Abstract
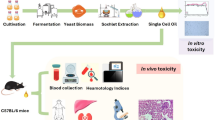
The aim of the study was to evaluate cyto- and genotoxic effects in populations living in subnormal clusters in Santos São Vicente estuary. For in vivo study, samples of buccal mucosa and peripheral blood cells were collected. Micronucleus assay and single-cell gel (comet) assay were performed. For in vitro study, Chinese ovary hamster (CHO) cells were exposed to contaminated water. The results showed that people living in the contaminated estuary have increased DNA damage in oral mucosa and peripheral blood cells, as detected in the micronucleus and comet assays respectively. In addition, estuarine water was able to promote cytotoxicity at the highest concentrations, as well as decrease the number of cells in the G1 phase. In summary, our results indicate that water from the Santos-São Vicente estuary is capable of inducing cytogenotoxicity in mammalian cells in vivo and in vitro.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amorim LC (2003) Os biomarcadores e sua aplicação na avaliação da exposição aos agentes químicos ambientais. Rev Bras Epidemiol 6:158–170 [in Portuguese]
Azqueta A, SAS L, Boutet-Robinet E, Duthie S, Ladeira C, Møller P, Collins AR, Godschalk RWL, Working Group 5 of the hCOMET project (CA15132) (2019) DNA repair as a human biomonitoring tool: comet assay approaches. Mutat Res 781:71–87
Banci KR, Mori GM, Oliveira MA et al (2017) Can environmental pollution by metals change genetic diversity? Ucides cordatus (Linnaeus, 1763) as a study case in Southeastern Brazilian mangroves. Mar Pollut Bull 116(1–2):440–447
Belien JA, Copper MP, Braakhuis BJ et al (1995) Standardization of counting micronuclei: definition of a protocol to measure genotoxic damage in human exfoliated cells. Carcinogenesis 16(10):2395–2400
Beyersmann D, Hartwig A (2008) Carcinogenic metal compounds: recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 82(8):493–512
Biswas D, Sen G, Sarkar A et al (2011) Atorvastatin acts synergistically with N-acetyl cysteine to provide therapeutic advantage against Fas-activated erythrocyte apoptosis during chronic arsenic exposure in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmcol 250(1):39–53
Bolognesi C, Knasmueller S, Nersesyan A, Thomas P, Fenech M (2013) The HUMNxl scoring criteria for different cell types and nuclear anomalies in the buccal micronucleus cytome assay - an update and expanded photogallery. Mutat Res 753:100–113
Cesar A, Pereira CDS, Santos AR, Others. (2006) Ecotoxicological assessment of sediments from the Santos and S{ã}o Vicente estuarine system-Brazil. Braz J Ocean 54(1):55–63
CETESB. Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental. Relatório de águas costeiras, (2016) 181p. Available em:http://cetesb.sp.gov.br/praias/wp-content/uploads/sites/31/2013/11/relatorio-praias-2016.pdf[in Portuguese]
Choueri RB, Cesar A, Abessa DMS, Torres RJ, Morais RD, Riba I, Pereira CD, Nascimento MR, Mozeto AA, DelValls T (2009) (2009). Development of site-specific sediment quality guidelines for North and South Atlantic littoral zones: comparison against national and international sediment quality benchmarks. J Hazard Mater 170(1):320–331
Cordeiro CA, Costa TM (2010) Evaluation of solid residues removed from a mangrove swamp in the São Vicente estuary, SP, Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 60(10):1762–1767
Costa C, Teixeira JP, Silva S, Roma-Torres J, Coelho P, Gaspar J, Alves M, Laffon B, Rueff J, Mayan O (2006) Cytogenetic and molecular biomonitoring of a Portuguese population exposed to pesticides. Mutagenesis 21(5):343–350
de Oliveira BF, Chacra AP, Frauches TS, Vallochi A, Hacon S (2014) A curated review of recent literature of biomarkers used for assessing air pollution exposures and effects in humans. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 17(7–8):369–410
De Vizcaya-Ruiz A, Barbier O, Ruiz-Ramos R et al (2009) Biomarkers of oxidative stress and damage in human populations exposed to arsenic. Mutat Res 674(1–2):85–92
Dingemans MM, Baken KA, van der Oost R, Schriks M, van Wezel AP (2019) Risk-based approach in the revised European Union drinking water legislation: opportunities for bioanalytical tools. Integr Environ Assess Manag 15(1):126–134
Dorne JL, Kass GE, Bordajandi LR et al (2011) Human risk assessment of heavy metals: principles and applications. Metals Ions Life Sci 8:27–60
Fernandes BS (2003) Nova abordagem para o grave problema da desnutrição infantil. Estudos Avançados 17(48):77–92 [in Portuguese]
Gimiliani GT, Fontes RFC, de Souza Abessa DM (2016) Modeling the dispersion of endocrine disruptors in the Santos Estuarine System (Sao Paulo State, Brazil). Brazilian J Oceanogr 64(1):1–8
Groten JP, Feron VJ, Sühnel J (2001) Toxicology of simple and complex mixtures. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22(6):316–322
Hernández AF, Tsatsakis AM (2017) Human exposure to chemical mixtures: challenges for the integration of toxicology with epidemiology data in risk assessment. Food Chem Toxicol 103:188–193
Hou H, Yu Y, Shen Z, Liu S, Wu B (2017) Hepatic transcriptomic responses in mice exposed to arsenic and different fat diet. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(11):10621–10629
IBGE. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Censo (2010) Disponível em: [www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/censo2010/]. Assessed em 05/09/2018 [in Portuguese]
Jiang X, Chen C, Zhao W, Zhang Z (2013) Sodium arsenite and arsenic trioxide differently affect the oxidative stress, genotoxicity and apoptosis in A549 cells: an implication for the paradoxical mechanism. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36(3):891–902
Kennish MJ (2002) Environmental threats and environmental future of estuaries. Enviorn Conserv 29(1):78–107
Kim BSM, Salaroli AB, de Lima Ferreira PA, Sartoretto JR, de Mahiques MM, Figueira RCL (2016) Spatial distribution and enrichment assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from Baixada Santista, Southeastern Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 103(1–2):333–338
Krämer O, Klausing S, Noll T (2010) Methods in mammalian cell line engineering: from random mutagenesis to sequence-specific approaches. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88(2):425–436
Neumann B, Vafeidis AT, Zimmermann J, Nicholls RJ (2015) Future coastal population growth and exposure to sea-level rise and coastal flooding-a global assessment. PLoS One 10(3):e0118571
Perina FC, Torres RJ, Mozeto AA, Nascimento MRL, Abessa DMS (2018) Sediment quality assessment of the tributaries of the Santos-São Vicente Estuarine System – Brazil. Ecotoxicol Environ Contam [Internet] 13(2):25–38 Available from: http://ecotoxbrasil.org.br/upload/a44358a45e8efe76c53b4398f1cfa78c-005-eec-12196-25-38.pdf
Sampaio A, Mateus M, Ribeiro R (2008) Assessing the impact of several development scenarios on the water quality in Santos Estuary. In: Neves R, Baretta J, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisboa, pp 435–444
Souza ACF, Yujra VQ, Pisani LP, De Barros VM, De Castro GM, Ribeiro DA (2019) The use of single-cell comet assay on oral cells: a critical review. Anticancer Res 39(8):4011–4017
Thomas P, Harvey S, Gruner T, Fenech M (2008) The buccal cytome and micronucleus frequency is substantially altered in Down's syndrome and normal ageing compared to young healthy controls. Mutat Res 638(1):37–47
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu J.-C Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guideline for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutag 35 (3): 206–221
Tolbert PE, Shy CM, Allen JW (1992) Micronuclei and other nuclear anomalies in buccal smears: methods development. Mutat Res 271(1):69–77
Torres RJ, Cesar A, Pastor VA, Pereira CD, Choueri RB, Cortez FS, Morais RD, Abessa DM, do Nascimento MR, Morais CR, Fadini PS (2015) A critical comparison of different approaches to sediment-quality assessments in the Santos estuarine system in Brazil. Arch Environ Contamin Toxicol 68(1):132–147
Umbuzeiro GA, Kummrow F, Roubicek DA, Tominaga MY (2006) Evaluation of the water genotoxicity from Santos Estuary (Brazil) in relation to the sediment contamination and effluent discharges. Environ Int 32(3):359–364
Vuyyuri SB, Ishaq M, Kuppala D, Grover P, Ahuja YR (2006) Evaluation of micronucleus frequencies and DNA damage in glass workers exposed to arsenic. Environ Mol Mutag 47(7):562–570
Yamaguchi Y, Madhyastha H, Madhyastha R, Choijookhuu N, Hishikawa Y, Pengjam Y, Nakajima Y, Maruyama M (2016) Arsenic acid inhibits proliferation of skin fibroblasts, and increases cellular senescence through ROS mediated MST1-FOXO signaling pathway. J Toxicol Sci 41(1):105–113
Acknowledgments
EAC, DMFS, CDSP, CMC, and DAR are recipients of the CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnologico) fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by Human Ethics Committee from Federal University of São Paulo, UNIFESP, Number # 1.955.311.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alpire, M.E.S., de Camargo, E.A., Cardoso, C.M. et al. In vivo and in vitro analysis of cytogenotoxicity in populations living in abnormal conditions from Santos-Sao Vicente estuary. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 12039–12046 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07602-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07602-0