Abstract
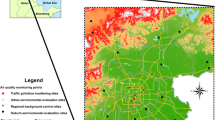
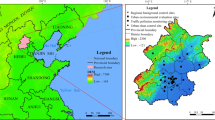
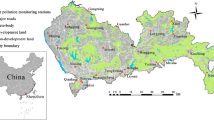
In order to calculate the spatial distribution of high-resolution air-pollutant levels, the land use regression (LUR) model can be an effective method due to the comprehensive consideration of various factors. Traditional LUR models mostly use predefined buffers, which have the disadvantage of not matching high-resolution data well. In order to get a better-fitting model, a few researches have proposed new buffer selection methods. To solve this problem, we propose a new optimal buffer selection method based on the dichotomy to improve the correlation between predicted variables and pollutant concentration. For some socioeconomic data with high spatial resolution that cannot be obtained, for example, building data is used instead of population density data. Compared with the model with the predefined buffers, the model with our buffer selection strategy explained additional 5% variability in measured concentrations, in terms of the R2 of the final model. Our model explained 98% of the samples, and the deviation (1.78%) and root mean square error (5.17 μg/m) were small. It means that the LUR model with our buffer selection strategy can be used as a fit method to better describe spatial variability in atmospheric pollutant levels, which will be conducive to epidemiological research and urban environmental planning.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Basu B, Alam MS, Ghosh B, Gill L, Mcnabola A (2019) Augmenting limited background monitoring data for improved performance in land use regression modelling: using support vector regression and mobile monitoring. Atmos Environ 201:310–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.12.048
Beelen R, Hoek G, Vienneau D, Eeftens M, Dimakopoulou K, Pedeli X, Tsai M-Y, Künzli N, Schikowski T, Marcon A, Eriksen KT, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Stephanou E, Patelarou E, Lanki T, Yli-Tuomi T, Declercq C, Falq G, Stempfelet M, Birk M, Cyrys J, Von Klot S, Nádor G, Varró MJ, Dėdelė A, Gražulevičienė R, Mölter A, Lindley S, Madsen C, Cesaroni G, Ranzi A, Badaloni C, Hoffmann B, Nonnemacher M, Krämer U, Kuhlbusch T, Cirach M, De Nazelle A, Nieuwenhuijsen M, Bellander T, Korek M, Olsson D, Strömgren M, Dons E, Jerrett M, Fischer P, Wang M, Brunekreef B, De Hoogh K (2013) Development of NO2 and NOx land use regression models for estimating air pollution exposure in 36 study areas in Europe – the ESCAPE project. Atmos Environ 72:10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.02.037
Briggs D, Susancollins P, Paulfischer S, Eriklebret K, Reeuwijk H, Kirstysmallbone, Veen AD (1997) Mapping urban air pollution using GIS: a regression-based approach. Int J Geogr Inf Syst 11:699–718. https://doi.org/10.1080/136588197242158
Chen L, Gao S, Zhang H, Sun Y, Ma Z, Vedal S, Mao J, Bai Z (2018) Spatiotemporal modeling of PM2.5 concentrations at the national scale combining land use regression and Bayesian maximum entropy in China. Environ Int 116:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.03.047
De Marco A, Amoatey P, Khaniabadi YO, Sicard P, Hopke PK (2018) Mortality and morbidity for cardiopulmonary diseases attributed to PM2.5 exposure in the metropolis of Rome, Italy. Eur J Intern Med 57:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2018.07.027
Dehghani, Keshtgar, Javaheri, Derakhshan, Conti O, Zuccarello, Ferrante (2017) The effects of air pollutants on the mortality rate of lung cancer and leukemia. Mol Med Rep 15:3390–3397. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6387
Eeftens M, Tsai M-Y, Ampe C, Anwander B, Beelen R, Bellander T, Cesaroni G, Cirach M, Cyrys J, De Hoogh K, De Nazelle A, De Vocht F, Declercq C, Dėdelė A, Eriksen K, Galassi C, Gražulevičienė R, Grivas G, Heinrich J, Hoffmann B, Iakovides M, Ineichen A, Katsouyanni K, Korek M, Krämer U, Kuhlbusch T, Lanki T, Madsen C, Meliefste K, Mölter A, Mosler G, Nieuwenhuijsen M, Oldenwening M, Pennanen A, Probst-Hensch N, Quass U, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Ranzi A, Stephanou E, Sugiri D, Udvardy O, Vaskövi É, Weinmayr G, Brunekreef B, Hoek G (2012) Spatial variation of PM2.5, PM10, PM2.5 absorbance and PMcoarse concentrations between and within 20 European study areas and the relationship with NO2 – results of the ESCAPE project. Atmos Environ 62:303–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.08.038
Fang D, Wang QG, Li H, Yu Y, Lu Y, Qian X (2016) Mortality effects assessment of ambient PM2.5 pollution in the 74 leading cities of China. Sci Total Environ 569:1545–1552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.248
Feng Y, Huang X, Sun H, Liu C, Zhang B, Zhang Z, Tengur VS, Chen W, Wu T, Yuan J (2015) Framingham risk score modifies the effect of PM10 on heart rate variability. Sci Total Environ 523:146–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.009
Fu H, Chen J (2017) Formation, features and controlling strategies of severe haze-fog pollutions in China. Sci Total Environ 578:121–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.201
Ghassoun Y, Löwner M-O (2017) Land use regression models for total particle number concentrations using 2D, 3D and semantic parameters. Atmos Environ 166:362–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.07.042
Gillespie J, Beverland IJ, Hamilton S, Padmanabhan S (2016) Development, evaluation, and comparison of land use regression modeling methods to estimate residential exposure to nitrogen dioxide in a cohort study. Environ Sci Technol 50:11085–11093. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02089
Guan QY, Cai A, Wang FF, Yang LQ, Xu CQ, Liu ZY (2017) Spatio-temporal variability of particulate matter in the key part of Gansu Province, Western China. Environ Pollut 230:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.045
Guan QY, Liu Z, Yang L, Luo H, Yang Y, Zhao R, Wang F (2019) Variation in PM2.5 source over megacities on the ancient Silk Road, northwestern China. J Clean Prod 208:897–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.199
Gulliver J, Hoohg KD, Hansell A, Vienneau D (2013) Development and backextrapolation of NO2 land use regression models for historic exposure assessment in Great Britain. Environ Sci Technol 47:7804e7811. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1021/es4008849
Gulliver J, Morley D, Dunster C, Mccrea A, Van Nunen E, Tsai MY, Probst-Hensch N, Eeftens M, Imboden M, Ducret-Stich R, Naccarati A, Galassi C, Ranzi A, Nieuwenhuijsen M, Curto A, Donaire-Gonzalez D, Cirach M, Vermeulen R, Vineis P, Hoek G, Kelly FJ (2018) Land use regression models for the oxidative potential of fine particles (PM2.5) in five European areas. Environ Res 160:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.10.002
Henderson SB, Beckerman B, Jerrett M, Brauer M (2007) Application of land use regression to estimate long-term concentrations of traffic-related nitrogen oxides and fine particulate matter. Environ Sci Technol 41:2422–2428. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0606780
Hoek G, Beelen R, De Hoogh K, Vienneau D, Gulliver J, Fischer P, Briggs D (2008) A review of land-use regression models to assess spatial variation of outdoor air pollution. Atmos Environ 42:7561–7578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.05.057
Huang J, Zhou C, Lee X, Bao Y, Zhao X, Fung J, Richter A, Liu X, Zheng Y (2013) The effects of rapid urbanization on the levels in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide and ozone over East China. Atmos Environ 77:558–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.05.030
Huang L, Zhang C, Bi J (2017) Development of land use regression models for PM2.5, SO2, NO2 and O3 in Nanjing, China. Environ Res 158:542–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.07.010
Lee M, Brauer M, Wong P, Tang R, Tsui TH, Choi C, Cheng W, Lai PC, Tian L, Thach TQ, Allen R, Barratt B (2017) Land use regression modelling of air pollution in high density high rise cities: a case study in Hong Kong. Sci Total Environ 592:306–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.094
Li X, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Zheng B, Wang K, Chen Y, Wallington TJ, Han W, Shen W, Zhang X, He K (2015) Source contributions of urban PM2.5 in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region: changes between 2006 and 2013 and relative impacts of emissions and meteorology. Atmos Environ 123:229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.10.048
Li R, Ma T, Xu Q, Song X (2018) Using MAIAC AOD to verify the PM2.5 spatial patterns of a land use regression model. Environ Pollut 243:501–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.026
Liu C, Henderson BH, Wang D, Yang X, Peng ZR (2016) A land use regression application into assessing spatial variation of intra-urban fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) concentrations in City of Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 565:607–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.189
Liu M, Huang Y, Ma Z, Jin Z, Liu X, Wang H, Kinney PL (2017) Spatial and temporal trends in the mortality burden of air pollution in China: 2004–2012. Environ Int 98:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.10.003
Liu Z, Guan Q, Luo H, Wang N, Pan N, Yang L, Xiao S, Lin J (2019) Development of land use regression model and health risk assessment for NO2 in different functional areas: a case study of Xi’an, China. Atmos Environ 213:515–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.07.008
Lu X, Lin C, Li Y, Yao T, Fung JCH, Lau AKH (2017) Assessment of health burden caused by particulate matter in southern China using high-resolution satellite observation. Environ Int 98:160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.11.002
Maji KJ, Ye WF, Arora M, Shiva Nagendra SM (2018) Pm2.5-related health and economic loss assessment for 338 Chinese cities. Environ Int 121:392–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.09.024
Meng X, Chen L, Cai J, Zou B, Wu CF, Fu Q, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Kan H (2015) A land use regression model for estimating the NO2 concentration in Shanghai, China. Environ Res 137:308–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.01.003
Miri M, Derakhshan Z, Allahabadi A, Ahmadi E, Oliveri Conti G, Ferrante M, Aval HE (2016) Mortality and morbidity due to exposure to outdoor air pollution in Mashhad metropolis, Iran. The AirQ model approach. Environ Res 151:451–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.07.039
Miri M, Ghassoun Y, Dovlatabadi A, Ebrahimnejad A, Lowner MO (2019) Estimate annual and seasonal PM1, PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations using land use regression model. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.070
Morley DW, Gulliver J (2018) A land use regression variable generation, modelling and prediction tool for air pollution exposure assessment. Environ Model Softw 105:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.03.030
Naughton O, Donnelly A, Nolan P, Pilla F, Misstear BD, Broderick B (2018) A land use regression model for explaining spatial variation in air pollution levels using a wind sector based approach. Sci Total Environ 630:1324–1334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.317
Olden JD, Jackson DA (2000) Torturing data for the sake of generality: how valid are our regression models. Écoscience 7:501–510. https://doi.org/10.1080/11956860.2000.11682622
Oliveri Conti G, Heibati B, Kloog I, Fiore M, Ferrante M (2017) A review of AirQ Models and their applications for forecasting the air pollution health outcomes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:6426–6445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8180-1
Peng L, Liu J-P, Wang Y, Chan P-W, Lee T-C, Peng F, Wong M-S, Li Y (2018) Wind weakening in a dense high-rise city due to over nearly five decades of urbanization. Build Environ 138:207–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2018.04.037
Querol X, Alastuey A, Pandolfi M, Reche C, Perez N, Minguillon MC, Moreno T, Viana M, Escudero M, Orio A, Pallares M, Reina F (2014) 2001-2012 trends on air quality in Spain. Sci Total Environ 490:957–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.074
Saha PK, Li HZ, Apte JS, Robinson AL, Presto AA (2019) Urban ultrafine particle exposure assessment with land-use regression: influence of sampling strategy. Environ Sci Technol 53:7326–7336. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b02086
Sanchez M, Ambros A, Mila C, Salmon M, Balakrishnan K, Sambandam S, Sreekanth V, Marshall JD, Tonne C (2018) Development of land-use regression models for fine particles and black carbon in peri-urban South India. Sci Total Environ 634:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.308
Shi Y, Ho HC, Xu Y, Ng E (2018) Improving satellite aerosol optical Depth-PM2.5 correlations using land use regression with microscale geographic predictors in a high-density urban context. Atmos Environ 190:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.07.021
Signorelli SS, Oliveri CG, Zanobetti A, Baccarelli A, Fiore M, Ferrante M (2019) Effect of particulate matter-bound metals exposure on prothrombotic biomarkers: a systematic review. Environ Res 177:108573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108573
Song C, Wu L, Xie Y, He J, Chen X, Wang T, Lin Y, Jin T, Wang A, Liu Y, Dai Q, Liu B, Wang YN, Mao H (2017) Air pollution in China: status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ Pollut 227:334–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.075
Stone R, Anderson G, Andrews E, et al. (2005) Asian dust signature at Barrow: observed and simulated incursions and impact of Asian dust over Northern Alaska. IEEE Workshop on Remote Sensing of Atmospheric Aerosols, pp. 74-79
Su JG, Brauer M, Ainslie B, Steyn D, Larson T, Buzzelli M (2008) An innovative land use regression model incorporating meteorology for exposure analysis. Sci Total Environ 390:520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.10.032
Su JG, Jerrett M, Beckerman B (2009a) A distance-decay variable selection strategy for land use regression modeling of ambient air pollution exposures. Sci Total Environ 407:3890–3898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.01.061
Su JG, Jerrett M, Beckerman B, Wilhelm M, Ghosh JK, Ritz B (2009b) Predicting traffic-related air pollution in Los Angeles using a distance decay regression selection strategy. Environ Res 109:657–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2009.06.001
Wang F, Lin T, Feng J, Fu H, Guo Z (2015) Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2. 5 using positive matrix factorization modeling in Shanghai, China. Environ Sci-Process Impacts 17:197–205. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2014.12.02
Wild RJ, Dubé WP, Aikin KC, Eilerman SJ, Neuman JA, Peischl J, Ryerson TB, Brown SS (2017) On-road measurements of vehicle NO2 /NOx emission ratios in Denver, Colorado, USA. Atmos Environ 148:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.10.039
World Health Organization (2016) Ambient air pollution: a global assessment of exposure and burden of disease. Accessed on 10/23/2017 @. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/250141/1/9789241511353-eng.pdf.
Wu J, Wilhelm M, Chung J, Ritz B (2011) Comparing exposure assessment methods for traffic-related air pollution in an adverse, pregnancy outcome study. Environ Res 111:685e692–685e692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2011.03.008
Wu J, Li J, Peng J, Li W, Xu G, Dong C (2015) Applying land use regression model to estimate spatial variation of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:7045–7061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3893-5
Yang X, Zheng Y, Geng G, Liu H, Man H, Lv Z, He K, De Hoogh K (2017) Development of PM2.5 and NO2 models in a LUR framework incorporating satellite remote sensing and air quality model data in Pearl River Delta region, China. Environ Pollut 226:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.079
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the editors and reviewers who have put considerable time and effort into their comments on this paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41671188).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Zeyu Liu, Jinkuo Lin, Liqin Yang, Haiping Luo, and Ning Wang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Zeyu Liu, and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable. The manuscript does not report on or involve the use of any animal or human data or tissue.
Consent for publication
All the authors contributed to the study conception and agreed to publish this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Guan, Q., Lin, J. et al. A new buffer selection strategy for land use regression model of PM2.5 in Xi’an, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 21245–21255 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11770-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11770-4