lei X, Meng G, Liu J, Zhang C (2020) Evaluation and transcriptome analysis of the novel oleaginous microalga Lobosphaera bisecta (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) for arachidonic acid production. Mar Drugs 18(5):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050229
Glaser K, Baumann K, Leinweber P, Mikhailyuk T, Karsten U (2018) Algal richness in BSCs in forests under different management intensity with some implications for P cycling. Biogeosciences 15:4181–4192. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-15-4181-2018
Heidarpour A, Aliasgharzad N, Khoshmanzar E, Khoshru B, Lajayer BA (2019) Bio-removal of Zn from contaminated water by using green algae isolates. Environ Technol Innov 16:100464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100464
Horvatić J, Peršić V (2007) The effect of Ni2+, Co2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ on the growth rate of marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin: microplate growth inhibition test. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:494–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00128-007-9291-7
Hu Q, Sommerfeld M, Jarvis E, Ghirardi M, Posewitz M, Seibert M, Darzins A (2008) Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: perspectives and advances. Pl J 54:621–639. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03492.x
Javed M, Usmani N (2019) An overview of the adverse effects of heavy metal contamination on fish health. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 89:389–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40011-017-0875-7
Kacholi DS, Sahu M (2018) Levels and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil, water, and vegetables of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. J Chemother 2018(9):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1402674
Kamyab H, Md Din MF, Ponraj M, Keyvanfar A, Rezania S, Taib SM, Abd Majid MZ (2016) Isolation and screening of microalgae from agro-industrial wastewater (POME) for biomass and biodiesel sources. Desalin Water Treat 57:29118–29125. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1139101
Khaneghah AM, Fakhri Y, Nematollahi A, Pirhadi M (2020) Potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in cereal-based foods: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Trends Food Sci Technol 96:30–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2019.12.007
Koller M, Saleh HM (2018) Introductory chapter: introducing heavy metals. In: Saleh H, Aglan R (eds) Heavy metals. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.74783
Kondzior P, Butarewicz A (2018) Effect of heavy metals (Cu and Zn) on the content of photosynthetic pigments in the cells of algae Chlorella vulgaris. J Ecol Eng 19(3):18–28
Krishnamurti GSR, Subashchandrabose SR, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2015) Assessment of bioavailability of heavy metal pollutants using soil isolates of Chlorella sp. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8826–8832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1799-2
Krustok I, Nehrenheim E, Odlare M (2012) Cultivation of microalgae for potential heavy metal reduction in a wastewater treatment plant. International conference on applied energy, Suzhou
Kumar N, Hans S, Verma R, Srivastava A (2020) Acclimatization of microalgae Arthrospira platensis for treatment of heavy metals in Yamuna River. Water Sci Eng 13:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WSE.2020.09.005
Laghlimi M, Baghdad B, El Hadi H, Bouabdli A (2015) Phytoremediation mechanisms of heavy metal contaminated soils: a review. Open J Ecol 5:375–388. https://doi.org/10.4236/OJE.2015.58031
Lemieux C, Otis C, Turmel M (2014) Chloroplast phylogenomic analysis resolves deep-level relationships within the green algal class Trebouxiophyceae. BMC Evol Biol 211:211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-014-0211-2
Li C, Quan Q, Gan Y, Dong J, Fang J, Wang L, Liu J (2020) Effects of heavy metals on microbial communities in sediments and establishment of bioindicators based on microbial taxa and function for environmental monitoring and management. Sci Total Environ 749:141555. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.141555
Liu W, Sun Z, Chen C-X, Liu J-G, Zhou Z-G (2020) Novel insights into type 2 diacylglycerol acyltransferases in microalga Myrmecia incisa. J Appl Phycol 33:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02071-x
Lukešová A (2001) Soil algae in brown coal and lignite post-mining areas in Central Europe (Czech Republic and Germany). Restor Ecol 9:341–350. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1526-100X.2001.94002.x
Magdaleno A, Vélez CG, Wenzel MT, Tell G (2014) Effects of cadmium, copper and zinc on growth of four isolated algae from a highly polluted Argentina river. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92(2):202–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1171-8
Maltsev Y, Maltseva I (2018) The influence of forest-forming tree species on diversity and spatial distribution of algae in forest litter. Folia Oecologica 45(2):12–21. https://doi.org/10.2478/foecol-2018-0008
Maltsev YI, Konovalenko TV, Barantsova IA, Maltseva IA, Maltseva KI (2017a) Prospects of using algae in biofuel production. Regul Mech Biosyst 8(3):455–460. https://doi.org/10.15421/021770
Maltsev YI, Maltseva IA, Solonenko AN, Bren AG (2017b) Use of soil biota in the assessment of the ecological potential of urban soils. Biosyst Divers 25(4):257–262. https://doi.org/10.15421/011739
Maltsev Y, Gusev E, Maltseva I, Kulikovskiy M, Namsaraev Z, Petrushkina M, Filimonova A, Sorokin B, Golubeva A, Butaeva G, Khrushchev A, Kuzmin D (2018) Description of a new species of soil algae, Parietochloris grandis sp. nov., and study of its fatty acid profiles under different culturing conditions. Algal Res 33:358–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.06.008
Maltsev YI, Maltseva IA, Kulikovskiy MS, Maltseva SY, Sidorov RA (2019a) Analysis of a new strain of Pseudomuriella engadinensis (Sphaeropleales, Chlorophyta) for possible use in biotechnology. Russ J Pl Physiol 66(4):609–617. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443719040083
Maltsev Y, Maltseva I, Maltseva S, Kociolek JP, Kulikovskiy M (2019b) Fatty acid content and profile of the novel strain of Coccomyxa elongata (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) cultivated at reduced nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations. J Phycol 55:1154–1165. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.12903
Maltsev YI, Maltseva IA, Maltseva SY, Kulikovskiy MS (2020) Biotechnological potential of a new strain of Bracteacoccus bullatus (Sphaeropleales, Chlorophyta) as a promising producer of omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Russ J Pl Physiol 67:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443720010124
Maltseva IA, Maltsev YI (2021) Diversity of cyanobacteria and algae in dependence to forest-forming tree species and properties rocks of dump. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18:545–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02868-w
Maltseva IA, Maltsev YI, Solonenko AN (2017) Soil algae of the oak groves of the steppe zone of Ukraine. Int J Algae 19(3):215–226. https://doi.org/10.1615/InterJAlgae.v19.i3.20
Mamaeva A, Petrushkina M, Maltsev Y, Gusev E, Kulikovskiy M, Filimonova A, Sorokin B, Zotko N, Vinokurov V, Kopitsyn D, Petrova D, Novikov A, Namsaraev Z, Kuzmin D (2018) Simultaneous increase in cellular content and volumetric concentration of lipids in Bracteacoccus bullatus cultivated at reduced nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations. J Appl Phycol 30(4):2237–2246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1471-9
Marinova G, Ivanova J, Pilarski P, Chernev G, Chaneva G (2018) Effect of heavy metals on the green alga Scenedesmus incrassatulus. Oxid Commun 41:318–328
Meena RAA, Sathishkumar P, Ameen F, Yusoff ARM, Gu FL (2018) Heavy metal pollution in immobile and mobile components of lentic ecosystems-a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:4134–4148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0966-2
Moenne A, González A, Sáez CA (2016) Mechanisms of metal tolerance in marine macroalgae, with emphasis on copper tolerance in Chlorophyta and Rhodophyta. Aquat Toxicol 176:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQUATOX.2016.04.015
Monteiro CM, Brandão TRS, Castro PML, Malcata FX (2012) Modelling growth of, and removal of Zn and Hg by a wild microalgal consortium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3826-x
Muñoz R, Guieysse B (2006) Algal-bacterial processes for the treatment of hazardous contaminants: a review. Water Res 40(15):2799–2815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.011
Muradov SV (2014) The impact of heavy metals on algae-macrophytes of Avacha Bay. Fundam Res 9(9):1998–2002 http://www.fundamental-research.ru/ru/article/view?id=35176
Naorbe MC, Serrano JAE (2018) Effects of heavy metals on cell density, size, specific growth rate and chlorophyll a of Tetraselmis tetrathele under controlled laboratory conditions. AACL Bioflux 11(3):589–597
Napan K, Teng L, Quinn JC, Wood BD (2015) Impact of heavy metals from flue gas integration with microalgae production. Algal Res 8:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.01.003
Novakovskaya IV, Patova EN (2008) Green algae in spruce forests in the north-east of European Russia. Biol 63:836–842. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-008-0109-9
Nyenda T, Jacobs SM, Gwenzi W, Muvengwi J (2019) Biological crusts enhance fertility and texture of gold mine tailings. Ecol Eng 135:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.03.007
Odobašić A, Šestan I, Begić S (2019) Biosensors for determination of heavy metals in waters, biosensors for environmental monitoring. In: Rinken T, Kivirand K (eds) Biosensors for environmental monitoring. IntechOpen, London. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.84139
OECD (2011) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Freshwater alga and cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test. Organ Econ Coop Dev 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069923-en
Omar HH (2002) Adsorption of zinc ions by Scenedesmus obliquus and Scenedesmus quadricauda and its effect on growth and metabolism. Biol Pl 45:261–266. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015157009150
Pan L, Fang G, Wang Y, Wang L, Su B, Li D, Xiang B (2018) Potentially toxic element pollution levels and risk assessment of soils and sediments in the upstream river, Miyun Reservoir, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH15112364
Pena-Castro JM, Martinez-Jeronimo F, Esparza-Garsia F, Canizares-Villanueva RO (2004) Phenotypic plasticity in Scenedesmus incrassatulus (Chlorophyceae) in response to heavy metals stress. Chemosphere 57(11):1629–1636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.06.041
Perrineau M-M, Zelzion E, Gross J, Price DC, Boyd J, Bhattacharya D (2014) Evolution of salt tolerance in a laboratory reared population of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Microbiol 16(6):1755–1766. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12372
Pittman JK, Dean AP, Osudenko O (2011) The potential of sustainable algal biofuel production using wastewater resources. Bioresour Technol 102:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.035
Polechońska L, Klink A (2021) Validation of Hydrocharis morsus-ranae as a possible bioindicator of trace element pollution in freshwaters using Ceratophyllum demersum as a reference species. Environ Pollut 269:116145. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2020.116145
Qadariyah L, Mujaddid F, Bhuana DS, Mahfud M (2018) Biodiesel production from microalgae with transesterification method using microwave. IOP Conf Ser, Mater Sci Eng 543:012073. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/543/1/012073
Rani N, Sharma HR, Kaushik A, Sagar A (2019) Bioremediation of mined waste land. In: Hussain C (ed) Handbook of environmental materials management. Springer, Cham, pp 557–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-73645-7_79
Rawat J, Gupta PK, Pandit S, Prasad R, Pande V (2021) Current perspectives on integrated approaches to enhance lipid accumulation in microalgae. 3 Biotech 11:303. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205-021-02851-3
Reis LLD, Alho LOG, Abreu CB, Melao MDGG (2021) Using multiple endpoints to assess the toxicity of cadmium and cobalt for chlorophycean Raphidocelis subcapitata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111628. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2020.111628
Reisigl H (1964) Zur systematik und ökologie alpiner Bodenalgen. Österr Bot Z 111:402–499
Rodgher S, Contador TM, Rocha GS, Espindola ELG (2020) Effect of phosphorus on the toxicity of zinc to the microalga Raphidocelis subcapitata. An Acad Bras Cienc 92:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202020190050
Rostern NT (2017) The effects of some metals in acidified waters on aquatic organisms. Oceanogr Fish Open Access J 4. https://doi.org/10.19080/OFOAJ.2017.04.555645
Salama ES, Roh HS, Dev S, Khan MA, Abou-Shanab RAI, Chang SW, Jeon BH (2019) Algae as a green technology for heavy metals removal from various wastewater. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2648-3
Samolov E, Baumann K, Büdel B, Jung P, Leinweber P, Mikhailyuk T, Karsten U, Glaser K (2020) Biodiversity of algae and cyanobacteria in biological soil crusts collected along a climatic gradient in Chile using an integrative approach. Microorganisms 8(7):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071047
Seraj F, Rahman T (2018) Heavy metals, metalloids, their toxic effect and living systems. Am J Plant Sci 9:2626–2643. https://doi.org/10.4236/AJPS.2018.913191
Sharma J, Kumar V, Kumar SS, Malyan SK, Mathimani T, Bishnoi NR, Pugazhendhi A (2020) Microalgal consortia for municipal wastewater treatment – lipid augmentation and fatty acid profiling for biodiesel production. J Photochem Photobiol B 202:111638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111638
Shcherbyna VV, Maltseva IA, Maltsev YI, Solonenko AN (2017) Post-pyrogenic changes in vegetation cover and biological soil crust in steppe ecosystems. Regul Mech Biosyst 25(4):633–638. https://doi.org/10.15421/021797
Shekhovtseva OG, Mal’tseva IA (2015) Physical, chemical, and biological properties of soils in the city of Mariupol, Ukraine. Eurasian Soil Sci 48(12):1393–1400. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229315120145
Song Y, Shu W, Wang A, Liu W (2014) Characters of soil algae during primary succession on copper mine dumps. J Soils Sediments 14(3):577–583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0815-y
Stankovic S, Stankovic AR (2013) Bioindicators of toxic metals. In: Lichtfouse E, Schwarzbauer J, Robert D (eds) Green materials for energy, products and depollution. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 151–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6836-9_5
Subramaniyam V, Subashchandrabose SR, Thavamani P, Chen Z, Krishnamurti GSR, Naidu R, Megharaj M (2016) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of iron in soil microalgae. J Appl Phycol 28:2767–2776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0837-0
Sultana N, Hossain SMZ, Mohammed ME, Irfan MF, Haq B, Faruque MO, Razzak SA, Hossain MM (2020) Experimental study and parameters optimization of microalgae based heavy metals removal process using a hybrid response surface methodology-crow search algorithm. Sci Rep 10:15068. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72236-8
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Experientia Suppl 101:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Tripathi BN, Mehta SK, Amar A, Gaur JP (2006) Oxidative stress in Scenedesmus sp. during short- and long-term exposure to Cu2+ and Zn2+. Chemosphere 62:538–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2005.06.031
Vannela R, Verma S (2006) Co2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ accumulation bycyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. Biotechnol Prog 22:1282–1293. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp060075s
Vodyanitskii YN (2016) Standards for the contents of heavy metals in soils of some states. Ann Agrar Sci 14(3):257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aasci.2016.08.011
Wajda Ł, Duda-Chodak A, Tarko T, Kamiński P (2017) Application of principal component analysis for the optimisation of lead(II) biosorption. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2358-7
Wang Z, Chen S, Cao X (2010) Micro-nutrients effects on algae colony: growth rate and biomass response to various micro-nutrients and competitive inhibitions among multi-microelements. 4th Int Conf Bioinforma Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBBE.2010.5516174
Watanabe S, Hirabayashi S, Boussiba S, Cohen Z, Vonshak A, Richmond A (1996) Parietochloris incisa comb. nov. (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta). Phycol Res 44:107–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1835.1996.tb00383.x
Wong PTS, Chau YK (1990) Zinc toxicity to freshwater algae. Toxicity Assessm 5(2):167–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.2540050205
Wong SC, Li XD, Zhang G, Qi SH, Min YS (2002) Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Pollut 119(1):33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00325-6
World Health Organization (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th ed. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44584
Xu D, Zhan C, Liu H, Lin H (2019) A critical review on environmental implications, recycling strategies, and ecological remediation for mine tailings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(35):35657–35669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06555-3
Yakovyshyna TF (2009) Ecological assessment of toxic effects of heavy metals and measures for their detoxification on biological activity of soil. Visnyk ZhNAEU 1:36–45
Yang J, Cao J, Xing G, Yuan H (2015) Lipid production combined with biosorption and bioaccumulation of cadmium, copper, manganese and zinc by oleaginous microalgae Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341. Bioresour Technol 175:537–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.124
Zaghloul A, Saber M, Gadow S, Awad F (2020) Biological indicators for pollution detection in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Bull Natl Res Cent 44:127. https://doi.org/10.1186/S42269-020-00385-X
Zamani-Ahmadmahmoodi R, Malekabadi MB, Rahimi R, Johari SA (2020) Aquatic pollution caused by mercury, lead, and cadmium affects cell growth and pigment content of marine microalga, Nannochloropsis oculata. Environ Monit Assess 192:330. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-020-8222-5
Zhang Y, Li C, Xie Z, Zhang Y (2012) A modeling method of state prediction for algae growth in coastal water. In: Hu W (ed) Advances in electric and electronics. Lecture notes in electrical engineering, vol 155. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28744-2_20
Zienkiewicz K, Benning U, Siegler H, Feussner I (2018) The type 2 acyl-CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase family of the oleaginous microalga Lobosphaera incisa. BMC Pl Biol 18(1):298. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1510-3
Zwolak A, Sarzyńska M, Szpyrka E, Stawarczyk K (2019) Sources of soil pollution by heavy metals and their accumulation in vegetables: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 230:164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4221-y
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This publication is based on research carried out with financial support by Russian Science Foundation (project number 20-74-10076) and within the state assignment of Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (theme No.121041200194-7) for finishing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. Maltsev: conceptualization (lead); data curation (lead); writing—original draft (lead). A. Maltseva: writing—original draft (equal). S. Maltseva: investigation (equal); resources (equal).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(XLSX 24 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maltsev, ., Maltseva, A. & Maltseva, S. Differential Zn and Mn sensitivity of microalgae species from genera Bracteacoccus and Lobosphaera. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 57412–57423 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15981-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15981-1