Abstract
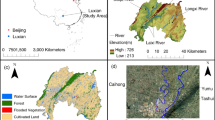
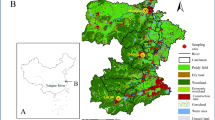
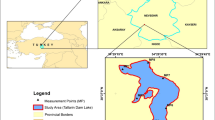
Proper evaluation of water quality is pertinent to estuarine habitat restoration. Identifying the degrading factors of the water environment and predicting the trend of eutrophication are key to restore the habitat. Through trophic level index (TLI), water quality index (WQI), modified Nemerow pollution index (NPI), and the Random Forest (RF) model, water samples collected from various estuaries of Taihu Lake from 2017 to 2019 were evaluated. To predict the water quality development, four scenarios were set viz. S1: add or remove an ecological buffer, S2: increase or reduce the external nutrients, S3: open or close the dam/gate, and S4: increase or decrease the internal release. In Wuli Lake, the nutrient concentrations in the river regions were higher than in the lake regions, while a contrary trend was observed in Gonghu Bay. The estuarine water quality in the dry season (WQI = 40.91, NPI = 1.73) was merely worse than that in the wet season (WQI = 47.27, NPI = 1.67). On the other hand, the eutrophic status in the wet season (TLIWet = 57.93) was worse than that in the dry season (TLIDry = 57.23). The estuarine water quality of Taihu Lake has improved from 2017 to 2019 but still belongs to medium level. The principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that dam construction, land use types, unstable hydrodynamic conditions, and trumpet-shaped estuary were the main factors that aggravated the water quality degradation. The RF model has strong forecasting capabilities for estuarine water quality. When the estuaries are close to residential and industrial districts, controlling the surface runoff and improving sewage treatment efficiency are the most effective measures to improve the water quality. In the estuaries, the sediments are usually disturbed by the wind-waves. Conclusively, reducing sediment disturbance and internal contamination accumulation via biological and engineering measures is the key to estuarine restoration.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Bahar MM, Ohmori H, Yamamuro M (2008) Relationship between river water quality and land use in a small river basin running through the urbanizing area of central Japan. Limnology 9:19–26
Barbier EB, Silliman BR (2011) The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol Monogr 81:169–193
Baudron P, Alonso-Sarría F, García-Aróstegui JL, Cánovas-García F, Martínez-Vicente D, Moreno-Brotóns J (2013) Identifying the origin of groundwater samples in a multi-layer aquifer system with random Forest classification. J Hydrol 499:3030–3315
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Bugica K, Blair SB, Michael SW (2020) Water quality trends in Texas estuaries. Mar Pollut Bull 152:110903
Chen X, Wang YH, Cai ZC, Zhang MH, Ye C (2020a) Response of the nitrogen load and its driving forces in estuarine water to dam construction in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:31458–31467
Chen X, Wang YH, Cai ZC, Wu CB, Ye C (2020b) Effects of land-use and land-cover change on nitrogen transport in northern Taihu Basin, China during 1990–2017. Sustainability 12:3895
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (2001) Lakes (reservoirs) eutrophication assessment methods and classification technology requirement (in Chinese). Natl Environ Monit Centre, Beijing
Dalal SG, Shiirodkar PV, Jagtap TG, Naik BG, Rao GS (2010) Evaluation of significant sources influencing the variation of water quality of Kandla creek, Gulf of Katchchh, using PCA. Environ Monit Assess 163:49–56
Dean TL, Richardson J (1999) Responses of seven species of native freshwater fish and a shrimp to low levels of dissolved oxygen. New Zeal J Mar Fresh 33:99–106
Dilek EA, Luo LC, David PH (2014) Temporal and spatial trends in water quality of Lake Taihu, China: analysis from a north to mid-lake transect, 1991–2011. Environ Monit Assess 186:3891–3904
Domingues RB, Anselmo TP, Barbosa AB, Sommer U, Galvao HM (2011) Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in the freshwater tidal zone of a turbid, Mediterranean estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf S 91:282–297
Elser JJ, Dobberfuhl DR, MacKay NA, Schampel JH (1996) Organism size, life history, and N: P stoichiometry. Bio-Science 46:674–684
Garnier J, Némery J, Billen G, Théry S (2005) Nutrient dynamics and control of eutrophication in the Marne River system: modelling the role of exchangeable phosphorus. J Hydrol 304:397–412
Gertru KM, Bruce DL, Pei SL, Lewis AM (2013) Quantification of internal phosphorus load in large, partially polymictic and mesotrophic Lake Simcoe Ontario. J Great Lakes Res 39:271–279
Guan YF, Wang JZ, Ni HG, Zeng EY (2009) Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta, China: assessment of mass loading, input source and environmental fate. Environ Pollut 157:618–624
Guo HY, Wang XR, Zhu JG (2004) Quantification and index of non-point source pollution in Taihu Lake region with GIS. Environ Geochem Health 26:147–156
Güsewell S (2004) N: P ratios in terrestrial plants: variation and functional significance. New Phytol 164:243–266
Han W, Fang JY, Guo D, Zhang Y (2005) Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol 168:377–385
He JS, Han XG (2010) Ecological stoichiometry: searching for unifying principles from individuals to ecosystems (in Chinese). Chinese J Plant Ecol 34:2–6
Hong YT, Chou L (2015) Analysis of prevention and control measures on agricultural non-point source pollution in Taihu Basin (in Chinese). Environ Sci Techonl 28:17–26
Hong H, Lu J (2014) Identification of river water pollution characteristics based on projection pursuit and factor analysis. Environ Earth Sci 72:3409–3417
Huang L, Fang HW, He GJ, Jiang HL, Wang CH (2016) Effects of internal loading on phosphorus distribution in the Taihu Lake driven by wind waves and lake currents. Environ Pollut 219:760–773
Ji XL, Randy AD, Zhang MH (2016) Comparison of seven water quality assessment methods for the characterization and management of highly impaired river systems. Environ Monit Assess 188:1–15
Jin XC, Liu SK, Zhang ZS, Tu QY, Xu NN (1995) Lake environment in China. Ocean Press, Beijing (In Chinese)
Jing LD, Bai S, Li YH, Peng Y, Wu CX, Liu JT (2019) Dredging project caused short-term positive effects on lake ecosystem health: a five-year follow-up study at the integrated lake ecosystem level. Sci Total Environ 686:753–763
Jones RA, Lee GF (1982) Recent advances in assessing impact of phosphorus loads on eutrophication-related water quality. Water Res 16:503–515
José M, José AGO, Alejandro DLS (2006) Assessing the improvement of the Bilbao estuary water quality in response to pollution abatement measures. Water Res 40:951–960
Kannel PR, Lee S, Lee YS, Kanel SR, Khan SP (2007) Application of water quality indices and dissolved oxygen as indicators for river water classification and urban impact assessment. Environ Monit Assess 132:93–110
Kocer MAT, Sevgili H (2014) Parameters selection for water quality index in the assessment of the environmental impacts of land-based trout farms. Ecol Indic 36:672–681
Kong FS, Ma RH, Gao JF, Wu XD (2009) The theory and practice of prevention, forecast and warning on cyanobacteria bloom in Lake Taihu (in Chinese). J Lake Sci 03:314–328
Lai YC, Yang CP, Hsieh CY, Wu CY, Kao CM (2011) Evaluation of non-point source pollution and river water quality using a multimedia two-model system. J Hydrol 409:583–595
Lee GF, Rast W, Jones RA (1978) Water report: eutrophication of water bodies: insights for an age-old problem. Environ Sci Technol 12:900–908
Lock A, Spiers G, Hostetler B, Ray J, Wallschlã GD (2016) Multi-dimensional water quality assessment of an urban drinking water source elucidated by high resolution underwater towed vehicle mapping. Water Res 93:289–295
Lu JJ, Zhang M, Quan SQ, Liu ZG, Chen WH, Yin Q, Ou YCY (2018) Integrated effects of hypoxia, high ammonia and low light on the growth and physiological C-N metabolism indices of Vallisneria natans (in Chinese). J Lake Sci 30:1064–1074
National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), China (2013) Cyanobacteria salvage in Taihu Lake. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/. Accessed 1 Jan 2020
National Environmental Protection Administration (NEPA) (2002) Monitoring and analysis method of water and waste water, 4th edn. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (In Chinese)
Paerl HW, Valders LM, Peierls BL, Adolf JE, Harding LJW (2006) Anthropogenic and climatic influences on the eutrophication of large estuarine ecosystems. Limnol Oceanogr 51:448–442
Pesce SF, Wunderlin DA (2000) Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Cordoba city (Argentina) on Suquya River. Water Res 34:2915–2926
Petit GD (1973) Effects of dissolved oxygen on survival and behavior of selected fishes of western Lake Erie. Bull Ohio Biol Surv 4:1–76
Qin BQ (2009) Lake eutrophication: control countermeasures and recycling exploitation. Ecol Eng 35:1569–1573
Qin BQ, Zhu GW (2006) The nutrient forms, cycling and exchange flux in the sediment and overlying water system in lakes from the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Sci China Ser D 49:1–13
Qin BQ, Paerl HW, Brookes JD (2019) Why Lake Taihu continues to be plagued with cyanobacterial blooms through 10 years (2007-2017) effects. Sci Bull 64:354–356
R Development Core Team (2018) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R 21 Foundation for statistical computing, Vienna
Redfield AC (1958) The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am Sci 46:205–221
Rodrigues AM, Cravo A, Freire P, Rosa A, Santos D (2020) Temporal assessment of the water quality along an urban estuary (Tagus estuary, Portugal). Mar Chem 223:103824
Shen ZY, Hou XS, Li W, Aini G, Chen L, Gong YW (2015) Impact of landscape pattern at multiple spatial scales on water quality: a case study in a typical urbanized watershed in China. Ecol Indic 48:417–427
State of China's Ecological Environment Bulletin (SCEEB), China (2020) China's ecological environmental bulletin. http://www.mee.gov.cn/. Accessed 1 Jan 2020
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Stone R (2011) China aims to turn tide against toxic lake pollution. Science 333:1210–1211
Taihu Basin Authority of Ministry of Water Resources (TBMWR), China (2020) The health status report of Taihu Lake. http://www.tba.gov.cn/. Accessed 1 Jan 2020
Tang CY, Li YP, He C, Acharya K (2019) Dynamic behavior of sediment resuspension and nutrients release in the shallow and wind-exposed Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu. Sci Total Environ 708:135131
Thingstad TF, Zweifei UL, Rassoulzadegan F (1998) P limitation of heterotrophic bacteria and phytoplankton in the Northwest Mediterranean. Limnol Oceanogr 43:88–94
Turo FD, Proietti C, Screpanti A, Fornasier MF, Cionni I, Favero G, Marco AD (2016) Impacts of air pollution on cultural heritage corrosion at European level: what has been achieved and what are the future scenarios. Environ Pollut 218:586–594
Verma AK, Singh TN (2013) Prediction of water quality from simple field parameters. Environ Earth Sci 69:821–829
Victor RG, Maria PM, Maria JGS, Mario CO, Luis R (2014) Predictive modeling of groundwater nitrate pollution using random forest and multisource variables related to intrinsic and specific vulnerability: a case study in an agricultural setting (southern Spain). Sci Total Environ 476-477:189–206
Vollenweider RA, Giovanardi F, Montanari G, Rinaldi A (1998) Characterization of the trophic conditions of marine coastal waters with special reference to the NW Adriatic Sea: proposal for a trophic scale, turbidity and generalized water quality index. Environmetrics 9:329–357
Wang JJ, Pang Y, Li YP, Huang YW, Luo J (2015) Experimental study of wind-induced sediment suspension and nutrient release in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10471–10479
Wang SL, Li JS, Zhang B, Spyrakos E, Tyler AN, Shen Q, Zhang FF, Kuster T, Lehmann MK, Wu YH, Peng DL (2018) Trophic state assessment of global inland waters using a MODIS-derived Forel-Ule index. Remote Sens Environ 217:444–460
Wang JL, Fu ZS, Qiao HX, Liu FX (2019) Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci Total Environ 650:1392–1402
Wang S, Xu Y, Wang D, Gao B, Lu M, Wang Q (2020) Effects of industry structures on water quality in different urbanized regions using an improved entropy-weighted matter-element methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:7549–7558
Wei GL, Yang ZF, Cui BS, Li B, Chen H, Bai JH, Dong SK (2009) Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water Resour Manag 23:1763–1780
Wu Z, Liu Y, Liang ZY, Wu SF, Guo HC (2017) Internal cycling, not external loading, decides the nutrient limitation in eutrophic lake: a dynamic model with temporal Bayesian hierarchical inference. Water Res 116:231–240
Wuxi City Bureau of Statistics (WXBS), China (2020) Statistical yearbook of Wuxi City. http://tj.wuxi.gov.cn/. Accessed 1 Jan 2020
Wuxi City Conservancy Bureau (WXCB), China (2007-2020) New chapter of water governance in Wuxi city for 70 years. http://water.wuxi.gov.cn/. Accessed 1 Jan 2020
Yang HC, Wang GQ, Wang LJ, Zheng BH (2015) Impact of land use changes on water quality in headwaters of the three gorges reservoir. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11448–11460
Yi QT, Chen QW, Hu LM, Shi WM (2017) Tracking nitrogen sources, transformation, and transport at a basin scale with complex plain river networks. Environ Sci Technol 51:539–5403
Yin P, Zhang JH, Kong XP (2019) Current situation analysis and countermeasure research on the harmless disposal and resource utilization of cyanobacteria in Taihu Lake (in Chinese). Jiangsu Water Resources 09:23–25
Zhu QD, Sun JH, Hua GF, Wang JH, Wang H (2015) Runoff characteristics and non-point source pollution analysis in the Taihu Lake Basin: a case study of the town of Xueyan, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:15029–15036
Acknowledgments
We thank the Taihu Laboratory for Lake Ecosystem Research, for Providing laboratory assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41673107), National Water Pollution Control and Treatment Science and Technology Major Project (2017ZX07203-005), Major project of Jiangsu Provincial Department of Education (20KJA170001), and PAPD (164320H116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed extensively to the work. YH Wang proposed and designed this research. X Chen performed the data interpretation and analysis and wrote the original draft. MH Zhang and C Ye supported the data collection and reviewed the draft. Y Chen and T Sun sampled and pretreated the samples.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Clinical trial registration
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 10907 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Wang, Y., Sun, T. et al. Evaluation and prediction of water quality in the dammed estuaries and rivers of Taihu Lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 12832–12844 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12063-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12063-6