Abstract
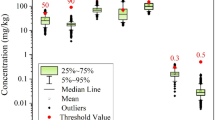
Wetland environmental pollution has become a global problem involving the ecological environment and human health. This study measured the concentration of seven potentially toxic elements (PTEs Hg, Cd, Zn, Cu, Cr, Pb, and As) in the soil upstream of the Xinli Lake wetland in China. Based on the fuzzy theory, the sources, spatial distribution, ecological risks, and health risks of pollutants are studied. The result shows that the concentrations of the seven potentially toxic elements are close to or exceed the background value, and their spatial distribution showed irregular changes. The soil upstream of the wetland has not been seriously polluted, and Cd, which has higher bioavailability, is the priority element for ecological risk. Pollutants do not harm human health; children face higher health risks; Pb and As have the highest carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks, respectively. Zn, Cu, Cr, Pb, and As in the study area are derived from agricultural activities, while Hg and Cd are mainly affected by soil-forming parent materials. Attention should be paid to controlling the intensity of agricultural activities to avoid excessive input and accumulation of pollutants that would harm the ecological environment and human health.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuduwaili J, Fengqing J, Zhaoyong Z (2015) Heavy metal contamination, sources, and pollution assessment of surface water in the Tianshan Mountains of China. Environ Monit Assess 187(2):33
Acosta JA, Faz A, Martínez-Martínez S, Arocena JM (2011) Enrichment of metals in soils subjected to different land uses in a typical Mediterranean environment (Murcia city, southeast Spain). Appl Geochem 26:405–414
Afzali KN, Jahan S, Strezov V, Soleimani-Sardo M, Shirani M (2020) Pollution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Jazmurian Playa in Southeast Iran. Sci Rep 10(1):4775
Bai JH, Jia J, Zhang GL et al (2016) Spatial and temporal dynamics of heavy metal pollution and source identification in sediment cores from the short-term flooding riparian wetlands in a Chinese delta. Environ Pollut 219:379–388
Bastami KD, Neyestani MR, Esmaeilzadeh M, Haghparast S, Alavi C, Fathi S, Nourbakhsh S, Shirzadi EA, Parhizgar R (2017) Geochemical speciation,bioavailability and source identification of selected metals in surface sediments of the Southern Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 114:1014–1023
Boruvka L, Vacek O, Jehlicka J (2005) Principal component analysis as a tool to indicate the origin of potentially toxic elements in soils. Geoderma 128:289–300
Cao H (1981) The pollution of heavy metals in terrestrial ecosystems. Environ Sci 1981(02):61–64 in chinese
Chen B, Su W, Luo S et al (2017a) The features and the pollution assessments of heavy metals in the surface sediments of mangrove wetland in Techeng Island, Zhanjiang. Ecol Environ Sci 26(1):159–165 in chinese
Chen Q, Deng M, Japenga J, Li T, Huang Y, Yang X, He Z (2018) Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in Southeast China. J Environ Manag 207:159–168
Chen J, Wu H, Qian H (2016) Groundwater nitrate contamination and associated health risk for the rural communities in an agricultural area of Ningxia, northwest China. Expos Health 8(3):349–359
Chen J, Wu H, Qian H, Gao Y (2017b) Assessing nitrate and fluoride contaminants in drinking water and their health risk of rural residents living in a semiarid region of Northwest China. Expos Health 9(3):183–195
Chen J, Wu H, Qian H, Gao Y et al (2020) Insights into hydrological and hydrochemical processes in response to water replenishment for lakes in arid regions. J Hydrol 581:124386
Duffus J (2002) Heavy metals —a meaningless term?. Pure Appl. Chem. 74(5):793–807
Drohan PJ, Yang M, Li H, Yang P, Drohan PJ (2020) Spatial variability of heavy metal ecological risk in urban soils from Linfen, China. Catena 190:104554
Ennaji W, Krimissa S, Bouzaid M, Barakat A (2020) Heavy metal contamination and ecological-health risk evaluation in peri-urban wastewater-irrigated soils of Beni-Mellal City (Morocco). Int J Environ Health Res 30(4):372–387
Fan M,Yuan X, Zhu H, Huang H, Zeng G, Liang Y (2010) Assessment model for heavy metal pollution in river sediment based on triangular fuzzy numberss. Acta Sci Circumst 30(08):1700–1706 in chinese
Fang H, Xu Y, Ye Z, Zhang Z, Pan S, Deng L et al (2015) Impact of urbanization on nutrients and heavy metal pollution of Napahai Wetland, Shangri-La County, China. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 22(2):117–126
Ferreira-baptista L, De Miguelb E (2005) Geochemistry and risk assessment of streetdust in Luanda, Angola: a tropical urban environment. Atmos Environ 39(25):4501–4512
Greve MH, Deroin JP, Rebai N, Kheir RB, Greve MH (2013) Implementing GIS regression trees for generating the spatial distribution of copper in Mediterranean environments: the case study of Lebanon. Int J Environ Anal Chem 93(1):75–92
Haximu S, Zhang ZY, Aji R, Mamat Z, Zhang ZY (2016) An ecological risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Bosten Lake, northwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(8):7255–7265
Huang B, Hong T, Li R, Shi Y (2009) Pollution risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments based on triangular fuzzy number theory. J Hefei Univ Technol (Nat Sci Ed) 32(9):1386–1390 in chinese
Hua L, Yang X, Liu Y et al (2018) Spatial Distributions, Pollution assessment, and qualified source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a typical mineral mining city in China. Sustainability 10(9):3115
Kabata-Pendias A, Mukherjee AB (2007) Trace elements from soil to human. Springer Science &Business Media, Berlin
Kelepertzis E (2014) Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: insights from Argolida Basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma 221:82–90
Liu X, Liu Z, Li G, Guo W (2010) Pollution and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the sediments around Dongjiang Harbor, Tianjin. Procedia Environ Sci 2:729–736
Li J, Mamat Z, Ye QF, Zhang Z, Juying L, QingFu Y (2016) Sources identification and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Bortala River, Northwest China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:94–101
Liu J, Yuan X, Zeng G, Lai X, Liang J, Li X, Wu H, Yuan Y, Li F (2015) Spatial and temporal variation of heavy metal risk and source in sediments of Dongting Lake Wetland, Mid-south China. J Environ Sci Health 50(1):100–108
Li F, Zhang J, Liu C, Xiao M, Wu Z (2018a) Distribution, bioavailability and probabilistic integrated ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from Honghu Lake, China. Proc Safe Environ Protec Transac Inst Chem Eng Part B 116:169–179
Li F, Huang J, Zeng G, Tang X, Yuan X, Liang J, Zhu H (2012) An integrated assessment model for heavy metal pollution in soil based on triangular fuzzy numbers and chemical speciation of heavy metal. Acta Sci Circumst 32:432–439 in Chinese
Li F, Zhenzhen Q, Jingdong Z, Chaoyang L, Ying C, Minsi X (2017) Spatial distribution and fuzzy health risk assessment of trace elements in surface water from Honghu Lake. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(9):1011
Li F, Zhang J, Liu W, Liu J, Huang J, Zeng G (2018b) An exploration of an integrated stochastic-fuzzy pollution assessment for heavy metals in urban topsoil based on metal enrichment and bioaccessibility. Sci Total Environ 644:649–660
Liu J, Qiao S, Zhang H, Zhu A (2020) Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Bohai Sea of China. Mar Pollut Bull 153:110901
Luo F, Gu A, Chu X, Younas H, Lu X, Hu X (2020) Sources and risk assessment of toxic elements in the agricultural soil of Tiantai County of Zhejiang Province, China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 26(3):586–607
Mahesh MK, Ramachandra TV, Sudarshan P, Mahesh MK, Ramachandra TV (2020) Dynamics of metal pollution in sediment and macrophytes of Varthur Lake, Bangalore. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 104(4):411–417
Mungai TM, Owino AA, Makokha VA et al (2016) Occurrences and toxicological risk assessment of eight heavy metals in agricultural soils from Kenya, Eastern Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(18):18533–18541
Ma J, Hu Y, Su B, Fang G, Pan L, Wang Y, Wang Z, Wang L, Xiang B (2016) Assessments of levels, potential ecological risk, and human health risk of heavy metals in the soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(19):19330–19340
Namaghi HH, Ghorbani H, Dahrazma B, Hafezi Moghaddas N, Hadi HN (2013) The effects of agricultural practice and land-use on the distribution and origin of some potentially toxic metals in the soils of Golestan Province, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 68(2):487–497
Ni S, Wang J, Zuo R, Yang J, Teng Y (2010) A geochemical survey of trace elements in agricultural and non-agricultural topsoil in Dexing area, China. J Geochem Explor 104(3):118–127
Peng S-C, Chen T-H, Zhang L, Wang J-Z (2016) Occurrence, source identification and ecological risk evaluation of metal elements in surface sediment: toward a comprehensive understanding of heavy metal pollution in Chaohu Lake, Eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(1):307–314
Pourret O, Hursthouse (2019) It’s time to replace the term “heavy metals” with “potentially toxic elements” when reporting environmental research. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:4446
Pourret O (2018) On the necessity of banning the term “heavy metal” from the scientific literature. Sustainability. 10:2879
Qian H, Chen J, Ken WFH (2020) I Assessing groundwater pollution and potential remediation processes in a multi-layer aquifer system. Environ Pollut 263:114669
Rasmussen P, Subramanian K, Jessiman B (2001) A multi-element pro-file of house dust in relation to exterior dust and soils in the city of Ottawa, Canada. Sci Total Environ 267:125–140
Shi Y, Zhao J, Wang Y (2014) Environment study on Liaohe River Basin ecological footprint and ecological restoration measures. Adv Mater Res 830:372–375
Sun H, Wan S, Li L, Liu D (2015) Distribution of heavy metals in soil and plant of reed wetland in the Dongting Lake of China during different seasons. J Soil Water Conserv 29(5):289–293 in chinese
Shahab A, Li J, Xi B, Sun X, Xiao H, He H, Yu G (2019) Distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of Huixian Karst Wetland, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 185:109700
Tian K, Wu Q, Liu P (2020) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments and water from the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Environ Int 3:105512
Ullah R, Jadoon IAK, Muhammad S, Jadoon IAK (2019) Heavy metals contamination in soil and food and their evaluation for risk assessment in the Zhob and Loralai Valleys, Baluchistan Province, Pakistan. Microchem J 149:103971
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang J, Xu M, Zhao L, Wang Z, Liu B (2019a) Spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Haizhou Bay National Ocean Park, China. Mar Pollut Bull 149:110651
Wang S, Mo L, Zou J, Zhou Y, Gopalakrishnan G, Wang S, Mo L, Zou J, Zhou Y (2020a) Distribution determination, risk assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in mangrove wetland sediments from Qi’ao Island, South China. Reg Stud Mar Sci 33:100961
Wang Z, Liu J, Zhong S, Wei C, Du J (2020b) Distribution characteristics of soil heavy metals, their source identification and their changes influenced by anthropogenic cultivation activities in Purple Hilly Regions of Sichuan Basin, China. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20(3):1080–1091
Wang D, Wang Q, Liu S, Zhu Y, Li W, Wu W (2017) Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(3):336
Wang X, Sun Y, Li S, Wang H (2019b) Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil from the Raoyanghe Wetland, China. PLoS One 14(08):e0220409
Xun J (2015) Study on the speciation of soil heavy metals copper, chromium, cadmium and mercury in sewage irrigation area of Jinzhou City. Environ Protec Circul Econ 35(03):66–68 in chinese
Xu Y-n, Zhang J-H, Hu S-H, Wu Y-G, Xu Y-N, Zhang J-H, Hu S-H (2010) Evaluation of ecological risk and primary empirical research on heavy metals in polluted soil over Xiaoqinling Gold Mining Region, Shaanxi, China. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 20(4):688–694
Xu Z, Da Q (2003) The possibility degree method for sorting interval numbers and its application. J Syst Eng 2003(01):67–70 in chinese
Xiong Z, Liu H, Liu G, Liu W, Jiang X (2017) Distribution, source identification, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in wetland soils of a river–reservoir system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(1):436–444
Xie Z, Zhang H, Zhao X et al (2016) Assessment of heavy metal contamination and wetland management in a newly created coastal natural reserve, China. J Coast Res 32(2):374–386
Yang L, Han X, Dai J, Pang X, Guo H, Ren M, Zhang W (2019) Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in surface soils from the western area of Nansi Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 191(5):262
Yu L, Chai M, Niu Z, Li R, Shi C (2020) The distribution and risk of mercury in Shenzhen mangroves, representative urban mangroves affected by human activities in China. Mar Pollut Bull 151:110866
Zhang G (2015) Characterization and ecological risk assessment of nutrients and heavy metal pollution in the surface sediments of Dongting Lake. J Hydroecol 36(2):25–31 in chinese
Zhang C-P (2016) Spatial distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Yalu River Estuary Wetland Mudflat. [[Ying Yung Sheng T'Ai Hsueh Pao]] 27(9):2884–2890
Zhao J, Zhou X, Ma C, Wang L, Zheng R, Zhao J, Zhou X, Ma C, Wang L, And Gao X (2016) Land use effects on the distribution and speciation of heavy metals and arsenic in coastal soils on Chongming Island in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Pedosphere. 26(1):74–84
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Fund of China (grant no. 51604140), National Key R&D Program of China (grant no. 2017YFC1503102), and the project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant no. 2018 M631815).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.X. and Z.C. conceived the idea and performed the laboratory analysis. W.X. and Z.C also analyzed the data and wrote the paper. L.S, W.C, W.H, and C.Y designed the investigation and validation. All of the authors contributed to finalizing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alexandros Stefanakis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Zhang, C., Li, S. et al. Ecological risk, health risk assessment, and pollution source analysis of Xinli Lake wetland based on triangular fuzzy number. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 22334–22347 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12301-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12301-x