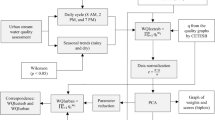
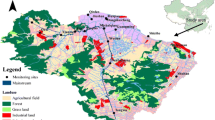
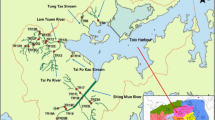
Abstract
Urbanization and industrialization significantly impact water quality, and detecting the specific factors which influence water quality change would greatly improve urban water environment management. In this study, an improved entropy-weighted matter-element method is used to assess the variations of water quality in two regions with different levels of urbanization in the Yangtze River Delta. Redundancy analysis was used to detect the effects of different industries on water quality. Results show that (1) an improved entropy weight-based matter-element method measures weights of pollutants and water quality levels more reliably and accurately; (2) the improvement rate of water quality in highly urbanized regions is 42.9% during 2005–2014 which is 17.2% higher than that in regions with low urbanization; (3) a decreasing concentration of total phosphorus is the main reason for changes of water quality in both regions, with decreasing concentrations of permanganate index and ammonium nitrogen having a strong influence on changes of water quality in the highly urbanized regions; (4) the decreasing proportion of fishery and heavy industries and the increasing proportion of the tertiary industries significantly influence water quality in highly urbanized regions while the decreasing proportion of animal husbandry is the most important factor influencing the changes of water quality in lowly urbanized regions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Kharabsheh A (1999) Influence of urbanization on water quality at Wadi Kufranja basin (Jordan). J Arid Environ 43(1):79–89
Brenner RP (2010) The low countries in the transition to capitalism. J Agrar Change 1(2):169–241
Chang F, Tsai YH, Chen P, Coynel A, Vachaud G (2015) Modeling water quality in an urban river using hydrological factors-data driven approaches. J Environ Manag 151:87–96
Chinese Environmental Protection Agency (2002) Technical specifications requirements for monitoring of surface water and waste water (HJ/T91–2002). China Environ Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Deng X, Xu Y, Han L, Yu Z, Yang M, Pan G (2015) Assessment of river health based on an improved entropy-based fuzzy matter-element model in the Taihu Plain, China. Ecol Indic 57:85–95
Ding J, Jiang Y, Liu Q, Hou Z, Liao J, Fu L, Peng Q (2016) Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: a multi-scale analysis. Sci Total Environ 551–552:205–216
Du C, Li Y, Wang Q, Liu G, Zheng Z, Mu M, Li Y (2017) Tempo-spatial dynamics of water quality and its response to river flow in estuary of Taihu Lake based on GOCI imagery. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(36):1–23
Franz C, Abbt-Braun G, Lorz C, Roig HL, Makeschin F (2014) Assessment and evaluation of metal contents in sediment and water samples within an urban watershed: an analysis of anthropogenic impacts on sediment and water quality in Central Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 72:4873–4890
Griffiths JA, Chan FKS, Zhu F, Wang V, Higgitt DL (2017) Reach-scale variation surface water quality in a reticular canal system in the lower Yangtze River Delta region, China. J Environ Manag 196:80–90
Guo H, Hu Q, Zhang Q, Feng S (2012) Effects of the three gorges dam on Yangtze river flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003-2008. J Hydrol 416:19–27
Hatano R, Nagumo T, Hata H, Kuramochi K (2005) Impact of nitrogen cycling on stream water quality in a basin associated with forest, grassland, and animal husbandry, Hokkaido, Japan. Ecol Eng 24:509–515
Hong H, Lu J (2014) Identification of river water pollution characteristics based on projection pursuit and factor analysis. Environ Earth Sci 72(9):3409–3417
Howell ET, Chomicki KM, Kaltenecker G (2012) Patterns in water quality on Canadian shores of Lake Ontario: correspondence with proximity to land and level of urbanization. J Great Lakes Res 38:32–46
Huang B, Shi X, Yu D, Öborn I, Blombäck K, Pagella TF, Wang H (2006) Environmental assessment of small-scale vegetable farming systems in peri-urban areas of the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 112:391–402
Jia S, Shi P, Hu Q, Li B, Zhang T, Zhang X (2015) Bacterial community shift drives antibiotic resistance promotion during drinking water chlorination. Environ Sci Technol 49(20):12271–12279
Le L, Wang S, Wang H, Zhang R, Jiao L, Ding S, Yu Y (2016) Temporal and spatial variations of phosphorus loading and the forms, compositions and contributions in inlet river of Lake Dianchi. J Lake Sci 28:951–960 (in Chinese)
Li B, Yang G, Wan R, Hörmann G (2017) Dynamic water quality evaluation based on fuzzy matter-element model and functional data analysis, a case study in Poyang Lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(7):1–11
Lin CH, Wu CH, Huang P (2009) Grey clustering analysis for incipient fault diagnosis in oil-immersed transformers. Expert Syst Appl 36(2):1371–1379
Lock A, Spiers G, Hostetler B, Ray J, Wallschlã Ger D (2016) Multi-dimensional water quality assessment of an urban drinking water source elucidated by high resolution underwater towed vehicle mapping. Water Res 93:289–295
Luo K, Hu X, He Q, Wu Z, Cheng H, Hu Z, Mazumder A (2017) Impacts of rapid urbanization on the water quality and macroinvertebrate communities of streams: a case study in Liangjiang New Area, China. Sci Total Environ 621:1601–1614
Ma L, Li J, Sun B, Xu X, Yang S, Duan X (2010) Water quality evaluation of drinking water sources based on matter-element extension and partial entropy weight—a case study of Dagang, Tianjin. Environl Sci Technol 33:177–179 (in Chinese)
Mainali J, Chang H (2018) Landscape and anthropogenic factors affecting spatial patterns of water quality trends in a large river basin, South Korea. J Hydrol 564:26–40
Muttil N, Chau KW (2007) Machine-learning paradigms for selecting ecologically significant input variables. Eng Appl Artif Intell 20(6):735–744
Netusil NR, Kincaid M, Chang H (2014) Valuing water quality in urban watersheds: a comparative analysis of Johnson Creek, Oregon and Burnt Bridge Creek, Washington. Water Resour Res 50:4254–4268
Pan G, Xu Y, Yu Z, Song S, Zhang Y (2015) Analysis of river health variation under the background of urbanization based on entropy weight and matter-element model: a case study in Huzhou City in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ Res 139:31–35
Pechar L, Mülle R, Naeve H (2010) Impacts of long-term changes in fishery management on the trophic level water quality in Czech fish ponds. Fisheries Manag Ecol 7:23–31
Shrestha S, Kazama F (2007) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ Model Softw 22:464–475
Singh KP, Basant A, Malik A, Jain G (2009) Artificial neural network modeling of the river water quality—a case study. Ecol Model 220(6):888–895
Sun C, Wu H (2012) Pollution from animal husbandry in China: a case study of the Han River basin. Water Sci Technol 66:872–878
Tang W, Shan B, Hong Z, Mao Z (2010) Heavy metal sources and associated risk in response to agricultural intensification in the estuarine sediments of Chaohu Lake Valley, East China. J Hazard Mater 176:945–951
Vanlandeghem MM, Meyer MD, Cox SB, Sharma B, Patiño R (2012) Spatial and temporal patterns of surface water quality and ichthyotoxicity in urban and rural river basins in Texas. Water Res 46:6638–6651
Wang J, Da L, Song K, Li B (2008) Temporal variations of surface water quality in urban, suburban and rural areas during rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China. Environl Pollut 152:387–393
Wang J, Jin F (2007) China’s air passenger transport: an analysis of recent trends. Eurasian Geogr Econ 48(4):469–480
Wilson C, Weng Q (2010) Assessing surface water quality and its relation with urban land cover changes in the Lake Calumet Area, Greater Chicago. Environ Manag 45:1096–1111
Wu J, Hong Y, Long M, Xu L, Qin B (2012) Water and sediment quality in lakes along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Water Resour Manag 26:3601–3618
Wu Z, Wang X, Chen Y, Cai Y, Deng J (2018) Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci Total Environ 612:914–922
Xue L, Li L, Zhang Q (2008) Hydrological behaviour and water balance analysis for Xitiaoxi catchment of Taihu Basin. Water Sci Eng 1(3):44–53
Ye X, Qi Z, Jian L, Li X, Xu C (2013) Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J Hydrol 494:83–95
Yu J, Li F, Ding C, Lin Z, Bian Z (2012) Evaluation of land eco-security in Wanjiang district base on entropy weight and matter element model. Transact Chinese Society Agri Eng 28:260–266 (in Chinese)
Zhang C, Zhang B, Li W, Liu M (2013) Response of streamflow to climate change and human activity in Xitiaoxi river basin in China. Hydrol Process 28(1):43–50
Zhao G, Gao J, Tian P, Tian K, Ni G (2011) Spatial–temporal characteristics of surface water quality in the Taihu Basin, China. Environ Earth Sci 64(3):809–819
Zhang J, Xu M, Zhang J, Guo Y (2015) Application of entropy weight matter-element extension model in black and smelly river evaluation. Yellow River 37:85–88 (in Chinese)
Zhang X, Wang C, Li E, Xu C (2014) Assessment model of environmental vulnerability based on improved entropy weight method. J Scientific World 2014:797–814
Zhang X, Liang C (2005) Application of fuzzy matter-element model based on coefficients of entropy in comprehensive evaluation of water quality. J Hydraul Eng 36:1057–1061 (in Chinese)
Zhang X, He S, Zhang Y, Chen S, Gao J (2010) Study on grey relational analysis method for water quality assessment. J Water Resour Water Eng 21(5):117–119
Funding
Financial support for this study was provided by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1508201), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41771032), and the Water Conservancy Science and Technology Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. 2015003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Xu, Y., Wang, D. et al. Effects of industry structures on water quality in different urbanized regions using an improved entropy-weighted matter-elementmethodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 7549–7558 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07400-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07400-3