Abstract
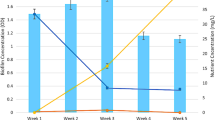
Chromium (Cr) is one of the most widely used heavy metals in industrial processes, resulting in water and soil pollution that seriously threaten environmental safety. In this paper, we have directionally enriched a Cr(VI)-reducing bacterial community YEM001 from no-Cr(VI) polluted pond sedimental sludge by selectively growing it in Cr(VI)-containing media. This community could effectively reduce Cr(VI) in laboratory rich media containing different concentrations of Cr(VI), such as 61% reduction at 435 mg/L Cr(VI), 85% reduction at 355 mg/L Cr(VI), and complete reduction at 269 mg/L Cr(VI) in 93.5 h. It was also able to completely reduce 100 mg/L and 300 mg/L Cr(VI) in landfill leachate and natural sludge in 48 h, respectively. Optimal pH for Cr(VI) reduction of the YEM001 is between 7 and 8 and the best efficiency for Cr(VI) reduction occurs at 30 °C. Metagenomic data demonstrated that the YEM001 community was composed of multiple bacteria, including well-known Cr(VI)-reducing bacteria and non-Cr(VI)-reducing bacteria. Delftia, Comamonas, Alicycliphilus, Acidovorax, Bacillus, and Clostridioides account for 83% of total community abundance. The stability of the composition of the YEM001 community and its Cr(VI)-reducing activity allows for its application in bioremediation of environmental Cr(VI) pollution.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adams AS, Jordan MS, Adams SM, Suen G, Goodwin LA, Davenport KW, Currie CR, Raffa KF (2011) Cellulose-degrading bacteria associated with the invasive woodwasp Sirex noctilio. ISME J 5:1323–1331
Arias YM, Tebo BM (2003) Cr(VI) reduction by sulfidogenic and nonsulfidogenic microbial consortia. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1847–1853
Baral A, Engelken RD (2002) Chromium-based regulations and greening in metal finishing industries in the USA. Environ Sci Pol 5:121–133
Biswas J, Bose P, Mandal S, Paul AK (2018) Reduction of hexavalent chromium by a moderately halophilic bacterium, Halomonas smyrnensis KS802 under saline environment. Environ Sustain 1:411–423
de Boer W, Verheggen P, Gunnewiek K, Paulien JA, Kowalchuk GA, van Veen JA (2003) Microbial community composition affects soil fungistasis. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:835–844
Cheung KH, Gu J-D (2007) Mechanism of hexavalent chromium detoxification by microorganisms and bioremediation application potential: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 59:8–15
Dong Q-Y, Wang Z, Shi L-D, Lai C-Y, Zhao H-P (2019) Anaerobic methane oxidation coupled to chromate reduction in a methane-based membrane biofilm batch reactor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:26286–26292
Francisco R, Alpoim MC, Morais PV (2002) Diversity of chromium-resistant and -reducing bacteria in a chromium-contaminated activated sludge. J Appl Microbiol 92:837–843
Gao Y, Xia J (2011) Chromium contamination accident in China: viewing environment policy of China. Environ Sci Technol 45:8605–8606
Gong Y, Lyu Y, Li P, Gong D, Gao Z, Chen J, Qi J, Liu Z, Li N, Guo J, Tian Y, Shen H, Tan X, Ren W, Zhang Y (2019) Characterization of anaerobic digestion of Chinese cabbage waste by a thermophilic microorganism community. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:1144–1154
He Z, Hu Y, Yin Z, Hu Y, Zhong H (2016) Microbial diversity of chromium-contaminated soils and characterization of six chromium-removing bacteria. Environ Manag 57:1319–1328
Kabir MM, Fakhruddin ANM, Chowdhury MAZ, Pramanik MK, Fardous Z (2018) Isolation and characterization of chromium(VI)-reducing bacteria from tannery effluents and solid wastes. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:126
Kato S, Haruta S, Cui ZJ, Ishii M, Igarashi Y (2004) Effective cellulose degradation by a mixed-culture system composed of a cellulolytic Clostridium and aerobic non-cellulolytic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 51:133–142
Kato S, Haruta S, Cui ZJ, Ishii M, Igarashi Y (2005) Stable coexistence of five bacterial strains as a cellulose-degrading community. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7099–7106
Khalifa AYZ, AlMalki M (2019) Polyphasic characterization of Delftia acidovorans ESM-1, a facultative methylotrophic bacterium isolated from rhizosphere of Eruca sativa. Saudi J Biol Sci 26:1262–1267
Lai C-Y, Zhong L, Zhang Y, Chen J-X, Wen L-L, Shi L-D, Sun Y-P, Ma F, Rittmann BE, Zhou C, Tang Y, Zheng P, Zhao H-P (2016) Bioreduction of chromate in a methane-based membrane biofilm reactor. Environ Sci Technol 50:5832–5839
Lennartson A (2014) The colours of chromium. Nat Chem 6:942
Li G-X, Zhou S-Y-D, Ren H-Y, Xue X-M, Xu Y-Y, Bao P (2018) Extracellular biomineralization of gold by Delftia tsuruhatensis GX-3 isolated from a heavy metal contaminated paddy soil. ACS Earth Space Chem 2:1294–1300
Li M, Zhuo Y, Hu Y, Li S, Hu L, Zhong H, He Z (2019) Exploration on the bioreduction mechanism of Cr(VI) by a gram-positive bacterium: Pseudochrobactrum saccharolyticum W1. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 184
Lin H, You S, Liu L (2019) Characterization of microbial communities, identification of Cr(VI) reducing bacteria in constructed wetland and Cr(VI) removal ability of Bacillus cereus. Sci Rep 9:12873
Liu B, Su G, Yang Y, Yao Y, Huang Y, Hu L, Zhong H, He Z (2019) Vertical distribution of microbial communities in chromium-contaminated soil and isolation of Cr(VI)-Reducing strains. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:242–251
Lv P-L, Shi L-D, Wang Z, Rittmann B, Zhao H-P (2019) Methane oxidation coupled to perchlorate reduction in a membrane biofilm batch reactor. Sci Total Environ 667:9–15
Ma Y, Zhong H, He Z (2019) Cr(VI) reductase activity locates in the cytoplasm of Aeribacillus pallidus BK1, a novel Cr(VI)-reducing thermophile isolated from Tengchong geothermal region, China. Chem Eng J 371:524–534
He M, Li X, Liu H, Miller SJ, Wang G, Rensing C (2011) Characterization and genomic analysis of a highly chromate resistant and reducing bacterial strain Lysinibacillus fusiformis ZC1. J Hazard Mater 185:682–688
Ohtake H, Cervantes C, Silver S (1987) Decreased chromate uptake in Pseudomonas fluorescens carrying a chromate resistance plasmid. J Bacteriol 169:3853–3856
Reddy GKK, Nancharaiah YV (2018) Sustainable bioreduction of toxic levels of chromate in a denitrifying granular sludge reactor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1969–1979
Sahinkaya E, Kilic A, Calimlioglu B, Toker Y (2013) Simultaneous bioreduction of nitrate and chromate using sulfur-based mixotrophic denitrification process. J Hazard Mater 262:234–239
Saluja B, Sharma V (2014) Cadmium resistance mechanism in acidophilic and alkalophilic bacterial isolates and their application in bioremediation of metal-contaminated soil. Soil Sediment Contam 23:1–17
Shen H, Wang YT (1995) Simultaneous chromium reduction and phenol degradation in a coculture of Escherichia coli ATCC 33456 and Pseudomonas putida DMP-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2754–2758
Shetty AR, de Gannes V, Obi CC, Lucas S, Lapidus A, Cheng J-F, Goodwin LA, Pitluck S, Peters L, Mikhailova N, Teshima H, Han C, Tapia R, Land M, Hauser LJ, Kyrpides N, Ivanova N, Pagani I, Chain PSG, Denef VJ, Woyke T, Hickey WJ (2015) Complete genome sequence of the phenanthrene-degrading soil bacterium Delftia acidovorans Cs 1-4. Stand Genomic Sci 10:55
Solis-Gonzalez CJ, Loza-Tavera H (2019) Alicycliphilus: current knowledge and potential for bioremediation of xenobiotics. J Appl Microbiol 126:1643–1656
Su X, Zhang S, Mei R, Zhang Y, Hashmi MZ, Liu J, Lin H, Ding L, Sun F (2018) Resuscitation of viable but non-culturable bacteria to enhance the cellulose-degrading capability of bacterial community in composting. Microb Biotechnol 11:527–536
Tariq M, Waseem M, Rasool MH, Zahoor MA, Hussain I (2019) Isolation and molecular characterization of the indigenous Staphylococcus aureus strain K1 with the ability to reduce hexavalent chromium for its application in bioremediation of metal-contaminated sites. PeerJ 7:e7726
Teles YV, de Castro LM, Sargentini Junior E, do Nascimento AP, da Silva HA, Costa RS, do Nascimento Souza RD, da Mota AJ, Pereira JO (2018) Potential of bacterial isolates from a stream in manaus-amazon to bioremediate chromium-contaminated environments. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:229–266
Terahara T, Xu X, Kobayashi T, Imada C (2015) Isolation and characterization of Cr(VI)-reducing actinomycetes from estuarine sediments. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:3297–3309
Thacker U, Parikh R, Shouche Y, Madamwar D (2007) Reduction of chromate by cell-free extract of Brucella sp. isolated from Cr(VI) contaminated sites. Bioresour Technol 98:1541–1547
Thatoi H, Das S, Mishra J, Rath BP, Das N (2014) Bacterial chromate reductase, a potential enzyme for bioremediation of hexavalent chromium: a review. J Environ Manag 146:383–399
Upreti RK, Shrivastava R, Chaturvedi UC (2004) Gut microflora & toxic metals: chromium as a model. Indian J Med Res 119:49–59
Wadgaonkar SL, Nancharaiah YV, Jacob C, Esposito G, Lens PNL (2019) Microbial transformation of Se oxyanions in cultures of Delftia lacustris grown under aerobic conditions. J Microbiol 57:362–371
Wilbur S, Ingerman L, Citra M, Osier M, Wohlers D (2000) Toxicological profile for chromium. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, Atlanta
Wu W, Huang H, Ling Z, Yu Z, Jiang Y, Liu P, Li X (2016) Genome sequencing reveals mechanisms for heavy metal resistance and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in Delftia lacustris strain LZ-C. Ecotoxicology 25:234–247
Yang J, He M, Wang G (2009) Removal of toxic chromate using free and immobilized Cr(VI)-reducing bacterial cells of Intrasporangium sp. Q5-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1579–1587
Ye J-X, Lin T-H, Hu J-T, Poudel R, Cheng Z-W, Zhang S-H, Chen J-M, Chen D-Z (2019) Enhancing chlorobenzene biodegradation by Delftia tsuruhatensis using a water-silicone oil biphasic system. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16
Zandt MHI’t, Bosch TJMD, Rijkers R, Kessel MAHJ, Jetten MSM, Welte CU (2018) Co-cultivation of the strictly anaerobic methanogen Methanosarcina barkeri with aerobic methanotrophs in an oxygen-limited membrane bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:5685–5694
Zhang X, Zhao S, Gao J, Lei Y, Yuan Y, Jiang Y, Xu Z, He C (2019) Microbial action and mechanisms for Cr(VI) removal performance by layered double hydroxide modified zeolite and quartz sand in constructed wetlands. J Environ Manag 246:636–646
Zhong L, Lai C-Y, Shi L-D, Wang K-D, Dai Y-J, Liu Y-W, Ma F, Rittmann BE, Zheng P, Zhao H-P (2017) Nitrate effects on chromate reduction in a methane-based biofilm. Water Res 115:130–137
Zhu Y, Yan J, Xia L, Zhang X, Luo L (2019) Mechanisms of Cr(VI) reduction by Bacillus sp. CRB-1, a novel Cr(VI)-reducing bacterium isolated from tannery activated sludge. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 186:109792
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Dr. Jinling Guo and Dr. Liwei Ren for valuable suggestions.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Major Project for Special Technology Innovation of Hubei Province (Nos. 2019ABA114 and 2017ABA157) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31370506, 21776162, and 31500422).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL and YZ designed the project, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript with input from all authors. TY, HL, ZQ, PL, ZS, and ZX conducted majority of the experiments. NL provided valuable suggestions. DG supervised all the work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Figure S1.
The change of pH of media during YEM001 was grown with different initial Cr(VI) concentration. The initial Cr(VI) concentration is A): 46.9 mg/L; B): 91.0 mg/L; C): 180.9 mg/L; D): 268.9 mg/L; E:) 355.3 mg/L; F): 435.2 mg/L (PNG 117 kb)
Figure S2.
The change of OD600 of YEM001culture during the growth at different initial Cr(VI) concentration. The initial Cr(VI) concentration is A): 50 mg/L; B): 100 mg/L; C): 200 mg/L; D): 300 mg/L; E): 400 mg/L; F): 500 mg/L (PNG 125 kb)
Figure S3.
The change of OD600 of YEM001culture at different pH during the growth in the presence of 100 mg/L Cr(VI) in the medium (PNG 57 kb)
Figure S4.
The change of OD600 (A) and Cr(VI) concentration (B) of YEM001 culture when grown at different temperatures in the presence of initial 100 mg/L Cr(VI) in the medium (PNG 383 kb)
Figure S5.
The Cr(VI) -reducing microorganism community structure and abundance without unclassified OTU (PNG 101 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, Y., Yang, T., Liu, H. et al. Enrichment and characterization of an effective hexavalent chromium-reducing microbial community YEM001. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 19866–19877 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11863-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11863-0