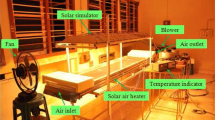
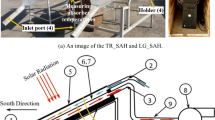
Abstract
In this study, an assessment based on energy, exergy, economic, and environmental approaches on a double-pass (DP) solar air heater (SAH) having pin finned absorber at different air mass ratios up and down the absorber is investigated experimentally. Four air mass ratios are considered: (i) all the air mass flow passes up the absorber and returns to pass down the absorber (DP), (ii) 2/3 of the airflow passes up the absorber and returns to mix with the remainder of air to pass down the absorber (2/3 DP), (iii) the same as (ii) but 1/3 of the air passes up the absorber (1/3 DP), and (iv) all the air mass passes only down the absorber (single pass, SP). For all mass ratios, the performance of pin finned SAH (P_SAH) is compared with that of flat SAH (F_SAH). The results indicated that the air temperature rise and energy and exergy efficiencies of P_SAH are highly greater than those of F_SAH. The highest average thermal efficiency of F_SAH is 56.7% obtained at DP flow condition, whereas the highest value of P_SAH is 65.21% obtained at 2/3 DP with an increase of 17.6% compared with F_SAH. Also, P_SAH has higher average exergy efficiency of about 34.7% compared to F_SAH. Furthermore, P_SAH achieves energy payback time (EPBT) lower than that of F_SAH, while P_SAH has higher embodied energy. The findings indicated that F_SAH at SP airflow pattern has the maximum energy cost (0.0427 $/kWh), whereas P_SAH at 2/3 DP airflow pattern achieves the minimum energy cost (0.037 $/kWh). Finally, the proposed P_SAH system appears to be more viable from exergoeconomic and enviroeconomic approaches compared to F_SAH.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included only in this paper and are not available in any other works.
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Inlet port cross-sectional area (m2)
- C p :
-
Specific heat, J/kg K
- E in :
-
Embodied energy in (kW h)
- EPBTen :
-
Energy payback time based on energy (years)
- EPBTex :
-
Energy payback time based on exergy (years)
- Enout :
-
Overall energy outlet (W)
- \( \dot{E}{x}_{\mathrm{in}} \) :
-
Exergy inlet (W)
- \( \dot{E}{x}_{\mathrm{out}} \) :
-
Exergy outlet (W)
- \( \dot{E}{x}_{\mathrm{heat}} \) :
-
Exergy of heat (W)
- \( \dot{E}{x}_{\mathrm{work}} \) :
-
Exergy of work (W)
- \( \dot{E}{x}_{\mathrm{mass},\mathrm{in}} \) :
-
Exergy of inlet mass (W)
- \( \dot{E}{x}_{\mathrm{mass},\mathrm{out}} \) :
-
Exergy of outlet mass (W)
- \( \dot{E}{x}_{\mathrm{dest}} \) :
-
Exergy destruction (W)
- h :
-
Specific enthalpy (J/kg K)
- I :
-
Incident solar radiation (W/m2)
- \( \dot{m} \) :
-
Mass flow rate (kg/s)
- n :
-
Day of the year
- p :
-
Pressure (pa)
- R :
-
Gas constant (J/mol K)
- R g,ex :
-
Exergoeconomic parameter (kWh/$)
- S :
-
entropy (J/K)
- T :
-
Temperature (°C)
- Q :
-
Energy rate (J/s)
- YC:
-
Annual cost ($)
- Z CO2 :
-
Enviroeconomic parameter ($)
- z CO2 :
-
International carbon price ($)
- ρ:
-
Density (kg/m3)
- σ :
-
Stefan Boltzmann constant (W/m2 K4)
- ε :
-
Emissivity
- ρ :
-
Reflectance
- η :
-
Efficiency
- ϕCO2 :
-
Environmental parameter (ton CO2)
- τ :
-
Transmissivity
- α :
-
Absorptivity
- ψ :
-
Specific exergy (J/kg)
- ∆s :
-
Entropy change (J/K)
- AMFR:
-
Air mass flow rate
- CFD:
-
Computational fluid dynamic
- DP:
-
Double pass
- F_SAH:
-
Flat solar air heater
- FYC:
-
First yearly cost
- GRF:
-
Global recovery factor
- MFR:
-
Mass flow rate
- PCM:
-
Phase change material
- P_SAH:
-
Pin fins solar air heater
- SAH:
-
Solar air heater
- SP:
-
Single pass
- SSF:
-
Sinking fund factor
- YSV:
-
Yearly salvage value
- a:
-
Ambient
- en:
-
Energy
- ex:
-
Exergy
- f:
-
Fluid
- in:
-
Inlet
- out:
-
Outlet
- s:
-
Sun
References
Abd Elbar AR, Hassan H (2020) An experimental work on the performance of new integration of photovoltaic panel with solar still in semi-arid climate conditions. Renew Energy 146:1429–1443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.07.069
Abd Elbar AR, Yousef MS, Hassan H (2019) Energy, exergy, exergoeconomic and enviroeconomic (4E) evaluation of a new integration of solar still with photovoltaic panel. J Clean Prod 233:665–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.111
Abdelkader TK, Zhang Y, Gaballah ES, Wang S, Wan Q, Fan Q (2020) Energy and exergy analysis of a flat-plate solar air heater coated with carbon nanotubes and cupric oxide nanoparticles embedded in black paint. J Clean Prod 250:119501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119501
Abo-Elfadl S, Hassan H, El-Dosoky MF (2020a) Study of the performance of double pass solar air heater of a new designed absorber: an experimental work. Sol Energy 198:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.01.091
Abo-Elfadl S, Hassan H, El-Dosoky MF (2020b) Energy and exergy assessment of integrating reflectors on thermal energy storage of evacuated tube solar collector-heat pipe system. Sol Energy 209:470–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.09.009
Abo-Elfadl S, Yousef MS, Hassan H (2020c) Energy, exergy, economic and environmental assessment of using different passive condenser designs of solar distiller. Process Saf Environ Prot 148:302–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.10.022
Abuşka M, Şevik S (2017) Energy, exergy, economic and environmental (4E) analyses of flat-plate and v-groove solar air collectors based on aluminium and copper. Sol Energy 158:259–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.09.045
Adedeji MJ, Ruwa TL, Abid M, Ratlamwala TAH, Dagbasi M (2017) Energy, exergy, economic and environmental analysis of photovoltaic thermal systems for absorption cooling application. Energy Procedia 142:916–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.12.147
Ahmadi Boyaghchi F, Nazer S (2017) Assessment and optimization of a new sextuple energy system incorporated with concentrated photovoltaic thermal - geothermal using exergy, economic and environmental concepts. J Clean Prod 164:70–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.194
Akpinar EK, Koçyiĝit F (2010) Energy and exergy analysis of a new flat-plate solar air heater having different obstacles on absorber plates. Appl Energy 87:3438–3450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.05.017
Anto Joseph Deeyoko L, Balaji K, Iniyan S, Sharmeela C (2019) Exergy, economics and pumping power analyses of flat plate solar water heater using thermal performance enhancer in absorber tube. Appl Therm Eng 154:726–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.03.135
Arunkumar HS, Vasudeva Karanth K, Kumar S (2020) Review on the design modifications of a solar air heater for improvement in the thermal performance. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 39:100685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2020.100685
Bazri S, Badruddin IA, Naghavi MS, Bahiraei M (2018) A review of numerical studies on solar collectors integrated with latent heat storage systems employing fins or nanoparticles. Renew Energy 118:761–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.11.030
Bensaci C, Sanchez FJ, Flor D et al (2020a) Numerical and experimental study of the heat transfer and hydraulic performance of solar air heaters with different baffle positions. Renew Energy 155:1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.017
Bensaci CE, Moummi A, Sanchez de la Flor FJ, Rodriguez Jara EA, Rincon-Casado A, Ruiz-Pardo A (2020b) Numerical and experimental study of the heat transfer and hydraulic performance of solar air heaters with different baffle positions. Renew Energy 155:1231–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.017
Bhushan B, Singh R (2011) Nusselt number and friction factor correlations for solar air heater duct having artificially roughened absorber plate. Sol Energy 85:1109–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2011.03.007
Bouadila S, Lazaar M, Skouri S, Kooli S, Farhat A (2014) Energy and exergy analysis of a new solar air heater with latent storage energy. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:15266–15274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.04.074
Caliskan H (2017) Energy, exergy, environmental, enviroeconomic, exergoenvironmental (EXEN) and exergoenviroeconomic (EXENEC) analyses of solar collectors. Renew Sust Energ Rev 69:488–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.203
Dezan DJ, Rocha AD, Ferreira WG (2020) Parametric sensitivity analysis and optimisation of a solar air heater with multiple rows of longitudinal vortex generators. Appl Energy 263:114556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114556
Ehyaei MA, Ahmadi A, Assad MEH, Hachicha AA, Said Z (2019) Energy, exergy and economic analyses for the selection of working fluid and metal oxide nanofluids in a parabolic trough collector. Sol Energy 187:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.05.046
Ghiami A, Ghiami S (2018) Comparative study based on energy and exergy analyses of a baffled solar air heater with latent storage collector. Appl Therm Eng 133:797–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.111
Hassan H, Abo-elfadl S (2018) Experimental study on the performance of double pass and two inlet ports solar air heater (SAH) at different configurations of the absorber plate. Renew Energy 116:728–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.09.047
Hassan H, Yousef MS (2021) An assessment of energy, exergy and CO2 emissions of a solar desalination system under hot climate conditions. Process Saf Environ Prot 145:157–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.07.043
Hassan H, Abo-Elfadl S, El-Dosoky MF (2020a) An experimental investigation of the performance of new design of solar air heater (tubular). Renew Energy 151:1055–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.11.112
Hassan H, Ahmed MS, Fathy M, Yousef MS (2020b) Impact of salty water medium and condenser on the performance of single acting solar still incorporated with parabolic trough collector. Desalination 480:114324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114324
Hassan H, Yousef MS, Ahmed MS, Fathy M (2020c) Energy, exergy, environmental, and economic analysis of natural and forced cooling of solar still with porous media. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:38221–38240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09995-4
Hassan H, Yousef MS, Fathy M (2020d) Productivity, exergy, exergoeconomic, and enviroeconomic assessment of hybrid solar distiller using direct salty water heating. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10803-2
Hassan H, Yousef MS, Fathy M, Ahmed MS (2020e) Assessment of parabolic trough solar collector assisted solar still at various saline water mediums via energy, exergy, exergoeconomic, and enviroeconomic approaches. Renew Energy 155:604–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.03.126
Hassan H, Yousef MS, Fathy M, Ahmed MS (2020f) Assessment of parabolic trough solar collector assisted solar still at various saline water mediums via energy, exergy, exergoeconomic, and enviroeconomic approaches. Renew Energy 155:604–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.03.126
Hassan H, Yousef MS, Fathy M, Ahmed MS (2020g) Impact of condenser heat transfer on energy and exergy performance of active single slope solar still under hot climate conditions. Sol Energy 204:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2020.04.026
Kabeel AE, Hamed MH, Omara ZM, Kandeal AW (2017) Solar air heaters: design configurations , improvement methods and applications – a detailed review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 70:1189–1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.021
Kalaiarasi G, Velraj R, Swami MV (2016) Experimental energy and exergy analysis of a flat plate solar air heater with a new design of integrated sensible heat storage. Energy 111:609–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.05.110
Khanlari A, Sözen A, Afshari F, Şirin C, Tuncer AD, Gungor A (2020) Drying municipal sewage sludge with v-groove triple-pass and quadruple-pass solar air heaters along with testing of a solar absorber drying chamber. Sci Total Environ 709:136198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136198
Kumar A (2014) Analysis of heat transfer and fluid flow in different shaped roughness elements on the absorber plate solar air heater duct. Energy Procedia 57:2102–2111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.10.176
Luan NT, Phu NM (2020) Thermohydraulic correlations and exergy analysis of a solar air heater duct with inclined baffles. Case Stud Therm Eng 21:100672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2020.100672
Matheswaran MM, Arjunan TV, Somasundaram D (2019) Energetic, exergetic and enviro-economic analysis of parallel pass jet plate solar air heater with artificial roughness. J Therm Anal Calorim 136:5–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7727-4
Mesut Abuşkaa SŞ (2017) Energy, exergy, economic and environmental (4E) analyses of flat plate and v-groove solar air collectors based on aluminium and copper. Sol Energy 158:259–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.09.045
Michael JJ, Selvarasan I (2017) Economic analysis and environmental impact of flat plate roof mounted solar energy systems. Sol Energy 142:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.12.019
Mittal MK, Varun SRP, Singal SK (2007) Effective efficiency of solar air heaters having different types of roughness elements on the absorber plate. Energy 32:739–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2006.05.009
Nidhul K, Kumar S, Yadav AK, Anish S (2020) Enhanced thermo-hydraulic performance in a v-ribbed triangular duct solar air heater: CFD and exergy analysis. Energy 200:117448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.117448
Perwez A, Kumar R (2019) Thermal performance investigation of the flat and spherical dimple absorber plate solar air heaters. Sol Energy 193:309–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.09.066
Sahu MK, Prasad RK (2016) Exergy based performance evaluation of solar air heater with arc-shaped wire roughened absorber plate. Renew Energy 96:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.04.083
Saravanakumar PT, Somasundaram D, Matheswaran MM (2020) Exergetic investigation and optimization of arc shaped rib roughened solar air heater integrated with fins and baffles. Appl Therm Eng 175:115316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.115316
Sharma VK, Colangelo A, Spagna G, Pistocchi F (1994) Preliminary economic appraisal of solar air heating system used for drying of agricultural products. Energy Convers Manag 35:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/0196-8904(94)90069-8
Singh A, Sarkar J, Sahoo RR (2020a) Experimental energy, exergy, economic and exergoeconomic analyses of batch-type solar-assisted heat pump dryer. Renew Energy 156:1107–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.100
Singh S, Chaurasiya SK, Negi BS, Chander S, Nemś M, Negi S (2020b) Utilizing circular jet impingement to enhance thermal performance of solar air heater. Renew Energy 154:1327–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.03.095
Sivakandhan C, Arjunan TV, Matheswaran MM (2019) Thermohydraulic performance enhancement of a new hybrid duct solar. Renew Energy 147:2345–2357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.10.007
Srivastava A, Kumar Chhaparwal G, Kumar Sharma R (2020) Numerical and experimental investigation of different rib roughness in a solar air heater. Therm Sci Eng Prog 100576:100576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2020.100576
Taylor JR (1997) An introduction to error analysis, the study of uncertainties in physical measurements. University Science Books, California
Wang D, Liu J, Liu Y, Wang Y, Li B, Liu J (2020) Evaluation of the performance of an improved solar air heater with “S” shaped ribs with gap. Sol Energy 195:89–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.11.034
Wenceslas KY, Ghislain T (2019) Experimental validation of exergy optimization of a flat-plate solar collector in a thermosyphon solar water heater. Arab J Sci Eng 44:2535–2549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3227-x
Yadav KD, Prasad RK (2020) Performance analysis of parallel flow flat plate solar air heater having arc shaped wire roughened absorber plate. Renew Energy Focus 32:23–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ref.2019.10.002
Yousef MS, Hassan H (2019a) Energetic and exergetic performance assessment of the inclusion of phase change materials (PCM) in a solar distillation system. Energy Convers Manag 179:349–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.10.078
Yousef MS, Hassan H (2019b) Assessment of different passive solar stills via exergoeconomic, exergoenvironmental, and exergoenviroeconomic approaches: a comparative study. Sol Energy 182:316–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.02.042
Yousef MS, Hassan H (2020) Energy payback time, exergoeconomic and enviroeconomic analyses of using thermal energy storage system with a solar desalination system: an experimental study. J Clean Prod 270:122082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122082
Yousef MS, Hassan H, Kodama S, Sekiguchi H (2019a) An experimental study on the performance of single slope solar still integrated with a PCM-based pin-finned heat sink. Energy Procedia 156:100–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.11.102
Yousef MS, Hassan H, Sekiguchi H (2019b) Energy, exergy, economic and enviroeconomic (4E) analyses of solar distillation system using different absorbing materials. Appl Therm Eng 150:30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.01.005
Zuhur S, Ceylan İ, Ergün A (2019) Energy, exergy and environmental impact analysis of concentrated PV/cooling system in Turkey. Sol Energy 180:567–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.01.060
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Saleh Abo-Elfadl: Carried out experimental work and measurements, wrote the draft paper, and revised the manuscript.
Mohamed S. Yousef: Wrote the draft paper and analysis results, prepared the data, revised the manuscript, and answered reviewers’ comments.
Hamdy Hassan: Carried out experimental work and measurements, wrote the draft paper and analysis results, prepared the data, revised the manuscript, prepared the revised version, and answered reviewers’ comments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors disclose any actual or potential conflict of interest including any financial, personal, or other relationships with other people or organizations within 3 years of the beginning of the submitted work that could inappropriately influence, or perceived to influence, this work.
Consent to publish
The authors grant the publisher the sole and exclusive license of the full copyright of this contribution.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research and ethical standards.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abo-Elfadl, S., Yousef, M.S. & Hassan, H. Assessment of double-pass pin finned solar air heater at different air mass ratios via energy, exergy, economic, and environmental (4E) approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 13776–13789 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11628-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11628-9