Abstract
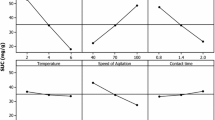
Response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) were used to generate a model for the optimization of fluoride removal using chemically activated Dalbergia sissoo sawdust (CADS). The single and collective effects of process parameters, i.e., solution pH, CADS dose, initial fluoride concentration, and contact time, were studied. The point of zero charge was found to be 4.2 with zeta potential analysis. In the first phase, a single-parameter study was performed to reveal dependency of fluoride removal on a particular process parameter. Positive effects of increment in CADS dose and contact time and negative effects of solution pH and initial fluoride concentration were observed. The second phase included RSM in which analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied to test the feasibility of the mathematical model. The F value 1.91, R2 value 0.87, and P value 0.11 show significance of the proposed model. Results obtained from the experiment set for central composite design (CCD) were used to predict the ANN response. Reasonable acceptable values of regression for training, test, and validation (0.76, 0.93, and 0.37) represent the suitability of the model. The ANN predicted 22.1% fluoride removal, which was close to the actual value (20.1%) and was comparable with CCD prediction (25.0%). BET surface area of CADS was found to be 76.33 m2/g. FTIR was performed to recognize the functional groups available for fluoride binding while SEM and EDX were conducted to ensure the changes in adsorbent surface morphology. Regeneration of CADS was feasible using an alkali medium. This study shows that CADS can be used for fluoride removal from aqueous stream in an efficient way.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber S, Daneshvar N, Soroureddin SM, Chabok A, Asadpour-Zeynali K (2007) Study of acid orange 7 removal from aqueous solutions by powdered activated carbon and modeling of experimental results by artificial neural network. Desalination 211(1–3):87–95
Agarwal M, Dubey S, Gupta AB (2017) Coagulation process for fluoride removal by comparative evaluation of alum and PACl coagulants with subsequent membrane micro-filtration. Int J Environ Technol Manag 20:200–225
Al-Qodah Z, Shawabkah R (2009) Production and characterization of granular activated carbon from activated sludge. Braz J Chem Eng 26(1):127–136
Anupam K, Dutta S, Bhattacharjee C, Datta S (2011) Adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution over powdered activated carbon: optimization through response surface methodology. Chem Eng J 173(1):135–143
Araga R, Soni S, Sharma CS (2017) Fluoride adsorption from aqueous solution using activated carbon obtained from KOH-treated jamun (Syzygiumcumini) seed. J Environ Chem Eng 5:5608–5616
Baird RB, Bridgewater L, Clesceri LS, Eaton AD, Rice EW (eds) (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American public health association
Balci B, Keskinkan O, Avci M (2011) Use of BDST and an ANN model for prediction of dye adsorption efficiency of Eucalyptus camaldulensis barks in fixed-bed system. Expert Syst Appl 38(1):949–956
Baş D, Dudak FC, Boyacı IH (2007) Modeling and optimization III: reaction rate estimation using artificial neural network (ANN) without a kinetic model. J Food Eng 79(2):622–628
Baskan MB, Pala A (2010) A statistical experiment design approach for arsenic removal by coagulation process using aluminum sulfate. Desalination 254(1–3):42–48
Bhattacharya M, Singh A, Ramrakhyani C (2014) Dalbergi asissoo-an important medical plant. J Med Plants 2(2):76–82
Bhatti MS, Reddy AS, Kalia RK, Thukral AK (2011a) Modeling and optimization of voltage and treatment time for electrocoagulation removal of hexavalent chromium. Desalination 269(1–3):157–162
Bhatti MS, Kapoor D, Kalia RK, Reddy AS, Thukral AK (2011b) RSM and ANN modeling for electrocoagulation of copper from simulated wastewater: multi objective optimization using genetic algorithm approach. Desalination 274(1–3):74–80
Biswas K, Bandhoyapadhyay D, Ghosh UC (2007) Adsorption kinetics of fluoride on iron (III)-zirconium (IV) hybrid oxide. Adsorption 13(1):83–94
Biswas G, Kumari M, Adhikari K, Dutta S (2017) Application of response surface methodology for optimization of biosorption of fluoride from groundwater using Shorearobusta flower petal. Appl Water Sci 7(8):4673–4690
Boubakri A, Helali N, Tlili M, Amor MB (2014a) Fluoride removal from diluted solutions by Donnan dialysis using full factorial design. Korean J Chem Eng 31(3):461–466
Boubakri A, Bouchrit R, Hafiane A, Bouguecha SAT (2014b) Fluoride removal from aqueous solution by direct contact membrane distillation: theoretical and experimental studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(17):10493–10,501
Bureau of Indian Standards (2009) Draft Indian standard-drinking water specification Second Revision of IS 10500. New Delhi
Çelekli A, Birecikligil SS, Geyik F, Bozkurt H (2012) Prediction of removal efficiency of Lanaset Red G on walnut husk using artificial neural network model. Bioresour Technol 103(1):64–70
Cronje KJ, Chetty K, Carsky M, Sahu JN, Meikap BC (2011) Optimization of chromium (VI) sorption potential using developed activated carbon from sugarcane bagasse with chemical activation by zinc chloride. Desalination 275(1–3):276–284
Drouiche N, Aoudj S, Lounici H, Drouiche M, Ouslimane T, Ghaffour N (2012) Fluoride removal from pretreated photovoltaic wastewater by electrocoagulation: an investigation of the effect of operational parameters. Procedia Eng 33:385–391
Elsayed K, Lacor C (2011) Modeling, analysis and optimization of aircyclones using artificial neural network, response surface methodology and CFD simulation approaches. Powder Technol 212(1):115–133
Emmanuel KA, Ramaraju KA, Rambabu G, Rao AV (2008) Removal of fluoride from drinking water with activated carbons prepared from HNO3 activation-a comparative study. Rasayan J Chem 1(4):802–818
Fitzgerald J (2000) Groundwater quality and environmental health implications, Anangu Pitjantjatjara Lands, South Australia. Bureau of Rural Sciences, Canberra
Fordyce FM, Vrana K, Zhovinsky E, Povoroznuk V, Toth G, Hope BC, Baker J (2007) A health risk assessment for fluoride in Central Europe. Environ Geochem Health 29(2):83–102
Fu JF, Zhao YQ, Xue XD, Li WC, Babatunde AO (2009) Multivariate-parameter optimization of acid blue-7 wastewater treatment by Ti/TiO2 photoelectrocatalysis via the Box–Behnken design. Desalination 243(1–3):42–51
Garg UK, Kaur MP, Sud D, Garg VK (2009) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by adsorption on treated sugarcane bagasse using response surface methodological approach. Desalination 249(2):475–479
Getachew T, Hussen A, Rao VM (2015) Defluoridation of water by activated carbon prepared from banana (Musa paradisiaca) peel and coffee (Coffea arabica) husk. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(6):1857–1866
Giovanni M (1983) Response surface methodology and product optimization. Food Technol 37:41–45
Giri AK, Patel RK, Mahapatra SS (2011) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling of arsenic (III) biosorption from aqueous solution by living cells of Bacillus cereus biomass. Chem Eng J 178:15–25
Güven G, Perendeci A, Tanyolaç A (2009) Electrochemical treatment of simulated beet sugar factory wastewater. Chem Eng J 151(1–3):149–159
Hammoudi A, Moussaceb K, Belebchouche C, Dahmoune F (2019) Comparison of artificial neural network (ANN) and response surface methodology (RSM) prediction in compressive strength of recycled concrete aggregates. Constr Build Mater 209:425–436
Kagne S, Jagtap S, Thakare D, Devotta S, Rayalu SS (2009) Bleaching powder: a versatile adsorbent for the removal of fluoride from aqueous solution. Desalination 243(1–3):22–31
Karimi F, Rafiee S, Taheri-Garavand A, Karimi M (2012) Optimization of an air drying process for Artemisia absinthium leaves using response surface and artificial neural network models. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43(1):29–39
Khayet M, Cojocaru C, Essalhi M (2011) Artificial neural network modeling and response surface methodology of desalination by reverse osmosis. J Membr Sci 368(1–2):202–214
Ku Y, Chiou HM, Wang W (2002) The removal of fluoride ion from aqueous solution by a cation synthetic resin. Sep Sci Technol 37(1):89–103
Kumar S, Singh B (2018) Prediction of tool chatter in turning using RSM and ANN. Mater Today Proc 5(11):23806–23,815
Ma W, Ya F, Wang R, Zhao YQ (2008) Fluoride removal from drinking water by adsorption using bone char as a biosorbent. Int J Environ Technol Manag 9(1):59–69
Mistry BD (2009) A handbook of spectroscopic data-chemistry (UV, IR, PRM, 13CNMR and Mass Spectroscopy) Jaipur India
Mourabet M, El Rhilassi A, El Boujaady H, Bennani-Ziatni M, El Hamri R, Taitai A (2012) Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by adsorption on apatitic tricalcium phosphate using Box–Behnken design and desirability function. Appl Surf Sci 258(10):4402–4410
Mukherjee I, Ray PK (2006) A review of optimization techniques in metal cutting processes. Comput Ind Eng 50(1–2):15–34
Murugesan K, Dhamija A, Nam IH, Kim YM, Chang YS (2007) Decolourization of reactive black 5 by laccase: optimization by response surface methodology. Dyes Pigments 75(1):176–184
Myers RH, Montgomery DC, Anderson-Cook CM (2016) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. John Wiley & Sons
Nath K, Das D (2011) Modeling and optimization of fermentative hydrogen production. Bioresour Technol 102(18):8569–8581
National Research Council (2007) Fluoride in drinking water: a scientific review of EPA’s standards. National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Nazghelichi T, Aghbashlo M, Kianmehr MH (2011) Optimization of an artificial neural network topology using coupled response surface methodology and genetic algorithm for fluidized bed drying. Comput Electron Agric 75(1):84–91
Oguz E, Ersoy M (2010) Removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution by adsorption in a fixed bed column and neural network modelling. Chem Eng J 164(1):56–62
Özdemir U, Özbay B, Veli S, Zor S (2011) Modeling adsorption of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) onto polyaniline (PANI) by using multi linear regression and artificial neural networks. Chem Eng J 178:183–190
Ping ZY, Ya LX, Lu L, Hua CF (2005) Investigation of performances and mechanism of fluoride removal by Fe(Hl) loaded ligand exchange cotton cellulose adsorbent. Wuhan Univ J Nat Sci 10:936–940
Rajendra M, Jena PC, Raheman H (2009) Prediction of optimized pretreatment process parameters for biodiesel production using ANN and GA. Fuel 88(5):868–875
Reardon EJ, Wang Y (2000) A limestone reactor for fluoride removal from wastewaters. Environ Sci Technol 34(15):3247–3253
Sahu JN, Acharya J, Meikap BC (2009) Response surface modeling and optimization of chromium (VI) removal from aqueous solution using tamarind wood activated carbon in batch process. J Hazard Mater 172(2–3):818–825
Sasikumar E, Viruthagiri T (2008) Optimization of process conditions using response surface methodology (RSM) for ethanol production from pretreated sugarcane bagasse: kinetics and modeling. Bioenergy Res 1(3–4):239–247
Singh K, Lataye DH, Wasewar KL (2017) Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by using bael (Aeglemarmelos) shell activated carbon: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. J Fluor Chem 194:23–32
Srividya K, Mohanty K (2009) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by Catlacatla scales: equilibrium and kinetics studies. Chem Eng J 155(3):666–673
Suresh MVJJ, Reddy KS, Kolar AK (2011) ANN-GA based optimization of a high ash coal-fired supercritical power plant. Appl Energy 88(12):4867–4873
Tir M, Moulai-Mostefa N (2008) Optimization of oil removal from oily wastewater by electrocoagulation using response surface method. J Hazard Mater 158(1):107–115
Tripathi P, Srivastava VC, Kumar A (2009) Optimization of an azo dye batch adsorption parameters using Box–Behnken design. Desalination 249(3):1273–1279
Tripathy SS, Bersillon JL, Gopal K (2006) Removal of fluoride from drinking water by adsorption onto alum-impregnated activated alumina. Sep Purif Technol 50(3):310–317
Turan NG, Mesci B, Ozgonenel O (2011) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling Zn (II) adsorption from leachate using a new biosorbent. Chem Eng J 173(1):98–105
Yang Y, Wang G, Wang B, Li Z, Jia X, Zhou Q, Zhao Y (2011) Biosorption of Acid Black 172 and Congo Red from aqueous solution by nonviable Penicillium YW 01: kinetic study, equilibrium isotherm and artificial neural network modeling. Bioresour Technol 102(2):828–834
Yetilmezsoy K, Demirel S (2008) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling of Pb (II) adsorption from aqueous solution by Antep pistachio (Pistacia Vera L.) shells. J Hazard Mater 153(3):1288–1300
Zhang Y, Xu J, Yuan Z, Xu H, Yu Q (2010) Artificial neural network-genetic algorithm based optimization for the immobilization of cellulase on the smart polymer Eudragit L-100. Bioresour Technol 101(9):3153–3158
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, S., Bajpai, S. & Jana, S. Application of ANN and RSM on fluoride removal using chemically activated D. sissoo sawdust. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 17717–17729 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08153-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08153-0