Abstract
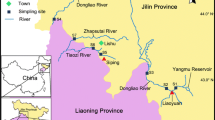
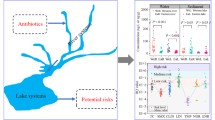
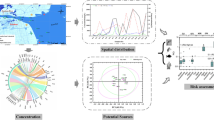
Twenty antibiotics were investigated to evaluate the degree of antibiotic pollution, the temporal and spatial antibiotic distribution and the ecological risks in the Xiaoqing River basin (main stream). The total antibiotic concentrations in surface water and sediment were 0.99 to 832.4 ng L−1 and 9.71 to 7841.61 ng g−1, respectively, and that ofloxacin was the dominant antibiotic. However, ofloxacin, erythromycin, clarithromycin and sulfamethoxazole posed high risks to algae, among which clarithromycin presented the highest risk quotients (23.8). In addition, there were spatial and temporal differences in the antibiotic concentration distribution. Temporally, the following trend was detected: dry season > normal season > wet season; spatially, the following trend was detected: Jinan > Dongying > Binzhou > Zibo > Weifang. Meanwhile, we used the PCA-MLR model to quantify the contribution rate of the four sewage treatment plants A, B, C and D. Factor 1 (co-sources A, B, C, D) contributed 64.1% of the total antibiotic concentration in the Xiaoqing River. According to the estimated flux into the sea, approximately 972.31 kg of antibiotics were discharged into Bohai Bay in 2017, posing a potential threat to the marine ecosystem. As a comprehensive river channel used for flood control, waterlogging, irrigation and shipping, its water quality safety is of great significance to the surrounding residents and ecological safety. Therefore, further investigations of antibiotic pollution and source contribution are necessary.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Aydin S, Aydin ME, Ulvi A, Kilic H (2019) Antibiotics in hospital effluents: occurrence, contribution to urban wastewater, removal in a wastewater treatment plant, and environmental risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:544–558
Baran W, Adamek E, Ziemiańska J, Sobczak A (2011) Effects of the presence of sulfonamides in the environment and their influence on human health. J Hazard Mater 196:1–15
Bullman S, Pedamallu CS, Sicinska E, Clancy TE, Zhang X, et al (2017) Analysis of Fusobacterium persistence and antibiotic response in colorectal cancer. Science (New York, N.Y.) 358, 1443-1448
Chee-Sanford JC, Aminov RI, Krapac IJ, Garrigues-Jeanjean N, Mackie RI (2001) Occurrence and diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in lagoons and groundwater underlying two swine production facilities. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1494–1502
Deng W, Li N, Zheng H, Lin H (2016) Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in river water in Hong Kong. Ecotox Environ Safe 125:121–127
Feng SP, Du XL, Liu YL, Zhang NN, Lin H (2011) Chemical fractionation and bioavailability of Cd, Ni, Cu, Zn and Pb in sewage-irrigated soils from Xiaoqing River, Zhangqiu Area. China Adv Mater Res 356-360:891–895
Gao L, Shi Y, Li W, Niu H, Liu J, Cai Y (2012) Occurrence of antibiotics in eight sewage treatment plants in Beijing, China. Chenmosphere 86:665–671
García-Galán MJ, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2011) Occurrence of sulfonamide residues along the Ebro river basin: removal in wastewater treatment plants and environmental impact assessment. Environ Int 37:462–473
Gräslund S, Bengtsson BE (2001) Chemicals and biological products used in south-east Asian shrimp farming, and their potential impact on the environment - a review. Sci Total Environ 280:93–131
Hu S, Liu X, Peng Y (2003) Assessment of antibiotic prescription in hospitalised patients at a Chinese University Hospital. J Inf Secur 46:161–163
Hu Y, Yan X, Shen Y, Di M, Wang J (2018) Antibiotics in surface water and sediments from Hanjiang River, Central China: occurrence, behavior and risk assessment. Ecotox Environ Safe 157:150–158
Hu W, Luo Y, Hu W (2019) Analysis of pollution characteristics of 12 antibiotics in Yongding River System. Haihe Water Resources 04, 18–20 (in Chinese)
Huang CH, Renew JE, Smeby KL, Pinkston K, Sedlak DL (2011) Assessment of potential antibiotic contaminants in water and preliminary occurrence analysis. J Contemp Water Res Educ 120(1)
Huang YQ, Wang Y, Huang YZ et al (2020) Impact of sediment characteristics on adsorption behavior of typical antibiotics in Lake Taihu. China Sci Total Environ 718:137329.1–137329.12
Jia L (2018) Simulation and mechanism of antibiotics reactive transport in the tidal estuary. Dissertation, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese)
Jiang L, Hu X, Yin D, Zhang H, Yu Z (2011) Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of antibiotics in the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 82:822–828
Jiang J, Lee C, Brimblecombe P, Vydrova L, Fang M (2016) Source contributions and mass loadings for chemicals of emerging concern: chemometric application of pharmaco-signature in different aquatic systems. Environ Pollut 208:79–86
Karcı A, Balcıoğlu IA (2009) Investigation of the tetracycline, sulfonamide, and fluoroquinolone antimicrobial compounds in animal manure and agricultural soils in Turkey. Sci Total Environ 407:4652–4664
Kümmerer K (2009) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment-a review-part I. Chemosphere 75:417–434
Lei X, Lu J, Liu Z, Tong Y, Li S (2015) Concentration and distribution of antibiotics in water–sediment system of Bosten Lake. Xinjiang Environ Sci Pollut R 22:1670–1678
Li J, Zhang RJ, Li RM, Zhang H, Jiang DJ, Zou T, Tang JH, Lv J (2016) Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of antibiotic pollution in Xiaoqing River watershed. J Agro-Environ Sci 35, 1384–1391 (in Chinese)
Liang X, Chen B, Nie X, Shi Z, Huang X, Li X (2013) The distribution and partitioning of common antibiotics in water and sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Chemosphere 92:1410–1416
Liu XH, Wang WL, Guo XC, Lu SY (2015) Occurrence, toxicity and risk of antibiotics in water. Water Wastewater Eng 51, 116–121 (in Chinese)
Liu X, Lu S, Guo W, Xi B, Wang W (2018) Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: a review of lakes. China Sci Total Environ 627:1195–1208
Lundén T, Miettinen S, Lönnström LG, Lilius EM, Bylund G (1998) Influence of oxytetracycline and oxolinic acid on the immune response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol 8:217–230
Luo X, Lin S, Yang J, Shen J, Fan Y, Zhang L (2017) Benthic habitat quality assessment based on biological indices in Xiaoqing River estuary and its adjacent sea of Laizhou Bay, China J Ocean Univ China 16, 537–546
Ma JG, Mei ZB, Xia Q, Hou BL, Zhao J (2003) Status quo and improvement measure of the Xiaoqing River sewage in Shandong Province. Research of Soil and Water Conservation 10, 108–111 (in Chinese)
Managaki S, Murata A, Takada H, Tuyen BC, Chiem NH (2007) Distribution of macrolides, sulfonamides, and trimethoprim in tropical waters: ubiquitous occurrence of veterinary antibiotics in the Mekong Delta. Environ Sci Technol 41:8004–8010
Nödler K, Licha T, Barbieri M, Pérez S (2012) Evidence for the microbially mediated abiotic formation of reversible and non-reversible sulfamethoxazole transformation products during denitrification. Water Res 46:2131–2139
Ouyang W, Huang F, Zhao Y, Li H, Su J (2015) Increased levels of antibiotic resistance in urban stream of Jiulongjiang River. China Appl Microbiol Boit 99:5697–5707
Pan X, Qiang Z, Ben W, Chen M (2011) Residual veterinary antibiotics in swine manure from concentrated animal feeding operations in Shandong Province, China. Chemosphere 84:695–700
Park J, Han E, Lee SO, Kim D (2017) Antibiotic use in South Korea from 2007 to 2014: a health insurance database-generated time series analysis. PLoS One 12:e177435
Sedgley CM, Lee EH, Martin MJ, Flannagan SE (2008) Antibiotic resistance gene transfer between Streptococcus gordonii and Enterococcus faecalis in root canals of teeth ex vivo. J Endodont 34:570–574
Shimizu A, Takada H, Koike T, Takeshita A, Saha M et al (2013) Ubiquitous occurrence of sulfonamides in tropical Asian waters. Sci Total Environ 452–453:108–115
Song C (2016) Enhanced biodegradation of tetracycline and its fate and behavior in natural environment. Dissertation, Shandong University (in Chinese)
Sun W, Zhang SB, Zhang JS, Wei X, Zhu JL, Liu YJ (2017) Quality assessment of aquatic environment and fluxes of major pollutants to the Xiaoqing River estuary. Mar Environ Sci 36, 366–371 (in Chinese)
Tamtam F, Mercier F, Le Bot B, Eurin J, Tuc Dinh Q, Clément M, Chevreuil M (2008) Occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Seine River in various hydrological conditions. Sci Total Environ 393:84–95
Thiele S (2000) Adsorption of the antibiotic pharmaceutical compound sulfapyridine by a long-term differently fertilized loess chernozem. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 168:589–594
Tong L, Qin L, Xie C, Liu H, Wang Y, Guan C, Huang S (2017) Distribution of antibiotics in alluvial sediment near animal breeding areas at the Jianghan Plain, Central China. Chemosphere 186:100–107
Wang M, Yu S, Hong YW, Sun LL (2011) Residual characteristics of various antibiotics in five typical coastal aquaculture waters. Ecol & Environ Sci 20, 934–939 (in Chinese)
Wang W, Wang H, Zhang W, Liang H, Gao D (2017) Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the Songhua River in China. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:19282–19292
Wang L, Luo X, Fan Y (2018) Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in Xiaoqing river estuary and its adjacent sea of Laizhou bay. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 128:12184
Watkinson AJ, Murby EJ, Kolpin DW, Costanzo SD (2009) The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: from wastewater to drinking water. Sci Total Environ 407:2711–2723
WHO (2015) Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance. http://wwwwhoint/antimicrobial-resistance/global-action-plan/en/
Wu YB, Liao XD, Wang ZS, Chen ZL, Zhou Y (2006) Hydrolysis characteristics of enrofloxacin. Chin J Appl Ecol 17, 1086–1090 (in Chinese)
Xu WH, Zhang G, Zou SC, Li XD, Liu YC (2006) Occurrence and seasonal changes of antibiotics in the Victoria harbour and the Pearl River, South China. Chin J Envir Sci 27 2458–2462 (in Chinese)
Xu W, Zhang G, Zou S, Li X, Liu Y (2007) Determination of selected antibiotics in the Victoria Harbour and the Pearl River, South China using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Environ Pollut 145:672–679
Xu W, Zhang G, Zou S, Ling Z, Wang G, Yan W (2009a) A preliminary investigation on the occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Yellow River and its tributaries, China. Water Environ Res 81:248–254
Xu WH, Zhang G, Zou SC, Yan W, Yang C (2009b) Behavior and fate of antibiotics in a lid-driven elongated annular flume. Res Environ Sci 22, 1213–1217 (in Chinese)
Xu W, Yan W, Li X, Zou Y, Chen X, Huang W, Miao L, Zhang R, Zhang G, Zou S (2013) Antibiotics in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta and Pearl River Estuary, China: concentrations, mass loading and ecological risks. Environ Pollut 182:402–407
Xue BM (2013) Contamination and risks assessment of typical antibiotics in the Yongjiang River, Guangxi Provence. Dissertation Guangxi, University (in Chinese)
Yan C, Yang Y, Zhou J, Liu M, Nie M, Shi H, Gu (2013) Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ Pollut 175, 22–29
Yang JF, Ying GG, Zhao JL, Tao R, Su HC, Chen F (2010) Simultaneous determination of four classes of antibiotics in sediments of the Pearl Rivers using RRLC–MS/MS. Sci Total Environ 408:3424–3432
Yang JF, Ying GG, Zhao JL, Tao R, Su HC, Liu YS (2011) Spatial and seasonal distribution of selected antibiotics in surface waters of the Pearl Rivers. China J Environ Sci Heal B 46:272–280
Yao L, Wang Y, Tong L, Deng Y, Li Y, Gan Y, Guo W, Dong C, Duan Y, Zhao K (2017) Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in surface water and groundwater from different depths of aquifers: a case study at Jianghan Plain, central China. Ecotox Environ Safe 135:236–242
Yu H, An YK, Shen ZY, Li ZX (2008) Water environmental carrying capacity in Xiaoqing River in Jinan. Water Resour Prot 24, 34–37 (in Chinese)
Yu S, Pang Y, Wang Y, Li J, Qin S (2017) Spatial variation of microbial communities in sediments along the environmental gradients from Xiaoqing River to Laizhou Bay. Mar Pollut Bull 120:90–98
Zhang LY (2016) Optimization of quinolone antibiotics detection method and in qater photolysis and hydrolysis characteristics research. Dissertation, Jilin Agricultural University (in Chinese)
Zhang Q, Ying G, Pan C, Liu Y, Zhao J (2015) Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ Sci Technol 49:6772–6782
Zhang PW, Zhou HD, Zhao GF, Li K, Zhao XH, et al (2017) Potential risk and distribution characteristics of PPCPs in surface water and sediment from rivers and lakes in Beijing, China Chin J Envir Sci 38, 1852–1862 (in Chinese)
Zhang LL, Shen L, Qin S, Cui JS, Liu Y (2020) Quinolones antibiotics in the Baiyangdian Lake, China: occurrence, distribution, predicted no-effect concentrations (PNECs) and ecological risks by three methods. Environ Pollut 256:113458.1–113458.9
Zhao FK, Chen LX, Yang L, Fang L, Sun L, Li SJ (2017) Composition and distribution of antibiotics in soils with different land use types in a typical peri-urban area of the Yangtze River delta. Chin J Envir Sci 38, 5237–5246 (in Chinese)
Zheng Q, Zhang R, Wang Y, Pan X, Tang J, Zhang G (2012) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Beibu Gulf, China: impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities. Mar Environ Res 78:26–33
Zhou L, Ying G, Zhao J, Yang J, Wang L, Yang B, Liu S (2011) Trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River in northern China. Environ Pollut 159:1877–1885
Zhu L, Zhang Y, Qu XD, Ma XP, Xu CB, Ding S (2014) Occurrence of antibiotics in aquatic plants and organisms from Qing River, Beijing Res Environ Sci 27, 139–146 (in Chinese)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41672340).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Miaowei Ci participates in all processes including the experimental part and article writing; Guodong Zhang is responsible for the analysis of the chapter of the article “Source contribution-a case of Jinan city” and experimental; Xianshou Yan is responsible for sampling and experiment; Wenping Dong and Wenfeng Xu are responsible for providing technical support for the experiment and Weiliang Wang and Yuqi Fan are responsible for providing opinions on the revision of the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ester Heath
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1005 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ci, M., Zhang, G., Yan, X. et al. Occurrence of antibiotics in the Xiaoqing River basin and antibiotic source contribution-a case study of Jinan city, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 25241–25254 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12202-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12202-z