Abstract
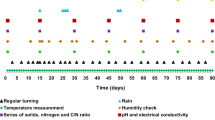
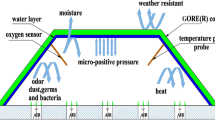
Little is known about the effect of adding crude glycerin (CG) as a carbon source during the composting of agro-industrial residues, such as those generated in the swine production chain, especially concerning the impact on organic matter humification. Therefore, the aim of this work was to study the effect of adding crude glycerin during the composting of organic swine waste, using appropriate analyses to determine the degree of maturation of the organic material. The experiment was performed using composters constructed from pallets. The variables considered were temperature, mass, volume, organic matter, functional groups, carboxylic acids, pH, electrical conductivity, total organic carbon, total Kjeldahl nitrogen, total phosphorus, potassium, basal respiration, and germination index. For all the CG concentrations tested, thermophilic temperatures were reached, while higher amounts of CG (4.5 and 6.0%) maintained temperatures above 55 °C for longer periods (28 days). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis showed the presence of an aromatic stretching vibration signal at 1620 cm−1, confirming mineralization of the organic matter, while the decrease of carboxylic acids at the end of the composting period indicated stabilization. The organic composts presented high nutrient contents and absence of toxicity, indicating that they could be safely used in agriculture.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Aguelmous A, El Fels L, Souabi S, Zamama M, Lahsaini S, Lebrihi A, Bekkaoui F, Hafidi M (2020) Humification process and total petroleum hydrocarbons assessment during oily sludge composting. Waste Biomass Valorization 11:6625–6635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-00941-6
Agyarko-Mintah E, Cowie A, Singh BP, Joseph S, Zwieten LV, Cowie A, Harden S, Smillie R (2017) Biochar increases nitrogen retention and lowers greenhouse gas emissions when added to composting poultry litter. Waste Manag 61:138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.11.027
Alburquerque JA, Gonzálvez J, Tartosa GA, Cegarra J (2009) Evaluation of “alperujo” composting based on organic matter degradation, humification and compost quality. Biodegradation 20:257–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-008-9218-y
Alvares CA, Stape JL, Sentelhas PC, de Moraes Gonçalves JL, Sparovek G (2014) Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol Z 22:711–728. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2013/0507
Asses N, Farhat A, Cherif S, Hamdi M, Bouallagui H (2018) Comparative study of sewage sludge co-composting with olive mill wastes or green residues: process monitoring and agriculture value of the resulting composts. Process Saf Environ Prot 114:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.12.006
Asses N, Farhat W, Hamdi M, Bouallagui H (2019) Large scale composting of poultry slaughterhouse processing waste: Microbial removal and agricultural biofertilizer application. Process Saf Environ Prot 124:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.02.004
Awasthi MK, Awasthi SK, Wang Q, Wang Z, Lahori AH, Ren X, Chen H, Wang M, Zhao J, Zhang Z (2018) Influence of biochar on volatile fatty acids accumulation and microbial community succession during biosolids composting. Bioresour Technol 251:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.037
Baskar G, Gurugulladevi A, Nishanthini T, Aiswarya R, Tamilarasan K (2017) Optimization and kinetics of biodiesel production from Mahua oil using manganese doped zinc oxide nanocatalyst. Renew Energy 103:641–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.10.077
Bernal MP, Alburquerque JA, Moral R (2009) Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour Technol 100:5444–5453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.11.027
Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation EMBRAPA (1999) Manual of chemical analysis of soils, plants and fertilizers. Embrapa Soils/Embrapa Computing/Embrapa Agriculture. Communication for Technology Transfer, Brasília, 370p. (In Portuguese).
Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics IBGE (2020) Growth in the slaughter of cattle, pigs and poultry in 2019. Accessed 17 April 2020. https://agenciadenoticias.ibge.gov.br/ agencia-sala-de-imprensa/2013-agencia-de-noticias/releases/27167-em-2019-cresce-o-abate-de-bovinos-suinos-e-frangos. (In Portuguese).
Bustamante MA, Paredes C, Marhuenda-Egea FC, Pérez-Espinosa A, Bernal MP, Moral R (2008) Co-composting of distillery wastes with animal manures: carbon and nitrogen transformations in the evaluation of compost stability. Chemosphere 72:551–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.03.030
Canellas LP, Rumjanek VM (2005) Distribution of organic matter and characteristics of humic acids in soils with additions of residues of urban origin. Pesq Agropec Brasil 36:1529–1538. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2001001200010 (In Portuguese)
Caunii A, Cuciureanu R, Zakar AM, Tonea E, Giuchici C (2010) Chemical composition of common leafy vegetables. Stud Univ 20:45–48
Chen H, Awasthi SK, Liu T, Duan Y, Ren X, Zhang Z, Pandey A, Awasthi MK (2020) Effects of microbial culture and chicken manure biochar on compost maturity and greenhouse gas emissions during chicken manure composting. J Hazard Mater 398:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121908
Chiarelotto M, Damaceno FM, Lorin HEF, Tonial LA, Costa LAM, Bustamante MA, Moral R, Marhuenda-Egea FC, Costa MSSM (2019) Reducing the composting time of broiler agro-industrial wastes: The effect of process monitoring parameters and agronomic quality. Waste Manag 96:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.07.012
Costa MSSM, Cestonaro T, Costa LAM, Rozatti MAT, Carneiro LJ, Pereira DC, Lorin HEF (2015) Improving the nutrient content of sheep bedding compost by adding cattle manure. J Clean Prod 86:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.08.093
Costa MSSM, Bernardi FH, Costa LAM, Pereira DC, Lorin HEF, Rozatti MAT (2017) Composting as a cleaner strategy to broiler agro-industrial wastes: selecting carbon source to optimize the process and improve the quality of the final compost. J Clean Prod 142:2084–2092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.11.075
Cunha-Queda ACF, Vallini G, Bruno de Sousa RFX, Almeida Duarte ECNF (2003) Study of the evoluation of enzymatic activities during the compositn of residues from horticultural and fruit markets. An Inst Super Agron:193–208 In Portuguese
Dick DP, Knicker H, Ávila LG, Inda JRAV, Giasson E, Bissani CA (2006) Organic matter in constructed soils from a coal mining area in southern Brazil. Org Geochem 37:1537–1545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2006.06.017
Dores-Silva PR, Landgraf MD, Rezende MO (2013) Processo de estabilização de resíduos orgânicos: vermicompostagem versus compostagem. Quím Nova 36:640–645. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422013000500005 In Portuguese
Duan Y, Awasthi SK, Liu T, Zhang Z, Awasthi MK (2019) Response of bamboo biochar amendment on volatile fatty acids accumulation reduction and humification during chicken manure composting. Bioresour Technol 291:1218–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121845
El Glauoi GEM, El Hayany B, El Fels L, El Faiz A, Ezzariai A, Rihani M, Lebrihi A, Bekkaoui F, Hafidi M (2020) Physico-chemical and spectroscopy assessment of sludge biodegradation during semi-industrial composting under semi-arid climate. Waste Biomass Valoriz 11:1217–1228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0442-3
Fan YV, Lee CT, Klemeš JJ, Chua LS, Sarmidi MR, Leow CW (2017) Evaluation of Effective microorganisms on home scale organic waste composting. J Environ Manag 216:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.019
Fehmberger C, dos Santos FT, Aloisio CM, Hermes E, Zenatti DC, Bautitz IR (2020) Effectiveness of incorporation of crude glycerin as a source of labile carbono in the composting of poultry production residues. J Clean Prod 251:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119739
Fialho LL, Silva WTL, Milori DMBP, Martin-Neto L, Saab SC (2010) Lignin interference in the quantification of free radicals in the composting process. Quím Nova 33:364–369. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422010000200024 In Portuguese
Garcia-Gomez A, Roig A, Bernal MP (2003) Composting of the solid fraction of olive mill wastewater with olive leaves: organic matter degradation and biological activity. Bioresour Technol 86:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00106-2
Gavilanes-Terán I, Jara-Samaniego J, Idrovo-Novillo J, Bustamante MA, Moral R, Paredes C (2016) Windrow composting as horticultural waste management strategy—a case study in Ecuador. Waste Manag 48:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.11.026
Hachicha R, Hachicha S, Trabelsi I, Woodward S, Mechichi T (2009) Evolution of the fatty fraction during co-composting of olive oil industry wastes animal manure: Maturity assessment of the end product. Chemosphere 75:382–1386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.02.064
Hajjari M, Tabatabaei M, Aghbashlo M, Ghanavati H (2017) A review on the prospects of sustainable biodiesel production: a global scenario with an emphasis on waste-oil biodiesel utilization. Renew Sust Energ Rev 72:445–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.034
Haron R, Mat R, Abdullah TAT, Rahman RA (2018) Overview on utilization of biodiesel by-product for biohydrogen production. J Clean Prod 172:314–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.160
Huang GF, Wu QT, Wong JWC, Nagar BB (2006) Transformation of organic matter during co-composting of pig manure with sawdust. Bioresour Technol 97:1834–1842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.08.024
Jiang J, Wang Y, Guo F, Zhang X, Dong W, Zhang X, Zhang X, Zhang C, Cheng K, Li Y, Zhu G (2020) Composting pig manure and sawdust with urease inhibitor: succession of nitrogen functional genes and bacterial community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:36160–36171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09696-y
Jouraiphy A, Amir S, Gharous M, Revel JC, Hafidi M (2005) Chemical and spectroscopic analysis of organic matter transformation during composting of sewage sludge and green plant waste. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 56:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2005.06.002
Jurado MM, Suarez-Estrella F, Vargas-García MC, Lopez MJ, Lopez-Gonzalez JA, Moreno J (2014) Increasing native microbiota in lignocellulosic waste composting: effects on process efficiency and final product maturity. Process Biochem 49:1958–1969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.08.003
Kiehl EJ (2010) New organic fertilizers. Degaspari, Piracicaba (In Portuguese)
Kong Z, Wang X, Liu Q, Li T, Chen X, Chai L, Liu D, Shen Q (2018) Evolution of various fractions during the windrow composting of chicken manure with rice chaff. J Environ Manag 207:366–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.023
Kramer RW, Kujawinski EB, Hatcher PG (2004) Identification of black carbon derived structures in a volcanic ash soil humic acid by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 38:3387–3395. https://doi.org/10.1021/es030124m
Kulikowska D, Sindrewicz S (2018) Effect of barley straw and coniferous bark on humification process during sewage sludge composting. Waste Manag 79:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.07.042
Lazaro CZ, Vich DV, Hirasawa JS, Varesche MBA (2012) Hydrogen production and consumption of organic acids by a phototropic microbial consortium. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:11691–11700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.05.088
Lee MH, Han SJ, Lee YK, Ike IA, Ok YS, Hur J (2020) Enhancing copper binding property of compost-derived humic substances by biochar amendment: further insight from two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy. J Hazard Mater 390:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121128
Li H, Zhang T, Tsang DCW, Li G (2020) Effects of external additives: biochar, bentonite, phosphate, on co-composting for swine manure and corn straw. Chemosphere 248:12592–12597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125927
Liu B, Li Y, Zhang X, Feng C, Gao M, Shen Q (2015) Effects of composting process on the dissipation of extractable sulfonamides in swine manure. Bioresour Technol 175:284–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.098
Liu H (2019) Biochar is conductive to reduce thermal loss caused by mechanical turning during swine manure composting. Bioresour Technol 290:121810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121810
Malavolta E, Vitti GC, Oliveira AS (1997) Assessment of the nutritional status of plants. Potafos, Piracicaba In Portuguese
Matos AT (2014) Treatment and agricultural use of solid waste. UFV, Viçosa In Portuguese
Meng L, Li W, Zhang S, Wu C, Wang K (2016) Effects of sucrose amendment on ammonia assimilation during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour Technol 210:160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.094
Orrico Junior MAP, Orrico ACA, Fava AF, Sunada NS, Schwingel AW, Garcia RG, Borquis RRA (2018) Crude glycerin in co-composting with laying hen manure reduces N losses. Sci Agric 75:361–367. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-992x-2016-0478
Pachapur VL, Sarma SJ, Brar SK, Bihan YL, Buelna G, Verma M (2018) Energy balance of hydrogen production from wastes of biodiesel production. Biofuels 9:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2016.1153361
Pang W, Dejia H, Nowar EE, Chen H, Zhang J, Zhang G, Li Q, Wang S (2020) The influence on carbon, nitrogen recycling, and greenhouse gas emissions under different C/N ratios by black soldier fly. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:42767–42777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09909-4
Paredes C, Roig A, Bernal MP, Sanchez-Monedero MA, Cegarra J (2000) Evolution of organic matter and nitrogen during co-composting of olive mill wastewater with solid organic wastes. Biol Fertil Soils 32:222–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000239
Penteado ED, Lazaro CZ, Sakamoto IK, Zaiat M (2013) Influence of seed sludge and pretreatment method on hydrogen Production in packed-bed anaerobic reactors. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:6137–6145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.01.067
Schwingel AW, Orrico ACA, Lucas Junior J, Orrico Junior MAP, Borquis RRA, Fava AF (2019) Laying hen manure in anaerobic co-digestion with glycerin containing different glycerol and impurity levels. J Clean Prod 215:1437–1444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.125
Silva RR, Silva MLN, Cardoso EL, Moreira FMS, Curi N, Alovisi AMT (2010) Biomassa e atividade microbiana em solo sob diferentes sistemas de manejo na região fisiográfica campos das Vertentes – MG. Rev Brasil Ciên Solo 34:1585–1592. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832010000500011 In Portuguese
Silva EMB, Frigo GR, Bezerra MDL, Santos CSA, Sousa HHF, Silva TJA (2015) Adubação fosfatada em rúcula: produção e eficiência no uso da água. Agrociências 6:1–11 In Portuguese
Smidt E, Meissl K (2007) The applicability of Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy in waste management. Waste Manag 27:268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.01.016
Stevenson FJ (1994) Humus Chemistry: genesis, composition, reactions. John Wiley, New York
Takane RJ, Siqueira PTV, Kampf NA (2012) Técnica de preparo de substratos para aplicação em hortaliças. LK Editora, Brasília, p 100 In Portuguese
Valente BS, Xavier EG, Morselli TBGA, Jahnke DS, Brum Junior BS, Cabrera BR, Moraes PO, Lopes DCN (2009) Factors affecting the development of organic waste composting. Archiv Zootec 58 In Portuguese
Veroneze ML, Schwantes D, Gonçalves AC Jr, Richart A, Manfrin J, Schiller AP, Schuba TB (2019) Production of biogas and biofertilizer using anaerobic reactors with swine manure and glycerin doses. J Clean Prod 213:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.181
Wang C, Tu Q, Dong D, Strong PJ, Wang H, Sun B, Wu W (2014) Spectroscopic evidence for biochar amendment promoting humic acid synthesis and intensifying humification during composting. J Hazard Mater 280:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.030
Wang K, Mao H, Wang Z, Tian Y (2018a) Succession of organics metabolic function of bacterial community in swine manure composting. J Hazard Mater 360:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.032
Wang K, Chu C, Li X, Wang W, Ren N (2018b) Succession of bacterial community function in cow manure composting. Bioresour Technol 267:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.06.028
Wang J, Gu J, Wang X, Song Z, Dai X, Guo H, Yu J, Zhao W, Lei L (2021) Enhanced removal of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements during swine manure composting inoculated with mature compost. J Hazard Mater 411:125135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125135
Wu N, Xie S, Zeng M, Xu X, Li Y, Liu X, Wang X (2020) Impacts of pile temperature on antibiotic resistance, metal resistance and microbial community during swine manure composting. Science of The Total Environment 744:140920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140920
Wu S, He H, Inthapanya X, Yang C, Lu L, Zeng G, Han Z (2017) Role of biochar on composting of organic wastes and remediation of contaminated soils—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:16560–16577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9168-1
Yu H, Xie B, Khan R, Shen G (2019) The changes in carbono, nitrogen, components and humic substances during organic-inorganic aerobic co-composting. Bioresour Technol 271:228–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.088
Zhang L, Sun X (2016) Influence of bulking agents on physical, chemical, and microbiological properties during the two-stage composting of green waste. Waste Manag 48:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.11.032
Zhang C, Liu L, Zhao M, Rong H, Xu Y (2018a) The environmental characteristics and applications of biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:21525–21534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2521-1
Zhang R, Gu J, Wang X, Li Y, Zhang K, Yin Y, Zhang X (2018b) Contributions of the microbial community and environmental variables to antibiotic resistance genes during co-composting with swine manure and cotton stalks. J Hazard Mater 358:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.06.052
Zhou Q, Zhang H, Chang F, Li H, Pan H, Xue W, Hu D, Yang S (2015) Nano La2O3 as a heterogeneous catalyst for biodiesel synthesis by transesterification of Jatropha curcas L. oil. J Ind Eng Chem 31:385–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.07.013
Zhu F, Pan Z, Hong C, Wang W, Chen X, Zhiyong Xue Z, Yao Y (2016) Analysis of volatile organic compounds in compost samples: a potential tool to determine appropriate composting time. Waste Manag 58:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.06.021
Zucconi F, Pera A, Forte M, De Bertoldi M (1981) Evaluating toxicity of immature compost. BioCycle 22:54–57
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of the Coordination of Improvement of Higher Education Personnel—Brazil (CAPES)—Financing Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FTDS: presented the idea of the work; proposed the methodology; collected, analyzed, and interpreted the data obtained; and was one of the main contributors in the writing of the manuscript. CF: collected, analyzed, and interpreted the data obtained. CMA: collected, analyzed, and interpreted the data obtained. IRB: obtained the necessary resources for the execution of the research, supervised the project, interpreted the data obtained, and was one of the main contributors in the writing of the manuscript. EH: obtained the necessary resources to carry out the research, supervised the project, interpreted the data obtained, and was one of the main contributors in the writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos, F.T.D., Fehmberger, C., Aloisio, C.M. et al. Composting of swine production chain wastes with addition of crude glycerin: organic matter degradation kinetics, functional groups, and carboxylic acids. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 50542–50553 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14063-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14063-6