Abstract
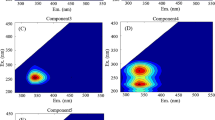
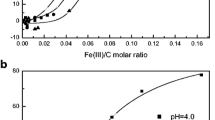
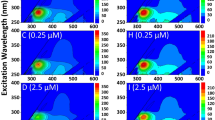
The precipitation of Cu(II) by phosphate and the influence of dissolved organic matter (DOM) on the precipitation are essential for the fate of Cu(II) in aquatic environments. In this study, the influence of DOM on the reaction of phosphate with Cu(II) was investigated. Here, 51.61%, 29.75%, and 24.32% of the added Cu(II) (50 μM) precipitated without DOM and with the addition of fulvic acid (FA) and humic acid (HA), respectively, owing to the reaction with phosphate (50 μM). Excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy-parallel factor (PARAFAC) and two-dimensional ultraviolet-visible correlation spectroscopy analyses were conducted to characterize the influence of DOM on the precipitation of Cu(II) with phosphate. One humic-like and two protein-like fluorescent components were identified by the PARAFAC model for FA, whereas two humic-like fluorescent components and one protein-like fluorescent component were validated for HA. The humic-like components had primary roles, whereas the protein-like components had secondary roles in limiting the precipitation of Cu(II) with phosphate. Cu(II) binding to DOM chromophores initially occurred at shorter wavelengths, and then at longer wavelengths. Phenolic and carboxylic constituents had important roles, and HA exhibited more binding sites than FA. Therefore, humic-like fluorescent components and chromophores containing phenolic and carboxylic groups and functional groups with peaks at short wavelengths (200–220 nm) were primarily responsible for restricting the precipitation of Cu(II) with phosphate.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Baghoth SA, Sharma SK, Amy GL (2011) Tracking natural organic matter (NOM) in a drinking water treatment plant using fluorescence excitation-emission matrices and PARAFAC. Water research 45(2):797–809
Bahram M, Bro R, Stedmon C, Afkhami A (2006) Handling of Rayleigh and Raman scatter for PARAFAC modeling of fluorescence data using interpolation. Journal of Chemometrics 20(3-4):99–105
Bing HJ, Wu YH, Sun ZB, Yao SC (2011) Historical trends of heavy metal contamination and their sources in lacustrine sediment from Xijiu Lake, Taihu Lake Catchment, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences 23(10):1671–1678
Bouyer F, Sanson N, Destarac M, Gerardin C (2006) Hydrophilic block copolymer-directed growth of lanthanum hydroxide nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 30(3):399–408
Cao X, Ma LQ, Rhue DR, Appel CS (2004) Mechanisms of lead, copper, and zinc retention by phosphate rock. Environmental Pollution 131(3):435–444
Carolin CF, Kumar PS, Saravanan A, Joshiba GJ, Naushad M (2017) Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: a review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 5(3):2782–2799
Chen Y, Wang LQ, Liang T, Xiao J, Li J, Wei HC, Dong LL (2019) Major ion and dissolved heavy metal geochemistry, distribution, and relationship in the overlying water of Dongting Lake, China. Environmental geochemistry and health 41(3):1091–1104
de Vicente I, Jensen HS, Andersen FO (2008) Factors affecting phosphate adsorption to aluminum in lake water: implications for lake restoration. Science of the Total Environment 389(1):29–36
Guo X-j, Li Y-z, Feng Y-h, Yuan D-h (2017) Using fluorescence quenching combined with two-dimensional correlation fluorescence spectroscopy to characterise the binding-site heterogeneity of dissolved organic matter with copper and mercury in lake sediments. Environmental Chemistry 14(2):91
Guo X-J, He X-S, Li C-W, Li N-X (2019) The binding properties of copper and lead onto compost-derived DOM using Fourier-transform infrared, UV–vis and fluorescence spectra combined with two-dimensional correlation analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials 365:457–466
Huang B, Li Z, Huang J, Guo L, Nie X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zeng G (2014) Adsorption characteristics of Cu and Zn onto various size fractions of aggregates from red paddy soil. Journal of hazardous materials 264:176–183
Huang G, Su X, Rizwan MS, Zhu Y, Hu H (2016) Chemical immobilization of Pb, Cu, and Cd by phosphate materials and calcium carbonate in contaminated soils. Environmental science and pollution research international 23(16):16845–16856
Huang M, Li Z, Chen M, Wen J, Xu W, Ding X, Yang R, Luo N, Xing W (2019) In situ investigation of intrinsic relationship between protonation behavior and HA characteristics in sediments. Science of the total environment 683:258–266
Huo SL, Zhang JT, Yeager KM, Xi BD, Qin YW, He ZS, Wu FC (2015) Mobility and sulfidization of heavy metals in sediments of a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Taihu, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences 31:1–11
Hur J, Lee BM (2011) Characterization of binding site heterogeneity for copper within dissolved organic matter fractions using two-dimensional correlation fluorescence spectroscopy. Chemosphere 83(11):1603–1611
Impellitteri CA (2005) Effects of pH and phosphate on metal distribution with emphasis on As speciation and mobilization in soils from a lead smelting site. Science of the Total Environment 345(1-3):175–190
Ishii SK, Boyer TH (2012) Behavior of reoccurring PARAFAC components in fluorescent dissolved organic matter in natural and engineered systems: a critical review. Environmental science & technology 46(4):2006–2017
Janot N, Reiller PE, Korshin GV, Benedetti MF (2010) Using spectrophotometric titrations to characterize humic acid reactivity at environmental concentrations. Environmental Science & Technology 44:6782–6788
Jin Z, Ding S, Sun Q, Gao S, Fu Z, Gong M, Lin J, Wang D, Wang Y (2019) High resolution spatiotemporal sampling as a tool for comprehensive assessment of zinc mobility and pollution in sediments of a eutrophic lake. Journal of Hazardous Materials 364:182–191
Jørgensen L, Stedmon CA, Kragh T, Markager S, Middelboe M, Søndergaard M (2011) Global trends in the fluorescence characteristics and distribution of marine dissolved organic matter. Marine Chemistry 126(1-4):139–148
Knoth de Zarruk K, Scholer G, Dudal Y (2007) Fluorescence fingerprints and Cu2+-complexing ability of individual molecular size fractions in soil- and waste-borne DOM. Chemosphere 69(4):540–548
Li WT, Chen SY, Xu ZX, Li Y, Shuang CD, Li AM (2014) Characterization of dissolved organic matter in municipal wastewater using fluorescence PARAFAC analysis and chromatography multi-excitation/emission scan: a comparative study. Environmental science & technology 48(5):2603–2609
Li X, Chen J, Zhang Z, Kuang Y, Yang R, Wu D (2020) Interactions of phosphate and dissolved organic carbon with lanthanum modified bentonite: implications for the inactivation of phosphorus in lakes. Water Research 181:115941
Lu W, Yao X, Ren H, Deng H, Yao M, Zhang B (2019) Characterizing the interactions between sediment dissolved organic matter and zinc using multispectroscopic techniques. Environmental pollution 261:113644
Lynch LM, Sutfin NA, Fegel TS, Boot CM, Covino TP, Wallenstein MD (2019) River channel connectivity shifts metabolite composition and dissolved organic matter chemistry. Nature communications 10(1):459
Ma Z, Chen K, Yuan Z, Bi J, Huang L (2013) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of six major Chinese freshwater lakes. J Environ Qual 42(2):341–350
Maizel AC, Li J, Remucal CK (2017) Relationships between dissolved organic matter composition and photochemistry in lakes of diverse trophic status. Environmental science & technology 51(17):9624–9632
Matusik J, Bajda T, Manecki M (2008) Immobilization of aqueous cadmium by addition of phosphates. Journal of hazardous materials 152(3):1332–1339
McElmurry SP, Long DT, Voice TC (2010) Simultaneous quantification of dissolved organic carbon fractions and copper complexation using solid-phase extraction. Applied Geochemistry 25(5):650–660
Murphy KR, Butler KD, Spencer RGM, Stedmon CA, Boehme JR, Aiken GR (2010) Measurement of dissolved organic matter fluorescence in aquatic environments: an interlaboratory comparison. Environmental Science & Technology 44(9405-9412):9405–9412
Murphy KR, Hambly A, Singh S, Henderson RK, Baker A, Stuetz R, Khan SJ (2011) Organic matter fluorescence in municipal water recycling schemes: toward a unified PARAFAC model. Environmental Science & Technology 45(7):2909–2916
Ni Z, Wang S, Wang Y (2016) Characteristics of bioavailable organic phosphorus in sediment and its contribution to lake eutrophication in China. Environmental pollution 219:537–544
Noda, I. and Ozaki, Y. 2005. Two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy: applications in vibrational and optical spectroscopy. John Wiley & Sons.
Peuravuori J, Pihlaja K (1997) Molecular size distribution and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Analytica Chimica Acta 337:133–149
Phong DD, Hur J (2015) Insight into photocatalytic degradation of dissolved organic matter in UVA/TiO(2) systems revealed by fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC. Water research 87:119–126
Pozdnyakov IP, Plyusnin VF, Grivin VP, Vorobyev DY, Bazhin NM, Vauthey E (2006) Photolysis of sulfosalicylic acid in aqueous solutions over a wide pH range. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 181(1):37–43
Stedmon CA, Markager S, Bro R (2003) Tracing dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments using a new approach to fluorescence spectroscopy. Marine Chemistry 82(3-4):239–254
Teixeira MR, Rosa MJ (2003) pH adjustment for seasonal control of UF fouling by natural waters. Desalination 151(2):165–175
van Dael T, De Cooman T, Verbeeck M, Smolders E (2020) Sediment respiration contributes to phosphate release in lowland surface waters. Water research 168:115168
Wang L, Dai L, Li L, Liang T (2018) Multivariable cokriging prediction and source analysis of potentially toxic elements (Cr, Cu, Cd, Pb, and Zn) in surface sediments from Dongting Lake, China. Ecological Indicators 94:312–319
Williams CJ, Yamashita Y, Wilson HF, Jaffe R, Xenopoulos MA (2010) Unraveling the role of land use and microbial activity in shaping dissolved organic matter characteristics in stream ecosystems. Limnology and Oceanography 55(3):1159–1171
Wu J, Zhang H, Yao QS, Shao LM, He PJ (2012) Toward understanding the role of individual fluorescent components in DOM-metal binding. Journal of hazardous materials 215-216:294–301
Xu H, Yu G, Yang L, Jiang H (2013) Combination of two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy and parallel factor analysis to characterize the binding of heavy metals with DOM in lake sediments. Journal of Hazardous Materials 263:412–421
Xu H, Zhong J, Yu G, Wu J, Jiang H, Yang L (2014) Further insights into metal-DOM interaction: consideration of both fluorescent and non-fluorescent substances. PloS one 9(11):e112272
Xu H, Zou L, Guan D, Li W, Jiang H (2019) Molecular weight-dependent spectral and metal binding properties of sediment dissolved organic matter from different origins. Science of The Total Environment 665:828–835
Yan M, Korshin GV (2014) Comparative examination of effects of binding of different metals on chromophores of dissolved organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology 48(6):3177–3185
Yan M, Dryer D, Korshin GV, Benedetti MF (2013) In situ study of binding of copper by fulvic acid: comparison of differential absorbance data and model predictions. Water research 47(2):588–596
Yan M, Ma J, Ji G (2016a) Examination of effects of Cu(II) and Cr(III) on Al(III) binding by dissolved organic matter using absorbance spectroscopy. Water Research 93:84–90
Yan MQ, Dryer D, Korshin GV (2016b) Spectroscopic characterization of changes of DOM deprotonation-protonation properties in water treatment processes. Chemosphere 148:426–435
Yan M, Han X, Zhang C (2017a) Investigating the features in differential absorbance spectra of NOM associated with metal ion binding: a comparison of experimental data and TD-DFT calculations for model compounds. Water research 124:496–503
Yan M, Ma J, Zhang C, Zhou Y, Liu F, Han X, Li M, Ni J (2017b) Optical property of dissolved organic matters (DOMs) and its link to the presence of metal ions in surface freshwaters in China. Chemosphere 188:502–509
Yang R, Li Z, Huang M, Luo N, Wen J, Zeng G (2019) Characteristics of fulvic acid during coprecipitation and adsorption to iron oxides-copper aqueous system. Journal of Molecular Liquids 274:664–672
Yin H, Gao Y, Fan C (2011) Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Taihu, China. Environmental Research Letters 6(4)
Yuan DH, Guo XJ, Wen L, He LS, Wang JG, Li JQ (2015) Detection of Copper (II) and Cadmium (II) binding to dissolved organic matter from macrophyte decomposition by fluorescence excitation-emission matrix spectra combined with parallel factor analysis. Environment Pollution 204:152–160
Zhang C, Yu ZG, Zeng GM, Jiang M, Yang ZZ, Cui F, Zhu MY, Shen LQ, Hu L (2014) Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environment international 73:270–281
Zhang Z, Ren J, Wang M, Song X, Zhang C, Chen J, Li F, Guo G (2016) Competitive immobilization of Pb in an aqueous ternary-metals system by soluble phosphates with varying pH. Chemosphere 159:58–65
Zhang Z, Lu Y, Li H, Tu Y, Liu B, Yang Z (2018) Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. The Science of the total environment 645:235–243
Zhang, X., Li, B., Deng, J., Qin, B., Wells, M. and Tefsen, B. 2020. Regional-scale investigation of dissolved organic matter and lead binding in a large impacted lake with a focus on environmental risk assessment. Water Research 115478.
Zhou M, Meng F (2015) Using UV-vis absorbance spectral parameters to characterize the fouling propensity of humic substances during ultrafiltration. Water research 87:311–319
Zhou A, Tang H, Wang D (2005) Phosphorus adsorption on natural sediments: modeling and effects of pH and sediment composition. Water Research 39(7):1245–1254
Zhu G, Yang Y (2018) Variation laws and release characteristics of phosphorus on surface sediment of Dongting Lake. Environmental science and pollution research international 25(13):12342–12351
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51879103), Key R&D Program of Science and Technology of Hunan Province in China (No. 2017SK2351), and Science and Technology Plan Project of Hunan Province in China (No. 2018SK2047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiang Ding: experiment design and operation, writing—original draft. Weihua Xu: writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. Zhongwu Li: data curation, supervision, funding acquisition. Mei Huang: conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Jiajun Wen: methodology. Changsheng Jin: software. Mi Zhou: experiment operation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 705 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, X., Li, Z., Xu, W. et al. Restriction of dissolved organic matter on the stabilization of Cu(II) by phosphate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 22902–22912 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12398-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12398-8