Abstract
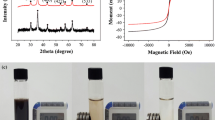
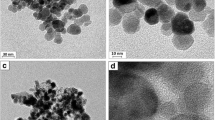
In this study, a magnetic metal–organic framework (MMOF) was synthesized and post-modified with poly(propyleneimine) dendrimer to fabricate a novel functional porous nanocomposite for adsorption and recovery of palladium (Pd(II)) from aqueous solution. The morphological and structural characteristics of the prepared material were identified by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Brunauer–Emmet–Teller (BET) isotherm, and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The results confirmed the successful synthesis and post-modification of MMOF. Semispherical shape particles (20–50 nm) with appropriate magnetic properties and a high specific surface area of 120 m2/g were obtained. An experimental design approach was performed to show the effect of adsorption conditions on Pd(II) uptake efficiency of the dendrimer-modified magnetic adsorbent. The study showed that the Pd(II) uptake on dendrimer-modified MMOF was well described by the Langmuir isotherm model with the highest uptake capacity of 291 mg/g under optimal condition (adsorbent content of 12.5 mg, Pd ion concentration of 80 ppm, pH = 4, and contact time of 40 min). The adsorption kinetics of Pd(II) ions was suggested to be a pseudo-first-order model. The results revealed a faster adsorption rate and higher adsorption capacity (about 43%) for dendrimer-modified MMOF. Finally, the reusability of the provided adsorbent was evaluated. This work provides a valuable strategy for designing and developing efficient magnetic adsorbents based on MOFs for the adsorption and recovery of precious metals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi J, Mahmoodi NM, Vossoughi M, Alemzadeh I (2019) Synthesis of magnetic metal-organic framework nanocomposite (ZIF-8@SiO2@MnFe2O4) as a novel adsorbent for selective dye removal from multicomponent systems. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 273:177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.06.040
Ayub S, Mohammadi AA, Yousefi M, Changani F (2019) Performance evaluation of agro-based adsorbents for the removal of cadmium from wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 142:293–299. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23455
Bagheri A, Taghizadeh M, Behbahani M, Asgharinezhad AA, Salarian M, Dehghani A, Ebrahimzadeh H, Amini MM (2012) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic metal-organic framework (MOF) as a novel sorbent, and its optimization by experimental design methodology for determination of palladium in environmental samples. Talanta 99:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.05.030
Baziar M, Zakeri HR, Ghalehaskar S, Nejad ZD, Shams M, Anastopoulos I, Giannakoudakis DA, Lima EC (2021) Metal-organic and zeolitic imidazole frameworks as cationic dye adsorbents: physicochemical optimizations by parametric modeling and kinetic studies. J Mol Liq 332(June):115832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115832
Chen G, Wang Y, Weng H, Wu Z, He K, Zhang P, Guo Z, Lin M (2019a) Selective separation of Pd(II) on pyridine-functionalized graphene oxide prepared by radiation-induced simultaneous grafting polymerization and reduction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(27):24560–24570. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b06162
Chen R, Tao CA, Zhang Z, Chen X, Liu Z, Wang J (2019b) Layer-by-layer fabrication of core-shell Fe3O4@UiO-66-NH2 with high catalytic reactivity toward the hydrolysis of chemical warfare agent simulants. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(46):43156–43165. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b14099
Daliran S, Ghazagh-Miri M, Oveisi AR, Khajeh M, Navalón S, Âlvaro M, Ghaffari-Moghaddam M, Delarami HS, García H (2020) A pyridyltriazol functionalized zirconium metal-organic framework for selective and highly efficient adsorption of palladium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(22):25221–25232. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c06672
Donia AM, Atia AA, Elwakeel KZ (2007) Recovery of gold(III) and silver(I) on a chemically modified chitosan with magnetic properties. Hydrometallurgy 87(3–4):197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2007.03.007
Dragan ES, Loghin DFA (2013) Enhanced sorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by semi-IPN composite cryogels with anionically modified potato starch entrapped in PAAm matrix. Chem Eng J 234:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.08.081
El Salam HMA, Zaki T (2018) Removal of hazardous cationic organic dyes from water using nickel-based metal-organic frameworks. Inorg Chim Acta 471:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2017.10.040
El-Shorbagy HG, El-Kousy SM, Elwakeel KZ, Abd El-Ghaffar MA (2021) Eco-friendly chitosan condensation adduct resins for removal of toxic silver ions from aqueous medium. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, April 100:410–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.04.029
Elwakeel KZ, El-Sayed GO, Darweesh RS (2013) Fast and selective removal of silver(I) from aqueous media by modified chitosan resins. Int J Miner Process 120:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2013.02.007
Elwakeel KZ, Al-Bogami AS, Guibal E (2021) 2-Mercaptobenzimidazole derivative of chitosan for silver sorption – contribution of magnetite incorporation and sonication effects on enhanced metal recovery. Chem Eng J 403(May 2020):126265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126265
Embaby MS, Elwany SD, Setyaningsih W, Saber MR (2018) The adsorptive properties of UiO-66 towards organic dyes: a record adsorption capacity for the anionic dye alizarin red S. Chin J Chem Eng 26(4):731–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2017.07.014
Far HS, Hasanzadeh M, Nashtaei MS, Rabbani M, Haji A, Moghadam BH (2020) PPI-dendrimer-functionalized magnetic metal-organic framework (Fe3O4@MOF@PPI) with high adsorption capacity for sustainable wastewater treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(22):25294–25303. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c04953
Guibal E, Von Offenberg Sweeney N, Vincent T, Tobin JM (2002) Sulfur derivatives of chitosan for palladium sorption. React Funct Polym 50(2):149–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-5148(01)00110-9
Hamedi A, Zarandi MB, Nateghi MR (2019) Highly efficient removal of dye pollutants by MIL-101(Fe) metal-organic framework loaded magnetic particles mediated by poly L-dopa. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 7(1):102882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102882
Hasanzadeh M, Simchi A, Far HS (2019) Kinetics and adsorptive study of organic dye removal using water-stable nanoscale metal organic frameworks. Mater Chem Phys 233(May):267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.05.050
Hasanzadeh M, Simchi A, Far HS (2020) Nanoporous composites of activated carbon-metal organic frameworks for organic dye adsorption: synthesis, adsorption mechanism and kinetics studies. J Ind Eng Chem 81:405–414
Hayati B, Arami M, Maleki A, Pajootan E (2015) Thermodynamic properties of dye removal from colored textile wastewater by poly (propylene imine) dendrimer. Desalin Water Treat 56:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.931529
Huang L, He M, Chen B, Bin H (2015) A designable magnetic MOF composite and facile coordination-based post-synthetic strategy for the enhanced removal of Hg2+ from water. J Mater Chem A 3(21):11587–11595. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta01484k
Huang L, He M, Chen B, Bin H (2016) A mercapto functionalized magnetic Zr-MOF by solvent-assisted ligand exchange for Hg2+ removal from water. J Mater Chem A 4(14):5159–5166. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta00343e
Huo J-B, Xu L, Chen X, Zhang Y, Yang J-CE, Yuan B, Ming-Lai F (2019) Direct epitaxial synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4@UiO-66 composite for efficient removal of arsenate from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 276(March):68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2018.09.017
Iqbal M, Iqbal N, Bhatti IA, Ahmad N, Zahid M (2016) Response surface methodology application in optimization of cadmium adsorption by shoe waste: a good option of waste mitigation by waste. Ecol Eng 88(March):265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.12.041
Kanani-Jazi MH, Akbari S, Kish MH (2020) Efficient removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by halloysite/poly(amidoamine) dendritic nano-hybrid materials: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Adv Powder Technol 31(9):4018–4030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.08.004
Kayal S, Chakraborty A (2018) Activated carbon (type Maxsorb-III) and MIL-101(Cr) metal organic framework based composite adsorbent for higher CH4 storage and CO2 capture. Chem Eng J 334:780–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.080
Khan NA, Khan SU, Ahmed S, Farooqi IH, Dhingra A, Hussain A, Changani F (2019) Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment: a review. Asian Journal of Water, Environment and Pollution 16(4):81–86. https://doi.org/10.3233/AJW190051
Khiarak BN, Hasanzadeh M, Mojaddami M, Far HS, Simchi A (2020) In situ synthesis of quasi-needle-like bimetallic organic frameworks on highly porous graphene scaffolds for efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation. Chem Commun 56(21):3135–3138. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc09908e
Kousha M, Daneshvar E, Esmaeli AR, Jokar M, Khataee AR (2012) Optimization of acid blue 25 removal from aqueous solutions by raw , esterified and protonated Jania adhaerens biomass. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 69:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.01.007
Krawczyk M, Akbari S, Jeszka-Skowron M, Pajootan E, Fard FS (2016) Application of dendrimer modified halloysite nanotubes as a new sorbent for ultrasound-assisted dispersive micro-solid phase extraction and sequential determination of cadmium and lead in water Samples. J Anal At Spectrom 31(7):1505–1514. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ja00096g
Li J, Wang S, Wang F, Xuran W (2019) Environmental separation and enrichment of gold and palladium ions by amino-modified three-dimensional graphene. RSC Adv 9(5):2816–2821. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra10506e
Li L, Xu Y, Zhong D, Zhong N (2020a) CTAB-surface-functionalized magnetic MOF@MOF composite adsorbent for Cr(VI) efficient removal from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 586(Vi):124255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124255
Li Y, Wang Y, He L, Meng L, Lu H, Li X (2020b) Preparation of poly(4-vinylpyridine)-functionalized magnetic Al-MOF for the removal of naproxen from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 383(August 2019):121144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121144
Lim CR, Lin S, Yun YS (2020) Highly efficient and acid-resistant metal-organic frameworks of MIL-101(Cr)-NH2 for Pd(II) and Pt(IV) recovery from acidic solutions: adsorption experiments, spectroscopic analyses, and theoretical computations. J Hazard Mater 387(Ii):121689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121689
Lima EC, Hosseini-bandegharaei A, Moreno-piraján JC, Anastopoulos I (2019) A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van â€TM T Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J Mol Liq 273:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.048
Lin S, Bediako JK, Cho CW, Song MH, Zhao Y, Kim JA, Choi JW, Yun YS (2018) Selective adsorption of Pd(II) over interfering metal ions (Co(II), Ni(II), Pt(IV)) from acidic aqueous phase by metal-organic frameworks. Chem Eng J 345(March):337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.173
Lin S, Zhao Y, Bediako JK, Cho CW, Sarkar AK, Lim CR, Yun YS (2019) Structure-controlled recovery of palladium(II) from acidic aqueous solution using metal-organic frameworks of MOF-802, UiO-66 and MOF-808. Chem Eng J 362(October 2018):280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.044
Liu Y, Liu YJ (2008) Biosorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Sep Purif Technol 61(3):229–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2007.10.002
Liu L, Li C, Bao C, Jia Q, Xiao P, Liu X, Zhang Q (2012) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/graphene oxide composites for the adsorption of Au(III) and Pd(II). Talanta 93:350–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.02.051
Liu J, Zeng M, Ronghai Y (2016) Surfactant-free synthesis of octahedral ZnO / ZnFe 2 O 4 heterostructure with ultrahigh and selective adsorption capacity of malachite green. Nat Publ Group 2015:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25074
Liu Q, Deng CH, Sun N (2018) Hydrophilic tripeptide-functionalized magnetic metal-organic frameworks for the highly efficient enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Nanoscale 10(25):12149–12155. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr03174f
Mergola L, Stomeo T, Del Sole R (2020) Synthesis of photoswitchable submicroparticles and their evaluation as ion-imprinted polymers for Pd(II) uptake. Polym J 52(7):743–754. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-020-0319-8
Mincke S, Asere TG, Verheye I, Folens K, Vanden Bussche F, Lapeire L, Verbeken K, Van Der Voort P (2019) Functionalized chitosan adsorbents allow recovery of palladium and platinum from acidic aqueous solutions. Green Chem 21(9):2295–2306. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC00166B
Moawed EA, El-Hagrasy MA, Kamal M, El-Shahat MF (2016) Recovery and determination of palladium from its alloys using iminodiacetic polyurethane/carbon nanofibers sorbent. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 39(8):415–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2016.1169428
Moghadam BH, Hasanzadeh M, Simchi A (2020) Self-powered wearable piezoelectric sensors based on polymer nanofiber-metal-organic framework nanoparticle composites for arterial pulse monitoring. ACS Applied Nano Materials 3(9):8742–8752. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c01551
Moghaddam H, Masoumeh RN, Dehghani MH, Akbarpour B, Azari A, Yousefi M (2019) Performance investigation of zeolitic imidazolate framework – 8 (ZIF-8) in the removal of trichloroethylene from aqueous solutions. Microchem J 150(August):104185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104185
Mohammad N, Hayati B, Arami M, Lan C (2011) Adsorption of textile dyes on pine cone from colored wastewater : kinetic , equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Desalination 268(1–3):117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.007
Molavi H, Shojaei A, Pourghaderi A (2018) Rapid and Tunable Selective adsorption of dyes using thermally oxidized nanodiamond. J Colloid Interface Sci 524:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.03.088
Myers RH, Montgomery DC, Anderson-cook CM (2009) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. John Wiley and Sons, USA
Nagarjuna R, Shivani S, Rajesh N, Ganesan R (2017) Effective adsorption of precious metal palladium over polyethyleneimine-functionalized alumina nanopowder and its reusability as a catalyst for energy and environmental applications. ACS Omega 2(8):4494–4504. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b00431
Natale F, Di M, Orefice FLM, Erto A, Lancia A (2017) Unveiling the potentialities of activated carbon in recovering palladium from model leaching solutions. Sep Purif Technol 174:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.10.022
Oladipo AA, Gazi M, Saber-samandari S (2014) Adsorption of anthraquinone dye onto eco-friendly semi-IPN biocomposite hydrogel : equilibrium isotherms, kinetic studies and optimization. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45(2):653–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.07.013
Parajuli D, Kawakita H, Inoue K, Funaoka M (2006) Recovery of gold(III), palladium(II), and platinum(IV) by aminated lignin derivatives. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(19):6405–6412. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0603518
Qiu J, Feng Y, Zhang X, Jia M, Yao J (2017) Acid-promoted synthesis of UiO-66 for highly selective adsorption of anionic dyes: adsorption performance and mechanisms. J Colloid Interface Sci 499(March):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.03.101
Ramesh A, Hasegawa H, Sugimoto W, Maki T, Ueda K (2008) Adsorption of gold(III), platinum(IV) and palladium(II) onto glycine modified crosslinked chitosan resin. Bioresour Technol 99(9):3801–3809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.07.008
Senosy IA, Lu ZH, Abdelrahman TM, Yang MNO, Guo HM, Yang ZH, Li JH (2020) The post-modification of magnetic metal-organic frameworks with β-cyclodextrin for the efficient removal of fungicides from environmental water. Environmental Science: Nano 7(7):2087–2101. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en01372e
Sharifi S, Nabizadeh R, Akbarpour B, Azari A, Ghaffari HR, Nazmara S, Mahmoudi B, Shiri L, Yousefi M (2019) Modeling and optimizing parameters affecting hexavalent chromium adsorption from aqueous solutions using Ti-XAD7 nanocomposite: RSM-CCD approach, kinetic, and isotherm studies. J Environ Health Sci Eng 17(2):873–888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00405-7
Sharma S, Wu CM, Koodali RT, Rajesh N (2016) An ionic liquid-mesoporous silica blend as a novel adsorbent for the adsorption and recovery of palladium ions, and its applications in continuous flow study and as an industrial catalyst. RSC Adv 6(32):26668–26678. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra26673d
Wu MX, Gao J, Wang F, Yang J, Song N, Jin X, Mi P, Tian J, Luo J, Liang F, Yang Y-W (2018) Multistimuli responsive core–shell nanoplatform constructed from Fe3O4@MOF equipped with Pillar[6]arene nanovalves. Small 14(17):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201704440
Yang J, Zhang Z, Pang W, Chen H, Yan G (2019) Polyamidoamine dendrimers functionalized magnetic carbon nanotubes as an efficient adsorbent for the separation of flavonoids from plant extraction. Sep Purif Technol 227(March):115710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115710
Yen CH, Lien HL, Chung JS, Der Yeh H (2017) Adsorption of precious metals in water by dendrimer modified magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 322(February):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.029
Yi Q, Fan R, Xie F, Zhang Q, Luo Z (2016) Recovery of palladium(II) from nitric acid medium using a natural resin prepared from persimmon dropped fruits residues. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 61:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.01.009
Zhang B, Likang F, Wang S, Zhang L (2018) Adsorption of palladium(II) from aqueous solution using nanosilica modified with imidazoline groups. Mater Chem Phys 214(Ii):533–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.04.120
Zhang W, Hu L, Hu S, Yang L (2019) Optimized synthesis of novel hydrogel for the adsorption of copper and cobalt ions in wastewater. RSC Adv 9(28):16058–16068. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra00227h
Zhang X, Wang J, Dong XX, Lv YK (2020) Functionalized metal-organic frameworks for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in environment. Chemosphere 242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125144
Zhao X, Liu S, Tang Z, Niu H, Cai Y, Meng W, Wu F, Giesy JP (2015) Synthesis of magnetic metal-organic framework (MOF) for efficient removal of organic dyes from water. Sci Rep 5(July):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11849
Zhou L, Liu J, Liu Z (2009) Adsorption of platinum(IV) and palladium(II) from aqueous solution by thiourea-modified chitosan microspheres. J Hazard Mater 172(1):439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.030
Zhou L, Xu J, Liang X, Liu Z (2010) Adsorption of platinum(IV) and palladium(II) from aqueous solution by magnetic cross-linking chitosan nanoparticles modified with ethylenediamine. J Hazard Mater 182(1–3):518–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.06.062
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Funding
MH thanks the Iran National Elites Foundation (INEF, Grant No. 15-89661) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hossein Shahriyari Far: investigation, methodology, visualization, and writing: original draft. Mahdi Hasanzadeh: conceptualization, supervision, resources, formal analysis, funding acquisition, project administration, and writing — review and editing. Mohammad Shabani Nashtaei: investigation, methodology, and visualization. Mahboubeh Rabbani: conceptualization, supervision, resources, formal analysis, and validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent forpublication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Magnetic hysteresis loops, comparison of experimental and predicted Pd(II) uptake, Langmuir, Freundlich, and Tempkin isotherm plots, regeneration cycles of adsorbents, structural stability of magnetic adsorbent, experimental results of Pd (II) uptakes, and ANOVA table.
ESM 1
(DOC 587 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Far, H.S., Hasanzadeh, M., Nashtaei, M.S. et al. Fast and efficient adsorption of palladium from aqueous solution by magnetic metal–organic framework nanocomposite modified with poly(propylene imine) dendrimer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 62474–62486 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15144-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15144-2