Abstract
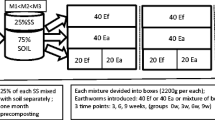
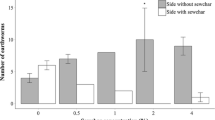
This study assessed the effects of salinity and sewage sludge on the fractionation of Zn and Cu in a soil around a lead-zinc mine as well as their uptake by earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in order to identify novel methods for employing the earthworms in waste management techniques. Eisenia fetida specimens were kept under laboratory conditions for 42 days. The first treatment involved the addition of 0%, 2%, 4%, and 8% (w/w) sewage sludge to contaminated soil. In the second treatment, NaCl was added to the soil at concentrations of 0, 1170, 2340, 3510, and 4680 mg L−1. The results indicated that the combined application of high salinity and sewage sludge had adverse effects on the survival of the earthworms. The presence of the earthworms increased the amount of Zn and Cu bound to organic matter. The organic fraction of Zn and Cu also significantly aggregated with increasing salinity levels. The interaction of salinity and earthworm showed that the residual Cu fraction increased with the presence of earthworm and decreased with increasing salinity. The residual fraction of Cu was significantly affected by the interactions of salinity and sewage sludge, where the highest amount was seen in the EC0 (distilled water) × SS8 (8% sewage sludge) treatment. The Zn and Cu contents increased with the earthworms when exposed to higher levels of salinity and sewage sludge.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour A, Kalbasi M, Hajrasuliha SH, Golchin A (2007) Effects of plant residue and salinity on fractions of cadmium and lead in three soils. Soil Sediment Contam 16:539–555. https://doi.org/10.22092/ijsr.2018.116561
Ahmed HK, Fawy ES, Abdel-Hady ES (2010) Study of sewage sludge use in agriculture and its effect on plant and soil. Agric Biol J N Am 1:1044–1049. https://doi.org/10.5251/abjna.2010.1.5.1044.1049
Angin I, Yaganogl AV (2011) Effects of sewage sludge application on some physical and chemical properties of a soil affected by wind erosion. J Agric Sci Technol 13:757–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10341-016-0303-9
Ashraf MA, Maah MJ, Yusoff L (2011) Heavy metals accumulation in plants growing in ex-tin mining catchment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8:401–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326227
Becquer T, Dai J, Quantin C, Lavelle P (2005) Source of bioavailable trace metals for earthworms from a Zn-, Pb- and Cd-contaminated soil. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1564–1568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.01.007
Canet R, Pomares F, Tarazona F, Estela M (1998) Sequential fractionation and plant availability of heavy metals as affected by sewage sludge applications to soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 29:697–716. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629809369978
Chang AC, Page AL, Warneke JE, Grgurevic E (1984) Sequential extraction of soil heavy-metals following a sludge application. J Environ Qual 13:33–38. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1984.00472425001300010006x
Chen Y (1996) Organic matter reactions involving micronutrients in soils and their effect on plants. In: Piccolo A (ed) Humic substances in terrestrial ecosystems. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 507–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-044481516-3/50014-1
Cheng J, Wong MH (2002) Effects of earthworms on Zn fractionation in soils. Biol Fertil Soils 36:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-002-0507-z
Chu B, Chen XJ, Li QS, Yang YF, Mei XQ, He BY, Li H, Tan L (2015) Effects of salinity on transformation of heavy metals in tropical estuary wetland soil. J Chem Ecol 31:186–198. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2014.917174
Conner JR (1990) Chemical fixation and solidification of hazardous wastes, vol 692. Van Nostrad Reinhold, New York, pp 20030–20039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2080-5
Cotter-Howells J, Charnock JM, Winters C, Kille P, Fry JC, Morgan AJ (2005) Metal compartmentation and speciation in a soil sentinel: the earthworm, Dendrodrilus rubidus. Environ Sci Technol 9:7731–7740. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050648h
Crouau Y, Moïa C (2006) The relative sensitivity of growth and reproduction in the springtail, Folsomia candida, exposed to xenobiotics in the laboratory: an indicator of soil toxicity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.06.002
Du Laing G, De Vos R, Vandecasteele B, Lesage E, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2008) Effect of salinity on heavy metal mobility and availability in intertidal sediments of the Scheldt estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 77:589–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2007.10.017
Edwards CA, Bohlen PJ (1996) Biology and ecology of earthworms, 3rd edn. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 207–210
Fujii Y, Kaneko N (2009) The effect of earthworms on copper fractionation of freshly and long-term polluted soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1754–1759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.04.020
Garcia-Montero LG, Valverde-Asenjo I, Grande-Ortiz MA, Menta C, Hernando I (2013) Impact of earthworm casts on soil pH and calcium carbonate in black truffle burns. Agrofor Syst 87:815–826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-013-9598-9
Gaur N, Dhankhar R (2009) Removal of Zn+2 ions from aqueous solution using Anabaena variabilis. Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Int J Environ Res 3:605–616. https://doi.org/10.22059/IJER.2010.76
Graff O (1982) Vergleich der Regenswurmaten Eisenia foetida and Eudrilus eugeniae Hinsichlich Ihrer Eignung zur Proteinwinnung aus Abfallstoffen. Pedobiologia 23:277–282
Gupta SK, Tewari A, Srivastava R, Murthy RC, Chandra S (2005) Potential of Eisenia foetida for sustainable and efficient vermicomposting of fly ash. Water Air Soil Pollut 163:293–302
Guzyte G, Sujetoviene G, Zaltauskaite J (2011) Effects of salinity on earthworm (Eisenia fetida). The 8th International Conference May 19–20, Vilnius, Lithuania. J Environ Eng:111–114
He Q, Ren Y, Mohamed I, Ali M, Hassan W, Zenga F (2013) Assessment of trace and heavy metal distribution by four sequential extraction procedures in a contaminated soil. SoilWater Res 8(2):71–76
Hlavay J, Prohaska T, Weisz M, Wenzel WW, Stingeder GJ (2004) Determination of trace elements bound to soils and sediment fractions., (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 76:415–442. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200476020415
Hobbelen PHF, Koolhaas JE, Van Gestel CAM (2006) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the earthworms Lumbricus rubellus and Aporrectodea caliginosa in relation to total and available metal concentrations in field soils. Environ Pollut 144(2):639–646
Illera V, Walter I, Souza UP, Cala V (2000) Short-term effects of biosolid and municipal solid waste applications on heavy metals distribution in a degraded soil under a semi-arid environment. Sci Total Environ 255:29–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00444-7
Jatwani CH, Gupta RK, Rai R, Bansal N (2016) Effects of Hg/Co toxicity in soil on biomolecules of earthworm, Eisenia Fetida. Procedia Environ Sci 35:450–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.07.028
Keshavarz P, Malakouti MJ, Karimian N, Fotovat A (2006) The effects of salinity on extractability and chemical fractions of zinc in selected calcareous soils of Iran. J Agric Sci Technol 8:181–190
Khattak RA, Jarrell WM (1989) Effect of saline irrigation waters on soil manganese leaching and bioavailability to sugar beet. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53:142–146. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1989.03615995005300010027x
Kızılkaya R (2004) Cu and Zn accumulation in earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L. in sewage sludge-amended soil and fractions of Cu and Zn in casts and surrounding soil. J Ecol Eng 22:141–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2004.04.002
Lambkin DC, Gwilliam KH, Layton C, Canti MG, Piearce TG, Hodson ME (2011) Production and dissolution rates of earthworm-secreted calcium carbonate. Pedobiologia 54:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedobi.2011.09.003
Lanno RP, Wells J, Conder J, Bradham K, Basta N (2004) The bioavailability of chemicals in soil for earthworms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 57:39–47
Lee BT, Lee SW, Kim KR, Kim KW (2013) Bioaccumulation and the soil factors affecting the uptake of arsenic in earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8326–8333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2087-x
Lemtiri A, Liénard A, Alabi T, Brostaux Y, Cluzeau D, Francis F, Colinet G (2016) Earthworms Eisenia fetida affect the uptake of heavy metals by plants Vicia faba and Zea mays in metal-contaminated soils. Appl Soil Ecol 104:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.11.021
Li XD, Thornton I (2001) Chemical partitioning of trace and major elements in soils contaminated by mining and smelting activities. Appl Geochem 16:1693–1706. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00065-8
Li L, Xu Z, Wu J, Tian G (2010) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the earthworm Eisenia fetida in relation to bioavailable metal concentrations in pig manure. Bioresour Technol 101:3430–3436
Li F, Li Z, Mao P, Li Y, Li Y, McBride MB, Wu J, Zhuang P (2018) Heavy metal availability, bioaccessibility, and leachability in contaminated soil: effects of pig manure and earthworms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:9–20039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2080-5
Liu XL, Hu CX, Zhang SZ (2005) Effects of earthworm activity on fertility and heavy metal bioavailability in sewage sludge. Environ Int 31:874–879
Lukkari T, Teno S, Vaeisaenen A, Haimi J (2006) Effects of earthworms on decomposition and metal availability in contaminated soil: microcosm studies of populations with different exposure histories. Soil Biol Biochem 38:359–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.05.015
Luo YM, Christie P (1998) Bioavailability of copper and zinc in soils treated with alkaline stabilised sewage sludge. J Environ Qual 27:335–342. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1998.00472425002700020013x
Martin A (1991) Short and long term effects of the endogenic earthworm Millsonia anomalia (Megascolecidae, Oligochaeta) of tropical savannas, on soil organic matter. Biol Fertil Soils 11:234–238
Mensah AK (2015) Role of revegetation in restoring fertility of degraded mined soils in Ghana: a review. Int J Biodivers Conserv 7:57–80. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJBC2014.0775
Miao-miao HE, Guang-ming T, Xing-qiang L, Yi-tong YU, Jian-yang WU, Gen-di Z (2007) Effects of two sludge application on fractionation and phytotoxicity of zinc and copper in soil. J Environ Sci 19:1482–1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60241-1
Morgan JE, Morgan AJ (1989) The effect of lead incorporation on the elemental composition of earthworm (Annelida: Oligochaeta) chloragosome granules. Histochemistry 92:237–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500924
Morgan JE, Morgan AJ (1999) The accumulation of metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn and Ca) by two ecologically contrasting earthworm species (Lumbricus rubellus and Aporrectodea caliginosa): implications for ecotoxicological testing. Appl Soil Ecol 13:9–20
Mosquera-Losada R, Amador-García A, Muñóz-Ferreiro N, Santiago-Freijanes J, Nuria Ferreiro-Domínguez N, Romero-Franco R, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A (2017) Sustainable use of sewage sludge in acid soils within a circular economy perspective. CATENA 149:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.10.007
Mountouris A, Voutsas E, Tassios D (2002) Bioconcentration of heavy metals in aquatic environments: the importance of bioavailability. Mar Pollut Bull 44:1136–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00168-6
Mumba PP, Chibambo BQ, Kadewa W (2008) A comparison of the levels of heavy metals in cabbages irrigated with reservoir and tap water. Int J Environ Res 2:61–64. https://doi.org/10.22059/IJER.2010.176
Nannoni F, Protano G, Riccobono F (2011) Uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy elements by two earthworm species from a smelter contaminated area in northern Kosovo. Soil Biol Biochem 43:2359–2367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.08.002
Natal-Da-Luz T, Tidona S, Jesus B, Morais PV, Sousa JP (2009) The use of sewage sludge as soil amendment: the need for an ecotoxicological evaluation. J Soils Sediments 9:246–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-009-0077-x
Nyamangara J (1998) Use of sequential extraction to evaluate zinc and copper in a soil amended with sewage sludge and inorganic metal salts. Agric Ecosyst Environ 69:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(98)00101-7
OECD (2004) Guideline for testing of chemicals 222 ‘earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida)’ adopted: 13 April
Owojori OJ, Reinecke AJ, Rozanov AB (2008) Effects of salinity on partitioning, uptake and toxicity of zinc in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2385–2393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.05.019
Pattnaik S, Reddy MV (2011) Heavy metals remediation from urban wastes using three species of earthworm (Eudrilus eugeniae, Eisenia fetida and Perionyx excavatus). J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 3(14):345–356. https://doi.org/10.5897/JECE11.036
Pramanik P, Ghosh G, Ghosal P, Banik P (2007) Changes in organic-C, N, P and K and enzyme activities in vermicompost of biodegradable organic wastes under liming and microbial inoculants. Bioresour Technol 98:2485–2494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.017
Rafiei B, Bakhtiari Nejad M, Hashemi M, Khodaei AS (2010) Distribution of heavy metals around the Dashkasan Au mine. Int J Environ Res 4:647–654. https://doi.org/10.22059/IJER.2010.250
Ragab AAMM, Hellal FA, Abd El-Hady M (2008) Irrigation water salinity effects on some soil water constants and plant. Twelfth International Water Technology Conference Egypt
Rahimi G, Karimi F (2016) The prolonged effect of salinity on growth and/or survival of earthworm Eisenia fetida. Int J Environ Waste Manag:18. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEWM.2016.080263
Reinecke AJ, Kriel JR (1981) Influence of temperature on the reproduction of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta). S Afr J Zool 16:96–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/02541858.1981.11447740
Rey A, Petsikos C, Jarvis PG, Grace J (2005) Effect of temperature and moisture on rates of carbon mineralization in a Mediterranean oak forest soil under controlled and field conditions. Eur J Soil Sci 56:589–599. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2004.00699.x
Richards KS, Ireland MP (1978) Glycogen-lead relationship in the earthworm Dendrobaena rubida from a heavy metal site. Histochemistry 56:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00492253
Ruiz E, Alonso-Azcárate J, Rodríguez L (2011) Lumbricus terrestris L. activity increases the availability of metals and their accumulation in maize and barley. Environ Pollut 159:722–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.11.032
Shaheen SM, Shams MS, Ibrahim SM, Elbehiry FA, Antoniadis V, Hooda PS (2014) Stabilization of sewage sludge by using various by-products: effects on soil properties, biomass production and bioavailability of copper and zinc. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2014-x
Shober AL, Richard CS, Kirsten EM (2007) Chemical fractionation of trace elements in biosolid-amended soils and correlation with trace elements in crop tissue. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 38:1029–1046. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620701280068
Singh RP, Agrawal M (2010) Variations in heavy metal accumulation, growth and yield of rice plants grown at different sewage sludge amendment rates. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:632–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.01.020
Sinha RK, Bharambe G, Chaudhari U (2008) Sewage treatment by vermifiltration with synchronous treatment of sludge by earthworms: a low-cost sustainable technology over conventional systems with potential for decentralization. Environmentalist 28:409–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-008-9162-8
Sivakumar S (2015) Effects of metals on earthworm life cycles: a review. Environ Monit Assess 187:530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4742-9
Sizmur T, Hodson ME (2009) Do earthworms impact metal mobility and availability in soil– a review. Environ Pollut 157:1981–1989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.02.029
Sizmur T, Palumbo Roe B, Watts MG, Hodson ME (2011) Impact of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (L.) on As, Cu, Pb and Zn mobility and speciation in contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 159:742–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.11.033
Sposito G, Lund LJ, Chang AC (1982) Trace metal chemistry in arid-zone field soils amended with sewage sludge. I. Fractionation of Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in solid phases. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:260–264. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1982.03615995004600020009x
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP, Jones DT (1994) Effects of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc on growth, reproduction and survival of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savingny): assessing the environmental impact of point-source metal contamination in terrestrial ecosystems. Environ Pollut 84:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(94)90094-9
Su C, Jiang L, Zhang WJ (2014) A review on heavy metal contamination in the soil worldwide: situation, impact and remediation techniques. Environ Skep Crit 3:24–38
Suthar S (2009) Vermistabilization of municipal sewage sludge amended with sugarcane trash using epigeic E. fetida (Oligochaeta). J Hazard Mater 163:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.106
Suthar S, Singh S, Dhawan S (2008) Earthworm as bioindicators of metals (Zn, Fe, Mn, Cu, Pb and Cd) in soils: is metal bioaccumulation affected by their ecological categories. Ecol Eng 32:99–107
Tao G, Wei G, Griffiths B, Xiaojing L, Yingjun X, Hua Z (2012) Maize residue application reduces negative effects of soil salinity on the growth and reproduction of the earthworm Aporrectodea trapezoids, in a soil mesocosm experiment. Soil Biol Biochem 49:46–51
Tewari G, Srivastava PC, Ram B, Tewari L (2006) Chemical fractions and bioavailability of heavy metals in polluted soils. In: Hudson Robert C (ed) Hazardous materials in the soil and atmosphere: treatment, removal and analysis. Nova Science Publishers, New York Chapter 4, pp 89–115
Theodoratos P, Moirou A, Xenidis A, Paspaliaris I (2000) The use of municipal sewage sludge for the stabilization of soil contaminated by mining activities. J Hazard Mater 77:177–191
Tsadilas CD, Theodora Matsi T, Barbayiannis N, Dimoyiannis D (1995) Influence of sewage sludge application on soil properties and on the distribution and availability of heavy metal fractions. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 26:2603–2619. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629509369471
Udovic M, Lestan D (2007) The effect of earthworms on the fractionation and bioavailability of heavy metals before and after soil remediation. Environ Pollut 148:663–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.11.010
van Gestel CAM, Dirven van Breemen EM, Baerselman R (1993) Accumulation and elimination of cadmium, chromium and zinc and effects on growth and reproduction in Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta, Annelida). Sci Total Environ Suppl 134:585–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(05)80061-0
Wen B, Hu XY, Liu Y, Wang WS, Feng MH, Shan XQ (2004) The role of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in influencing bioavailability of heavy metals in soils. Biol Fertil Soils 40:181–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0761-3
Wen B, Liu Y, Hu X, Shan X (2006) Effect of earthworms (Eisenia fetida ) on the fractionation and bioavailability of rare earth elements in nine Chinese soils. Chemosphere 63:1179–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.09.002
Zhang MK, Liu ZY, Wang H (2010) Use of single extraction methods to predict bioavailability of heavy metals in polluted soils to rice. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 41:820–831. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103621003592341
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Chris Lowe
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimi, F., Rahimi, G. & Kolahchi, Z. Interaction effects of salinity, sewage sludge, and earthworms on the fractionations of Zn and Cu, and the metals uptake by the earthworms in a Zn- and Cu-contaminated calcareous soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 10565–10580 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07719-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07719-2