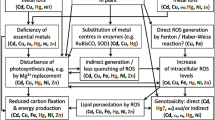
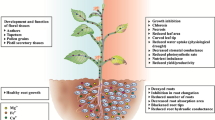
Abstract
Mining industry generates large volumes of waste known as mine tailings, which contain heavy metals (HMs) that generate a risk to environmental health. Thus, remediation of HM pollution requires attention. In this study, HM bioaccumulation, genotoxic damage, and morphological and physiological changes in the tree species Prosopis laevigata were evaluated in order to assess its potential for remediation of mine tailings. P. laevigata plants were established in two treatments (reference substrate and tailing substrate) under greenhouse conditions. Every 2 months, six individuals were selected per treatment for 1 year. From each individual, macromorphological (height, stem diameter, and number of leaves), micromorphological (stomatal coverage and stomatal index), and physiological parameters (chlorophyll content) were evaluated, as well as the concentration of Pb, Cu, Cd, Cr, Fe, and Zn in root and foliar tissue. Genetic damage was assessed by the comet assay in foliar tissue. These parameters were evaluated in adult individuals established in mine tailings. Roots bioaccumulated significantly more HM compared to foliar tissue. However, the bioaccumulation pattern in both tissues was Fe > Pb > Zn > Cu. The plants in tailing substrate reduced significantly the morphological and physiological characters throughout the experiment. Only the bioaccumulation of Pb affected significantly the levels of genetic damage and the number of leaves, while Zn reduced plant height. The percentage of plants that have translocation factor values greater than 1 are Cu (92.9) > Fe (85.7) > Pb (75.0) > Zn (64.3). P. laevigata has potential to phytoremediate environments contaminated with metals, due to its dominance and establishment in abandoned mine tailings, and its ability to bioaccumulate HM unaffecting plant development, as well as their high levels of HM translocation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal A, Sharma I, Tripathi B, Munjal A, Baunthiyal M, Sharma V (2012) Metal toxicity and photosynthesis. Photosynthesis: overviews on recent progress and future perspectives, 229–236
Alcalá Jáuregui J, Rodríguez Ortíz JC, Hernández Montoya A, Filippini MF, Martínez Carretero E, Díaz Flores PE (2018) Capacity of two vegetative species of heavy metal accumulation. Rev FCA UNCUYO 50(1):123–139
Ali H, Khan E, Sjad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Ali MR, Mehraj H, Jamal Uddin AFM (2015) Effects of foliar application of zinc and boron on growth and yield of summer tomato. Biosci Agric Res 06:512–517. https://doi.org/10.18801/jbar.060115.61
Ambler JE, Brown JC, Gauch HG (1971) Sites of Iron reduction in soybean plants. Agron J 63:9597
Arena C, Figlioli F, Sorrentino MC, Izzo LG, Capozzi F, Giordano S, Spagnuolo V (2017) Ultrastructural, protein and photosynthetic alterations induced by Pb and Cd in Cynara cardunculus L., and its potential for phytoremediation. Ecotox Environ Safe 145:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.07.015
Ayeni O, Ndakidemi PA, Snyman RG, Odendaal JP (2010) Chemical, biological and physiological indicators of metal pollution in wetlands. Sci Res Essays 5:1938–1949. https://doi.org/10.5897/SER
Batty LC, Younger PL (2003) Effects of external iron concentration upon seedling growth and uptake of Fe and phosphate by the common reed, Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin ex. Steudel. Ann Bot-London 92(6):801–806. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcg205
Benimeli CS, Medina A, Navarro CM, Medina RB, Amoroso MJ, Gómez MI (2010) Bioaccumulation of copper by Zea mays: impact on root, shoot and leaf growth. Water Air Soil Pollut 210(1–4):365–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0259-6
Bhatla SC (2018) Light perception and transduction. In: Bhatla SC, Lal MA (eds) Plant physiology. Development and Metabolism Springer, Singapore, pp 519–558
Buendía-González L, Orozco-Villafuerte B, Cruz-Sosa F, Barrera-Díaz CE, Vernon-Carte EJ (2010) Prosopis laevigata, a potencial chromium (VI) and cadmium (II) hyperaccumulator desert plant. Bio/Technology 101:5862–5867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.027
Buendía González L, Cruz Sosa F, Rodríguez Huezo ME, Barrera Díaz CE, Hernández Jaimes C, Orozco Villafuerte J (2019) In vitro simultaneous acummulation of multiple heavy metals by Prosopis laevigata seedlings cultures. Rev Mex Ing Quím 18(3):1167–1177
Capozzi F, Sorrentino MC, Caporate AG, Fiorentino N, Giordano S, Spagnuolo V (2020) Exploring the phytoremediation potencial of Cynara cardunculus: a trial on an industrial soil highly cobtaminated by heavy metals. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07575-9
Casana MM, Beltrán RA (2017) Bioacumulación de cobre, plomo, hierro y zinc en Lactuca sativa “lechuga”, Brassica oleracea “repollo”, Daucus carota “zanahoria” y Raphanus sativus “rabanito”. Conocimiento para el desarrollo 4(2) https://revista.usanpedro.edu.pe/index.php/CPD/article/view/167
Cenkci S, Cigerci IH, Yildiz M, Özay C, Bozdag A, Terzi H (2010) Lead contamination reduces chlorophyll biosynthesis and genomic template stability in Brassica rapa L. Environ Exp Bot 67:467–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.10.001
Chaoui A, El Ferjani E (2005) Effects of cadmium and copper on antioxidant capacities, lignification and auxin degradation in leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings. C R Biol 328(1):23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2004.10.001
Chaudhry H, Nisar N, Mehmood S, Iqbal M, Nazir A, Yasir M (2020) Indian mustard Brassica juncea efficiency for the accumulation, tolerance and traslocation of zinc from metal contaminated soil. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101489
Covarrubias SA, Peña Cabriales JJ (2017) Contaminación por metales pesados en México: Problemática y estrategias de fitorremediación. Rev Int Cont Amb 7-21. https://doi.org/10.20937/RICA.2017.33.esp01.01
Cuypers A, Remans T, Weyens N, Colpaert J, Vassilev A, Vangronsveld J (2013) Soil-plant relationships of heavy metals and metalloids. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soils: trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer, 161–193
DalCorso G (2012) Heavy metal toxicity in plants. In: Furini A (ed) Plants and heavy metals SpringerBriefs in Molecular Science. Springer, Dordrecht pp 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4441-7_1
De la Cruz-Landero N, Hernández VE, Guevara E, López-López MA, Santos AT, Ojeda-Trejo E, Alderete Chavez A (2010) Lipinus versicolor response in soils contaminated with heavy metals from a petroleum extraction field. J Appl Sci 10(8):694–609
De la Rosa G, Cruz G, Cano I, Fuentes R, Gardea JL (2008) Efecto de la edad de la planta y presencia de SS-EDDS en la tolerancia y absorción de Cr (III) por Helianthus annuus. Rev Mex Ing Quim 7:243–251
Delgadillo-López AE, González-Ramírez CA, Prieto-García F, Villagómez-Ibarra JR, Acevedo-Sandoval O (2011) Fitorremediación: Una alternativa para eliminar la contaminación. Tropic Subtropic Agroecosyst 14:597–612
Dinu C, Vasile GG, Buleandra M, Popa DE, Gheorghe S, Ungureanu EM (2020) Traslocation and accumulation of heavy metals in Ocimum basilicum L. plants grown in a mining-contaminated soil. J Soil Sedim 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02550-w
Dorado O, Arias D, Ramírez R, Sousa M (2005) Leguminosas de la Sierra de Huautla Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos Centro de Educación Ambiental e Investigación Sierra de Huautla 176
Ercal N, Gurer Orhan H, Aykin Burns N (2001) Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr Top Med Chem 1(6):529–539. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026013394831
Eun SO, Youn HS, Lee Y (2000) Lead disturbs microtubule organization in the root meristem of Zea mays. Physiol Plant 110:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2000.1100310.x
Frankenberger WT Jr, Arshad M (2020) Phytohormones in soils microbial production & function. CRC Press
García-Sánchez R, Camargo-Ricalde SL, García-Moya E, Luna-Cavazos M, Romero-Manzanarez A, Montaño M (2012) Prosopis laevigata and Mimosa biuncifera (Leguminosae), jointly influence plant diversity and soil fertility of a Mexican semiarid ecosystem. Rev Biol Trop 60:87–103
García V (2006) Efectos fisiológicos y compartametalización radicular en plantas de Zea mays L. expuestas a la toxicidad por plomo. Dissertation, Universidad Autónoma de Barcelona
Gichner T, Patková Z, Száková J, Demnerová K (2006) Toxicity and DNA damage in tobacco and potato plants growing on soil polluted with heavy metals. Ecotox Environ Safe 65:420–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.08.006
Gold-Bouchot G, Zapata-Pérez O (2004) Contaminación, ecotoxicología y manejo costero. In: El Manejo Costero en México. Rivera Arriaga E, Villalobos GJ, Azuz Adeath I, Rosado May F. (eds) Universidad Autónoma de Campeche, SEMARNAT, CETYS-Universidad, Universidad de Quintana Roo, Campeche, Mexico. 654: 277–286
Golubov J, Mandujano MC, Eguiarte LE (2001) The paradox of mesquites (Prosopis spp.): invading species or biodiversity enhancers? Bot Sci 69:23–30. https://doi.org/10.17129/botsci.1644
Gonçalves AC Jr, Schwantes D, Braga de Sousa RF, Benetoli da Silva TR, Guimar VF, Campagnolo MA, Soares de Vasconcelos E, Zimmermann J (2020) Phytoremediation capacity, growth and physiological responses of Crambe abyssinica Hochst on soil contaminated with Cd and Pb. J Environ Manag 262:110432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110342
Guala SD, Vega FA, Covelo EF (2010) The dynamics of heavy metals in plant–soil interactions. Ecol Model 221:1148–1152
Guo Z, Miao X (2010) Growth changes and tissues anatomical characteristics of giant reed (Arundo donax L.) in soil contaminated with arsenic, cadmium and lead. J Cent South Univ T 17:770–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771−010−0555−8
Guo J, Shi R, Cao Y, Luan Y, Zhou Y, Gao Y, Tian Y (2020) Genotoxic effects of imidacloprid in human lymphoblastoid TK6 cells. Drug Chem Toxicol 43:208–212. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2018.1497048
Helmstädter A (2008) Is there a tonic in the toxin? The Arndt–Schulze law as an explanation for non-linear dose–response relationships, In: Balz V, Schwerin A.v, Stoff H, Wahrig B (eds) Precarious Matters. The History of Dangerous and Endangered Substances in the 19th and 20th Centuries, Max Planck Institut für Wissenschaftsgeschichte, Berlin, pp. 29–37
Hernández-Acosta E, Mondragón-Romero E, Cristobal-Acevedo D, Rubiños-Panta JE, Robledo-Santoyo E (2009) Vegetación, residuos de mina y elementos potencialmente tóxicos de un jal de Pachuca, Hidalgo, México. Rev Chapingo Ser Cie 15(2):109–114
Hernández-Lorenzo B (2015) Análisis de la anatomía y morfología de Prosopis laevigata, por acumulación de metales pesados en la Sierra de Huautla, Morelos. Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos, Dissertation https://documentcloud.adobe.com/link/track?uri=urn:aaid:scds:US:f1e6be7a-3573-45ac-8d0f-bd0dd2f859d1
Huihuia Z, Xina L, Zisonga X, Yueb W, Zhiyuanb T, Meijunc A, Yuehuic Z, Wenxud Z, Nanb X, Guangyub S (2020) Toxic effects of heavy metals Pb and Cd on mulberry (Morus alba L.) seedling leaves: photosynthetic function and reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism responses. Ecotox Environ Safe 195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110469
Ibarra-García AR, Barceló-Quintal ID, García-Albortante J, López-Lafuente AL, González-Huecas C, Quintana-Nieto JR, Mugica-Alvarez V (2017) Phytoextraction of metals by native plants from mining wastes in Zacatecas, Mexico. Acta Hortic 1227:409–416. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2018.1227.51
INEGI (Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía) (2016) Sistema de cuentas nacionales de México. http://www.inegi.org.mx/sistemas/bie
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soil and plants, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kathpalia R, Bhatla SC (2018) Plant water relations. In: Bhatla SC, Lal MA (eds) Plant physiology. Development and Metabolism Springer, Singapore, pp 37–81
Kaya C, Higgsb D, Ashrafc M, Alyemenid MN, Ahmadd P (2020) Integrative roles of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in melatonin-induced tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants to iron deficiency and salt stress alone or in combination. Physiol Plant 168:256–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12976
Maestri E, Marmiroli M, Visioli G, Marmiroli N (2010) Metal tolerance and hyperaccumulation: costs and trade-offs between traits and environment. Environ Exp Bot 68:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.10.011
Mahar A, Wang P, Ali A, Awasthi MK, Lahori AH, Wang Q, Li R, Zhang Z (2016) Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.023
Manara A (2012) Plant responses to heavy metal toxicity. In: Furini A (ed) Plant and heavy metals. Springer Science & Business Media, Pisa, Italy, pp 27–53
Mei Y, Zhou H, Gao L, Zuo YM, Wei KH, Cui NQ (2020) Accumulation of Cu, Cd, Pb, Zn and total P fromsynthetic stormwater in 30 bioretention plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07731-6
Mojiri A, Aziz HA, Zahed MA, Aziz SQ, Selamat MRB (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals from urban waste leachate by southern cattail (Typha domingensis). Int J Sci Res Environ Sci 1:63–70
Mousavi Kouhi SM, Moudi M (2020) Assessment of phytoremediation potential of native plant species naturally growing in a heavy metal-polluted saline–sodic soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:10027–10038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07578-6
Murillo-Herrera AI (2015) Detección de daño genotóxico en Prosopis laevigata de los jales de Sierra de Huautla, Morelos, México provocado por metales pesados. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Dissertation https://documentcloud.adobe.com/link/track?uri=urn:aaid:scds:US:5d2461a0-1ec2-4d8a-96f3-1ea8ae5f5174
Mussali-Galante P, Ávila Costa MR, Piñón Zarate G, Martínez Levy G, Rodríguez Lara V, Rojas Lemus M, Fortoul TI (2005) DNA damage as an early biomarker of effect in human health. Toxicol Ind Health 21(5–6):155–166. https://doi.org/10.1191/0748233705th224oa
Mussali-Galante P, Tovar Sánchez E, Valverde M, Rojas del Castillo E (2013) Biomarkers of exposure for assessing environmental metal pollution: from molecules to ecosystems. Rev Int Contam Ambie 29:117–140
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8(3):199–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-010-0297-8
Navarrete Gutiérrez DM, Pons MN, Cuevas Sánchez JA, Echevarria G (2018) Is metal hyperaccumulation occurring in ultramafic vegetation of central and southern Mexico? Ecol Res 33:641–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-018-1574-4
Olguín E, Sánchez Galván G (2012) Heavy metal removal in phytofiltration and phycoremediation: the need to differentiate between bioadsorption and bioaccumulation. New Biotechnol 30:3–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2012.05.020
Paniagua-Ibáñez M, López-Caamal A, Mussali-Galante P, Sánchez-Salinas E, Ortiz-Hernández LM, Ramírez-Rodríguez R, Tovar-Sánchez E (2015) Morphological variation of Cosmos bipinnatus (Asteraceae) and its relation to abiotic variables in Central Mexico. Rev Chil Hist Nat:2–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40693-015-0044-4
Patra M, Bhowmik N, Bandopadhyay B, Sharma A (2004) Comparison of mercury, lead and arsenic with respect to genotoxic effects on plant systems and the development of genetic tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 52(3):199–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.02.009
Pedrosa-Gomes M, Lara Lanza T, Marques D, de Oliveira GM, de Castro E, Soares A (2011) Accumulation of heavy metal in Brachiaria decumbens. Sci Agrár 68:566–573. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162011000500009
Poschenrieder C, Cabot C, Martos S, Gallego B, Barceló J (2013) Do toxic ions induce hormesis in plants? Plant Sci 212:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.07.012
Pourrut B, Shahid M, Dumat C, Winterton P, Pinelli E (2011) Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. In: Whitacre D (ed) Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology Volume 213. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9860-6_4
Pourrout B, Shahid M, Douay F, Dumat C, Pinelli E (2013) Molecular mechanisms involved in lead uptake, toxicity and detoxification in higher plants. In: Gupta DK (ed) Heavy Metal Stress in Plants. Springer, Heidelberg, Berlin pp 121–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38469-1_7
Prasad A, Kumar S, Khaliq A, Pandey A (2011) Heavy metals and arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi can alter the yield and chemical composition of volatile oil of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Biol Fertil Soils 47:853–861
Prasad TNVKV, Sudhakar P, Sreenivasulu Y, Latha P, Munaswamy V, Reddy KR, Pradeep T (2012) Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. J Plant Nutr 35(6):905–927. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2012.663443
Rajakaruna N, Baker AJM (2006) Serpentine: a model hábitat for botanical research in Sri Lanka. Ceylon J Sci 32:1–19
Ramírez V, Baez A, López P, Bustillos B, Villalobos MA, Carreño R, Contreras JL, Muñoz Rojas J, Fuentes LE, Martínez J, Munive JA (2019) Chromium hyper-tolerant Bacillus sp. MH778713 assists phytoremediation of heavy metals by mesquite trees (Prosopis laevigata). Front Microbiol 10:1833. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01833
Rascio N, Navari-Izzo F (2011) Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: how and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting? Plant Sci 180(2):169–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.08.016
Rodríguez-Sauceda EN, Rojo Martínez GE, Valverde Ramírez B, Martínez Ruíz R, Cong Hermida MC, Medina Torres SM, Piña Ruíz HH (2014) Análisis técnico del árbol del Mezquite (Prosopis laevigata Humb. & Bonpl. ex Willd.) En México. Ra Ximhai 10(3):173–193
Rojas E, López MC, Valverde M (1999) Single cell gel electrophoresis assay: methodology and applications. J Chromatogr 722:225–254
Rosas-Ramírez ME (2018) Relación entre la bioacumulación de metales pesados y la concentración de clorofila en Sanvitalia procumbens. Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos, Dissertation https://documentcloud.adobe.com/link/review?uri=urn:aaid:scds:US:b942e10e-6309-4556-bb54-1a8c395dd158
Rout GR, Sahoo S (2015) Role of iron in plant growth and metabolism. Rev Agric Sci 3:1–24. https://doi.org/10.7831/ras.3.1
Ruiz HEA, Armienta HMA (2012) Acumulación de arsénico y metales pesados en maíz en suelos cercanos a jales o residuos mineros. Rev Int Contam Ambie:103–117
Sagardoy R, Vázquez S, Florez-Sarasa ID, Albacete A, Ribas-Carbó M, Flexas J, Abadıa J, Morales F (2010) Stomatal and mesophyll conductances to CO2 are the main limitations to photosynthesis in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) plants grown with excess zinc. New Phytol 187:145–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03241.x
Salas-Luévano MA, Manzanares-Acuña E, Letechipía-de León C, Vega-Carrillo HR (2009) Tolerant and hyperaccumulators autochthonous plant species from mine tailing disposal sites. Asian J Exp Sci 23(1):27–32
Salas Luévano MA, Mauricio-Castillo JA, González-Rivera ML, Vega-Carrillo HL, Salas-Muñoz S (2017) Accumulation and phytostabilization of As, Pb and Cd in plants growing inside mine tailings reforested in Zacatecas, Mexico. Environ Earth Sci 76: 806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7139-y
Salisbury FT (1968) Las plantas vasculares: forma y función. México: Herrero Hermanos Sucesores pp 598
Sánchez-Pinzón MS (2010) Contaminación por metales pesados en el Botadero de basuras de Moravia en Medellín: Transferencia a flora y fauna y evaluación del potencial fitorremediador de especies nativas producidas. Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Colombia, Dissertation
Santoyo-Martínez M, Mussali-Galante P, Hernández-Plata I, Valencia-Cuevas L, Flores-Morales A, Ortiz-Hernández L, Flores-Trujillo K, Ramos-Quintana F, Tovar-Sánchez E (2020) Heavy metal bioaccumulation and morphological changes in Vachellia campechiana (Fabaceae) reveal its potential for phytoextraction of Cr, Cu, and Pb in mine tailings. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07730-7
Secretaria de Economía (2011) Panorama Minero del estado de Morelos. Servicio Geológico Mexicano, serie panorama minero de los estados, Pachuca
SEMARNAT, Secretaria de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (2005) Dirección de Investigación en Residuos y Sitios Contaminados Subdirección de Investigación en Sitios Contaminados y Sustancias Tóxicas. Informe 42 anual de actividades. Evaluación de tecnologías de remediación para suelos contaminados con metales. Etapa II. [Fecha de consulta: 4 de noviembre de 2016]. http://www.inecc.gob.mx/descargas/dgcenica/metales_eii2005.pdf
Sharma P, Pandey S (2014) Status of phytoremediation in world scenario. Int J Environ Bioremediation & Biodegradation 2:178–191
Sharma RK, Agrawal M (2005) Biological effects of heavy metals: an overview. J Environ Biol 26(2):301–313. https://doi.org/10.12691/ijebb-2-4-5
Shiqi L, Yang B, Kou Y, Zeng J, Wang R, Xiao Y, Li F, Lu Y, Mu Y, Zhao C (2018) Assessing the difference of tolerance and phytoremediation potential in mercury contaminated soil of a nonfood energy crop, Helianthus tuberosus L. (Jerusalem artichoke). Peer J 6:1–18. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4325
Singh R, Tripathi RD, Dwivedi S, Kumar A, Trivedi PK, Chakrabarty D (2010) Lead bioaccumulation potential of an aquatic macrophyte Najas indica are related to antioxidant system. Bioresour Technol 101:3025–3032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.031
Solís-Miranda BA (2016) Aislamiento de bacterias de jales mineros y análisis de su potencial para la remediación de sitios contaminados con metales pesados. Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos, Dissertation https://documentcloud.adobe.com/link/track?uri=urn:aaid:scds:US:3a5f2873-da05-408d-b7d5-8b170013d30e
StatSoft (2000) Correspondence analysis. Tulsa, StatSoft Inc 2000 http://www.statsoftinc.com/textbook/stcoran.html
Suman J, Uhlik O, Viktorova J, Macek T (2018) Phytoextraction of heavy metals: a promising tool for clean-up of polluted environment? Front Plant Sci 9:1476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.0147
Talavera O, Yta M, Moreno R, Dótor A, Flores N, Durante C (2005) Mineralogy and geochemistry of sulfide-bearing tailings from silver mines in the Taxco, Mexico area to evaluate their potential environmental impact. Geofis Int 44:49–64
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H et al (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(2000)35:3<206::AID-EM8>3.0.CO;2-J
Tovar-Sánchez E, Mussali Galante P, Martínez-Pacheco M, Ortiz Hernández ML, Sánchez-salinas E, Olvera-Verona A (2016) Relationship between genotoxic damage and arsenic blood concentrations in individuals residing in an arsenic contaminated area in Morelos, Mexico. Rev Int Contam Ambie 32:101–117
Tovar-Sánchez E, Cervantes Ramírez T, Castañeda Bautista J, Gómez Arroyo S, Ortíz Hernández L, Sánchez Salinas E, Mussali Galante P (2018) Response of Zea mays to multimetal contaminated soils: a multibiomarker approach. Ecotoxicology 27:1161–1177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1974-9
Velasco J, De la Rosa D, Ramírez M, Volke T (2004) Evaluación de tecnologías de remediación para suelos contaminados con metales Etapa II. SEMARNAT-INE, México pp 46
Volke ST, Velasco TA, De la Rosa PA, Solórzano OG (2005) Evaluaciones de tecnologías de remediación para suelos contaminados con metales. Etapa II. Secretaria de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales, México
Wilson B, Pyatt FB (2007) Heavy metal bioaccumulation by the important food plant, Olea europaea L., in an ancient metalliferous polluted area of Cyprus. B Environ Contam Tox 78(5):390–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9162-2
Yadav SK (2010) Heavy metals toxicity in plants: an overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. S Afr J Bot 76:167–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2009.10.007
Yang Z, Chen J, Dou R, Gao X, Mao C, Wang L (2015) Assessment of the phytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles on two crop plants, maize (Zea mays L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Env Res Pub He 12:15100–15109
Yllanes P, Vélez A, Lozano S (2014) Efectos fitotóxicos del plomo en maíz híbrido Dekalb (Zea mays L.) en suelo arenoso y limoso. Biologist 12:337–248
Yoon J, Cao X, Zhou Q, Ma LQ (2006) Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci Total Environ 368:456–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.01.016
Zar JH (2010) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Acknowledgments
We thank the “Doctorado en Ciencias Naturales,” Autonomous University of Morelos State (UAEM), for the facilities granted to carry out this project. This research was supported by a CONACyT scholarship grant to M.S.M. (Grant: 429356). Also, we thank Rosalind Pearson Hedge for her comments and English edition that improved our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muro-González, D.A., Mussali-Galante, P., Valencia-Cuevas, L. et al. Morphological, physiological, and genotoxic effects of heavy metal bioaccumulation in Prosopis laevigata reveal its potential for phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 40187–40204 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10026-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10026-5