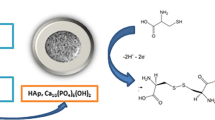
Abstract
A composite material prepared by polymerization of β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) on the surface of natural hydroxyapatite using citric acid as cross linker, was employed as electrode material for the detection of Pb(II). Hydroxyapatite was obtained from bovine bones, following a three-step procedure including pre-calcination, chemical treatment with (NH4)2HPO4, and calcination. The structure and morphology of the pristine hydroxyapatite (NHAPP0.5) and its functionalized counterpart (NHAPp0.5-CA-β-CD) were examined using XRD, FTIR, and SEM. Upon deposition as thin film on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE), the ion exchange ability of NHAPp0.5-CA-β-CD was exploited to elaborate a sensitive sensor for the detection of lead. The electroanalytical procedure was based on the chemical accumulation of Pb(II) ions under open-circuit conditions, followed by the detection of the preconcentrated species using differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. The reproducibility of the proposed method, based on a series of 8 measurements in a solution containing 2 μM Pb(II) gave a coefficient of variation of 1.27%. Significant parameters that can affect the stripping response of Pb(II) were optimized, leading to a linear calibration curve for lead in the concentration range of 2 × 10−8 mol L−1 – 20 × 10−8 mol L−1 (R2 = 0.998). The detection limit (3S/m) and the sensitivity of the proposed sensor were 5.06 × 10−10 mol L−1 and 100.80 μA.μM−1, respectively. The interfering effect of several ions expected to affect the determination of lead was evaluated, and the proposed sensor was successfully applied in the determination of Pb(II) ions in spring water, well water, river water and tap water samples.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebisi GA, Chowdhury ZZ, Alaba PA (2017) Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies of lead ion and zinc ion adsorption from aqueous solution onto activated carbon prepared from palm oil mill effluent. J Clean Prod 148:958–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.047
Ajab H, Khan AAA, Nazir MS (2019) Cellulose-hydroxyapatite carbon electrode composite for trace plumbum ions detection in aqueous and palm oil mill effluent: interference, optimization and validation studies. Environ Res 176:108563–108569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108563
Alam AU, Qin Y, Howlader MMR, Hu NX, Deen MJ (2018) Electrochemical sensing of acetaminophen using multi-walled carbon nanotube and β-cyclodextrin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 254:896–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.127
Amna T (2018) Valorization of bone waste of Saudi Arabia by synthesizing hydroxyapatite. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 186:779–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2768-5
Awual MR (2019) An efficient composite material for selective lead (II) monitoring and removal from wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 7(3):103087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103087
Bukkitgar SD, Shetti NP (2017) Fabrication of a TiO 2 and clay nanoparticle composite electrode as a sensor. Anal Methods 9(30):4387–4393. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AY01068K
Celebioglu A, Toput F, Yildiz ZI, Uyar T (2019) Efficient removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals from water by electrospun nanofibrous polycyclodextrin membranes. ACS Omega 4:7850–7860. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b00279
Chen J, Teo KC (2001) Determination of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in water samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Anal Chim Acta 540:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)01367-8
Chen W, Huang Z, Liu Y, He Q (2008) Preparation and characterization of a novel solid base catalyst hydroxyapatite loaded with strontium. Catal Commun 9:516–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2007.02.011
El Mhammedi MA, Bakasse M, Chtaini A (2007) Square-Wave Voltammetric Determination of Paraquat at Carbon Paste Electrode Modified with Hydroxyapatite. Electroanalysis 19:1727–1733. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200703927
El Mhammedi MA, Achak M, Bakasse M, Chtani A (2009a) Electrochemical determination of para-nitrophenol at apatite-modified carbon paste electrode: application in river water samples. J Hazard Mater 163:323–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.126
El Mhammedi MA, Achak M, Chtaini A (2009b) Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 modified carbon-paste electrode for the determination of trace lead (II) by square-wave voltammetry. J Hazard Mater 160:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.057
El Mhammedi MA, Achak M, Bakasse M (2013) Evaluation of a platinum electrode modified with hydroxyapatite in the lead(II) determination in a square wave voltammetric procedure. Arab J Chem 6:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.10.010
Elkabouss K, Kacimi M, Ziyad M, Ammar S, Verduraz FB (2004) Cobalt-exchanged hydroxyapatite catalysts: magnetic studies, spectroscopic investigations, performance in 2-butanol and ethane oxidative dehydrogenations. J Catal 226:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2004.05.007
Esmaeilkhanian A, Sharifianjazi F, Abouchenari A, Rouhani A, Parvin N, Irani M (2019) Synthesis and Characterization of Natural Nano-hydroxyapatite Derived from Turkey Femur-Bone Waste. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 189:919–932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03046-6
Fairuz L, Mohd RS, Mohamad NS, Abdul MHR, Nodeh (2016) Electrochemical determination of 24-dichlorophenol at β-cyclodextrin functionalized ionic liquid modified chemical sensor: voltammetric and amperometric studies. RSC Advances 6(102):100186–100194. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA19816C
Fakharzadeh A, Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi R (2017) Effect of dopant loading on the structural features of silver-doped hydroxyapatite obtained by mechanochemical method. Ceram Int 43:12588–12598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.06.136
Faksawat K, Sujinnapram S, Limsuwan P, Hoonnivathana E, Naemchanthara K (2015) Preparation and characteristic of hydroxyapatite synthesized from cuttlefish bone by precipitation. Method Adv Mat Res 1125:421–425. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1125.421
Flora G, Gupta D, Tiwari A (2012) Toxicity of lead: a review with recent updates. Interdiscip Toxicol 5:47–58. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10102-012-0009-2
Gao F, Gao N, Nishitani A, Tanaka H (2016) Rod-like hydroxyapatite and Nafion nanocomposite as an electrochemical matrix for simultaneous and sensitive detection of Hg2+, Cu2+, Pb2+ and Cd2+. J Electroanal Chem 775:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.05.032
Goto T, Sasaki K (2016) Synthesis of morphologically controlled hydroxyapatite from fish bone by urea-assisted hydrothermal treatment and its Sr2+ sorption capacity. Powder Technol 292:314–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2016.01.041
Hammood AS, Hassan SS, Alkhafagy MT (2017) Access to Optimal Calcination Temperature for Nanoparticles Synthesis from Hydroxyapatite Bovine Femur Bone Waste. Nano Biomed Eng 3:228–235. https://doi.org/10.5101/nbe.v9i3
He J, Li Y, Wang C, Zhang K, Lin D, Kong L, Liu J (2017) Rapid adsorption of Pb, Cu and Cd from aqueous solutions by β-cyclodextrin polymers. Appl Surf Sci 426:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.103
Heydari A, Sheibani H (2015) Fabrication of poly (β-cyclodextrin-co-citric acid)/bentonite clay nanocomposite hydrogel: thermal and absorption properties. RSC Adv 5:82438–82449. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA12423A
Horta M, Aguilar M, Moura F, Campos J, Ramos V, Quizunda A (2019) Synthesis and characterization of green nanohydroxyapatite from hen eggshell by precipitation method. Mater Today Proceed 14:716–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.02.011
Ilager D, Seo H, Shetti NP, Kalanur SS, Aminabhavi TM (2020a) Electrocatalytic detection of herbicide, amitrole at WO3·0.33H2O modified carbon paste electrode for environmental applications. Sci Total Environ 743:140691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140691
Ilager D, Seo H, Shetti NP, Kalanur SS (2020b) CTAB modified Fe-WO3 as an electrochemical detector of amitrole by catalytic oxidation. J Environ Chem Eng 8(6):104580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104580
Ilager D, Seo H, Kalanur SS, Shetti NP, Aminabhavi TM (2021) A novel sensor based on WO3·0.33H2O nanorods modified electrode for the detection and degradation of herbicide, carbendazim. J Environ Manag 279:111611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111611
Kanchana P, Sekar C (2014) EDTA assisted synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for electrochemical sensing of uric acid. Mater Sci Eng C 42:601–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.05.072
Koutsopoulos S (2002) Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite crystals: a review study on the analytical methods. J Biomed Mater Res 62:600–612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.10280
Lau OW, Ho SW (1993) Simultaneous determination of traces of iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, mercury and lead in water by energy-dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectrometry after preconcentration as their piperazino-1,4-bis(dithiocarbamate) complexes. Anal Chim Acta 280:269–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2670(93)85131-3
Leprêtre S, Chai F, Hildebrand JC, Martel B (2009) Prolonged local antibiotics delivery from hydroxyapatite functionalised with cyclodextrin polymers. Biomaterials 30:6086–6093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.07.045
Li Y, Liu X, Zeng X, Liu Y, Wei W, Luo S (2009) Simultaneous determination of ultra-trace lead and cadmium at a hydroxyapatite-modified carbon ionic liquid electrode by square-wave stripping voltammetry. Sensors Actuators B Chem 139:604–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2009.03.045
Li X, Zhou H, Fu C, Wang F, Ding Y, Kuang Y (2016) A novel design of engineered multi-walled carbon nanotubes material and its improved performance in simultaneous detection of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Sensors Actuators B Chem 236:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.05.149
Liu Q, de Wijn JR, de Groot K, van Blitterswijk CA (1998) Surface modification of nano-apatite by grafting organic polymer. Biomaterials 19:1067–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(98)00033-7
Liu Z, Xue Q, Guo Y (2017) Sensitive electrochemical detection of rutin and isoquercitrin based on SH-β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene-palladium nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 89:444–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.056
Longerich HP, Fryer BJ, Strong DF (1987) Determination of lead isotope ratios by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Spectrochim Acta Part B At Spectrosc 42:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/0584-8547(87)80048-4
Lv M, Wang X, Li J, Yang X, Zhang C, Yang J, Hu H (2013) Cyclodextrin-reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanosheets for the simultaneous determination of lead (II) and cadmium (II) using square wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Electrochim Acta 108:412–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.06.099
Malode SJ, Shetti NP, Reddy KR (2021) Highly sensitive electrochemical assay for selective detection of aminotriazole based on TiO2/poly (CTAB) modified sensor. Environ Technol Innov 21:101222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101222
Mobasherpour IL, Salahi E, Pazouki M (2011) Removal of divalent cadmium cations by means of synthetic nano crystallite hydroxyapatite. Desalination 266:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.08.016
Mohammadi S, Taher MA, Beitollahi H (2020) Synthesis and application of a natural-based nanocomposite with carbon nanotubes for sensitive voltammetric determination of lead (II) ions. Int J Environ Anal Chem 100:65–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1631300
Musa Y, Pudza ZZ, Abidin S, Abdul-Rashid F, Yasin ASM, Noor J, Abdullah (2020) Selective and simultaneous detection of cadmium lead and copper by tapioca-derived carbon dot–modified electrode. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(12):13315–13324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07695-7
Nandi SK, Kundu B, Mukherjee J, Mahato A, Datta S, Balla VK (2015) Converted marine coral hydroxyapatite implants with growth factors: in vivo bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C 49:816–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.078
Ngassa GBP, Tonle IK, Walcarus A (2014) One-step co-intercalation of cetyltrimethylammonium and thiourea in smectite and application of the organoclay to the sensitive electrochemical detection of Pb(II). Appl Clay Sci 99:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2014.07.014
Niu X, Mo Z, Yang X, Sun M, Zhao P, Li Z, Ouyang M, Liu Z, Gao H, Guo R, Liu N (2018) Advances in the use of functional composites of β-cyclodextrin in electrochemical sensors. Microchim Acta 185:328–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2859-6
Nouri-Felekori M, Khakbiz M, Nezafati N (2019) Synthesis and characterization of Mg, Zn and Sr-incorporated hydroxyapatite whiskers by hydrothermal method. Mater Lett 243:120–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.01.147
Oliveira VHB, Rechotnek F, da Silva EP, Marques VS, Rubira AF, Silva R, Lourenco SA, Muniz EC (2020) A sensitive electrochemical sensor for Pb2+ ions based on ZnO nanofibers functionalized by L-cysteine. J Mol Liq 309:113041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113041
Othmani M, Aissa A, Bac CG, Rachdi F, Debbabi M (2013) Surface modification of calcium hydroxyapatite by grafting of etidronic acid. Appl Surf Sci 274:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.03.002
Pal A, Maity S, Chabri S, Bera S, Chowdhury AR, Das M, Sinha A (2017) Mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite from mercenaria clam shells and phosphoric acid. Biomed Phys Eng Expr 3:015010. https://doi.org/10.1088/2057-1976/aa54f5
Pan W, Wang Y, Chen Z, Lou T, Qin W (2009) Nanomaterial/ionophore-based electrode for anodic stripping voltammetric determination of lead: an electrochemical sensing platform toward heavy metals. Anal Chem 81:5088–5094. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac900417e
Patel S, Han J, Qiu W, Gao W (2015) Synthesis and characterisation of mesoporous bone char obtained by pyrolysis of animal bones, for environmental application. J Environ Chem Eng 3:2368–2377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.07.031
Prongmanee W, Alam I, Asanithi P (2019) Hydroxyapatite/Graphene oxide composite for electrochemical detection of L-Tryptophan. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 102:415–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.06.004
Sadat-Shojai M, Khorasani MT, Dinpanah-Khoshdargi E, Jamshidi H (2013) Synthesis methods for nanosized hydroxyapatite with diverse structures. Acta Biomater 9:7591–7621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2013.04.012
Saoiabi S, EL Asri S, Laghzizil A, Coradin T, Lahlil K (2010) Nanoporous surface of organofunctionalized hydroxyapatite fabricated from natural phosphate rock. Mater Lett 64:2679–2681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2010.09.013
Shetti NP, Malode SJ, Nandibewoor ST (2015) Electro-oxidation of captopril at a gold electrode and its determination in pharmaceuticals and human fluids. Anal Methods 7(20):8673–8682. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AY01619C
Shetti NP, Malode SJ, Malladi RS, Nargund SL, Shukla SS, Aminabhavi TM (2019) Electrochemical detection and degradation of textile dye Congo red at graphene oxide modified electrode. Microchem J 146:387–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.01.033
Sinha A, Mishra T, Ravishankar N (2008) Polymer assisted hydroxyapatite microspheres suitable for biomedical application. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:2009–2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3286-0
Sun M, Li Z, Wu S, Gu Y, Li Y (2018) Simultaneous detection of Pb2+, Cu2+ and Hg2+ by differential pulse voltammetry at an indium tin oxide glass electrode modified by hydroxyapatite. Electrochim Acta 283:1223–1230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.07.019
Tang W, Zhao J, Sha B, Liu H (2013) Adsorption and drug release based on β-cyclodextrin-grafted hydroxyapatite composite. J Appl Polym Sci 127:2803–2808. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.37607
Tcheumi HL, Tassontio VN, Tonle IK, Ngameni E (2019) Surface functionalization of smectite-type clay by facile polymerization of β-cyclodextrin using citric acid cross linker: application as sensing material for the electrochemical determination of paraquat. Appl Clay Sci 173:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.03.013
Tchoffo R, Ngassa GBP, Tonle IK, Ngameni E (2021) Electroanalysis of diquat using a glassy carbon electrode modified with natural hydroxyapatite and β-cyclodextrin composite. Talanta 222:121550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121550
Tonle IK, Ngameni E, Tchieno FMM, Walcarius A (2015) Organoclay-modified electrodes: preparation, characterization and recent electroanalytical applications. J Solid State Electrochem 19:1949–1973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2728-0
Tseng YH, Kuo CS, Li YY, Huang CP (2009) Polymer-assisted synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticle. Mater Sci Eng C 29:819–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2008.07.028
Turk S, Altinsoy I, Efe G, Ipek M, Ozacar M, Bindal C (2019) Effect of Solution and Calcination Time on Sol-gel Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite. J Bionic Eng 16:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-019-0026-3
Xu T, Dai D, Jin Y (2020) Electrochemical sensing of lead (II) by differential pulse voltammetry using conductive polypyrrole nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 187:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4027-z
Yala S, Khireddine H, Sidane D, Ziane S, Bir F (2013) Surface modification of natural and synthetic hydroxyapatites powders by grafting polypyrrole. J Mater Sci 48:7215–7223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7538-8
Yang L, Zhao H, Li CP, Fan S, Li B (2015) Dual β-cyclodextrin functionalized Au@SiC nanohybrids for the electrochemical determination of tadalafil in the presence of acetonitrile. Biosens Bioelectron 64:126–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.08.068
Yin H, Zhou Y, Ai S, Liu X, Zhu L, Lu L (2010) Electrochemical oxidative determination of 4-nitrophenol based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a hydroxyapatite nanopowder. Microchim Acta 169:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0309-1
Youness AR, Taha MA, Elhaes H, Ibrahim M (2017) Molecular modeling FTIR spectral characterization and mechanical properties of carbonated-hydroxyapatite prepared by mechanochemical synthesis. Mater Chem Phys 190:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.01.004
Zhan F, Gao F, Wang X, Xie L, Gao F, Wang Q (2016) Determination of lead (II) by adsorptive stripping voltammetry using a glassy carbon electrode modified with β-cyclodextrin and chemically reduced graphene oxide composite. Microchim Acta 183:1169–1176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1754-2
Zhao HT, Ma S, Zheng SY, Han SW, Yao FX, Wang XZ, Wang SS, Feng K (2019) β–cyclodextrin functionalized biochars as novel sorbents for high-performance of Pb2+ removal. J Hazard Mater 362:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.027
Zhu G, Yi Y, Chen J (2016) Recent advances for cyclodextrin-based materials in electrochemical sensing. Trends Anal Chem 80:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.03.022
Acknowledgements
IKT acknowledges the support of the Alexander von Humboldt foundation (Germany).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was funded by the International Science Program (ISP, Sweden), via the support of the African Network of Electroanalytical Chemists (ANEC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rodrigue Tchoffo: data collection and formal analysis. Guy BP Ngassa: conceptualization and original draft writing. Giscard Doungmo: lab investigation. Arnaud T. Kamdem: data collection and analysis. Ignas K. Tonle: writing and editing, funding acquisition. Emmanuel Ngameni: project administration, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Weiming Zhang
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tchoffo, R., Ngassa, G.B.P., Doungmo, G. et al. Surface functionalization of natural hydroxyapatite by polymerization of β-cyclodextrin: application as electrode material for the electrochemical detection of Pb(II). Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 222–235 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15578-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15578-8