Abstract
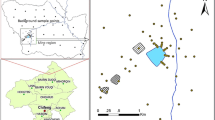
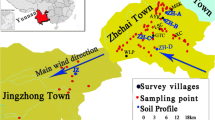
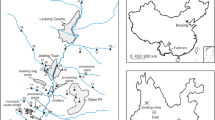
Mining activity is an important source of heavy metals in soil. Understanding the contents and distribution of heavy metals in mineral-waste soil and surrounding environments is important for the rational management of mines and reducing the migration of heavy metals to surrounding environments. We used a non-ferrous metal mine in southern China as a research object. Three types of sampling site (A–C) were established on the mineral-waste soil in the mining area and on nearby farmland (D) and along a river channel (E) outside the mining area: A, newly processed mineral-waste soil; B, steep 6-month-old stack of waste soil; C, gentle slope of 12-month-old waste soil; D, farmland soil within 1 km of the mine; and E, river water and adjacent soil. Soil samples were collected from the 0–10-cm layer at each site type. The contents and spatial distribution of Pb, Zn, and Cd at the sampling sites were analyzed, and the environmental risks were evaluated. The mean Pb, Zn, and Cd contents in the mining area (types A–C) were 2028, 3794, and 14.8 mg kg−1, respectively, which were 8-, 19-, and 49-fold higher than the second-level limits of the Environmental Quality Standard for Soils of China, and the mean contents of Pb, Zn, and Cd for sites D and E were 76.4, 131, and 0.18 mg kg−1 and 147, 194, and 0.95 mg kg−1, respectively, all of which were under the second-level limits. Sites C and E were also used to analyze the spatial distribution of the Pb, Zn, and Cd contents. Geostatistical analysis found that the Pb, Zn, and Cd contents had a clear and similar spatial pattern at site C and generally decreased from north to south. Soil Pb, Zn, and Cd contents at site E generally increased, and water Pb, Zn, and Cd concentrations decreased along the river channel. The soils at site types A–C in the mining area were heavily polluted, with a high potential threat to the surrounding environment, and the farmland and river-bank soils at D and E were free of pollution or were lightly polluted, with low potential ecological risks. This study provides a scientific basis and supporting data for heavy-metal treatment in mining areas.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alary C, Demougeot-Renard H (2010) Factorial kriging analysis as a tool for explaining the complex spatial distribution of metals in sediments. Environ Sci Technol 44:593–599
Bednářová Z, Kalina J, Hájek O, Sáňka M, Komprdová K (2016) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of metals in agricultural soils. Geoderma 284:113–121
Brocca L, Tullo T, Melone F, Moramarco T, Morbidelli R (2012) Catchment scale soil moisture spatial–temporal variability. J Hydrol 422:63–75
Cambardella CA, Moorman TB, Novak JM, Parkin TB, Karlen DL, Turco RF, Konopka AE (1994) Field-scale variability of soil properties in Central Iowa soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1501–1511
Chen T, Liu XM, Li X, Zhao KL, Zhang JB, Xu JM, Shi JC, Dahlgren RA (2009) Heavy metal sources identification and sampling uncertainty analysis in a field-scale vegetable soil of Hangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 157:1003–1010
Ding Q, Cheng G, Wang Y, Zhuang DF (2017) Effects of natural factors on the spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils surrounding mining regions. Sci Total Environ 578:577–585
Duan XW, Zhang GL, Rong L, Fang HY, He DM, Feng DT (2015) Spatial distribution and environmental factors of catchment-scale soil heavy metal contamination in the dry-hot valley of upper Red River in southwestern China. Catena 135:59–69
Fu S, Wei CY (2013) Multivariate and spatial analysis of heavy metal sources and variations in a large old antimony mine, China. J Soils Sediments 13:106–116
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Kim HK, Jang TI, Kim SM, Park SW (2015) Impact of domestic wastewater irrigation on heavy metal contamination in soil and vegetables. Environ Earth Sci 73:2377–2383
Krishna AK, Mohan KR, Murthy NN, Periasamy V, Bipinkumar G, Manohar K, Rao SS (2013) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils around chromite mining areas, Nuggihalli, Karnataka, India. Environ Earth Sci 70:699–708
Li YT, Becquer T, Dai J, Quantin C, Benedetti MF (2009) Ion activity and distribution of heavy metals in acid mine drainage polluted subtropical soils. Environ Pollut 157:1249–1257
Liang J, Feng CT, Zeng GM, Gao X, Zhong MZ, Li XD, Li X, He XY, Fang YL (2017) Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environ Pollut 225:681–690
Liu BL, Ma XW, Ai SW, Zhu SY, Zhang WY, Zhang YM (2016) Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in soils under different land uses in a sewage irrigation region, Northwest China. J Soils Sediments 16:1547–1556
Lu HZ, Cao LX, Liang Y, Yuan JQ, Zhu YY, Wang Y, Gu YL, Zhao QG (2017) Mineral-leaching chemical transport with runoff and sediment from severely eroded rare-earth tailings in southern China. Solid Earth 8:845–855
Ma L, Yang ZG, Li L, Wang L (2016) Source identification and risk assessment of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils of Changsha, a mine-impacted city in southern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:17058–17066
Maas S, Scheifler R, Benslama M, Crini N, Lucot E, Brahmia Z, Benyacoub S, Giraudoux P (2010) Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations in urban, suburban and agricultural soils in a Mediterranean city of Algeria. Environ Pollut 158:2294–2301
Marrugo-Negrete J, Pinedo-Hernández J, Díez S (2017) Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinu River basin, Colombia. Environ Res 154:380–388
National environmental monitoring Centre of China (1990) Background values of soil elements of China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Nielsen DR, Bouma J (1985) Soil spatial variability. Pudoc, Wageningen
Reza SK, Baruah U, Singh SK, Das TH (2015) Geostatistical and multivariate analysis of soil heavy metal contamination near coal mining area, northeastern India. Environ Earth Sci 73:5425–5433
Rodrigues S, Pereira ME, Sarabando L, Lopes L, Cachada A, Duarte A (2006) Spatial distribution of total hg in urban soils from an Atlantic coastal city (Aveiro, Portugal). Sci Total Environ 368:40–46
Rodríguez L, Ruiz E, Alonso-Azcárate RJ (2013) Heavy metal distribution and chemical speciation in tailings and soils around a Pb-Zn mine in Spain. J Environ Manag 90:1106–1116
Shen F, Liao RM, Ali A, Mahar A, Guo D, Li RH, Sun XN, Awasthi MK, Wang Q, Zhang ZQ (2017) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil near a Pb/Zn smelter in Feng County, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:254–262
Trangmar BB, Yost RS, Uehara G (1985) Application of geostatistics to spatial studies of soil properties. Adv Agron 38:45–94
Wang C, Liu SL, Zhao QH, Deng L, Dong SK (2012) Spatial variation and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediments in the Manwan reservoir, Lancang River. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 82:32–39
Wang LF, Yang LY, Kong LH, Li S, Zhu JR, Wang YQ (2014) Spatial distribution, source identification and pollution assessment of metal content in the surface sediments of Nansi Lake, China. J Geochem Explor 140:87–95
Wang YQ, Yang LY, Kong LH, Liu EF, Wang LF, Zhu JR (2015) Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. Catena 125:200–205
Yan WB, Mahmood Q, Peng DL, Fu WJ, Chen T, Wang Y, Song L, Chen JR, Liu D (2015) The spatial distribution pattern of heavy metals and risk assessment of moso bamboo forest soil around lead-zinc mine in southeastern China. Soil Tillage Res 153:120–130
Yin YC, Wang LL, Xiao L, Li YW, Peng H, Qi H, Deng SH (2015) Characteristics and sources of heavy metal pollution in urban suburban and rural domestic waste of Chengdu, China. Chin J Environ Eng 9:392–400
Yu DX, Jia XX, Huang LM, Shao MA, Wang J (2019) Spatial variaiton of soil bulk density in different soil layers in the loess area and simulation. Acta Pedol Sin 56:55–64
Zhang PP, Shao MA, Zhang XC (2015) Scale-dependence of temporal stability of surface-soil moisture in a desert area in northwestern China. J Hydrol 527:1034–1044
Zhu XC, Shao MA, Liang Y, Tian ZY, Wang X, Qu LL (2019) Mesoscale spatial variability of soil-water content in an alpine meadow on the northern Tibetan plateau. Hydrol Process:33 https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13479
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1801801), the Innovation Program of Institute of Soil Science, CAS (ISSASIP1617), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41807019, 41701250), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (Project BK20181109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Severine Le Faucheur
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Cao, L. & Liang, Y. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals inside and outside a typical lead-zinc mine in southeastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 26265–26275 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05724-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05724-8