Abstract
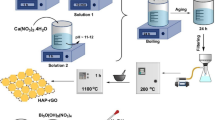
To improve the mass transfer efficiency of poly(m-phenylenediamine) for the effective removal of hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) from aqueous solution, a facile and one-step method to prepare two-dimensional poly(m-phenylenediamine) functionalized reduction graphene oxide (rGO-PmPD) by dilution polymerization is developed. The structure and morphology of rGO-PmPD as well as rGO and PmPD were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Raman, and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The preparation mechanism, adsorption performance, and mechanism of rGO-PmPD were then investigated in detail. The obtained rGO-PmPD exhibited thin 2D nanosheet morphology with much improved specific surface area and pore volume (18 and 25 times higher than that of PmPD, respectively). The Cr (VI) adsorption of rGO-PmPD was fitted well with the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm model, and the maximum adsorption capacity of rGO-PmPD reached 588.26 mg g−1, higher than that of PmPD (400 mg g−1) and rGO (156.25 mg g−1). Moreover, the regeneration efficiency of the rGO-PmPD nanosheet is also promising that the adsorption performance after five times of adsorption-desorption cycles still maintains more than 530 mg g−1. The removal mechanism involved reduction coupled with adsorption and electrostatic interaction between rGO-PmPD and Cr (VI), and ~ 65% of Cr (VI) removal was attributed to reduction and ~ 35% was ascribed to adsorption and electrostatic interaction. This study thus provides a simple and effective route to achieve high accessible surface area of adsorbent materials with enhanced mass transfer efficiency and thereafter improved adsorption performance.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansar MO, Kumar R, Ansari SA, Ansari SP, Barakat MA, Alshahrie A, Cho MH (2017) Anion selective pTSA doped polyaniline@graphene oxide-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite for Cr (VI) and Congo red adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 496:407–415
Celebi M, Yurderi M, Bulut A, Kaya M, Zahmakiran M (2016) Palladium nanoparticles supported on amine-functionalized SiO2 for the catalytic hexavalent chromium reduction. Appl Catal B Environ 180:53–64
Chai L, Wang T, Zhang L, Wang H, Yang W, Dai S, Meng Y, Li X (2015) A Cu–m-phenylenediamine complex induced route to fabricate poly(m-phenylenediamine)/reduced graphene oxide hydrogel and its adsorption application. Carbon 81:748–757
Chen B, Zhao X, Liu Y, Xu B, Pan X (2015) Highly stable and covalently functionalized magnetic nanoparticles by polyethyleneimine for Cr (VI) adsorption in aqueous solution. RSC Adv 5:1398–1405
Chen C, Zhu K, Chen K, Alsaedi A, Hayat T (2018) Synthesis of Ag nanoparticles decoration on magnetic carbonized polydopamine nanospheres for effective catalytic reduction of Cr (VI). J Colloid Interface Sci 526:1–8
Chen H, Dou J, Xu H (2017) Removal of Cr (VI) ions by sewage sludge compost biomass from aqueous solutions: reduction to Cr (III) and biosorption. Appl Surf Sci 425:728–735
Chen X, Yi Z, Lei J, Yi H, Yao W, Zhu W, Duan T (2016) Preparation and Perfomance of an aging-resistant nanocomposite film of binary natural polymer–graphene oxide. ACS Omega 1:1173–1181
Chigondo M, Paumo HK, Bhaumik M, Pillay K, Maity A (2019) Magnetic arginine-functionalized polypyrrole with improved and selective chromium (VI) ions removal from water. J Mol Liq 275:778–791
Choppala G, Bolan N, Kunhikrishnan A, Skinner W, Seshadri B (2015) Concomitant reduction and immobilization of chromium in relation to its bioavailability in soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:8969–8978
CMarcano D, VKosynkin D, MBerlin J, Sinitskii A, Sun Z, Slesarev A, BAlemany L, Wei L, MTour J (2010) Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4:4806–4814
Di Natale F, Erto A, Lancia A, Musmarra D (2015) Equilibrium and dynamic study on hexavalent chromium adsorption onto activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 281:47–55
Duan W, Chen G, Chen C, Sanghvi R, Iddya A, Walker S, Liu H, Ronen A, Jassby D (2017) Electrochemical removal of hexavalent chromium using electrically conducting carbon nanotube/polymer composite ultrafiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 531:160–171
El-Mehalmey WA, Ibrahim AH, Abugable AA, Hassan MH, Haikal RR, Karakalos SG, Zakid O, Alkordi MH (2018) Metal-organic framework@silica as a stationary phase sorbent for rapid and cost-effective removal of hexavalent chromium. J Mater Chem A 6:2742–2751
Fan S, Wang Y, Li Y, Tang J, Wang Z, Tang J, Li X, Hu K (2017) Facile synthesis of tea waste/Fe3O4 nanoparticle composite for hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 7:7576–7590
Fang W, Jiang X, Luo H, Geng J (2018) Synthesis of graphene/SiO2@polypyrrole nanocomposites and their application for Cr (VI) removal in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 197:594–602
Farokhi M, Parvareh A, Moraveji MK (2018) Performance of ceria/iron oxide nano-composites based on chitosan as an effective adsorbent for removal of Cr (VI) and Co (II) ions from aqueous systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:27059–27073
Gao Y, Chen C, Tan X, Xu H, Zhu K (2016) Polyaniline-modified 3D-flower-like molybdenum disulfide composite for efficient adsorption/photocatalytic reduction of Cr (VI). J Colloid Interface Sci 476:62–70
Gong X, Liu G, Li Y, Yu D, Teoh W (2016) Functionalized-graphene composites: fabrication and applications in sustainable energy and environment. Chem Mater 28:8082–8118
Huang J, Cao Y, Shao Q, Peng X, Guo Z (2017) Magnetic Nanocarbon adsorbents with enhanced hexavalent chromium removal: morphology dependence of Fibrillar vs particulate structures. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:10689–10701
Huang M, Lu H, Li X (2007) Efficient multicyclic sorption and desorption of lead ions on facilely prepared poly(m-phenylenediamine) particles with extremely strong chemoresistance. J Colloid Interface Sci 313:72–79
Jin L, Huang L, Ren L, He Y, Tang J, Wang S, Yang W, Wang H, Chai L (2019) Preparation of stable and high-efficient poly(m-phenylenediamine)/reduced graphene oxide composites for hexavalent chromium removal. J Mater Sci 54:383–395
Kwak HW, Lee KH (2018) Polyethylenimine-functionalized silk sericin beads for high-performance remediation of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 207:507–516
Li L, Feng X, Han R, Zang S, Yang G (2017) Cr (VI) removal via anion exchange on a silver-triazolate MOF. J Hazard Mater 321:622–628
Li X, Huang M, Duan W, Yang Y (2002) Novel multifunctional polymers from aromatic diamines by oxidative polymerizations. Chem Rev 102:2925–3030
Li X, Ma X, Sun J, Huang M (2009) Powerful reactive sorption of silver(I) and mercury (II) onto poly(o-phenylenediamine) microparticles. Langmuir 25:1675–1684
Liang Q, Luo H, Geng J, Chen J (2018) Facile one-pot preparation of nitrogen-doped ultra-light graphene oxide aerogel and its prominent adsorption performance of Cr (VI). Chem Eng J 338:62–71
Liu H, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Zou K, Wu R, Xia K, Xie S (2019) Synthesis of polyethylenimine/graphene oxide for the adsorption of U (VI) from aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 471:88–95
Lu X, Li L, Song B, Moon K-s HN, Liao G, Shi T, Wong C (2015) Mechanistic investigation of the graphene functionalization using p-phenylenediamine and its application for supercapacitors. Nano Energy 17:160–170
Lyu H, Tang J, Huang Y, Gai L, Zeng E, Liber K, Gong Y (2017) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite. Chem Eng J 322:516–524
Lyu L, Yu G, Zhang L, Hu C, Sun Y (2018) 4-Phenoxyphenol-functionalized reduced graphene oxide nanosheets: a metal-free Fenton-like catalyst for pollutant destruction. Environ Sci Technol 52:747–756
Olea-Mejía O, Cabral-Prieto A, Salcedo-Castillo U, López-Tellez G, Olea-Cardoso O, López-Castañares R (2017) Orange peel + nanostructured zero-valent-iron composite for the removal of hexavalent chromium in water. Appl Surf Sci 423:170–175
Pan C, Troyer LD, Liao P, Catalano JG, Li W, Giammar DE (2017) Effect of humic acid on the removal of chromium (VI) and the production of solids in Iron electrocoagulation. Environ Sci Technol 51:6308–6318
Qiu B, Xu C, Sun D, Wei H, Zhang X, Guo J, Wang Q, Rutman D, Guo Z, Wei S (2014) Polyaniline coating on carbon fiber fabrics for improved hexavalent chromium removal. RSC Adv 4:29855–29865
Qiu B, Xu C, Sun D, Wang Q, Gu H, Zhang X, Weeks BL, Hopper J, Ho TC, Guo Z, Wei S (2015) Polyaniline coating with various substrates for hexavalent chromium removal. Appl Surf Sci 334:7–14
Qiu B, Xing M, Zhang J (2018) Recent advances in three-dimensional graphene based materials for catalysis applications. Chem Soc Rev 47:2165–2216
Rapti S, Pournara A, Sarma D, Papadas IT, Armatas GS, Tsipis AC, Lazarides T, Kanatzidis MG, Manos MJ (2016) Selective capture of hexavalent chromium from an anion-exchange column of metal organic resin-alginic acid composite. Chem Sci 7:2427–2436
Rapti S, Sarma D, Diamantis SA, Skliri E, Armatas GS, Tsipis AC, Hassan YS, Alkordi M, Malliakas CD, Kanatzidis MG, Lazarides T, Plakatouras JC, Manos MJ (2017) All in one porous material: exceptional sorption and selective sensing of hexavalent chromium by using a Zr4+ MOF. J Mater Chem A 5:14707–14719
Shen Y, Chen B (2015) Sulfonated graphene nanosheets as a superb adsorbent for various environmental pollutants in water. Environ Sci Technol 49:7364–7372
Song B, Choi JI, Zhu Y, Geng Z, Zhang L, Lin Z, C-c T, K-s M, C-p W (2016) Molecular level study of graphene networks functionalized with Phenylenediamine monomers for supercapacitor electrodes. Chem Mater 28:9110–9121
Vilela PB, Dalalibera A, Duminelli EC, Becegato VA, Paulino AT (2018) Adsorption and removal of chromium (VI) contained in aqueous solutions using a chitosan-based hydrogel. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3372-5
Wang C, Wang S, Tang L, He Y, Gan L, Li J, Du H, Li B, Lin Z, Kang F (2016) A robust strategy for crafting monodisperse Li4Ti5O12 nanospheres as superior rate anode for lithium ion batteries. Nano Energy 21:133–144
Wang H, Li X, Chai L, Zhang L (2015a) Nano-functionalized filamentous fungus hyphae with fast reversible macroscopic assembly & disassembly features. Chem Commun 51:8524–8527
Wang H, Yuan X, Wu Y, Chen X, Leng L, Wang H, Li H, Zeng G (2015b) Facile synthesis of polypyrrole decorated reduced graphene oxide–Fe3O4 magnetic composites and its application for the Cr (VI) removal. Chem Eng J 262:597–606
Wang J, Zhang K, Zhao L (2014) Sono-assisted synthesis of nanostructured polyaniline for adsorption of aqueous Cr (VI): effect of protonic acids. Chem Eng J 239:123–131
Xie A, Ji L, Luo S, Wang Z, Xu Y, Kong Y (2014) Synthesis, characterization of poly(m-phenylenediamine)/palygorskite and its unusual and reactive adsorbability to chromium (VI). New J Chem 38:777–783
Xiong T, Yuan X, Wang H, Wu Z, Jiang L, Leng L, Xi K, Cao X, Zeng G (2019) Highly efficient removal of diclofenac sodium from medical wastewater by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide-poly(m-phenylenediamine) composite. Chem Eng J 366:83–91
Xu J, Wang K, Zu S, Han B, Wei Z (2010) Hierarchical nanocomposites of polyaniline nanowire arrays on graphene oxide sheets with synergistic effect for energy storage. ACS Nano 4:5019–5026
Yang W, Tian S, Tang Q, Chai L, Wang H (2017) Fungus hyphae-supported alumina: an efficient and reclaimable adsorbent for fluoride removal from water. J Colloid Interface Sci 496:496–504
Yang Z, Ren L, Jin L, Huang L, He Y, Tang J, Yang W, Wang H (2018) In-situ functionalization of poly(m-phenylenediamine) nanoparticles on bacterial cellulose for chromium removal. Chem Eng J 344:441–452
Yu W, Chai L, Zhang L, Wang H (2013a) Synthesis of poly (m-phenylenediamine) with improved properties and superior prospect for Cr (VI) removal. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 23:3490–3498
Yu W, Zhang L, Wang H, Chai L (2013b) Adsorption of Cr (VI) using synthetic poly(m-phenylenediamine). J Hazard Mater 260:789–795
Zhang J, Chen S, Zhang H, Wang X (2017) Removal behaviors and mechanisms of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by cephalosporin residue and derived chars. Bioresour Technol 238:484–491
Zhang L, Chai L, Liu J, Wang H, Yu W, Sang P (2011) pH manipulation: a facile method for lowering oxidation state and keeping good yield of poly(m-phenylenediamine) and its powerful Ag+ adsorption ability. Langmuir 27:13729–13738
Zhang L, Wang T, Wang H, Meng Y, Yu W, Chai L (2013) Graphene@poly(m-phenylenediamine) hydrogel fabricated by a facile post-synthesis assembly strategy. Chem Commun 49:9974–9976
Zhang L, Li X, Wang M, He Y, Chai L, Huang J, Wang H, Wu X, Lai Y (2016) Highly flexible and porous nanoparticle-loaded films for dye removal by graphene oxide-fungus interaction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:34638–34647
Zhang Y, Xu M, Li H, Ge H, Bian Z (2018) The enhanced photoreduction of Cr (VI) to Cr (III) using carbon dots coupled TiO2 mesocrystals. Appl Catal B Environ 226:213–219
Zhou L, Liu Y, Liu S, Yin Y, Zeng G, Tan X, Hu X, Hu X, Jiang L, Ding Y, Liu S, Huang X (2016) Investigation of the adsorption-reduction mechanisms of hexavalent chromium by ramie biochars of different pyrolytic temperatures. Bioresour Technol 218:351–359
Zhu K, Chen C, Xu H, Gao Y, Tan X, Alsaedi A, Hayat T (2017) Cr (VI) reduction and immobilization by core-double-shell structured magnetic polydopamine@zeolitic idazolate frameworks-8 microspheres. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:6795–6802
Zhu K, Chen C, Lu S, Zhang X, Alsaedi A, Hayat T (2019) MOFs-induced encapsulation of ultrafine Ni nanoparticles into 3D N-doped graphene-CNT frameworks as a recyclable catalyst for Cr (VI) reduction with formic acid. Carbon 148:52–63
Acknowledgements
This research is financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC0403003), the key project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (51634010), and Key R&D Program of Hunan Province (2018SK2026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1506 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, L., Chai, L., Ren, L. et al. Enhanced adsorption-coupled reduction of hexavalent chromium by 2D poly(m-phenylenediamine)-functionalized reduction graphene oxide. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 31099–31110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06175-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06175-x