Abstract
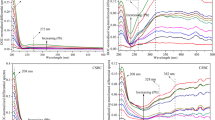
The fluorescent components of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in biogas slurry can react with heavy metals (HMs) and affect the migration, transformation, toxicity, and bioavailability of HMs in soil. Fluorescence quenching titration combined with two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy (2D-COS) can reveal the binding mechanism between HMs and different fluorescent components of biogas slurry DOM. The logarithmic-transformed (log-transformed) 2D-COS can be used to decrease the difference in the fluorescence intensity between low-intensity and high-intensity fluorophores that provides a better insight into the binding mechanism between biogas slurry DOM and HMs. Synchronous maps suggest that protein-like substances are more susceptive to the variation of the concentration of metal ions than fulvic-like substances. Asynchronous maps show that the preferential bonding of Cu(II) and Cr(III) to humic-like substances can be found in the biogas slurry DOM, as well as Fe(III) and Pb(II) to protein-like materials. DOM-Cu(II) may lead to an increasing risk of the migration of Cu(II) from soil to water environment due to the low log K values in the range from 2.93 to 3.46. Protein-like substances can also increase the environmental risk of HMs when these low-stable complexes occur migration and transformation. The potential environmental risk of protein-like with HMs follows the order: Pb(II) > Cu(II) > Cr(III). Here we demonstrate that the log-transformed 2D-COS can also identify fluorescence components at longer wavelength with relatively low content and reveals their preferential binding sequence and the number of binding sites. The study on the complexation between biogas slurry DOM and HMs provides a scientific basis for the environmental chemical behavior of HMs after the application of biogas slurry in agricultural soils.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthurson V (2009) Closing the global energy and nutrient cycles through application of biogas residue to agricultural land-potential benefits and drawbacks. Energies 2:226–242
Barker JD, Sharp MJ, Turner RJ (2009) Using synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy and principal components analysis to monitor dissolved organic matter dynamics in a glacier system. Hydrol Process 23:1487–1500
Chen G, Zhao G, Zhang H, Shen Y, Fei H, Cheng W (2017) Biogas slurry use as N fertilizer for two-season Zizaniaaquatica Turcz. in China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 107:1–18
Coban H, Miltner A, Centler F, Kästner M (2016) Effects of compost, biochar and manure on carbon mineralization of biogas residues applied to soil. Eur J Soil Sci 67:217–225
Eichgreatorex S, Vivekanand V, Estevez MM, Schnürer A, Børresen T, Sogn TS (2018) Biogas digestates based on lignin-rich feedstock-potential as fertilizer and soil amendment. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:347–359
Esteves da Silva JCG, Machado AASC, Oliveira CJS, Pinto MSSDS (1998) Fluorescence quenching of anthoropogenic fulvic acids by Cu (II), Fe (III) and UO22+. Talanta 45:1155–1165
Ferrari GM, Mingazzini M (1995) Synchronous fluorescence spectra of dissolved organic matter (DOM) of algal origin in marine coastal waters. Mar Ecol–Prog Ser 125:305–315
Guo X, Xie X, Liu Y, Wang C, Yang M, Huang Y (2020) Effects of digestate DOM on chemical behavior of soil heavy metals in an abandoned copper mining areas. J Hazard Mater:122436
Guo X, He X, Zhang H, Deng Y, Chen L, Jiang J (2012) Characterization of dissolved organic matter extracted from fermentation effluent of swine manure slurry using spectroscopic techniques and parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). Microchem J 102:115–122
Guo X, Li C, Zhu Q, Huang T, Cai Y, Li N, Liu J, Tan X (2018) Characterization of dissolved organic matter from biogas residue composting using spectroscopic techniques. Waste Manag 78:301–309
Guo X, Li Y, Feng Y, Yuan D (2017) Using fluorescence quenching combined with two-dimensional correlation fluorescence spectroscopy to characterise the binding-site heterogeneity of dissolved organic matter with copper and mercury in lake sediments. Environ Chem 14:91–98
Guo X-J, He X-S, Li C-W, Li N-X (2019) The binding properties of copper and lead onto compost-derived DOM using Fourier-transform infrared, UV–vis and fluorescence spectra combined with two-dimensional correlation analysis. J Hazard Mater 365:457–466
Guo X-J, Zhu N-M, Chen L, Yuan D-H, He L-S (2015) Characterizing the fluorescent properties and copper complexation of dissolved organic matter in saline-alkali soils using fluorescence excitation-emission matrix and parallel factor analysis. J Soils Sediments 15:1473–1482
Huang M, Li Z, Huang B, Luo N, Zhang Q, Zhai X, Zeng G (2018) Investigating binding characteristics of cadmium and copper to DOM derived from compost and rice straw using EEM-PARAFAC combined with two-dimensional FTIR correlation analyses. J Hazard Mater 344:539–548
Huang Y, Tian Y, Xie L, Liu Y, Dai B, Guo X, Yang Y (2020) The application of two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy for the binding properties of heavy metals onto digestate-derived DOM from anaerobic digestion of chicken manure. Ecotox Environ Safe 204:111129
Hur J, Lee B (2011) Characterization of binding site heterogeneity for copper within dissolved organic matter fractions using two-dimensional correlation fluorescence spectroscopy. Chemosphere 83:1603–1611
Kadam R, Panwar NL (2017) Recent advancement in biogas enrichment and its applications. Renew Sust Energ Rev 73:892–903
Luo T, Huang H, Mei Z, Shen F, Ge Y, Hu G, Meng X (2019) Hydrothermal pretreatment of rice straw at relatively lower temperature to improve biogas production via anaerobic digestion. Chin Chem Lett 30:1219–1223
Miano TM, Senesi N (1992) Synchronous excitation fluorescence spectroscopy applied to soil humic substances chemistry. Sci Total Environ 117(118):41–51
Monlau F, Sambusiti C, Ficara E, Aboulkas A, Barakat A, Carrère H (2015) New opportunities for agricultural digestate valorization: current situation and perspectives. Energy Environ Sci 8:2600–2621
Noda I, Ozaki Y (2005) Two-dimensional Correlation Spectroscopy: Applications in Vibrational and Optical Spectroscopy. John Wiley & Sons
Ozaki Y, Czarnik-Matusewicz B, Šašic S (2001) Two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy in analytical chemistry. Anal Sci 17:i663–i666
Qu H-L, Guo X-J, Chen Y-S, Dai B-L, He J, Zhu D-W (2017) Characterization of dissolved organic matter from effluents in a dry anaerobic digestion process using spectroscopic techniques and multivariate statistical analysis. Waste Biomass Valori 8:793–802
Ryan DK, Weber JH (1982) Fluorescence quenching titration for determination of complexing capacities and stability constants of fulvic acid. Anal Chem 54:986–990
Singh S, D’Sa EJ, Swenson EM (2010) Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) variability in Barataria Basin using excitation–emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence and parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). Sci Total Environ 408:3211–3222
Tan F, Zhu Q, Guo X, He L (2020) Effects of digestate on biomass of a selected energy crop and soil properties. J Sci Food Agr (In Press). https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10700
van de Weert M, Stella L (2011) Fluorescence quenching and ligand binding: a critical discussion of a popular methodology. J Mol Struct 998:144–150
Wang Y, Shen F, Liu R, Wu L (2008) Effects of anaerobic fermentation residue of biogas production on the yield and quality of Chinese cabbage and nutrient accumulations in soil. Int J Glob Energ 29:284–293
Yamashita Y, Tanoue E (2003) Chemical characterization of protein-like fluorophores in DOM in relation to aromatic amino acids. Mar Chem 82:255–271
Yang C, Zheng M, Zhang Y, Xi B, Tian Z, He X (2020) Bioreduction of hexavalent chromium: Effect of compost-derived humic acids and hematite. Chin Chem Lett (In Press) 31:2693–2697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.04.001
Yao Y, Li Y, Guo X, Huang T, Gao P, Zhang Y, Yuan F (2016) Changes and characteristics of dissolved organic matter in a constructed wetland system using fluorescence spectroscopy. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:12237–12245
Yuan D, Cui L, An Y, Chen B, Guo X, Li Y, Zhao R, Cui S, Wang S, Kou Y (2019b) Investigating the pollutant-removal performance and DOM characteristics of rainfall surface runoff during different ecological concrete revetments treatment. Ecol Indic 105:655–662
Yuan DH, Guo XJ, Wen L, He LS, Wang JG, Li JQ (2015) Detection of copper (II) and cadmium (II) binding to dissolved organic matter from macrophyte decomposition by fluorescence excitation-emission matrix spectra combined with parallel factor analysis. Environ Pollut 204:152–160
Yuan DH, Wang HT, An YC, Guo XJ, He LS (2019a) Insight into the binding properties of carbamazepine onto dissolved organic matter using spectroscopic techniques during grassy swale treatment. Ecotox Environ Safe 173:444–451
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Li R, Chen Y, Meng Q (2017) Investigating the behavior of binding properties between dissolved organic matter (DOM) and Pb(II) during the soil sorption process using parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy (2D-COS). Environ Sci Pollut R 24:25156–25165
Zheng X, Fan J, Cui J, Wang Y, Zhou J, Ye M, Sun M (2016) Effects of biogas slurry application on peanut yield, soil nutrients, carbon storage, and microbial activity in an ultisol soil in southern China. J Soils Sediments 16:449–460
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41503110); Science and Technology Major Project of Sichuan Province (2018SZDZX0024); and the Project Funding of Chengdu University of Information Technology (KYTZ201744).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Wu, Y., Peng, Y. et al. Study on the complexation of heavy metals onto biogas slurry DOM using two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy combined with the log-transformed synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 22878–22885 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12401-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12401-2