Abstract
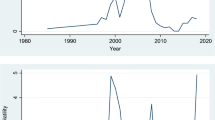
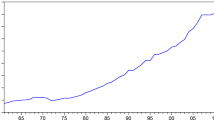
The objective of this research is to examine the effects of stock market on air pollution in Malaysia during the period 1980–2017. To realize this aim, a nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) model is constructed. The short results in general revealed that the increase in stock markets will increase CO2 emissions and its significance increases in the long run. Moreover, the decline in stock market will reduce Malaysia’s CO2 emissions but only in the long run. From the outcomes obtained, a number of policy recommendations were provided for the investigated country.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Ahmad N, Du L, Lu J, Wang J, Li HZ, Hashmi MZ (2017) Modelling the CO2 emissions and economic growth in Croatia: is there any environmental Kuznets curve? Energy 123:164–172
Alam MM, Murad MW, Noman AHM, Ozturk I (2016) Relationships among carbon emissions, economic growth, energy consumption and population growth: testing Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis for Brazil, China, India and Indonesia. Ecol Indic 70:466–479
Ali G, Ashraf A, Bashir MK, Cui S (2017) Exploring Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) in relation to green revolution: a case study of Pakistan. Environ Sci Policy 77:166–171
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2015) The effect of energy consumption, urbanization, trade openness, industrial output, and the political stability on the environmental degradation in the MENA (Middle East and North African) region. Energy 84:3382–3389
Balaguer J, Cantavella M (2018) The role of education in the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Evidence from Australian data. Energy Econ 70:289–296
Dietz T, Rosa EA (1994) Rethinking the environmental impacts of population, affluence and technology. Hum Ecol Rev 1:277–300
Ehrlich, P. R. & Holdren, J. P. (1071). Impact of population growth. Science 171, 1212–1217
Harvey DI, Leybourne SJ, Xiao B (2008) A powerful test for linearity when the order of integration is unknown. Studies in Nonlinear Dynamics & Econometrics 12(3)
He X, Liu Y (2018) The public environmental awareness and the air pollution effect in Chinese stock market. J Clean Prod 185:446–454
Kapetanios G, Shin Y, Snell A (2003) Testing for a unit root in the nonlinear STAR framework. J Econ 112:359–379
Kruse R (2011) A new unit root test against ESTAR based on a class of modified statistics. Stat Pap 52(1):71–85
Levy, T. & Yagil (2011) Air pollution and stock returns in the US. Journal of Economic Psychology 32, 374–383
Malaysia Energy Information Hub (2019) Energy Commission. Retrieved from https://meih.st.gov.my/. Acessed 20 June 2019
OECD (2018) OECD Equity Market Review of Asia 2018 www.oecd.org/corporate/OECD-Asia-Equity-Market-Review-2018.pdf Accessed 5 June 2019
Özokcu S, Özdemir Ö (2017) Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renew Sust Energ Rev 72:639–647
Paramati SR, Ummalla M, Apergis N (2016) The effect of foreign direct investment and stock market growth on clean energy use across a panel of emerging market economies. Energy Econ 56:29–41
Paramati SR, Mo D, Gupta R (2017) The effects of stock market growth and renewable energy use on CO2 emissions: evidence from G20 countries. Energy Econ 66:360–371
Paramati SR, Alam MS, Apergis N (2018) The role of stock markets on environmental degradation: a comparative study of developed and emerging market economies across the globe. Emerg Mark Rev 35:19–30
Pesaran, M. H., Shin, Y., & Smith, R. J. (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. Journal of applied econometrics 16(3), 289–326
Ramiah V, Martin B, Moosa I (2013) How does the stock market react to the announcement of green policies? J Bank Financ 37:1747–1758
Rodríguez M, Pena-Boquete Y, Pardo-Fernández JC (2016) Revisiting Environmental Kuznets Curves through the energy price lens. Energy Policy 95:32–41
Shin Y, Yu B, Greenwood-Nimmo M (2011) Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multiplier in a nonlinear ARDL framework. Mimeo, New York
Sim, Y.L., Putuhena, F.J. (2015). Green building technology initiatives to achieve construction quality and environmental sustainability in the construction industry in Malaysia. Manag Environ Qual Int J 26, 233–249.
World Bank (2019) World development indicators 2019. World Bank Publications
Wu X, Chen S, Guo J, Gao G (2018) Effect of air pollution on the stock yield of heavy pollution enterprises in China’s key control cities. J Clean Prod 170:399–406
Xu T (2018) Investigating Environmental Kuznets Curve in China–aggregation bias and policy implications. Energy Policy 114:315–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-mulali, U., Solarin, S.A. & Ozturk, I. Examining the asymmetric effects of stock markets on Malaysia’s air pollution: a nonlinear ARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 34977–34982 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06710-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06710-w