Abstract
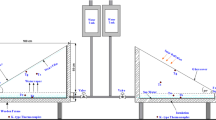
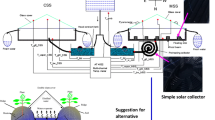
The proposed research study aims to improve the productivity of solar still (SS) by using low-cost and eco-friendly materials. The aforementioned objective was achieved by enhancing the evaporation rate of seawater in the absorber basin and the condensation rate over the glass cover of the solar still. In this study, the low-cost and eco-friendly materials used for enhancing the evaporation rate in the solar still were molasses powder (MP), sawdust (SD) and rice husk (RH). In addition to these materials, bamboo straw (BS), banana leaf stem (BL) and rice straw (RS) were used as absorbing materials over the glass cover for enhancing the condensation rate. The experiments were carried out under similar meteorological conditions, and the results of the modified solar still were compared with the conventional solar still (CSS). The productivities of CSS, SSMP, SSRH, SSSD, SSBS, SSBL and SSRS were about 2250 mL/m2, 2383 mL/m2, 2467 mL/m2, 3033 mL/m2, 2700 mL/m2, 2683 mL/m2 and 3367 mL/m2, respectively. The results of the experimental investigation highlighted that the SSSD had a comparatively better evaporation rate and 34.81% higher yield than CSS. Besides, SSRS had a comparatively better condensation rate and a 51.88% higher yield than CSS. Furthermore, the combination of sawdust (SD) and rice straw (RS) was investigated for the combined enhancement of evaporation and condensation. The solar still with sawdust and rice straw (SSSDRS) showed a 62.88% improvement in productivity with 3633 mL/m2 when compared to CSS. Also, the economic analysis showed that the cost per litre (CPL) of freshwater obtained from SSSDRS was about ₹ 1.9 ($ 0.025) with a payback period of 4.4 months which was the least when compared to all the considered cases.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Datasets related to this research article can be found at https://doi.org/10.17632/4s875xzmx8.1 an open-source online data repository hosted at Mendeley Data (Suraparaju and Natarajan 2021c).
References
Agboola OP, Atikol U, Assefi H (2015) Feasibility assessment of basin solar stills. Int J Green Energy 12:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2014.889006
Akash BA, Mohsen MS, Nayfeh W (2000) Experimental study of the basin type solar still under local climate conditions. Energy Convers Manag 41:883–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6701(00)93188-6
Al-Nimr MA, Al-Ammari WA (2016) A novel hybrid PV-distillation system. Sol Energy 135:874–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.06.061
Arunkumar T, Jayaprakash R, Denkenberger D, Ahsan A, Okundamiya MS, kumar S, Tanaka H, Aybar HŞ (2012) An experimental study on a hemispherical solar still. Desalination 286:342–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.047
Assis FS, Margem FM, Cordeiro TC et al (2015) Photoacoustic thermal characterization of banana fibers. Materials Research. Universidade Federal de Sao Carlos, In, pp 240–245
Attia MEH, Driss Z, Kabeel AE, et al (2021a) Phosphate bags as energy storage materials for enhancement of solar still performance. Environ Sci Pollut Res
Attia MEH, Kabeel AE, Abdelgaied M, Essa FA, Omara ZM (2021b) Enhancement of hemispherical solar still productivity using iron, zinc and copper trays. Sol Energy 216:295–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2021.01.038
Balachandran GB, David PW, Rajendran G, Ali MNA, Radhakrishnan V, Balamurugan R, Athikesavan MM, Sathyamurthy R (2020) Investigation of performance enhancement of solar still incorporated with Gallus gallus domesticus cascara as sensible heat storage material. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:611–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10470-3
Bello RS, Onilude MA (2017) Characterization of sawdust produced from circular, chain and band sawing machines 1:21–29. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.be.20170101.14
Bhargva M, Yadav A (2019) Productivity augmentation of single-slope solar still using evacuated tubes, heat exchanger, internal reflectors and external condenser. Energy Sources, Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 00:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1691291
Chamkha AJ, Rufuss DDW, Kabeel AE, Sathyamurthy R, Abdelgaid M, Manokar AM, Madhu B (2020) Augmenting the potable water produced from single slope solar still using CNT-doped paraffin wax as energy storage: an experimental approach. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02703-w
Costes JP, Evrard A, Biot B, Keutgen G, Daras A, Dubois S, Lebeau F, Courard L (2017) Thermal conductivity of straw bales: full size measurements considering the direction of the heat flow. Buildings 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings7010011
Dev R, Abdul-Wahab SA, Tiwari GN (2011) Performance study of the inverted absorber solar still with water depth and total dissolved solid. Appl Energy 88:252–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.08.001
Dhivagar R, Mohanraj M, Raj P, Gopidesi RK (2021) Thermodynamic analysis of single slope solar still using graphite plates and block magnets at seasonal climatic conditions. Water Sci Technol:1–17. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.156
El M, Attia H, Kabeel AE, Abdelgaied M (2021) Optimal concentration of El Oued sand grains as energy storage materials for enhancement of hemispherical distillers performance. J Energy Storage 36:102415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2021.102415
Elango T, Kannan A, Kalidasa Murugavel K (2015) Performance study on single basin single slope solar still with different water nanofluids. Desalination 360:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.01.004
El-gazar EF, Zahra WK, Hassan H, Rabia SI (2021) Fractional modeling for enhancing the thermal performance of conventional solar still using hybrid nanofluid: energy and exergy analysis. Desalination 503:114847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114847
Elmaadawy K, Kandeal AW, Khalil A, Elkadeem MR, Liu B, Sharshir SW (2021) Performance improvement of double slope solar still via combinations of low cost materials integrated with glass cooling. Desalination 500:114856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114856
Gad HE, Shams El-Din S, Hussien AA, Ramzy K (2015) Thermal analysis of a conical solar still performance: An experimental study. Sol Energy 122:900–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2015.10.016
Ghaly AE, Zhang Y, Li B (t) (2012) Physical properties of rice residues as affected by variety and climatic and cultivation conditions in three continents. Am J Appl Sci 9:1757–1768. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajassp.2012.1757.1768
Hassan H, Abo-Elfadl S (2017) Effect of the condenser type and the medium of the saline water on the performance of the solar still in hot climate conditions. Desalination 417:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.05.014
Huang P, Chang WS, Ansell MP, John CYM, Shea A (2017) Porosity estimation of Phyllostachys edulis (moso bamboo) by computed tomography and backscattered electron imaging. Wood Sci Technol 51:11–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-016-0865-6
Jafari Mosleh H, Mamouri SJ, Shafii MB, Hakim Sima A (2015) A new desalination system using a combination of heat pipe, evacuated tube and parabolic through collector. Energy Convers Manag 99:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.04.028
Jagannadha Rao PVK, Das M, Das SK (2008) Thermophysical properties of sugarcane, palmyra palm, and date-palm granular jaggery. Int J Food Prop 11:876–886. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942910701671281
Jani HK, Modi KV (2019) Experimental performance evaluation of single basin dual slope solar still with circular and square cross-sectional hollow fins. Sol Energy 179:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.12.054
Judawisastra H, Sitohang RDR, Rosadi MS (2017) Water absorption and tensile strength degradation of Petung bamboo (Dendrocalamus asper) fiber-reinforced polymeric composites. Mater Res Express 4:094003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa8a0d
Kabeel AE, Abdelgaied M (2016) Improving the performance of solar still by using PCM as a thermal storage medium under Egyptian conditions. Desalination 383:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.01.006
Kabeel AE, Khairat Dawood MM, Ramzy K, Nabil T, Elnaghi B, elkassar A (2019a) Enhancement of single solar still integrated with solar dishes: an experimental approach. Energy Convers Manag 196:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.05.112
Kabeel AE, Manokar AM, Sathyamurthy R et al (2019b) A review on different design modifications employed in inclined solar still for enhancing the productivity. J Sol Energy Eng Trans ASME 141:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4041547
Kabeel AE, Sathyamurthy R, Sharshir SW, Muthumanokar A, Panchal H, Prakash N, Prasad C, Nandakumar S, el Kady MS (2019c) Effect of water depth on a novel absorber plate of pyramid solar still coated with TiO 2 nano black paint. J Clean Prod 213:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.185
Kabeel AE, El-Maghlany WM, Abdelgaied M, Abdel-Aziz MM (2020) Performance enhancement of pyramid-shaped solar stills using hollow circular fins and phase change materials. J Energy Storage 31:101610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101610
Kalita P, Clifford MJ, Jiamjiroch K et al (2013) Characterization and analysis of thermal response of rice husk for gasification applications. In, J Renew. Sust. Energ, p 013119
Khalifa AJN, Hamood AM (2009) Effect of insulation thickness on the productivity of basin type solar stills : An experimental verification under local climate. Energy Convers Manag 50:2457–2461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2009.06.007
Kumar S, Dubey A, Tiwari GN (2014) A solar still augmented with an evacuated tube collector in forced mode. Desalination 347:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.05.019
Kumar RA, Esakkimuthu G, Murugavel KK (2016) Performance enhancement of a single basin single slope solar still using agitation effect and external condenser. Desalination 399:198–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.09.006
Mande AB, Manickam P (2019) Enhanced solar still productivity using transparent walls with an integral trough and organic porous absorber material. Int J Green Energy 16:211–227. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2018.1549995
Manokar AM, Ravishankar MV, Kabeel AE (2020) Enhancement of potable water production from an inclined photovoltaic panel absorber solar still by integrating with flat-plate collector. Environ Dev Sustain 22:4145–4167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00376-7
Modi KV, Modi JG (2019) Performance of single-slope double-basin solar stills with small pile of wick materials. Appl Therm Eng 149:723–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.12.071
Mohanraj M, Karthick L, Dhivagar R (2021) Performance and economic analysis of a heat pump water heater assisted regenerative solar still using latent heat storage. Appl Therm Eng 196:117263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117263
Morad MM, El-Maghawry HAM, Wasfy KI (2015) Improving the double slope solar still performance by using flat-plate solar collector and cooling glass cover. Desalination 373:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.06.017
Mounika M, Ramaniah K, Ratna Prasad AV et al (2012) Thermal conductivity characterization of bamboo fiber reinforced polyester Composite. J Mater Environ Sci 3:1109–1116
Mukherjee K, Tiwari GN (1986) Economic analyses of various designs of conventional solar stills. Energy Convers Manag 26:155–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0196-8904(86)90049-X
Muthu Manokar A, Kalidasa Murugavel K, Esakkimuthu G (2014) Different parameters affecting the rate of evaporation and condensation on passive solar still - a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 38:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.05.092
Nagarajan PK, El-Agouz SA, Harris HS et al (2017) Analysis of an inclined solar still with baffles for improving the yield of fresh water. Process Saf Environ Prot 105:326–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.11.018
Nayi KH, Modi KV (2020) Effect of cost-free energy storage material and saline water depth on the performance of square pyramid solar still: a mathematical and experimental study. J Therm Anal Calorim 144:1351–1368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09598-8
Omara ZM, Kabeel AE (2014) The performance of different sand beds solar stills. Int J Green Energy 11:240–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2013.769881
Omara ZM, Hamed MH, Kabeel AE (2011) Performance of finned and corrugated absorbers solar stills under Egyptian conditions. Desalination 277:281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.042
Panchal H, Sathyamurthy R, Kabeel AE, el-Agouz SA, Rufus DS, Arunkumar T, Muthu Manokar A, Winston DP, Sharma A, Thakar N, Sadasivuni KK (2019) Annual performance analysis of adding different nanofluids in stepped solar still. J Therm Anal Calorim 138:3175–3182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08346-x
Patel SK, Modi KV (2020) Techniques to improve the performance of enhanced condensation area solar still: A critical review. J Clean Prod:122260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122260
Pounraj P, Winston DP, Kabeel AE et al (2018) Experimental investigation on Peltier based hybrid PV / T active solar still for enhancing the overall performance. Energy Convers Manag 168:371–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.05.011
Prakash P, Velmurugan V (2015) Parameters influencing the productivity of solar stills – a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 49:585–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.136
Rabhi K, Nciri R, Nasri F, Ali C, Ben Bacha H (2017) Experimental performance analysis of a modified single-basin single-slope solar still with pin fins absorber and condenser. Desalination 416:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.04.023
Raj G, Prabhansu D, Kumar R, Chandra P, Saurabh S (2020) Experimental study of solar still augmented with low-cost energy absorbing and releasing materials. Energy Sources, Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 42:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1587054
Reddy KS, Sharon H, Krithika D, Philip L (2018) Performance, water quality and enviro-economic investigations on solar distillation treatment of reverse osmosis reject and sewage water. Sol Energy 173:160–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.07.033
Saadi Z, Rahmani A, Lachtar S, Soualmi H (2018) Performance evaluation of a new stepped solar still under the desert climatic conditions. Energy Convers Manag 171:1749–1760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.06.114
Sampathkumar K, Arjunan TV, Senthilkumar P (2013) The experimental investigation of a solar still coupled with an evacuated tube collector. Energy Sources, Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 35:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2010.511426
Sathish Kumar TR, Jegadheeswaran S, Chandramohan P (2019) Performance investigation on fin type solar still with paraffin wax as energy storage media. J Therm Anal Calorim 136:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7882-7
Sathyamurthy R, El-Agouz SA, Dharmaraj V (2015) Experimental analysis of a portable solar still with evaporation and condensation chambers. Desalination 367:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2015.04.012
Sathyamurthy R, Kabeel AE, Balasubramanian M, Devarajan M, Sharshir SW, Manokar AM (2020) Experimental study on enhancing the yield from stepped solar still coated using fumed silica nanoparticle in black paint. Mater Lett 272:127873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127873
Sengphet KKD, Sato T, Ahmad Fauzi MN, Othman R (2014) Porous ceramic bodies using banana stem waste as a pore-forming agent. In: Advanced Materials Research. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, pp 131–136
Sharma B, Gatóo A, Bock M, Ramage M (2015) Engineered bamboo for structural applications. Constr Build Mater 81:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.01.077
Sharon H, Reddy KS (2015) A review of solar energy driven desalination technologies. Renew Sust Energ Rev 41:1080–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.09.002
Sharshir SW, Peng G, Yang N, Eltawil MA, Ali MKA, Kabeel AE (2016) A hybrid desalination system using humidification-dehumidification and solar stills integrated with evacuated solar water heater. Energy Convers Manag 124:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.07.028
Sharshir SW, Peng G, Elsheikh AH, Edreis EMA, Eltawil MA, Abdelhamid T, Kabeel AE, Zang J, Yang N (2018) Energy and exergy analysis of solar stills with micro/nano particles: a comparative study. Energy Convers Manag 177:363–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.09.074
Sharshir SW, Kandeal AW, Ismail M, Abdelaziz GB, Kabeel AE, Yang N (2019) Augmentation of a pyramid solar still performance using evacuated tubes and nanofluid: experimental approach. Appl Therm Eng 160:113997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.113997
Sharshir SW, Ellakany YM, Eltawil MA (2020) Exergoeconomic and environmental analysis of seawater desalination system augmented with nanoparticles and cotton hung pad. J Clean Prod 248:119180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119180
Shehata AI, Kabeel AE, Khairat Dawood MM, Elharidi AM, Abd Elsalam A, Ramzy K, Mehanna A (2020) Enhancement of the productivity for single solar still with ultrasonic humidifier combined with evacuated solar collector: an experimental study. Energy Convers Manag 208:112592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.112592
Singh HN, Tiwari GN (2004) Monthly performance of passive and active solar stills for different Indian climatic conditions. Desalination 168:145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2004.06.180
Sleiti AK, Al-Ammari WA, Al-Khawaja M (2020) A novel solar integrated distillation and cooling system – design and analysis. Sol Energy 206:68–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.05.107
Sleiti AK, Al-Ammari WA, Al-Khawaja M (2021a) Integrated novel solar distillation and solar single-effect absorption systems. Desalination 507:115032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2021.115032
Sleiti AK, Al-Khawaja H, Al-Khawaja H, Al-Ali M (2021b) Harvesting water from air using adsorption material – prototype and experimental results. Sep Purif Technol 257:117921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117921
Suraparaju SK, Natarajan SK (2020) Performance analysis of single slope solar desalination setup with natural fiber. Desalin Water Treat 193:64–71. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25679
Suraparaju SK, Natarajan SK (2021a) Experimental investigation of single-basin solar still using solid staggered fins inserted in paraffin wax PCM bed for enhancing productivity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:20330–20343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11980-w
Suraparaju SK, Natarajan SK (2021b) Productivity enhancement of single-slope solar still with novel bottom finned absorber basin inserted in phase change material (PCM): techno-economic and enviro-economic analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13495-4
Suraparaju SK, Natarajan SK (2021c) Solar still - combined evaporation and condensation with eco-friendly materials. Mendeley Data V1. https://doi.org/10.17632/4S875XZMX8.1
Suraparaju SK, Sampathkumar A, Natarajan SK (2021) Experimental and economic analysis of energy storage - based single - slope solar still with hollow-finned absorber basin. Heat Transf:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/htj.22136
Tabrizi FF, Dashtban M, Moghaddam H, Razzaghi K (2010) Effect of water flow rate on internal heat and mass transfer and daily productivity of a weir-type cascade solar still. Desalination 260:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.03.037
Taheri Mousavi SM, Egelioglu F, Ilkan M (2020) Experimental and numerical study of the effect of various design configurations on the thermal performance of solar still desalination. Energy Sources, Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 00:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1826018
Thirugnanasambandam M, Iniyan S, Goic R (2010) A review of solar thermal technologies. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:312–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.07.014
Tiwari GN, Sahota L (2017) Review on the energy and economic efficiencies of passive and active solar distillation systems. Desalination 401:151–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.08.023
Tiwari AK, Tiwari GN (2006) Effect of water depths on heat and mass transfer in a passive solar still: in summer climatic condition. Desalination 195:78–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.11.014
Tripathi R, Tiwari GN (2005) Effect of water depth on internal heat and mass transfer for active solar distillation. Desalination 173:187–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2004.08.032
Velmurugan V, Deenadayalan CK, Vinod H, Srithar K (2008a) Desalination of effluent using fin type solar still. Energy 33:1719–1727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2008.07.001
Velmurugan V, Gopalakrishnan M, Raghu R, Srithar K (2008b) Single basin solar still with fin for enhancing productivity. Energy Convers Manag 49:2602–2608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2008.05.010
Velmurugan V, Pandiarajan S, Guruparan P, Subramanian LH, Prabaharan CD, Srithar K (2009) Integrated performance of stepped and single basin solar stills with mini solar pond. Desalination 249:902–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.06.070
Xevgenos D, Moustakas K, Malamis D, Loizidou M (2016) An overview on desalination & sustainability: renewable energy-driven desalination and brine management. Desalin Water Treat 57:2304–2314. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.984927
Zanganeh P, Goharrizi AS, Ayatollahi S, Feilizadeh M (2019) Productivity enhancement of solar stills by nano-coating of condensing surface. Desalination 454:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.12.007
Zanganeh P, Goharrizi AS, Ayatollahi S, Feilizadeh M, Dashti H (2020) Efficiency improvement of solar stills through wettability alteration of the condensation surface: an experimental study. Appl Energy 268:114923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114923
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sendhil Kumar Natarajan: Conceptualization, validation, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration.
Subbarama Kousik Suraparaju: Conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, visualization, writing—original draft.
Rajvikram Madurai Elavarasan: Validation, writing—review and editing.
Rishi Pugazhendhi: Formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Eklas Hossain: Writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
•The performance of solar still was examined with low-cost and eco-friendly materials.
•SSSD had a better evaporation rate and enhanced yield by 34.81%.
•SSRS had a better condensation rate and enhanced yield by 51.88%.
•SSSDRS enhanced evaporation and condensation rates with a 62.88% increase in yield.
•Cost/litre and payback period of SSSDRS were ₹1.9 and 4.4 months, respectively.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natarajan, S.K., Suraparaju, S.K., Elavarasan, R.M. et al. An experimental study on eco-friendly and cost-effective natural materials for productivity enhancement of single slope solar still. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 1917–1936 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15764-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15764-8