Abstract
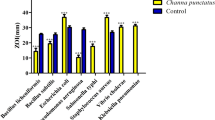
The epidermal mucus of fish performs diverse functions from prevention of mechanical abrasion to limit pathogen invasions. The current experiment was designed to extract skin mucus proteins of three freshwater fish, i.e. common carp (Cyprinus carpio), mrigal (Cirrhinus mrigala) and rohu (Labeo rohita) with organic solvent (methanol) and dissolve in different pH of Tris-HCl buffers to examine the significance of pH in the solubilisation of skin mucus proteins. The protein profiles of different pH solubilised methanol fish skin mucus extracts were determined by SDS-PAGE. The non-specific immune enzymes, alkaline phosphatase, lysozyme and protease of fish skin mucus were compared and this present study demonstrated that these enzymes differed in their activity depending on pH buffers. The higher lysozyme and protease activity were observed at the pH of 8.0 and higher alkaline phosphatase activity in the pH 9.0 of C. mrigala fish skin mucus methanol extract. In addition, the bactericidal activity was evaluated against the pathogens Proteus vulgaris and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The pH 8.0 of C. mrigala skin mucus extract revealed better bactericidal activity than other fish species mucus pH buffers against both P. vulgaris and P. aeruginosa. In the case of protein profile from SDS-PAGE, based on pH buffers and the solubilisation of proteins, differences in the resolution of bands were observed. The higher alkaline pH of 9.0 showed smeared gel bands in all the three fish skin mucus methanol extract. The present study suggests that methanol extracted C. mrigala fish skin mucus at pH 8.0 showed better innate immune enzymes and bactericidal activity. The additional examinations of C. mrigala skin mucus methanol extract in this pH aids in identifying novel bioactive molecules. This is the study of proteome of three fish species skin mucus in the effect of pH. Further analyses are required to evaluate proteins present in fish skin mucus extracted with methanol and the influence of pH on protein solubility. These findings could be helpful in exploring natural alternatives to antibiotics in aquaculture industry against infectious pathogens.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abbas F, Hafeez-ur-Rehman M, Ashraf M et al (2020) Mucus properties of Chinese carp and Indian carp: physical barrier to pathogens. Iran J Fish Sci 193:1221–1236. https://doi.org/10.22092/ijfs.2019.119394.0
Abdollahi Y, Ahmadifard N, Agh N, Rahmanifarah K, Hejazi MA (2019) β-Carotene-enriched artemia as a natural carotenoid improved skin pigmentation and enhanced the mucus immune responses of platyfish Xiphophorus maculatus. Aquac Int 27:1847–1858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-019-00437-8
al-Arifal N, Sharif Mughal M, Hanif A, Batool A (2011) Effect of alkaline pH on bioactive molecules of epidermal mucus from Labeo rohita (Rahu). Turk J Biochem 36:29–34
Alexander JB, Ingram GA (1992) Noncellular nonspecific defence mechanisms of fish. Annu Rev Fish Dis 2:249–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-8030(92)90066-7
Alexov E (2003) Numerical calculations of the pH of maximal protein stability. Eur J Biochem 271:173–185. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03917.x
Arun C, Durdana S, Shweta K et al (2015) Drug’s resistant activity of Proteus vulgaris isolated from gut of Mystus seenghala of northern Punjab region. J Chem Pharm Res 7:284–288
Bergsson G, Agerberth B, Jörnvall H, Gudmundsson GH (2005) Isolation and identification of antimicrobial components from the epidermal mucus of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). FEBS J 272:4960–4969. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04906.x
Borzooeian Z, Taslim ME, Borzooeian G, Ghasemi O, Aminlari M (2017) Activity and stability analysis of covalent conjugated lysozyme-single walled carbon nanotubes: potential biomedical and industrial applications. RSC Adv 7:48692–48701. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA07189B
Boutin S, Bernatchez L, Audet C, Derôme N (2013) Network analysis highlights complex interactions between pathogen, host and commensal microbiota. PLoS One 8:e84772. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084772
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Bragadeeswaran S, Priyadharshini S, Prabhu K, Rani SRS (2011) Antimicrobial and hemolytic activity of fish epidermal mucus Cynoglossus arel and Arius caelatus. Asian Pac J Trop Med 4:305–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(11)60091-6
Burns DB, Zydney AL (1999) Effect of solution pH on protein transport through ultrafiltration membranes. Biotechnol Bioeng 64:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19990705)64:1<27::AID-BIT3>3.0.CO;2-E
Cho JH, Park IY, Kim MS, Kim SC (2002) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 is involved in the regulation of the antimicrobial peptide parasin I production in catfish skin mucosa. FEBS Lett 531:459–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03584-6
Cone RA (2009) Barrier properties of mucus. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2008.09.008
Cordero H, Brinchmann MF, Cuesta A, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2015) Skin mucus proteome map of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Proteomics 15:4007–4020. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201500120
Dash S, Das SK, Samal J, Ojha PK, Patra JK, Thatoi H (2011) Dose dependence specific and non-specific immune responses of Indian major carp (L. rohita Ham) to intraperitoneal injection of formalin killed Aeromonas hydrophila whole cell vaccine. Vet Res Commun 35:541–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-011-9498-2
Dash S, Samal J, Thatoi H (2014) A comparative study on innate immunity parameters in the epidermal mucus of Indian major carps. Aquac Int 22:411–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9649-2
Dash S, Das SK, Samal J, Thatoi HN (2018) Epidermal mucus, a major determinant in fish health: a review. Iran J Vet Res 19:72–81. https://doi.org/10.22099/ijvr.2018.4849
Davies RC, Neuberger A, Wilson BM (1969) The dependence of lysozyme activity on pH and ionic strength. Biochim Biophys Acta Enzymol 178:294–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2744(69)90397-0
Dean Goldring JP (2015) Measuring protein concentration on nitrocellulose and after the electrophoretic transfer of protein to nitrocellulose. Methods Mol Biol 1314:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2718-0_3
El Barbary M, Hal AM (2017) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of some Pseudomonas sp. associated with Burkholderia cepacia isolated from various infected fishes. J Aquac Res Dev 8:499. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9546.1000499
Elavarasi K, Ranjini S, Rajagopal T et al (2013) Bactericidal proteins of skin mucus and skin extracts from fresh water fishes, Clarias batrachus and Tilapia mossambicus. Thai J Pharm Sci 37:194–200
El-Deen AGS (2013) Susceptibility rate of nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) to Proteus vulgaris infection. Assiut Vet Med J 59:138–145
Esteban MÁ (2012) An overview of the immunological defenses in fish skin. ISRN Immunol 2012:1–29. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/853470
Fic E, Kedracka-Krok S, Jankowska U, Pirog A, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M (2010) Comparison of protein precipitation methods for various rat brain structures prior to proteomic analysis. Electrophoresis 31:3573–3579. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201000197
Gómez GD, Balcázar JL (2008) A review on the interactions between gut microbiota and innate immunity of fish. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 52:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695X.2007.00343.x
Grote-Koska D, Klauke R, Brand K, Schumann G (2017) Alkaline phosphatase activity – pH impact on the measurement result. Clin Chem Lab Med 55:e146–e149. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2016-0771
Guardiola FA, Cuesta A, Abellán E, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2014a) Comparative analysis of the humoral immunity of skin mucus from several marine teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 40:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.06.018
Guardiola FA, Cuesta A, Arizcun M et al (2014b) Comparative skin mucus and serum humoral defence mechanisms in the teleost gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Fish Shellfish Immunol 36:545–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.01.001
Guardiola FA, Bahi A, Bakhrouf A, Esteban MA (2017) Effects of dietary supplementation with fenugreek seeds, alone or in combination with probiotics, on gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) skin mucosal immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol 65:169–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.04.014
Harper C, Wolf JC (2009) Morphologic effects of the stress response in fish. ILAR J 50:387–396. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.50.4.387
Hussain B, Sultana T, Sultana S, Ahmed Z, Mahboob S (2018) Study on impact of habitat degradation on proximate composition and amino acid profile of Indian major carps from different habitats. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:755–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.02.004
Iger Y, Abraham M (1990) The process of skin healing in experimentally wounded carp. J Fish Biol 36:421–437. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1990.tb05622.x
Ivanova L, Tartor H, Grove S, Kristoffersen A, Uhlig S (2018) Workflow for the targeted and untargeted detection of small metabolites in fish skin mucus. Fishes 3:21. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3020021
Jurado J, Fuentes-Almagro CA, Guardiola FA et al (2015) Proteomic profile of the skin mucus of farmed gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). J Proteome 120:21–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2015.02.019
Kumar P, Rajeshwaran T, Priya P, Kailasam M, Biswas G, Ghoshal TK, Vijayan KK, Arasu ART (2019) Comparative immunological and biochemical properties of the epidermal mucus from three brackishwater fishes. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 89:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-017-0923-3
Kumari U, Nigam AK, Mittal S, Mittal AK (2011) Antibacterial properties of the skin mucus of the freshwater fishes, Rita rita and Channa punctatus. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 15:781–786
Kumari S, Tyor AK, Bhatnagar A (2019) Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of skin mucus of three carp species. Int Aquat Res 11:225–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40071-019-0231-z
Kuppulakshmi C, Prakash M, Gunasekaran G, Manimegalai G, Sarojini S (2008) Antibacterial properties of fish mucus from Channa punctatus and Cirrhinus mrigala. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 12:149–153
Kusuda R, Kawahara I, Hamaguchi M (1987) Activities and characterization of lysozyme in skin mucus extract, serum and kidney extract of yellowtail. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 53:211–224. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.53.211
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Lai SK, Wang YY, Wirtz D, Hanes J (2009) Micro- and macrorheology of mucus. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:86–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2008.09.012
Lesnierowsk G, Kijowski J (2007) Lysozyme. In: Huopalahti R, Fandino RL, Anton M, Schade R (eds) Bioactive egg compounds. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 33–42
Li P, Liu W, Gao K (2013) Effects of temperature, pH, and UV radiation on alkaline phosphatase activity in the terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme. J Appl Phycol 25:1031–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9936-8
Li J, Jiang M, Wang Y (2014) Expression, purification, and characteristic of tibetan sheep breast lysozyme using Pichia pastoris expression system. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 27:574–579. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2013.13529
Lin CY, Wu H, Tjeerdema RS, Viant MR (2007) Evaluation of metabolite extraction strategies from tissue samples using NMR metabolomics. Metabolomics 3:55–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-006-0043-1
Magnadottir B (2010) Immunological control of fish diseases. Mar Biotechnol 12:361–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-010-9279-x
Mahadevan G, Mohan K, Vinoth J, Ravi V (2019) Biotic potential of mucus extracts of giant mudskipper Periophthalmodon schlosseri (Pallas, 1770) from Pichavaram, southeast coast of India. J Basic Appl Zool 80:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41936-019-0084-4
Minniti G, Hagen LH, Porcellato D, Jørgensen SM, Pope PB, Vaaje-Kolstad G (2017) The skin-mucus microbial community of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Front Microbiol 8:2043. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02043
Mo WY, Cheng Z, Choi WM, Lun CHI, Man YB, Wong JTF, Chen XW, Lau SCK, Wong MH (2015) Use of food waste as fish feeds: effects of prebiotic fibers (inulin and mannanoligosaccharide) on growth and non-specific immunity of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:17663–17671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4971-z
Nagashima Y, Kikuchi N, Shimakura K, Shiomi K (2003) Purification and characterization of an antibacterial protein in the skin secretion of rockfish Sebastes schlegeli. Comp Biochem Physio C Toxicol Pharmacol 136:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1532-0456(03)00174-1
Niemi P, Martins D, Buchert J, Faulds CB (2013) Pre-hydrolysis with carbohydrases facilitates the release of protein from brewer’s spent grain. Bioresour Technol 136:529–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.076
Noya M, Magarinos B, Toranzo AE, Lamas J (1995) Sequential pathology of experimental pasteurellosis in gilthead seabream Sparus aurata. A light- and electron-microscopic study. Dis Aquat Org 21:177–186. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao021177
Nybo K (2012) Native PAGE. Biotechniques 52:20–21. https://doi.org/10.2144/000113797
Palaksha KJ, Shin GW, Kim YR, Jung TS (2008) Evaluation of non-specific immune components from the skin mucus of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 24:479–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2008.01.005
Patel DM, Brinchmann MF (2017) Skin mucus proteins of lumpsucker (Cyclopterus lumpus). Biochem Biophys Rep 9:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2016.12.016
Raimi O, Hammed A, Alaebo P et al (2014) Partial Characterization of Alkaline Phosphatase in Some Species of Fresh Water Cichlids (‘Wesafu’, Oreochromis niloticus and Sarotherodon melanotheron). Int J Mod Biochem 3:7–17
Rakers S, Niklasson L, Steinhagen D, Kruse C, Schauber J, Sundell K, Paus R (2013) Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) from fish epidermis: perspectives for investigative dermatology. J Investig Dermatol 133:1140–1149. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2012.503
Ravi VK, Swain T, Chandra N, Swaminathan R (2014) On the characterization of intermediates in the isodesmic aggregation pathway of hen lysozyme at alkaline pH. PLoS One 9:e87256
Reverter M, Tapissier-Bontemps N, Lecchini D, Banaigs B, Sasal P (2018) Biological and ecological roles of external fish mucus: a review. Fishes 3:41. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3040041
Riès-kautt M, Ducruix A (1997) Inferences drawn from physicochemical studies of crystallogenesis and precrystalline state. In: Carter CWJ (ed) Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, New York, pp 23–59
Ross NW, Firth KJ, Wang A, Burka JF, Johnson SC (2000) Changes in hydrolytic enzyme activities of naive Atlantic salmon Salmo salar skin mucus due to infection with the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis and cortisol implantation. Dis Aquat Org 41:43–51. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao041043
Salinas I (2015) The mucosal immune system of teleost fish. Biology (Basel) 4:525–539. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4030525
Salles CMC, De-Simone SG, Leitão SAT et al (2007) Identification and characterization of proteases from skin mucus of tambacu, a Neotropical hybrid fish. Fish Physiol Biochem 33:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-007-9128-7
Sanahuja I, Fernández-Alacid L, Sánchez-Nuño S, Ordóñez-Grande B, Ibarz A (2019) Chronic cold stress alters the skin mucus interactome in a temperate fish model. Front Physiol 9:1916. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01916
Sanchooli O, Moradloo AH, Ghorbani R (2012) Measurement of alkaline phosphatase and lysozyme enzymes in epidermal mucus of different weights of Cyprinus carpio. World J Fish Mar Sci 4:521–524. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wjfms.2012.04.05.64202
Sathe SK, Kshirsagar HH, Sharma GM (2012) Solubilization, fractionation, and electrophoretic characterization of inca peanut (Plukenetia volubilis L.) proteins. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 67:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-012-0301-5
Saurabh S, Sahoo PK (2008) Lysozyme: An important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac Res 39:223–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2007.01883.x
Schägger H (2006) Tricine–SDS-PAGE. Nat Protoc 1:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.4
Shahjahan M, Al-Emran M, Majharul Islam SM et al (2020) Prolonged photoperiod inhibits growth and reproductive functions of rohu Labeo rohita. Aquac Rep 16:100272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2019.100272
Shaw KL, Grimsley GR, Yakovlev GI, Makarov AA, Pace CN (2001) The effect of net charge on the solubility, activity, and stability of ribonuclease Sa. Protein Sci 10:1206–1215. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.440101
Shephard KL (1994) Functions for fish mucus. Rev Fish Biol Fish 4:401–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00042888
Shibuya K, Tsutsui S, Nakamura O (2019) Fugu, Takifugu ruberipes, mucus keratins act as defense molecules against fungi. Mol Immunol 116:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.09.012
Strader MB, Tabb DL, Hervey WJ, Pan C, Hurst GB (2006) Efficient and specific trypsin digestion of microgram to nanogram quantities of proteins in organic−aqueous solvent systems. Anal Chem 78:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac051348l
Subramanian S, MacKinnon SL, Ross NW (2007) A comparative study on innate immune parameters in the epidermal mucus of various fish species. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 148:256–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2007.06.003
Subramanian S, Ross NW, MacKinnon SL (2008) Comparison of antimicrobial activity in the epidermal mucus extracts of fish. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 150:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2008.01.011
Sunyer JO, Tort L (1995) Natural hemolytic and bactericidal activities of sea bream Sparus aurata serum are effected by the alternative complement pathway. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 45:333–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-2427(94)05430-Z
Sylvain FÉ, Cheaib B, Llewellyn M, Gabriel Correia T, Barros Fagundes D, Luis Val A, Derome N (2016) PH drop impacts differentially skin and gut microbiota of the Amazonian fish tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum). Sci Rep 6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32032
Takahashi Y, Itami T, Konegawa K (1986) Enzymatic properties of partially purified lysozyme from the skin mucus of carp. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 52:120–1214. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.52.1209
Talley K, Alexov E (2010) On the pH-optimum of activity and stability of proteins. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinf 78:2699–2706. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22786
Taylor EB, Williams MA (2010) Microbial protein in soil: influence of extraction method and C amendment on extraction and recovery. Microb Ecol 59:390–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9593-x
Thomas J, Thanigaivel S, Vijayakumar S, Acharya K, Shinge D, Seelan TSJ, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2014) Pathogenecity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Oreochromis mossambicus and treatment using lime oil nanoemulsion. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 116:372–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.01.019
Ueki N, Matsuoka Y, Wan J, Watabe S (2019) Quality improvement of thermally induced surimi gels by extensive washing for dressed white croaker to remove contamination by body surface mucus proteases. Fish Sci 85:883–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-019-01335-x
Uribe C, Folch H, Enriquez R, Moran G (2011) Innate and adaptive immunity in teleost fish: a review. Vet Med (Praha) 56:486–503. https://doi.org/10.17221/3294-VETMED
Ursu A-V, Marcati A, Sayd T, Sante-Lhoutellier V, Djelveh G, Michaud P (2014) Extraction, fractionation and functional properties of proteins from the microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour Technol 157:134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.071
Veide Vilg J, Undeland I (2017) pH-driven solubilization and isoelectric precipitation of proteins from the brown seaweed Saccharina latissima—effects of osmotic shock, water volume and temperature. J Appl Phycol 29:585–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0957-6
Vilizzi L (2018) Age determination in common carp Cyprinus carpio: history, relative utility of ageing structures, precision and accuracy. Rev Fish Biol Fish 28:461–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-018-9514-5
Wainwright DK, Lauder GV (2017) Mucus matters: the slippery and complex surfaces of fish. In: Gorb S, Gorb E (eds) Functional Surfaces in Biology III. Springer, Cham, pp 223–246
Wang H, Tang W, Zhang R, Ding S (2019) Analysis of enzyme activity, antibacterial activity, antiparasitic activity and physico-chemical stability of skin mucus derived from Amphiprion clarkii. Fish Shellfish Immunol 86:653–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.11.066
Want EJ, O’Maille G, Smith CA et al (2006) Solvent-dependent metabolite distribution, clustering, and protein extraction for serum profiling with mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 78:743–752. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac051312t
Wei OY, Xavier R, Marimuthu K (2010) Screening of antibacterial activity of mucus extract of snakehead fish, Channa striatus (Bloch). Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 14:675–681
Whyte SK (2007) The innate immune response of finfish–a review of current knowledge. Fish Shellfish Immunol 23:1127–1151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2007.06.005
Xu Z, Parra D, Gómez D et al (2013) Teleost skin, an ancient mucosal surface that elicits gut-like immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:13097–13102. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1304319110
Yinchun Y, Yanmei H, Xinyi W (2015) Identification of pathogenic from Carassius auratus triploid with skin bleeding and ulcers and its prevention of drug screening. J Agric Catastrophol 5:28–30
Zayas JF (2012) Functionality of proteins in food. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Zhong S, Liu S, Cao J, Chen S, Wang W, Qin X (2016) Fish protein isolates recovered from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) by-products using alkaline ph solubilization and precipitation. J Aquat Food Prod Technol 25:400–413. https://doi.org/10.1080/10498850.2013.865282
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the funding agencies DST Fast Track (SR/FT/LS-21/2012), DST-FIST Level-I (stage-II) (Ref. No. SR/FST/LSI-647/2015 (C) Date.11.08.2016) and DST PURSE (Phase-II) (Ref. No. SR/PURSE PHASE 2/16(G)/& 16(C) Date. 21.02.2017) for providing instrumentation facility to Department of Animal Science, School of Life Sciences, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India. The first author Arun Sridhar was supported by the EMBO Short-Term Fellowship (STF-8388).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Arun Sridhar: investigation, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Rajkumar Krishnasamy Sekar: investigation, resources, data curation. Dinesh Babu Manikandan: investigation, visualization. Manikandan Arumugam: investigation, resources. Srinivasan Veeran: formal analysis, data curation. Thirumurugan Ramasamy: conceptualization, project administration, supervision, validation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed by the authors.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sridhar, A., Krishnasamy Sekar, R., Manikandan, D.B. et al. Activity profile of innate immune-related enzymes and bactericidal of freshwater fish epidermal mucus extract at different pH. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 33914–33926 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11173-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11173-5