Abstract
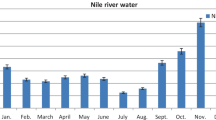
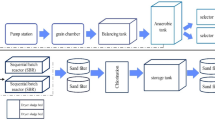
This work aims to study the technical problems of algal blooms that hinder the purification process of surface water used for drinking purposes and not its harmful effect on human health and the surrounding environment. It is also related to the demonstration of the improved coagulation process as an efficient technique in the algal removal from surface water by its application in jar tests. The study was carried out in the water purification plant in Nazlet Abdellah near the city of Assiut, Egypt. To achieve that, many ores and natural materials which aid in the removing of the algal blooms from surface water during the purification processes were tested. The examined materials should be technically and economically proper for improving the removal of algae from treated surface water for drinking purposes. The results showed that the kaolinite and bentonite (K and B) when coupled separately with aluminum sulfate (alum.) (the main coagulant agent) associated with the raw surface water in the flocculation basin were more efficient in the algae removal from treated surface water before reaching the sand filters by ratio up to 90%.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Alshahri AH, Fortunato L, Ghaffour N, Leiknes T (2021) Controlling harmful algal blooms (HABs) by coagulation-flocculation-sedimentation using liquid ferrate and clay. Chemosphere 274:129676
Bello O, Hamam Y , Djouani K (2014) Modelling of a coagulation chemical dosing unit for water treatment plants using fuzzy inference system. Proceedings of the 19th world congress, the International Federation of Automatic Control Cape Town, South Africa 3985-3991
El-Dars FMSE, Abdel Rahman MAM, Salem OMA, Abdel-Aal EA (2015) Algal control and enhanced removal in drinking waters in Cairo, Egypt: a case study. Environ Sci 10(8):295–307
Ewerts H, Swanepoel A, Du Preez HH (2013) Efficacy of conventional drinking water treatment processes in removing problem-causing phytoplankton and associated organic compounds. Water SA 39(5):739–749
Ferreira L, Du Preez HH (2012) Investigation into the occurrence of aquatic invertebrates throughout drinking water purification plants. Water Supply 12(2):250–257
Foroughi M, Chavoshi S, Bagheri M, Yetilmezsoy K, Samadi MT (2018) Alum-based sludge (AbS) recycling for turbidity removal in drinking water treatment: an insight into statistical, technical, and health-related standpoints. J Mater Cycl Waste Manag 20(4):1999–2017
Forson AM, van der Mei HC, Sjollema J (2020) Impact of solid surface hydrophobicity and micrococcal nuclease production on Staphylococcus aureus Newman biofilms. Sci Rep 10(1):1–10
Ghernaout B, Ghernaout D, Saiba A (2010) Algae and cyanotoxins removal by coagulation/flocculation. Desalin Water Treat 20:133–143
Huang Y, Zheng Y, Li J, Liao Q, Fu Q, Xia A, Fu J, Sun Y (2018) Enhancing microalgae biofilm formation and growth by fabricating microgrooves onto the substrate surface. Bioresour Technol 261:36–43
Köseoglu K, Cengizler H, İsrail Lİ, Polat H (2017) Tannery wastewater sediments produced by clinoptiolite/polyacrylamide-aided flocculation as a clay additive in brick making. J Aust Ceram Soc 53(2):719–731
Kuranga IA, Alafara AB, Halimah FB, Fausat AM, Mercy OB, Tripathy BC (2018) Production and characterization of water treatment coagulant from locally sourced kaolin clays. J ApplSci Environ Manage 22(1):103–109
Łukasiewicz E (2016) Post-coagulation sludge management for water and wastewater treatment with focus on limiting its impact on the environment. Econ Environ Stud 16(4):831–841
Nasrollahzadeh M, Baran T, Sajjadi M, Baran NY, Shokouhimehr M (2020) Bentonite-supported furfural-based Schiff base palladium nanoparticles: an efficient catalyst in treatment of water/wastewater pollutants. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31(15):12856–12871
Pestana CJ, Lawton LA, Kaloudis T (2020) Removal and/or destruction of cyanobacterial taste and odour compounds by conventional and advanced oxidation processes. Water treatment for purification from Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins 207-230
Poleneni SR, Inniss E, Shi H, Yang J, Hua B, Clamp J (2019) Enhanced flocculation using drinking water treatment plant sedimentation residual solids. Water 11(9):1821
Prabhu PP, Prabhu B (2018) A review on removal of heavy metal ions from waste water using natural/modified bentonite. MATEC Web Conf 144:02021
Ranga S (2018) Bentonite used as natural coagulant and adsorbent. Pharm Innov J 7(7):155–157
Rice EW, Baird RB, Eaton AD (2017) Physical and aggregate properties in standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 23th edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association. Water Environment Federation, Washington, pp 2–99
Srinivasan R (2011) Advances in application of natural clay and its composites in removal of biological, organic, and inorganic contaminants from drinking water. Hindawi Publishing Corporation. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2011:1–17
Swanepoel A (2015) Early warning system for the prediction of algal-related impacts on drinking water purification. PhD thesis, North West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa, 152
Taheriyoun M, Memaripour A, Nazari-Sharabian M (2020) Using recycled chemical sludge as a coagulant aid in chemical wastewater treatment in Mobarakeh Steel Complex. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 1-12
Verma AK, Dash RR, Bhunia P (2012) A review on chemical coagulation/flocculation technologies for removal of colour from textile wastewater. J Environ Manag 93(1):154–168
Walker DB, Baumgartner DJ, Gerba CP, Fitzsimmons K (2019) Chapter 16 - surface water pollution, In: Brusseau ML, Pepper IL, Gerba CP(ed) Environmental and pollution science, 3rd edn. Academic Press, pp 261-292
Wang J, Ren H, Li X, Li J, Ding L, Geng J, Xu K, Huang H, Hu H (2018) In situ monitoring of wastewater biofilm formation process via ultrasonic time domain reflectometry (UTDR). Chem Eng J 334:2134–2141
Zeng F, Cao S, Jin W, Zhou X, Ding W, Tu R, Han SF, Wang C, Jiang Q, Huang H, Ding F (2020) Inactivation of chlorine-resistant bacterial spores in drinking water using UV irradiation, UV/hydrogen peroxide and UV/peroxymonosulfate: efficiency and mechanism. J Clean Prod 243:118666
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Eman Abdel Rahman Mahmoud, Atef Mohamed Gad, Abd El Hay Ali Farrag, and Shaimaa Abdo Mohammed Aboeldahb. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Eman Abdel Rahman Mahmoud and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The manuscript did not contain any reporting studies involving human data.
Consent for publication
The manuscript does not contain any individual person data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philipp Gariguess
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoud, E.A., Gad Mohamed, A.M., Farrag, A.E.H.A. et al. Evaluation of the most promising techniques overcoming the algal problems takes place during the purification of drinking water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 44239–44248 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13674-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13674-3