Abstract
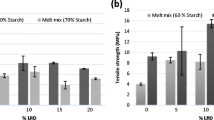
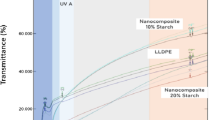
Starch was transformed to hydrophobic starch phthalate (contact angle 109°) in order to achieve a good dispersion in LDPE matrix. Nanosilica derived from rice husk after aminopropyltrimethoxysilane functionalization was also incorporated into the blend as property-enhancing filler. The produced crystalline starch phthalate had a lower particle size of 9.87 μm and a higher surface area of 2.87 m2/g compared to starch (40.28 μm, 1.91 m2/g). The potential quality modification of starch phthalate as a substitute for starch towards the production of a perfect biodegradable blend was quantified in terms of mechanical (tensile, tear, stiffness), optical (haze, transmittance), and biodegradation assessments. Interfacial adhesion between LDPE and starch phthalate was well justified by the morphology and enhancement in mechanical properties like tensile and tear strength from 8.87 to 12.67 MPa and 96.57 to 187.10 N/mm for 30% of starch or starch phthalate in LDPE matrix, respectively. Starch phthalate compared to starch blended films showed a higher biodegradation rate of 14.8 and 13.5% in garden soil and vegetable waste respectively in 1 year (at 30% biofiller), with a good first-order kinetics fit of the weight loss data having a higher degradation rate constant at higher content of biofiller in the blend.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajili SH, Ebrahimi NG, Khorasani MT (2003) Study on thermoplastic polyurethane/polypropylene (TPU/PP) blend as a blood bag material. J Appl Polym Sci 89(9):2496–2501
Anjana R, George KE (2012) Reinforcing effect of nano kaolin clay on PP/HDPE blends. Int J Eng Res Appl 2(4):868–872
Araujo LMG, Morales AR (2018) Compatibilization of recycled polypropylene and recycled poly (ethylene terephthalate) blends with SEBS-g-MA. Polímeros 27(8):84–91
Arvanitoyannis I, Biliaderis CG, Ogawa H, Kawasaki N (1998) Biodegradable films made from low-density polyethylene (LDPE), rice starch and potato starch for food packaging applications: part 1. Carbohydr Polym 36(2–3):89–104
Athauda TJ, Williams W, Roberts KP, Ozer RR (2013) On the surface roughness and hydrophobicity of dual-size double-layer silica nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 48(18):6115–6120
Biliaderis CG (1998) Structures and phase transitions of starch polymers. In: Walter RH (ed) Polysaccharide association structures in food. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 57–168
Chandra R, Rustgi R (1997) Biodegradation of maleated linear low-density polyethylene and starch blends. Polym Degrad Stab 56(2):185–202
Chauhan K, Priya V, Singh P, Chauhan GS, Kumari S, Singhal RK (2015) A green and highly efficient sulfur functionalization of starch. RSC Adv 5(64):51762–51772
Chen Y, Stark NM, Cai Z, Frihart CR, Lorenz LF, Ibach RE (2014) Chemical modification of kraft lignin: effect on chemical and thermal properties. BioResources 9(3):5488–5500
Datta D, Halder G (2019a) Effect of rice husk derived nanosilica on the structure, properties and biodegradability of corn-starch/LDPE composites. J Polym Environ 27(4):710–727
Datta D, Halder G (2019b) Effect of media on degradability, physico-mechanical and optical properties of synthesized polyolefinic and PLA film in comparison with casted potato/corn starch biofilm. Process Saf Environ Prot 124:39–62
Datta D, Samanta S, Halder G (2019) Surface functionalization of extracted nanosilica from rice husk for augmenting mechanical and optical properties of synthesized LDPE-starch biodegradable film. Polym Test 77:105878–105897
Demirkan ES, Mikami B, Adachi M, Higasa T, Utsumi S (2005) α-Amylase from B. amyloliquefaciens: purification, characterization, raw starch degradation and expression in E. coli. Process Biochem 40(8):2629–2636
Dilfi KFA (2011) Linear low density polyethylene biodegradability using bacteria from marine benthic environment and photodegradability using ultraviolet light. Ph.D. Thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Kerala
Dominic CM, Begum PMS, Joseph R, Jose AR (2014) Rice husk silica-efficient bio filler in high density polyethylene. Int J Adv Sci Tech Res 2(4):561–569
Ek S, Root A, Peussa M, Niinisto L (2001) Determination of the hydroxyl group content in silica by thermogravimetry and a comparison with 1H MAS NMR results. Thermochim Acta 379(1–2):201–212
Gajendiran A, Krishnamoorthy S, Abraham J (2016) Microbial degradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) by Aspergillus clavatus strain JASK1 isolated from landfill soil. Biotechnology 6(1):52–61
Ghani SA, Feng YZ, Ismail H (2012) Properties of tyre dust-filled low density polyethylene composites: the effect of phthalic anhydride. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 51(4):358–363
Gharehbash N, Shakeri A (2015) Preparation and thermal and physical properties of nano-silica modified and unmodified. Orient J Chem 31:207–212
Golebiewski J, Galeski A (2007) Thermal stability of nanoclay polypropylene composites by simultaneous DSC and TGA. Compos Sci Technol 67(15–16):3442–3447
Guzmán M, Giraldo D, Murillo E (2017) Hyperbranched polyester polyol plasticized tapioca starch/low density polyethylene blends. Polímeros 27(1):1–7
Han JA, Lim ST (2004) Structural changes in corn starches during alkaline dissolution by vortexing. Carbohydr Polym 55(2):193–199
Jackson DS (1993) Starch: functional properties. In: Macrae R, Robinson RK, Sadler MJ (eds) Encyclopaedia of food science, food technology, and nutrition. Academic press, London, pp 4377–4381
Jakab E, Faix O, Till F (1997) Thermal decomposition of milled wood lignins studied by thermogravimetry/mass spectrometry. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 40:171–186
Jeang CL, Chen LS, Chen MY, Shiau RJ (2002) Cloning of a gene encoding raw-starch-digesting amylase from a Cytophaga sp. and its expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(7):3651–3654
Kadhim LF, Kadhim ZF (2017) Studying the properties of PP/LDPE polymer blend. J Univ Babylon 25(1):193–201
Lazghab M, Saleh K, Pezron I, Guigon P, Komunjer L (2005) Wettability assessment of finely divided solids. Powder Technol 157(1–3):79–91
Lu X, Luo Z, Fu X, Xiao Z (2013) Two-step method of enzymatic synthesis of starch laurate in ionic liquids. J Agric Food Chem 61(41):9882–9891
Ma X, Yu J (2004) Studies on the properties of formamide plasticized-thermoplastic starch. Acta Polym Sin (2):240–245
Mathew S, Abraham TE (2007) Physico-chemical characterization of starch ferulates of different degrees of substitution. Food Chem 105(2):579–589
Musa MB, Yoo MJ, Kang TJ, Kolawole EG, Ishiaku US, Whang DJ (2013) Characterization and thermochemical properties of thermoplastic potato starch. J Eng Technol 2(4):9–16
Nielsen LE (1974) Mechanical properties of polymers and composites, chapter 7(2). Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 255–301
Obuz E, Herald TJ, Rausch K (2001) Characterization of extruded plant protein and petroleum based packaging sheets. Cereal Chem 78(1):97–100
Omemu AM, Akpan I, Bankole MO, Teniola OD (2005) Hydrolysis of raw tuber starches by amylase of Aspergillus niger AM07 isolated from the soil. Afr J Biotechnol 4:19–25
Rahmat AR, Rahman WAWA, Sin LT, Yussuf AA (2009) Approaches to improve compatibility of starch filled polymer system: a review. Mater Sci Eng C 29(8):2370–2377
Raj B (2004) Low density polyethylene/starch blend films for food packaging applications. Adv Polym Technol 23(1):32–45
Rosa DS, Guedes CGF, Carvalho CL (2007) Processing and thermal, mechanical and morphological characterization of post-consumer polyolefins/thermoplastic starch blends. J Mater Sci 42(2):551–557
Sabetzadeh M, Bagheri R, Masoomi M (2014) Effect of organomodified montmorillonite concentration on tensile and flow properties of low-density polyethylene–thermoplastic corn starch blends. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 27(8):1022–1036
Sagar AD, Merrill EW (1995) Properties of fatty-acid esters of starch. J Appl Polym Sci 58(9):1647–1656
Sapkota J, Natterodt JC, Shirole A, Foster EJ, Weder C (2017) Fabrication and properties of polyethylene/cellulose nanocrystal composites. Macromol Mater Eng C 29(8):2370–2377
Scott G, Gilead D (1995) Degradable polymers-principles and applications. Chapman and Hall, London, UK
Sekharan RV, Abraham BT, Thachil ET (2012) Utilization of waste expanded polystyrene: blends with silica-filled natural rubber. Mater Des 40:221–228
Sen SK, Raut S (2015) Microbial degradation of low density polyethylene (LDPE): a review. J Environ Chem Eng 3(1):462–473
Spathis G, Niaounakis M, Kontou E, Apekis L, Pissis P, Christodoulides C (1994) Morphological changes in segmented polyurethane elastomers by varying the NCO/OH ratio. J Appl Polym Sci 54(7):831–842
Thakore IM, Desai S, Sarawade BD, Devi S (2001) Studies on biodegradability, morphology and thermo-mechanical properties of LDPE/modified starch blends. Eur Polym J 3:151–160
Tiptipakorn S, Punuch W, Okhawilai M, Rimdusit S (2015) Property enhancement of polybenzoxazine modified with monoanhydrides and dianhydrides. J Polym Res 22:132–141
Valk V, Eeuwema W, Sarian FD, van der Kaaij RM, Dijkhuizen L (2015) Degradation of granular starch by the bacterium Microbacteriumaurum strain B8. A involves a modular α-amylase enzyme system with FNIII and CBM25 domains. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(19):6610–6620
Vinhas GM, Lima SMD, Santos LA, Lima MAGDA, Almeida YMBD (2007) Evaluation of the types of starch for preparation of LDPE/starch blends. Braz Arch Biol Technol 50(3):361–370
Wijbenga DJ, Beldman G, Veen A, Binnema DJ (1991) Production of native-starch-degrading enzymes by a Bacillus firmus/lentus strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35(2):180–184
Zarski A, Ptak S, Siemion P, Kapusniak J (2016) Esterification of potato starch by a biocatalysed reaction in an ionic liquid. Carbohydr Polym 137:657–663
Zuo YF, Gu J, Qiao Z, Tan H, Cao J, Zhang Y (2015) Effects of dry method esterification of starch on the degradation characteristics of starch/polylactic acid composites. Int J Biol Macromol 72:391–402
Acknowledgments
The technical support from the technicians of Central Institute of Plastic Engineering & Technology - Institute of Plastic Technology, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, is gratefully appreciated.
Funding
This study is financially supported by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of West Bengal, India, through research project ST/P/S&T/IG-9/2016 (File no. 680(Sanc.)/ST/P/S&T/15G-3/2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
•Starch was esterified using phthalic anhydride to enhance its compatibility with LDPE.
•Different composition of starch phthalate/LDPE/modified nanosilica films was produced.
•Interfacial adhesion of the biofiller with LDPE was proved by chemical reactions.
•Optimum modified biofiller (30%) films have tensile strength 12.67 MPa and transmittance 89.3%.
•Biodegradability and biodegradation kinetics was tested under soil and vegetable waste.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Datta, D., Halder, G. Blending of phthalated starch and surface functionalized rice husk extracted nanosilica with LDPE towards developing an efficient packaging substitute. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 1533–1557 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06430-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06430-1