Abstract
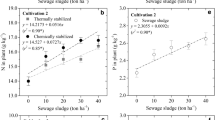
Stabilization of sewage sludge (SS) prior to its land disposal may help control the mobility of SS-borne contaminants, particularly potentially toxic metals. We examined the effects of stabilized SS application on soil properties, biomass production, and phytoavailability of Cu and Zn to plants grown in two contrasting soils, Entisol and Aridisol. Stabilized SS mixtures were created by mixing SS in a 3-to-1 ratio with bentonite (B), sugar beet factory lime (SL), brick factory fly ash (BFA), rice straw (RS), water hyacinth (WH), and 50:50 mixture of RS and SL. Mixtures were applied at 50 Mg ha−1, and Sorghum vulgare L. and Eurica sativa were grown in a pot experiment. All the amendments increased plant availability and uptake of both Cu and Zn compared to the unamended control. The application of stabilized SS increased dry plant biomass significantly and decreased DTPA-extractable elements compared to the non-stabilized SS treatment. We conclude that of the six amendments studied, especially sugar beet factory lime (SL) and bentonite (B), are promising for the stabilization of metal-contaminated biosolids and should be tested under field conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniadis, V., Robinson, J. S., & Alloway, B. J. (2008). Effect of short-term pH fluctuations on cadmium, nickel, lead, and zinc availability to ryegrass in a sewage sludge-amended field. Chemosphere, 71, 759–764.
Antoniadis, V., Tsadilas, C. D., & Samaras, V. (2010). Trace element availability in a sewage sludge-amended cotton grown Mediterranean soil. Chemosphere, 80, 1308–1313.
Chaney, R. L. (2010). Cadmium and zinc. In P. S. Hooda (Ed.), Trace elements in soils (pp. 409–440). Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Dudley, L. M., McLean, J. E., Sims, R. C., & Jurinak, J. J. (1988). Sorption of copper and cadmium from the water-soluble fraction of an acid mine waste by two calcareous soils. Soil Science, 145, 207–214.
El-Motaium, R. A., & Abo El-Seoud, M. A. (2007). Irradiated sewage sludge for production of fennel plants in sandy soil. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 78, 133–142.
Havlin, J. L., Beaton, J. D., Tisdale, S. L., & Melson, W. L. (2005). Soil fertility and fertilizers: an introduction to nutrient management (7th ed.). Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, USA: Pearson.
Hooda, P. S., & Alloway, B. J. (1994a). The plant availability and DTPA extractability of trace metals in sludge-amended soils. Science of the Total Environment, 149, 39–51.
Hooda, P. S., & Alloway, B. J. (1994b). Changes in operational fractions of trace metals in two soils during two-years of reaction time following sewage sludge treatment. International Journal of Environmental and Analytical Chemistry, 57, 289–311.
Hooda, P. S., & Alloway, B. J. (1996). The effect of liming on heavy metal concentrations in wheat, carrots and spinach grown on previously sludge-applied soils. Journal of Agricultural Science, 127, 289–294.
Hooda, P. S., McNaulty, D., Alloway, B. J., & Aitken, M. N. (1997). Plant availability of heavy metals in soils previously amended with sewage sludges. Journal of Science of Food and Agriculture, 73, 446–454.
Jamali, M. K., Kazi, T. G., Arain, M. B., Afridi, H. I., Memon, A. R., Jalbani, N., et al. (2008). Use of sewage sludge after liming as fertilizer for maize growth. Pedosphere, 18, 203–213.
Jones, J. B., Wolf, J. B., & Mills, H. A. (1991). Plant analysis handbook: a practical sampling, preparation, analysis, and interpretation guide. Athens Ga: Micro–macro Publishing.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants (4th ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Kanungo, S. P., Mukherjee, P. S., & Rout, S. K. (2000). Utilization of industrial wastes-fly ash and coir pith for cultivation of commercial aromatic crops. In G. V. Rao, B. Das, S. R. S. Sastri, & H. S. Ray (Eds.), Mineral processing waste and environment management (pp. 183–186). New Delhi: Allied Publishers Ltd.
Kiekens, L. (1995). Zinc. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils, 2nd Ed (pp. 284–305). London: Blackie Academic and Professional.
Kosobucki, P., Kruk, M., & Buszewski, B. (2008). Immobilization of selected heavy metals in sewage sludge by natural zeolites. Bioresource Technology, 99, 5972–5976.
Kumpiene, J., Lagerkvist, A., & Maurice, C. (2007). Stabilization of Pb- and Cu-contaminated soil using coal fly ash and peat. Environmental Pollution, 145, 365–373.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 4, 421–428.
McLean, J. E., & Bledsoe, B. E. (1992). Ground water issue: behavior of metals in soils. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, EPA/540/S-92/018. Available at http://www.epa.gov/superfund/remedytech/tsp/download/issue14.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2014).
Mendoza, J., Garrido, T., Castillo, G., & Martin, N. (2006). Element availability and uptake by sorghum plants grown in soils amended with sludge from different treatments. Chemosphere, 65, 2304–2312.
Murtaza, G., Haynes, R. J., & Naidu, R. (2011). Natural attenuation of Zn, Cu, Pb and Cd in three biosolids-amended soils of contrasting pH measured using rhizon pore water samplers. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 221, 351–363.
Nabulo, G., Black, C. R., & Young, S. D. (2011). Trace metal uptake by tropical vegetables grown on soil amended with urban sewage sludge. Environmental Pollution, 159, 368–376.
Oleszczuk, P., & Hollert, H. (2011). Comparison of sewage sludge toxicity to plants and invertebrates in three different soils. Chemosphere, 83, 502–509.
Sajwan, K. S., Paramasivam, S., Alva, A. K., Adriano, D. C., & Hooda, P. S. (2003). Assessing the feasibility of land application of fly ash, sewage sludge and their mixtures. Advances in Environmental Research, 8, 77–91.
Shaheen, S. M., & Tsadilas, C. D. (2011). Fractionation and bioavailability of trace elements in biosolid amended Alfisol ten years after biosolids application. Proceedings of the 11th international conference of bio-geochemistry of trace elements, part I (p. 463). July 3–7, 2011, Florence, Italy, 2011.
Shaheen, S. M., & Tsadilas, C. D. (2013a). Phosphorus sorption and availability to canola grown on an Alfisol amended with various soil amendments. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 44, 89–103.
Shaheen, S. M., & Tsadilas, C. D. (2013b). Utilization of biosolids in production of bioenergy crops. I: impact on canola biomass, soil properties and nutrient availability. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 44, 243–258.
Shaheen, S. M., Shams, M. S., Elbehiry, F. A., & Ibrahim, S. M. (2012). Influence of stabilized biosolids application on soil properties and availability of phosphorus, copper and zinc. Applied and Environmental Soil Science. doi:10.1155/2012/817158.
Shi, W., Liu, C., Ding, D., Lei, Z., Yang, Y., Fang, C., & Zhang, Z. (2013). Immobilization of heavy metals in sewage sludge by using subcritical water technology. Bioresource Technology, 137, 18–24.
Singh, R. P., & Agrawal, M. (2010). Effect of different sewage sludge applications on growth and yield of Vigna radiata L. field crop: element uptake by plant. Ecological Engineering, 969–972.
Sparks, D. L., Page, A. L., Helmke, P. A., Loppert, R. H., Soltanpour, P. N., Tabatabai, M. A., Johnston, C. T., & Summner, M. E. (1996). Methods of soil analysis: chemical methods, Part 3. Madison, WI: Agronomy Society of America and Soil Science Society of America.
Su, D. C., & Wong, J. W. C. (2004). Chemical speciation and phytoavailability of Zn, Cu, Ni and Cd in soil amended with fly ash-stabilized sewage sludge. Environment International, 29, 895–900.
Sukkariyah, B. F., Evanylo, G., Zelazny, L., & Chaney, R. L. (2005). Cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc availability in a biosolids-amended piedmont soil years after application. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 2255–2262.
Tsadilas, C. D., & Shaheen, S. M. (2013). Utilization of biosolids in production of bioenergy crops. II: impact of application rate on bioavailability and uptake of heavy metals by canola. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 44, 259–274.
United States Environmental Protection Agency. (1995). Test methods for evaluating solid wastes. Washington: USEPA SW 846, U.S. Gov. Print Office.
Wang, X., Chen, T., Ge, Y., & Jia, Y. (2008). Studies on land application of sewage sludge and its limiting factors. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160, 554–558.
Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Chao, J., Gao, Y., Yang, F., & Zhang, L. (2013). Impact of fly ash and phosphatic rock on metal stabilization and bioavailability during sewage sludge vermicomposting. Bioresource Technology, 136, 281–287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaheen, S.M., Shams, M.S., Ibrahim, S.M. et al. Stabilization of Sewage Sludge by Using Various By-products: Effects on Soil Properties, Biomass Production, and Bioavailability of Copper and Zinc. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 2014 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2014-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2014-x