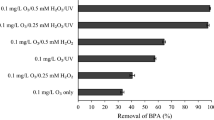
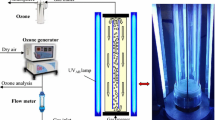
Abstract
Pharmaceuticals and their degradation products which are present in wastewater and superficial waters are becoming an ecological issue. This research investigated the degradation and mineralization of synthetic solutions of the pharmaceutical compound sildenafil citrate (SC) by single ozonation and ozonation jointed with UV radiation (O3/UV). The effects of initial drug concentration (50–125 mg L−1), inlet ozone concentration (35–125 g Nm−3), and UV radiation on SC degradation and decrease of total organic carbon (TOC) were investigated using response surface methodology based on a central composite experimental design. Through the RSM analysis, it was possible to confirm the removal of SC for the entire experimental range. Major intermediates of SC degradation were identified and a degradation pathway was proposed. The kinetics of SC degradation was modeled as a pseudo-first-order reaction with a rate constant ranging between 0.072 and 1.250 min−1. The SC degradation and TOC removal were strongly enhanced by increasing the concentration of gaseous ozone at the inlet and incorporating UV radiation. The highest TOC removal reached at 60 min was 75%, in the O3/UV system, with initial SC content of 50 mg L−1 and inlet ozone concentration of 125 g Nm−3. The degradation rate of SC was increased 3 to 9 times in the presence of UV radiation. Ozone-based advanced oxidation processes appear as a suitable alternative for treatment of the emerging pollutant SC.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abellán MN, Gebhardt W, Schröder HF (2008) Detection and identification of degradation products of sulfamethoxazole by means of LC/MS and - MSn after ozone treatment. Water Sci Technol 58:1803–1812. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2008.539
Abrile MG, Fiasconaro ML, Lovato ME (2020) Optimization of Reactive Blue 19 dye removal using ozone and ozone/UV employing response surface methodology. SN Appl Sci 2:995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2824-y
Al-Baldawi IAW, Sheikh Abdullah SR, Abu Hasan H et al (2014) Optimized conditions for phytoremediation of diesel by Scirpus grossus in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands (HSFCWs) using response surface methodology. J Environ Manag 140:152–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.03.007
Alharbi SK, Price WE, Kang J, Fujioka T, Nghiem LD (2016) Ozonation of carbamazepine, diclofenac, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim and formation of major oxidation products. Desalin Water Treat 57:29340–29351. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1172986
Almomani FA, Shawaqfah M, Bhosale RR, Kumar A (2016) Removal of emerging pharmaceuticals from wastewater by ozone-based advanced oxidation processes. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 35:982–995. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12306
Andreozzi R, Caprio V, Insola A, Marotta R (1999) Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery. Catal Today 53:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(99)00102-9
Antoniou MG, Hey G, Rodríguez Vega S, Spiliotopoulou A, Fick J, Tysklind M, la Cour Jansen J, Andersen HR (2013) Required ozone doses for removing pharmaceuticals from wastewater effluents. Sci Total Environ 456–457:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.03.072
Arslan A, Veli S, Bingöl D (2014) Use of response surface methodology for pretreatment of hospital wastewater by O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2 processes. Sep Purif Technol 132:561–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.05.036
Asaithambi P, Aziz ARA, Daud WMABW (2016) Integrated ozone—electrocoagulation process for the removal of pollutant from industrial effluent: optimization through response surface methodology. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 105:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2016.03.013
Bavasso I, Poggi C, Petrucci E (2020) Enhanced degradation of paracetamol by combining UV with electrogenerated hydrogen peroxide and ozone. J Water Process Eng 34:101102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101102
Beltrán F (2003) Ozone reaction kinetics for water and wastewater system. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Boleda MR, Galceran MT, Ventura F (2011) Behavior of pharmaceuticals and drugs of abuse in a drinking water treatment plant (DWTP) using combined conventional and ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis (UF/RO) treatments. Environ Pollut 159:1584–1591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.051
Chávez AM, Rey A, López J, Álvarez PM, Beltrán FJ (2021) Critical aspects of the stability and catalytic activity of MIL-100(Fe) in different advanced oxidation processes. Sep Purif Technol 255:117660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117660
Dang C, Sun F, Jiang H, Huang T, Liu W, Chen X, Ji H (2020) Pre-accumulation and in-situ destruction of diclofenac by a photo-regenerable activated carbon fiber supported titanate nanotubes composite material: intermediates, DFT calculation, and ecotoxicity. J Hazard Mater 400:123225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123225
Dantas RF, Contreras S, Sans C, Esplugas S (2008) Sulfamethoxazole abatement by means of ozonation. J Hazard Mater 150:790–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.034
Delgado N, Navarro A, Marino D, Peñuela GA, Ronco A (2019) Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from domestic wastewater using rotating biological contactors. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1658-2
Eichhorn P, Pérez S, Aceña J, Gardinali P, Abad JL, Barceló D (2012) Identification of phototransformation products of sildenafil (Viagra) and its N-demethylated human metabolite under simulated sunlight. J Mass Spectrom 47:701–711. https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.2998
Ganzenko O, Trellu C, Oturan N, Huguenot D, Péchaud Y, van Hullebusch ED, Oturan MA (2020) Electro-Fenton treatment of a complex pharmaceutical mixture: mineralization efficiency and biodegradability enhancement. Chemosphere 253:126659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126659
García-Espinoza JD, Nacheva MP (2019) Degradation of pharmaceutical compounds in water by oxygenated electrochemical oxidation: parametric optimization, kinetic studies and toxicity assessment. Sci Total Environ 691:417–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.118
Gilliard MB, Martín CA, Cassano AE, Lovato ME (2013) A reaction kinetic model for 2, 4-D decomposition in aqueous media including direct photolysis, direct ozonation, UVC and pH enhancemen. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:14034–14048. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie400957m
Gordon G, Bubnis B (2002) Residual ozone measurement: indigo sensitivity coefficient adjustment. Ozone Sci Eng 24:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919510208901591
Grossberger A, Hadar Y, Borch T, Chefetz B (2014) Biodegradability of pharmaceutical compounds in agricultural soils irrigated with treated wastewater. Environ Pollut 185:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.10.038
Guo WQ, Yin RL, Zhou XJ, Cao HO, Chang JS, Ren NQ (2015) Ultrasonic-assisted ozone oxidation process for sulfamethoxazole removal: impact factors and degradation process. Desalin Water Treat 57:21015–21022. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1115373
Herbert LP, Becker-Krail DB, Cory WC (2015) Persistent phototransformation products of vardenafil (Levitra®) and sildenafil (Viagra®). Chemosphere 134:557–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.12.011
Hübner U, Seiwert B, Reemtsma T, Jekel M (2014) Ozonation products of carbamazepine and their removal from secondary effluents by soil aquifer treatment - indications from column experiments. Water Res 49:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.11.016
Ji H, Du P, Zhao D et al (2020) 2D/1D graphitic carbon nitride/titanate nanotubes heterostructure for efficient photocatalysis of sulfamethazine under solar light: catalytic “hot spots” at the rutile–anatase–titanate interfaces. Appl Catal B Environ 263:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118357
Jiao W, Yang P, Gao W, Qiao J, Liu Y (2019) Apparent kinetics of the ozone oxidation of nitrobenzene in aqueous solution enhanced by high gravity technology. Chem Eng Process - Process Intensif 146:107690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2019.107690
Kaur H, Hippargi G, Pophali GR, Bansiwal AK (2019) Treatment methods for removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from domestic wastewater. In: Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products: Waste Management and Treatment Technology. Elsevier Inc., pp 129–150
Kharel S, Stapf M, Miehe U, Ekblad M, Cimbritz M, Falås P, Nilsson J, Sehlén R, Bester K (2020) Ozone dose dependent formation and removal of ozonation products of pharmaceuticals in pilot and full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 731:139064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139064
Lee Y, Gerrity D, Lee M, Bogeat AE, Salhi E, Gamage S, Trenholm RA, Wert EC, Snyder SA, von Gunten U (2013) Prediction of micropollutant elimination during ozonation of municipal wastewater effluents: use of kinetic and water specific information. Environ Sci Technol 47:5872–5881. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400781r
Liu X, Garoma T, Chen Z, Wang L, Wu Y (2012) SMX degradation by ozonation and UV radiation: a kinetic study. Chemosphere 87:1134–1140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.007
Lovato ME, Fiasconaro ML, Martín CA (2017) Degradation and toxicity depletion of RB19 anthraquinone dye in water by ozone-based technologies. Water Sci Technol 75:813–822. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.501
Ma M, Chen L, Zhao J, Liu W, Ji H (2019) Efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by hollow cobalt hydroxide for degradation of ibuprofen and theoretical study. Chinese Chem Lett 30:2191–2195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.09.031
Machrouhi A, Alilou H, Farnane M, el Hamidi S, Sadiq M, Abdennouri M, Tounsadi H, Barka N (2019) Statistical optimization of activated carbon from Thapsia transtagana stems and dyes removal efficiency using central composite design. J Sci Adv Mater Devices 4:544–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2019.09.002
Mcdowell DC, Huber MM, Wagner M et al (2005) Ozonation of carbamazepine in drinking water: identification and kinetic study of major oxidation products. Environ Sci Technol 39:8014–8022. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050043l
Medana C, Calza P, Giancotti V, Bello FD, Pasello E, Montana M, Baiocchi C (2011) Horse metabolism and the photocatalytic process as a tool to identify metabolic products formed from dopant substances: the case of sildenafil. Drug Test Anal 3:724–734. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.334
Montgomery DC (2013) Design and analysis of experiments, 8 th. John Wiley & Sons
Naddeo V, Uyguner-Demirel CS, Prado M, Cesaro A, Belgiorno V, Ballesteros F (2015) Enhanced ozonation of selected pharmaceutical compounds by sonolysis. Environ Technol 36:1876–1883. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2015.1014864
Nativelle C, Picard K, Valentin I, Lhuguenot JC, Chagnon MC (1999) Metabolism of n-butyl benzyl phthalate in the female Wistar rat. Identification of new metabolites. Food Chem Toxicol 37:905–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0278-6915(99)00071-x
Nieto A, Peschka M, Borrull F, Pocurull E, Marcé RM, Knepper TP (2010) Phosphodiesterase type V inhibitors: occurrence and fate in wastewater and sewage sludge. Water Res 44:1607–1615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.11.009
Pisarenko AN, Stanford BD, Yan D, Gerrity D, Snyder SA (2012) Effects of ozone and ozone/peroxide on trace organic contaminants and NDMA in drinking water and water reuse applications. Water Res 46:316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.10.021
Pocostales P, Álvarez P, Beltrán FJ (2011) Catalytic ozonation promoted by alumina-based catalysts for the removal of some pharmaceutical compounds from water. Chem Eng J 168:1289–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.02.042
Prieto-Rodríguez L, Oller I, Klamerth N, Agüera A, Rodríguez EM, Malato S (2013) Application of solar AOPs and ozonation for elimination of micropollutants in municipal wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res 47:1521–1528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.002
Rivera-Utrilla J, Sánchez-Polo M, Ferro-García MÁ, Prados-Joya G, Ocampo-Pérez R (2013) Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review Chemosphere 93:1268–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.059
Rodayan A, Roy R, Yargeau V (2010) Oxidation products of sulfamethoxazole in ozonated secondary effluent. J Hazard Mater 177:237–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.023
Sánchez-Albores RM, Pérez-Sariñana BY, Meza-Avendaño CA, Sebastian PJ, Reyes-Vallejo O, Robles-Ocampo JB (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis of bismuth vanadate-alumina assisted by microwaves to evaluate the photocatalytic activity in the degradation of methylene Blue. Catal Today 353:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.07.044
Sanusi SNA, Halmi MIE, Abdullah SRS, Hassan HA, Hamzah FM, Idris M (2016) Comparative process optimization of pilot-scale total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) degradation by Paspalum scrobiculatum L. hack using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural networks (ANNs). Ecol Eng 97:524–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.10.044
Schröder HF, Gebhardt W, Thevis M (2010) Anabolic, doping, and lifestyle drugs, and selected metabolites in wastewater-detection, quantification, and behaviour monitored by high-resolution MS and MS n before and after sewage treatment. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:1207–1229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3958-3
Sgroi M, Roccaro P, Oelker GL, Snyder SA (2014) N -nitrosodimethylamine formation upon ozonation and identification of precursors source in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 48:10308–10315. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5011658
Shen Y, Xu Q, Gao D, Shi H (2017) Degradation of an anthraquinone dye by ozone/Fenton: response surface approach and degradation pathway. Ozone Sci Eng 39:219–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2017.1301245
Soltani-nezhad F, Saljooqi A, Shamspur T, Mostafavi A (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of imidacloprid using GO/Fe3O4/TiO2-NiO under visible radiation: optimization by response level method. Polyhedron 165:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2019.02.012
Vera Candioti L, De Zan MM, Cámara MS, Goicoechea HC (2014) Experimental design and multiple response optimization. Using the desirability function in analytical methods development Talanta 124:123–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.01.034
Wang Y, Li H, Yi P, Zhang H (2019) Degradation of clofibric acid by UV, O3 and UV/O3 processes: performance comparison and degradation pathways. J Hazard Mater 379:120771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120771
Acknowledgments
Thanks are given to J.C. Andini, S.M. Addona, and F. Marino for technical assistance during the experimental work.
Funding
This work was partially financially supported by the following: (i) Project CAI+D 50020150100060LI funded by Universidad Nacional del Litoral and (ii) Project PICT 2015-2651funded by Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica. Mariana G. Abrile acknowledges Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET) for her scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mariana G. Abrile: investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing
María M. Ciucio: investigation
Lourdes M. Demarchi: investigation
Virginia M. Bono: Investigation
María L. Fiasconaro: formal analysis
María E. Lovato: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abrile, M.G., Ciucio, M.M., Demarchi, L.M. et al. Degradation and mineralization of the emerging pharmaceutical pollutant sildenafil by ozone and UV radiation using response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 23868–23886 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11717-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11717-9