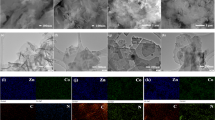
Abstract
Organic ZnCr-LDH (ST-LDH) was synthesized by a facile one-step hydrothermal technique using methyl orange (MO) as a soft template agent, which can efficiently remove methyl orange (MO), Congo red (CR), and orange II (OII) from aqueous solution. The microstructure of ST-LDH by modifying changed obviously, from the cellular structure to the stacking structure formed by the face-face contact of hydrotalcite nanosheets, which resulted in much more exchangeable nitrate ions to remain in the interlayer space. The pre-insertion of benzene sulfonate as a pillar expanded the interlayer gallery, which facilitated the pollutant anions (MO, CR, and OII) into the interlayer of LDH in the subsequent adsorption process. The maximum adsorption capacity of ST-LDH for MO, CR, and OII was 4200.8 mg/g, 1252.0 mg/g, and 1670.6 mg/g, respectively, which is approximately 1.86 times, 1.8 times, and 2.32 times that of the pristine NO3-LDH, respectively. The removal mechanism of anionic dyes was determined as anion exchange between NO3− anions and dye molecules. The adsorption behavior for MO and OII is multilayer adsorption, while the adsorption behavior for CR is monolayer adsorption. The adsorption process mainly was controlled by the chemical bonding between the dye molecules and adsorbent active sites. The LDH can be effectively regenerated by photocatalysis after MO adsorption. The ST-LDH has a great potential to be used as a high-efficient adsorbent to remove anionic dyes from aqueous solution.
Graphical abstract

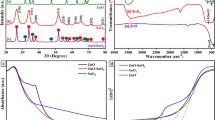
The schematic illustration of the synthetic process of soft template agent modified and unmodified hydrotalcites by one-pot hydrothermal method and the adsorption process of MO by ST-LDH were shown in Fig. 12. Modified hydrotalcite (ST-LDH) was prepared using methyl orange (MO) as a soft template agent. Compared with unmodified hydrotalcite (NO3-LDH), the insertion of benzene sulfonate anions into the hydrotalcite layer resulted in the increase of the interlayer spacing from 8.269 to 8.654Å. The LDH host structure pre-intercalated by benzene sulfonate anions evolved into pillared materials in interlayer; benzene sulfonate anions as a column expanded the interlayer spacing of (003) base plane, which facilitated the pollutant anions (MO, CR, and OII) into the interlayer of ST-LDH and exchanged with NO3− anion in the subsequent adsorption process. It can be inferred that in the process of modification hydrotalcite by benzene sulfonate, a small amount of benzene sulfonate anions pre-inserted into the gallery of hydrotalcite with a monolayer model in the process of hydrotalcite modification, and its inclination angle is calculated to be about 29.1°. After ST-LDH sample adsorbed the MO molecules, dye molecules intercalated into the LDH host, and successful exchange with NO3− anions, the d003 value increased to 24.78 Å. A large amount of MO− anions were intercalated into the gallery of ST-LDH with a bilayer model according to the Freundlich isotherm model, and the tilting angle increases to 53.6°. The adsorption capacity of MO by ST-LDH was significantly enhanced to 4200.8 mg/g, which was much higher than that of NO3-LDH (2252.8 mg/g). Schematic illustration of the synthetic process of LDH materials and adsorption process of MO by ST-LDH.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Costa FR, Leuteritz A, Wagenknecht U, Auf der Landwehr M, Jehnichen D, Haeussler L, Heinrich G (2009) Alkyl sulfonate modified LDH: effect of alkyl chain length on intercalation behavior, particle morphology and thermal stability. Appl Clay Sci 44:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2008.12.020
Darmograi G, Prelot B, Layrac G, Tichit D, Martin-Gassin G, Salles F, Zajac J (2015) Study of adsorption and intercalation of orange-type dyes into Mg–Al layered double hydroxide. J Phys Chem C 119:23388–23397. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b05510
Dinari M, Momeni MM, Ghayeb Y (2016) Photodegradation of organic dye by ZnCrLa-layered double hydroxide as visible-light photocatalysts. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27:9861–9869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5054-8
Dogan M, Karaoglu MH, Alkan M (2009) Adsorption kinetics of maxilon yellow 4GL and maxilon red GRL dyes on kaolinite. J Hazard Mater 165:1142–1151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.101
Dong W, Ding J, Wang W, Zong L, Xu J, Wang A (2020a) Magnetic nano-hybrids adsorbents formulated from acidic leachates of clay minerals. J Clean Prod 256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120383
Dong W, Lu Y, Wang W, Zhang M, Jing Y, Wang A (2020b) A sustainable approach to fabricate new 1D and 2D nanomaterials from natural abundant palygorskite clay for antibacterial and adsorption. Chem Eng J 382:122984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122984
El Khanchaoui A, Sajieddine M, Mansori M, Essoumhi A (n.d.) Anionic dye adsorption on ZnAl hydrotalcite-type and regeneration studies based on "memory effect". Int J Environ Anal Chem 19. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1772769
Elmoubarki R, Mahjoubi FZ, Tounsadi H, Moustadraf J, Abdennouri M, Zouhri A, el Albani A, Barka N (2015) Adsorption of textile dyes on raw and decanted Moroccan clays: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Water Resources and Industry 9:16–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2014.11.001
Gao W, Zhao S, Wu H, Deligeer W, Asuha S (2016) Direct acid activation of kaolinite and its effects on the adsorption of methylene blue. Appl Clay Sci 126:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.03.006
Gao J, Lu Y, Fang L, Wu F, Ling F, Guan T, Shi L, Hu B, Meng F (2018) Efficient removal of methyl orange and heavy metal ion from aqueous solution by NiFe-Cl-layered double hydroxide. Environ Eng Sci 35:373–381. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2017.0023
Géraud E, Bouhent M, Derriche Z, Leroux F, Prévot V, Forano C (2007) Texture effect of layered double hydroxides on chemisorption of orange II. J Phys Chem Solids 68:818–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2007.02.053
Guo X, Yin P, Yang H (2018) Superb adsorption of organic dyes from aqueous solution on hierarchically porous composites constructed by ZnAl-LDH/Al(OH)3 nanosheets. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 259:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.10.003
Jiehu C et al (2020) 2D to 3D controllable synthesis of three Zn-Co-LDHs for rapid adsorption of MO by TEA-assisted hydrothermal method. Appl Surf Sci 534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147564
Jing C, Chen Y, Zhang X, Guo X, Liu X, Dong B, Dong F, Zhang X, Liu Y, Li S, Zhang Y (2019) Low carbonate contaminative and ultrasmall NiAl LDH prepared by acid salt treatment with high adsorption capacity of methyl orange. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:11985–11998. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b01706
Kausar A, Iqbal M, Javed A, Aftab K, Nazli Z-i-H, Bhatti HN, Nouren S (2018) Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: a review. J Mol Liq 256:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.034
Kloprogge JT, Hickey L, Frost RL (2004) The effects of synthesis pH and hydrothermal treatment on the formation of zinc aluminum hydrotalcites. J Solid State Chem 177:4047–4057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2004.07.010
Kloprogge JT, Hickey L, Frost RL (2005) The effect of varying synthesis conditions on zinc chromium hydrotalcite: a spectroscopic study. Mater Chem Phys 89:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.08.035
Ko SJ, Yamaguchi T, Salles F, Oh JM (2021) Systematic utilization of layered double hydroxide nanosheets for effective removal of methyl orange from an aqueous system by pi-pi stacking-induced nanoconfinement. J Environ Manag 277:111455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111455
Lei C, Zhu X, Zhu B, Jiang C, Le Y, Yu J (2017) Superb adsorption capacity of hierarchical calcined Ni/Mg/Al layered double hydroxides for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. J Hazard Mater 321:801–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.070
Lei S, Wang S, Gao B, Zhan Y, Zhao Q, Jin S, Song G, Lyu X, Zhang Y, Tang Y (2020) Ultrathin dodecyl-sulfate-intercalated Mg-Al layered double hydroxide nanosheets with high adsorption capability for dye pollution. J Colloid Interface Sci 577:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.05.050
Li AY, Deng H, Ye CH, Jiang YH (2020a) Fabrication and characterization of novel ZnAl-layered double hydroxide for the superadsorption of organic contaminants from wastewater. ACS Omega 5:15152–15161. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c01092
Li J, Yu H, Zhang X, Zhu R, Yan L (2020b) Crosslinking acrylamide with EDTA-intercalated layered double hydroxide for enhanced recovery of Cr(VI) and Congo red: adsorptive and mechanistic study. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1229-x
Li M, Wu G, Liu Z, Xi X, Xia Y, Ning J, Yang D, Dong A (2020c) Uniformly coating ZnAl layered double oxide nanosheets with ultra-thin carbon by ligand and phase transformation for enhanced adsorption of anionic pollutants. J Hazard Mater 397:122766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122766
Ling F, Fang L, Lu Y, Gao J, Wu F, Zhou M, Hu B (2016) A novel CoFe layered double hydroxides adsorbent: high adsorption amount for methyl orange dye and fast removal of Cr(VI). Microporous Mesoporous Mater 234:230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.07.015
Liu X, Wang J (2021) Adsorptive removal of Sr(2+) and Cs(+) from aqueous solution by capacitive deionization. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:3182–3195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10691-6
Liu S-T, Huang J, Ye Y, Zhang A-B, Pan L, Chen X-G (2013) Microwave enhanced Fenton process for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 215-216:586–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.003
Liu T, Jing L, Cui L, Liu Q, Zhang X (2018) Facile one-pot synthesis of a porphyrin-based hydrophilic porous organic polymer and application as recyclable absorbent for selective separation of methylene blue. Chemosphere 212:1038–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.122
Lyu H, Hu K, Fan J, Ling Y, Xie Z, Li J (2020) 3D hierarchical layered double hydroxide/carbon spheres composite with hollow structure for high adsorption of dye. Appl Surf Sci 500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144037
Mahjoubi FZ, Khalidi A, Abdennouri M, Barka N (2018) Zn–Al layered double hydroxides intercalated with carbonate, nitrate, chloride and sulphate ions: synthesis, characterisation and dye removal properties. Journal of Taibah University for Science 11:90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtusci.2015.10.007
Mandal S, Tichit D, Lerner DA, Marcotte N (2009) Azoic Dye hosted in layered double hydroxide: physicochemical characterization of the intercalated materials. Langmuir 25:10980–10986. https://doi.org/10.1021/la901201s
Mandal S, Kalaivanan S, Mandal AB (2019) Polyethylene glycol-modified layered double hydroxides: synthesis, characterization, and study on adsorption characteristics for removal of acid orange II from aqueous solution. ACS Omega 4:3745–3754. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02743
Maneerung T, Liew J, Dai Y, Kawi S, Chong C, Wang CH (2016) Activated carbon derived from carbon residue from biomass gasification and its application for dye adsorption: kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic studies. Bioresour Technol 200:350–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.047
Mitani Y, Takei T, Yanagida S, Kumada N (2017) Hybridization of Ni-Cr, Cu-Cr, and Zn-Cr layered double hydroxides with polyoxometalates and their catalytic behavior. J Ceram Soc Jpn 125:747–752
Mohapatra L, Parida KM (2012) Zn–Cr layered double hydroxide: visible light responsive photocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Sep Purif Technol 91:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.10.028
Morshedi D, Mohammadi Z, Akbar Boojar MM, Aliakbari F (2013) Using protein nanofibrils to remove azo dyes from aqueous solution by the coagulation process. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 112:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.08.004
Moustafa D, Mahmoud R, El-Salam HMA, Shehata N (2021) Utilization of residual zinc–iron-layered double hydroxide after methyl orange management as a new sorbent for wastewater treatment. Appl Nanosci 11:709–723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01632-3
Mustapha Bouhent M, Derriche Z, Denoyel R, Prevot V, Forano C (2011) Thermodynamical and structural insights of orange II adsorption by MgRAlNO3 layered double hydroxides. J Solid State Chem 184:1016–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2011.03.018
Ou W, Zhang G, Yuan X, Su P (2015) Experimental study on coupling photocatalytic oxidation process and membrane separation for the reuse of dye wastewater. Journal of Water Process Engineering 6:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.04.001
Pakshirajan K, Kheria S (2012) Continuous treatment of coloured industry wastewater using immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium in a rotating biological contactor reactor. J Environ Manag 101:118–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.02.008
Parida K, Mohapatra L (2012) Recent progress in the development of carbonate-intercalated Zn/Cr LDH as a novel photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution aimed at the utilization of solar light. Dalton Trans 41:1173–1178. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1DT10957J
Rathee G, Singh N, Chandra R (2020) Simultaneous elimination of dyes and antibiotic with a hydrothermally generated NiAlTi layered double hydroxide adsorbent. ACS Omega 5:2368–2377. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03785
Rojas Delgado R, Arandigoyen Vidaurre M, De Pauli CP, Ulibarri MA, Avena MJ (2004) Surface-charging behavior of Zn-Cr layered double hydroxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:431–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.045
Rojas R, Barriga C, De Pauli CP, Avena MJ (2010) Influence of carbonate intercalation in the surface-charging behavior of Zn–Cr layered double hydroxides. Mater Chem Phys 119:303–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.09.001
Ruan X, Huang S, Chen H, Qian G (2013) Sorption of aqueous organic contaminants onto dodecyl sulfate intercalated magnesium iron layered double hydroxide. Appl Clay Sci 72:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2013.01.001
Saghir S, Xiao Z (2021) Hierarchical mesoporous ZIF-67@LDH for efficient adsorption of aqueous methyl orange and alizarine red. S Powder Technology 377:453–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.09.006
Sun Q, Chen B (2020) Biotemplated fabrication of 3D hierarchically porous MgAl-LDH/CF composites with effective adsorption of organic dyes from wastewater. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:16838–16850. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c02800
Sun Q, Tang M, Hendriksen PV, Chen B (2020) Biotemplated fabrication of a 3D hierarchical structure of magnetic ZnFe2O4/MgAl-LDH for efficient elimination of dye from water. J Alloys Compd 829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154552
Tao X, Liu D, Song J, Ye Q, Xu D (2017) Plasma modification of ZnMgAl-LDHs for adsorption property improvement. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 74:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.02.009
Taviot-Guého C, Prévot V, Forano C, Renaudin G, Mousty C, Leroux F (2018) Tailoring hybrid layered double hydroxides for the development of innovative applications. Adv Funct Mater 28:1703868. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201703868
Xu J, Deng H, Song J, Zhao J, Zhang L, Hou W (2017) Synthesis of hierarchical flower-like Mg2Al-Cl layered double hydroxide in a surfactant-free reverse microemulsion. J Colloid Interface Sci 505:816–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.06.080
Yan Z, Zhu B, Yu J, Xu Z (2016) Effect of calcination on adsorption performance of Mg-Al layered double hydroxide prepared by a water-in-oil microemulsion method. RSC Adv 6:50128–50137. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra05253c
Zhang Q, Yan Z, Ouyang J, Zhang Y, Yang H, Chen D (2018) Chemically modified kaolinite nanolayers for the removal of organic pollutants. Appl Clay Sci 157:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.03.009
Zhang P, Ouyang S, Li P, Huang Y, Frost RL (2019a) Enhanced removal of ionic dyes by hierarchical organic three-dimensional layered double hydroxide prepared via soft-template synthesis with mechanism study. Chem Eng J 360:1137–1149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.179
Zhang Q, Zhang YD, Chen JT, Liu QF (2019b) Hierarchical structure kaolinite nanospheres with remarkably enhanced adsorption properties for methylene blue. Nanoscale Res Lett 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-019-2934-x
Zheng Y-M, Li N, Zhang W-D (2012) Preparation of nanostructured microspheres of Zn–Mg–Al layered double hydroxides with high adsorption property. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 415:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.10.014
Zheng Y, Zhu B, Chen H, You W, Jiang C, Yu J (2017) Hierarchical flower-like nickel(II) oxide microspheres with high adsorption capacity of Congo red in water. J Colloid Interface Sci 504:688–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.06.014
Zheng Y, Cheng B, You W, Yu J, Ho W (2019) 3D hierarchical graphene oxide-NiFe LDH composite with enhanced adsorption affinity to Congo red, methyl orange and Cr(VI) ions. J Hazard Mater 369:214–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.013
Zhu B, Chen L, Yan T, Xu J, Wang Y, Chen M, Jiang H (2018) Fabrication of Fe3O4/MgAl-layered double hydroxide magnetic composites for the effective removal of orange II from wastewater. Water Sci Technol 78:1179–1188. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.388
Zubair M, Jarrah N, Ihsanullah KA, Manzar MS, Kazeem TS, Al-Harthi MA (2018) Starch-NiFe-layered double hydroxide composites: efficient removal of methyl orange from aqueous phase. J Mol Liq 249:254–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.022
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51104060, 51034006), Key Scientific Research Projects of Colleges and Universities of Henan Province Education Department (21A440004), Taihang scholar program of Henan Polytechnic University for 2015, and Jiangyin Science and Technology Innovation Special Fund project (JY0602A011002200024PB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL: investigation, formal analysis, writing and editing, conduct experiment. YZ: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing and editing. QZ: funding acquisition. JS: conduct experiment. FD: conduct experiment. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• ST-LDH was synthesized by a facile one-pot hydrothermal technique.
• ST-LDH is formed by the face-face contacted hydrotalcite nanosheets.
• The pre-inserted benzene sulfonate as a pillar expanded the interlayer gallery.
• ST-LDH exhibited high adsorption capacity for anionic dyes (MO, CR, and OII).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q. et al. Enhanced adsorption properties of organic ZnCr-LDH synthesized by soft template method for anionic dyes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 48236–48252 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14035-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14035-w