Abstract
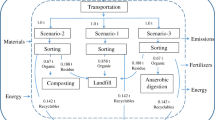
Municipal wastewater treatment facilities produce a lot of sludge which is concentrated with different pollutants. The sustainable design of the sludge disposal alternatives is of crucial importance for touristic cities like Mashhad in Iran. Increasing sludge generation and its accumulation in the city and more stringent legislations highlight the challenge of sludge disposal, recently. This study compares different alternatives to reach maximum possible environmental benefits as well as the most cost-effective technologies. In this study, life cycle analysis (LCA) assesses different scenarios for disposal of sewage sludge which is aerobically treated and dewatered for two real case studies. Alteymore and KhinArab are wastewater treatment units in the city. The scenarios include incineration, composting, and landfilling alternatives. The incineration and landfill scenarios are the least interesting solutions according to different life cycle impact categories. The heavy metals’ emission to the soil worsens their impacts. Also, lifecycle cost analysis reveals that composting scenario is more cost-saving than others. However, main disadvantage of the composting scenario is its contribution in freshwater eutrophication. To move towards sustainability, the composting scenario is here determined as the best scenario for sludge disposal in Mashhad.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This treatment plant is also named Al-Teymour treatment plant.
References
Ashwekar, P., Y. Jiang and H. Pan (2017). Feasibility study of energy recovery by incineration - a case study of the triangle wastewater treatment plant. Master of Science, Duke University
Behboodi, R. and S. MoradiKia (2014). Compost, research unit, deputy of urban planning and development, waste management organization of Tehran Municipality
Bonton A, Bouchard C, Barbeau B, Jedrzejak S (2012) Comparative life cycle assessment of water treatment plants. Desalination 284(Supplement C):42–54
Bryan-Brown, M and J Gage (n.d.) Lessons learned in aerated static pile (ASP) composting. GREEN MOUNTAIN TECHNOLOGIES, BAINBRIDGE ISLAND, WA
Buonocore E, Mellino S, De Angelis G, Liu G, Ulgiati S (2016) Life cycle assessment indicators of urban wastewater and sewage sludge treatment. Ecol Indic
Chen C, Habert G, Bouzidi Y, Jullien A (2010) Environmental impact of cement production: detail of the different processes and cement plant variability evaluation. J Clean Prod 18(5):478–485
Corominas L, Foley J, Guest JS, Hospido A, Larsen HF, Morera S, Shaw A (2013) Life cycle assessment applied to wastewater treatment: state of the art. Water Res 47(15):5480–5492
Ekhbari, M. and M. Alavi-Moghaddam (2004). Investigation of EPA standards for wastewater treatment plant sewage application in irrigation. 11th Conference of Iran’s civil engineering students. Iran
Gallego A, Hospido A, Moreira MT, Feijoo G (2008) Environmental performance of wastewater treatment plants for small populations. Resour Conserv Recycl 52(6):931–940
Gallego-Schmid A, Tarpani RRZ (2019) Life cycle assessment of wastewater treatment in developing countries: A review. Water Res 153:63–79
Godin, D, C Bouchard and PA Vanrolleghem (2011) LCA in wastewater treatment - applicability and limitations for constructed wetland systems: using vertical Reed Bed Filters. IWA Symposium on Systems Analysis and Integrated Assessment
Grönlund SE (2018) Indicators and methods to assess sustainability of wastewater sludge management in the perspective of two systems ecology models. Ecol Indic
Hiroko, Y (2014) Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment and its use on land. PHD, Technical University of Denmark
Hong J, Hong J, Otaki M, Jolliet O (2009) Environmental and economic life cycle assessment for sewage sludge treatment processes in Japan. Waste Manag 29(2):696–703
Hospido A, Moreira MT, Fernández-Couto M, Feijoo G (2004) Environmental performance of a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Int J Life Cycle Assess 9(4):261
Houillon G, Jolliet O (2005) Life cycle assessment of processes for the treatment of wastewater urban sludge: energy and global warming analysis. J Clean Prod 13(3):287–299
International Reference Life Cycle Data System (ILCD) handbook (2010) General guide for life cycle assessment - detailed guidance. Luxembourg. Publication office of the European Union, European commission - Joint Research center - Institute for Environmental and Sustainability
Iran, SCO (2016) Population and Housing Census. Presidency of I.R.I, Plan and Budget Organization
ISO (2006) Environmental management -- life cycle assessment -- Principles and framework
IWA BS (2007) Biological wastewater treatment series. LONDON, NEW YORK
Kacprzak M, Neczaj E, Fijałkowski K, Grobelak A, Grosser A, Worwag M, Rorat A, Brattebo H, Almås Å, Singh BR (2017) Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environ Res 156(Supplement C):39–46
Kelessidis A, Stasinakis AS (2012) Comparative study of the methods used for treatment and final disposal of sewage sludge in European countries. Waste Manag 32(6):1186–1195
Lombardi L, Nocita C, Bettazzi E, Fibbi D, Carnevale E (2017) Environmental comparison of alternative treatments for sewage sludge: an Italian case study. Waste Manag
McNamara, G. (2018). Economic and environmental cost assessment of wastewater treatment systems, a life cycle perspective. Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Dublin City University
Morera S, Corominas L, Rigola M, Poch M, Comas J (2017) Using a detailed inventory of a large wastewater treatment plant to estimate the relative importance of construction to the overall environmental impacts. Water Res, Supplement C 122:614–623
Nocita C, Lombardi L, Bettazzi E, Fibbi D, Carnevale E (2016) Environmental comparison of alternative scenarios for sewage sludge management. Sixth International Symposium on Energy from Biomass and Waste. CISA, Italy
Pan T, Zhu X-D, Ye Y-P (2011) Estimate of life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions from a vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland and conventional wastewater treatment plants: a case study in China. Ecol Eng 37(2):248–254
Piao W, Kim Y, Kim H, Kim M, Kim C (2016) Life cycle assessment and economic efficiency analysis of integrated management of wastewater treatment plants. J Clean Prod 113:325–337
Pradel, M, AL Reverdy, M Richard and L Chabat (2014) Environmental impacts of sewage sludge treatment and disposal routes: a life cycle assessment perspective. 4th European Conference on Sludge Management, Izmir, Turkey
Pradel, M., L. Aissani, J. Villot, J.-C. Baudez and V. Laforest (2016). From waste to added value product: towards a paradigm shift in life cycle assessment applied to wastewater sludge – a review
PRé, M. Goedkoop, M. Oele, J. Leijting, T. Ponsioen and E. Meijer (2013). Introduction to LCA with SimaPro. C. C. A.-N.-S. Alike and N. License. San Francisco, California
Renou S, Thomas JS, Aoustin E, Pons MN (2008) Influence of impact assessment methods in wastewater treatment LCA. J Clean Prod 16(10):1098–1105
Salado, R, D Vencovsky, E Daly, T Zamparutti and R Palfrey (2009) Environmental, economic and social impacts of the use of sewage sludge on land. Final Report, Part II: Report on Options and Impacts. European Commission, DG Environment, RPAMilieu LtdWRc
Sendoh Akwo, N (2008) A life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment options. Maester, Aalborg University
Silva C, Saldanha Matos J, Rosa MJ (2016) Performance indicators and indices of sludge management in urban wastewater treatment plants. J Environ Manag 184(Pt 2):307–317
Singh KP, Mohan D, Sinha S, Dalwani R (2004) Impact assessment of treated/untreated wastewater toxicants discharged by sewage treatment plants on health, agricultural, and environmental quality in the wastewater disposal area. Chemosphere 55(2):227–255
Suh Y-J, Rousseaux P (2002) An LCA of alternative wastewater sludge treatment scenarios. Resour Conserv Recycl 35(3):191–200
Tarantini, M, P Buttol and L Maiorino (2007) An environmental LCA of alternative scenarios of urban sewage sludge treatment and disposal
Trajkovska-Trpevska, M and S Dodeva (2017) Environmental impact assessment of the waste water treatment plant for city of Skopje
O. Williams, T., P. E. BCEE and R. Virginia (2009). The next generation of aerated static pile biosolids composting facilities. US Composting Council 17th Annual Conference and Tradeshow. Houstion, Texas
Yoshida H, Christensen TH, Scheutz C (2013) Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge management: a review. Waste Manag Res 31(11):1083–1101
Yoshida H, ten Hoeve M, Christensen TH, Bruun S, Jensen LS, Scheutz C (2018) Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge management options including long-term impacts after land application. Journal of Cleaner Production 174(Supplement C):538–547
Young, M (2014) A life cycle assessment of alternative wastewater treatment processes at forward operation bases (FOBs). ARIZONA ATATE UNIVERSITY, Center for Earth Systemes Engineering and Management
Zhao Y, Lu W, Damgaard A, Zhang Y, Wang H (2015) Assessment of co-composting of sludge and woodchips in the perspective of environmental impacts (EASETECH). Waste Manag 42:55–60
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the anonymous reviewers for their useful comments that help them a lot to improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Loubet
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rostami, F., Tafazzoli, S.M., Aminian, S.T. et al. Comparative assessment of sewage sludge disposal alternatives in Mashhad: a life cycle perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 315–333 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06709-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06709-3