Abstract
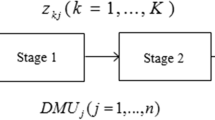
The objective of this paper is to assess the sustainability of supply chains by proposing a dynamic network data envelopment analysis (DNDEA) model in the presence of interval data, due to the fact that in many real-world applications, the condition of convexity in the production technology might be violated. To prevent this issue, a DNDEA model based on the free disposal hull (FDH) approach is developed. For the first time, this paper develops a DNDEA version of the free disposal hull (FDH) model in the context of the SCOR framework. It is also shown that this model always presents a finite efficiency score for assessing the sustainability of supply chains. Moreover, using this model, real benchmarks can be calculated to improve the sustainability of unsustainable supply chains. A case study in print industry is given. The results validate our proposed model.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset was derived from the archives and documents of the companies that were analyzed.
Notes
References
APICS, S and Council, ASC (2017) SCOR framework.
Avkiran NK (2009) Opening the black box of efficiency analysis: an illustration with UAE banks. Omega 37(4):930–941
Azadi M, Jafarian M, Farzipoor Saen R, Mirhedayatian SM (2015a) A new fuzzy DEA model for evaluation of efficiency and effectiveness of suppliers in a sustainable SCM context. Comput Oper Res 54:274–285
Azadi M, Shabani A, Khodakarami M, Farzipoor Saen R (2015b) Planning infeasible region by two-stage target-setting DEA methods: an application in green SCM of public transportation service providers. Transp Res E Logist Transp Rev 74:22–36
Azizi H, Kordrostami S, Amirteimoori A (2015) Slacks-based measures of efficiency in imprecise data envelopment analysis: an approach based on data envelopment analysis with double frontiers. Comput Ind Eng 79:42–51
Badiezadeh T, Farzipoor Saen R, Samavati T (2018) Assessing the sustainability of supply chains by double frontier network DEA: A big data approach. Comput Oper Res 98:284–290
Bai C, Sarkis J, Wei X, Koh L (2012) Evaluating ecological sustainable performance measures for supply chain management. Suppl Chain Manag Int J 17(1):78–92
Balfaqih H, Nopiah ZM, Saibani N, Al-Nory MT (2016) Review of supply chain performance measurement systems: 1998–2015. Comput Ind 82:135–150
Banker RD, Charnes A, Cooper WW (1984) Some models for estimating technical and scale inefficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Manag Sci 30(9):1078–1092
Charnes A, Cooper WW (1962) Programming with linear fractional functionals. Naval Res Logist Q 9(3-4):181–186
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision-making units. Eur J Oper Res 2(6):429–444
Chen CM, Delmas MA (2012) Measuring eco-inefficiency: a new frontier approach. Oper Res 60(5):1064–1079
Cook WD, Tone K, Zhu J (2014) Data Envelopment Analysis: Prior to Choosing a Model. Omega 44:1-4
Cook WD, Zhu J, Bi G, Yang F (2010) Network DEA: additive efficiency decomposition. Eur J Oper Res 207(2):1122–1129
Cooper WW, Seiford LM, Tone K (2007) Alternative DEA models. Data envelopment analysis: a comprehensive text with models, applications, references, and DEA-Solver software, pp 87–130
Daghfous A, Zoubi T (2017) An auditing framework for knowledge-enabled SCM: implications for sustainability. Sustainability 9(5):791
Deprins D, Simar L, Tulkens H (1984) Measuring Labor Inefficiency in PostOffices. InThe Performance of Public Enterprises: Concepts and Measurements, ed.M. Marchand, P. Pestieau, and H. Tulkens, 243–267. Amsterdam: North-Holland.
Dyllick T, Hockerts K (2002) Beyond the business case for corporate sustainability. Bus Strateg Environ 11(2):130–141
Färe R, Grosskopf S (2000) Theory and application of directional distance functions. J Prod Anal 13(2):93–103
Farzipoor Saen R (2010) Developing a new data envelopment analysis methodology for supplier selection in the presence of both undesirable outputs and imprecise data. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51(9-12):1243–1250
Fukuyama H, Weber WL (2015) Measuring Japanese bank performance: a dynamic network DEA approach. J Prod Anal 44(3):249–264
Fukuyama H, Leth Hougaard J, Sekitani K, Shi J (2016) Efficiency measurement with a non-convex free disposal hull technology. J Oper Res Soc 67(1):9–19
Georgise FB, Thoben KD, Seifert M (2014) Identifying the characteristics of the supply chain processes in developing country: a manufacturing industry perspective. WSEAS Trans Bus Econ 11(1):12–31
Gonzalez ED, Sarkis J, Huisingh D, Huatuco LH, Maculan N, Montoya-Torres JR, De Almeida CM (2015) Making real progress toward more sustainable societies using decision support models and tools: introduction to the special volume. J Clean Prod 105:1–13
Gunasekaran A, Spalanzani A (2012) Sustainability of manufacturing and services: investigations for research and applications. Int J Prod Econ 140(1):35–47
He B, Liu Y, Zeng L, Wang S, Zhang D, Yu Q (2019) Product carbon footprint across sustainable supply chain. J Clean Prod 241:118320
Hougaard JL, Overgaard C (2006) A note on health care products with uncertain data. Health Care Manag Sci 9(1):99–106
Izadikhah M, Farzipoor Saen R (2018) Assessing the sustainability of supply chains by chance-constrained two-stage DEA model in the presence of undesirable factors. Comput Oper Res 100:343–367
Izadikhah M, Saen RF, Ahmadi K (2017) How to assess sustainability of suppliers in volume discount context? A new data envelopment analysis approach. Transp Res Part D: Transp Environ 51:102–121
Jahanshahloo GR, Abbasian-Naghneh S (2011) Data envelopment analysis with imprecise data. Appl Math Sci 5(61-64):3089–3106
Jahanshahloo GR, Lotfi FH, Malkhalifeh MR, Namin MA (2009) A generalized model for data envelopment analysis with interval data. Appl Math Model 33(7):3237–3244
Kao C (2014) Efficiency decomposition in network data envelopment analysis with slacks-based measures. Omega 45:1–6
Kao C, Hwang SN (2010) Efficiency measurement for network systems: IT impact on firm performance. Decis Support Syst 48(3):437–446
Keshavarz E, Toloo M (2014) Finding efficient assignments: an innovative DEA approach. Measurement 58:448–458
Khalili-Damghani K, Shahmir Z (2015) Uncertain network data envelopment analysis with undesirable outputs to evaluate the efficiency of electric power production and distribution processes. Comput Ind Eng 88:131–150
Khoveyni M, Eslami R, Yang GL (2016) Data envelopment analysis in the absence of convexity: Specifying efficiency status and estimating returns to scale. J Comput Appl Math 304:172–200
Kordrostami S, Azmayandeh O, Bakhoda Z, Shokri S (2013) The new model in interval dynamic network DEA for parallel production systems; an illustration with Iranian banks. Indian J Sci Technol 6(1):3882–3891
Leleu H (2006) A linear programming framework for free disposal hull technologies and cost functions: primal and dual models. Eur J Oper Res 168(2):340–344
Leleu H (2009) Mixing DEA and FDH models together. J Oper Res Soc 60(12):1730–1737
Li Y, Yang F, Liang L, Hua Z (2009) Allocating the fixed cost as a complement of other cost inputs: A DEA approach. European Journal of Operational Research 197(1):389-401
Liang L, Cook WD, Zhu J (2008) DEA Models for Two-Stage Processes: Game Approach and Efficiency Decomposition. Naval Research Logistics 55:643–653
Liang L, Yang F, Cook WD, Zhu J (2006) DEA models for supply chain efficiency evaluation. Annals of Operations Research 145:35–49
Mahmoudi R, Emrouznejad A, Khosroshahi H, Khashei M, Rajabi P (2019) Performance evaluation of thermal power plants considering CO2 emission: a multistage PCA, clustering, game theory, and data envelopment analysis. J Clean Prod 223:641–650
Moreno P, Lozano S (2018) Super SBI dynamic network DEA approach to measuring efficiency in the provision of public services. Int Trans Oper Res 25(2):715–735
Ntabe EN, LeBel L, Munson AD, Santa-Eulalia LA (2015) A systematic literature review of the supply chain operations references (SCOR) model application with special attention to environmental issues. Int J Prod Econ 169:310–332
Omrani H, Soltanzadeh E (2016) Dynamic DEA models with network structure: an application for Iranian airlines. J Air Transp Manag 57:52–61
Portela MCAS, Borges PC, Thanassoulis E (2003) Finding the closest targets in non-oriented DEA models: the case of convex and non-convex technologies. J Prod Anal 19(2-3):251–269
Saleh C, Agitya RR, Badri HM, Deros BM (2015) Operation overlapping approach in MTS production typology to assist the accomplishment of sustainable supply chain management. Jurnal Teknologi 77(27)
Shabanpour H, Yousefi S, Farzipoor Saen R (2017) Forecasting efficiency of green suppliers by dynamic data envelopment analysis and artificial neural networks. J Clean Prod 142:1098–1107
Shokri Kahi V, Yousefi S, Shabanpour H, Farzipoor Saen R (2017) How to evaluate the sustainability of supply chains? A dynamic network DEA approach. Ind Manag Data Syst 117(9):1866–1889
Soleimani-Damaneh M, Mostafaee A (2015) Identification of the anchor points in FDH models. Eur J Oper Res 246(3):936–943
Soleimani-Damaneh M, Reshadi M (2007) A polynomial-time algorithm to estimate returns to scale in FDH models. Comput Oper Res 34(7):2168–2176
Tavassoli M, Farzipoor Saen R (2019) Predicting group membership of sustainable suppliers via data envelopment analysis and discriminant analysis. Sustain Prod Consum 18:41–52
Tone K (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 130(3):498–509
Tone K, Tsutsui M (2009) Network DEA: a slacks-based measure approach. Eur J Oper Res 197(1):243–252
Tone K, Tsutsui M (2010) Dynamic DEA: a slacks-based measure approach. Omega 38(3-4):145–156
Tone K, Tsutsui M (2014) Dynamic DEA with network structure: a slacks-based measure approach. Omega 42(1):124–131
Wang TF, Song DW, Cullinane K (2003) Container port production efficiency: a comparative study of DEA and FDH approaches. J East Asia Soc Transp Stud 5(10):698–713
Wang CN, Thanh NV, Chyou JT, Lin TF, Nguyen TN (2019) Fuzzy multicriteria decision-making model (MCDM) for raw materials supplier selection in plastics industry. Mathematics 7(10):981
Yousefi S, Shabanpour H, Fisher R, Farzipoor Saen R (2016) Evaluating and ranking sustainable suppliers by robust dynamic data envelopment analysis. Measurement 83:72–85
Yu M (2008) Assessing the technical efficiency, service effectiveness, and technical effectiveness of the world’s railways through NDEA analysis. Transportation Research Part A 42:1283–1294
Yu MM, Chen LH, Hsiao B (2016) Dynamic performance assessment of bus transit with the multi-activity network structure. Omega 60:15–25
Zailani S, Jeyaraman K, Vengadasan G, Premkumar R (2012) Sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) in Malaysia: a survey. Int J Prod Econ 140(1):330–340
Zha Y, Liang N, Wu M, Bian Y (2016) Efficiency evaluation of banks in China: a dynamic two-stage slacks-based measure approach. Omega 60:60–72
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to appreciate constructive comments of Reviewer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Farhad Ebrahimi worked on Sections 1 and 2. Reza Farzipoor Saen worked on analyzing the results and conclusions. He plays corresponding author role as well. Balal Karimi contributed to mathematical model section.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimi, F., Saen, R.F. & Karimi, B. Assessing the sustainability of supply chains by dynamic network data envelopment analysis: a SCOR-based framework. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 64039–64067 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12810-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12810-3