Abstract
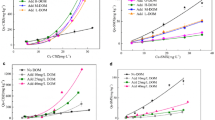
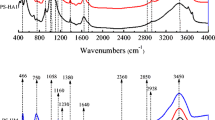
Sedimentary soil was selected as the original sample (SOS). The adsorption fractions were obtained by the removal of dissolved organic matter (SRDOM), removal of minerals (SRM), removal of free fat (SRLF), and removal of nonhydrolyzable organic carbon (SNHC) respectively to investigate the adsorption characteristic of oxytetracycline (OTC) by different fractions of organic matter in sedimentary soil. The adsorption mechanism was investigated by elemental analysis, infrared spectra, and UV-visible spectroscopy. The results showed that the DOM in the sedimentary soil inhibited the adsorption of OTC, but the adsorption of different fractions of organic matter was quite different. The sorption kinetics of OTC were fitted to the pseudo-second-order model and the adsorption capacity of each fraction was: SNHC≈SRDOM > SOS > SRLF> SRM. The adsorption processes of OTC by different fractions were spontaneous. Alkaline pH condition had an effect on the adsorption of four fractions except for SNHC, while neutral and acidic pH affects SOS and SRDOM more obviously, the SNHC fraction was almost free from pH varies. Mechanism analysis showed that the main factors determining the adsorption capacity were the aromaticity and polarity of organic matter fractions. For the organic matter–based fractions (SRM, SRLF, and SNHC), the adsorption coefficient was positively correlated with the aromaticity. Furthermore, for SOS and SRDOM based on inorganic minerals, it was not only related to aromaticity, but also the content and composition of inorganic minerals.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiken GR, Mcknight DM, Wershaw RL, Maccarthy P (1986) Humic substances in soil, sediment, and water: geochemistry, isolation and characterization. Soil Sci 142:323
Bao G (2013) Effects of different organic matter components in soil on environmental behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Dissertation, Fujian Normal University (In Chinese)
Bao Y (2008) Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of tetracycline antibiotics in soil. Dissertation, Nankai University (In Chinese)
Bao Y, Zhou Q, Wan Y, Xie X (2009) Effects of soil organic matter on adsorption-desorption of oxytetracycline in soil China. Environ Sci 29:651–655 (In Chinese)
Briones RM, Sarmah AK, Padhye LP (2016) A global perspective on the use, occurrence, fate and effects of anti-diabetic drug metformin in natural and engineered ecosystems. Environ Pollut 219:1007–1020
Chang P-H, Li Z, Jiang W-T, Jean J-S (2009) Adsorption and intercalation of tetracycline by swelling clay minerals. Appl Clay Sci 46:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2009.07.002
Chen B, Johnson EJ, Chefetz B, Zhu L, Xing B (2005) Sorption of polar and nonpolar aromatic organic contaminants by plant cuticular materials: role of polarity and accessibility. Environ Sci Technol 39:6138–6146
Chen B, Wu M, Zhang D, Ning P, Zhong Z, Mao Z (2012) Research advance in sorption mechanisms of antibiotics in soil inorganic minerals. Chem Indus Eng Progress 31:193–200 (In Chinese)
Chen K-L, Liu L-C, Chen W-R (2017) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics in high organic content soils. Environ Pollut 231:1163–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.011
Cheng R (2016) Two-stage model predict the time-dependent toxicity of antibiotics and mixtures to Chlorella pyrenoidosa Dissertation, Anhui Jianzhu University (In Chinese)
Fakhri A, Adami S (2014) Adsorption and thermodynamic study of Cephalosporins antibiotics from aqueous solution onto MgO nanoparticles. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:1001–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.09.028
Figueroa RA, Leonard A, Mackay AA (2004) Modeling tetracycline antibiotic sorption to clays. Environ Sci Technol 38:476–483
Figueroa RA, Mackay AA (2005) Sorption of oxytetracycline to iron oxides and iron oxide-rich soils. Environ Sci Technol 39:6664–6671
Fu X, Sheng W, Yao T (1990) Physical chemistry (fourth edition). Higher education press (In Chinese), Beijing
Gélinas Y, Prentice KM, Baldock JA, Hedges JI (2001) An improved thermal oxidation method for the quantification of soot/graphitic black carbon in sediments and soils. Environ Sci Technol 35:3519–3525. https://doi.org/10.1021/es010504c
Gu C, Karthikeyan KG, Sibley SD, Pedersen JA (2007) Complexation of the antibiotic tetracycline with humic acid. Chemosphere 66:1494–1501
Guo X et al (2016) Sorption mechanisms of sulfamethazine to soil humin and its subfractions after sequential treatments. Environ Pollut 221:266
He X, Xi B, Wei Z, Guo X, Li M, An D, Liu H (2011) Spectroscopic characterization of water extractable organic matter during composting of municipal solid waste. Chemosphere 82:541–548
Hendershot WH, Singleton GA, Lavkulich LM (1979) Variation in surface charge characteristics in a soil chronosequence soil. Sci Soc Am J 43:387–389. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1979.03615995004300020030x
Hu J, Zhang H, Peng PA (2006) Fatty acid composition of surface sediments in the subtropical Pearl River estuary and adjacent shelf, Southern China. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 66:346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2005.09.009
Jia M, Wang F, Bian Y, Jin X, Song Y, Kengara FO, Xu R, Jiang X (2013) Effects of pH and metal ions on oxytetracycline sorption to maize-straw-derived biochar. Bioresour Technol 136:87–93
Jia MY, Wang F, Bian YR, Yang XL, Cheng gang GU, Song Y, Jiang X (2014) Influencing factors of cu~ (2+) sorption to straw-derived. Biochar Soils 46(In Chinese):489–497
Jones AD, Bruland GL, Agrawal SG, Vasudevan D (2005) Factors influencing the sorption of oxytetracycline to soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:761–770
Kalbitz K, Schmerwitz J, Schwesig D, Matzner E (2003) Biodegradation of soil-derived dissolved organic matter as related to its properties. Geoderma 113:273–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00365-8
Kolz AC, Ong SK, Moorman TB (2005) Sorption of tylosin onto swine manure. Chemosphere 60:284–289
Korshin GV, Li C-W, Benjamin MM (1997) Monitoring the properties of natural organic matter through UV spectroscopy: a consistent theory. Water Res 31:1787–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00006-7
Kulshrestha P, Jr GR, Aga DS (2004) Investigating the molecular interactions of oxytetracycline in clay and organic matter: insights on factors affecting its mobility in soil. Environ Sci Technol 38:4097–4105
Kümmerer K (2009) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment – a review – part I. Chemosphere 75:417–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.086
Leal RM, Alleoni LR, Tornisielo VL, Regitano JB (2013) Sorption of fluoroquinolones and sulfonamides in 13 Brazilian soils. Chemosphere 92:979–985
LeBoeuf EJ, Weber WJ (1997) A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments. 8. Sorbent organic domains: discovery of a humic acid glass transition and an argument for a polymer-based model. Environ Sci Technol 31:1697–1702. https://doi.org/10.1021/es960626i
Li H, Zhang D, Han X, Xing B (2014) Adsorption of antibiotic ciprofloxacin on carbon nanotubes: pH dependence and thermodynamics. Chemosphere 95:150–155
Liu Q-S, Zheng T, Wang P, Jiang J-P, Li N (2010) Adsorption isotherm, kinetic and mechanism studies of some substituted phenols on activated carbon fibers. Chem Eng J 157:348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.11.013
Mackay AA, Canterbury B (2005) Oxytetracycline sorption to organic matter by metal-bridging. J Environ Qual 34:1964–1971
Mutavdžić Pavlović D, Ćurković L, Grčić I, Šimić I, Župan J (2017) Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic study of ciprofloxacin sorption on sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:10091–10106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8461-3
Nebbioso A, Piccolo A (2013) Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM): a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:109–124
Ni JZ, Luo YM, Wei R, Li XH (2008) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in particle-size separates and density fractions of typical agricultural soils in the Yangtze River Delta, East China. Eur J Soil Sci 59:1020–1026. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2008.01066.x
OECD (2000) Adsorption - desorption using a batch equilibrium method. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals 1:1–44
Okaikue-Woodi FEK, Kelch SE, Schmidt MP, Enid Martinez C, Youngman RE, Aristilde L (2018) Structures and mechanisms in clay nanopore trapping of structurally-different fluoroquinolone antimicrobials. J Colloid Interface Sci 513:367–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.11.020
OuYang T, Zhao Z, Gu X, Li X (2003) FTIR Study on the adsorption of bensulfuron-methyl by goethite. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 23:1097–1100 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2003.06.017
Pan P, Yang J, Deng S, Jiang H, Zhang J, Li L, Shen F (2011) Heavy metals and pesticides co-contamination in. Environ J Agro-Environ Sci 30:1925–1929 (In Chinese)
Peuravuori J, Pihlaja K (1997) Isolation and characterization of natural organic matter from lake water: comparison of isolation with solid adsorption and tangential membrane filtration. Environ Int 23:441–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(97)00049-4
Qin X, Du P, Chen J, Liu F, Wang G, Weng L (2018) Effects of natural organic matter with different properties on levofloxacin adsorption to goethite: experiments and modeling. Chem Eng J 345:425–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.125
Ran Y, Sun K, Yang Y, Xing B, Zeng E (2007) Strong sorption of phenanthrene by condensed organic matter in soils and sediments. Environ Sci Technol 41:3952–3958
Ren L, Ling W-T, Gao Y (2008) Enhanced fixation of phenanthrene in soils amended with exotic organic materials. Chin J Appl Ecol 19:647–652 (In Chinese)
Sakurai K, Ohdate Y, Kyuma K (1989) Potentiometric automatic titration (PAT) method to evaluate zero point of charge (ZPC) of variable charge soils. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 35:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.1989.10434740
Shao ZH, He PJ, Zhang DQ, Shao LM (2009) Characterization of water-extractable organic matter during the biostabilization of municipal solid waste. J Hazard Mater 164:1191–1197
Sheng G, Johnston CT, Teppen BJ, Boyd SA (2001) Potential contributions of smectite clays and organic matter to pesticide retention in soils. J Agric Food Chem 49:2899–2907
Strobel BW, Hansen HCB, Borggaard OK, Andersen MK, Raulund-Rasmussen K (2001) Composition and reactivity of DOC in forest floor soil solutions in relation to tree species and soil type. Biogeochemistry 56:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1011934929379
Sun H, Zhang W (2011) Existing state of hydrophobic organic compounds in soils and sediments. Environ Chem 30:231–241 (In Chinese)
ter Laak TL, Wouter AG, Tolls J (2006) The effect of pH and ionic strength on the sorption of sulfachloropyridazine, tylosin, and oxytetracycline to soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:904–911
Tolls J (2001) Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environ Sci Technol 35:3397–3406
Wahab M, Jellali S, Jedidi N (2010) Ammonium biosorption onto sawdust: FTIR analysis, kinetics and adsorption isotherms modeling. Bioresour Technol 101:5070–5075
Wang D, Xu HY, Yang SK, Wang WK, Wang YH (2018a) Adsorption property and mechanism of oxytetracycline onto willow residues. Int J Env Res Public Health 15(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010008
Wang RZ, Yang SK, Fang J, Wang ZZ, Chen YY, Zhang D, Yang CY (2018b) Characterizing the interaction between antibiotics and humic acid by fluorescence quenching method. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15071458
Wang ZZ, Jiang QL, Wang RZ, Yuan XY, Yang SK, Wang WK, Zhao YQ (2018c) Effects of dissolved organic matter on sorption of oxytetracycline to sediments. Geofluids 2018:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1254529
Wu Q, Mai B, Yang Q, Peng P, Fu J (2004) The distribution state of PAHs and organochlorine pesticides in sediments. China Environ Sci 24:89–93 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.01.021
Yu H, Huang GH, An CJ, Wei J (2011) Combined effects of DOM extracted from site soil/compost and biosurfactant on the sorption and desorption of PAHs in a soil-water system. J Hazard Mater 190:883–890
Yu Y, Zhuang YY, Wang ZH, Qiu MQ (2004) Adsorption of water-soluble dyes onto modified resin. Chemosphere 54:425–430
Zhang M, Wang L, Zheng S (2008) Adsorption and transport characteristics of two exterior-source antibiotics in some agricultural soils. Acta Ecol Sin 28:761–766 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.02.038
Zhao L, Wang C, Yang Z, Zhen X (2017) Ultraviolet-visible and fluorescence characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the fallen leaves of Populus tomentosa. Environ Sci Technol 40:98–102
Zhao X, Bi E (2014) Effects of dissolved organic matter on the sorption of organic pollutants to soils. Environ Chem 33:256–261 (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.02.019
Zhao Y (2013) Study on the adsorption behaviors of ppcps onto sediment in the Weihe River. Dissertation, Chang’an University (In Chinese)
Zhao Y, Geng J, Wang X, Gu X, Gao S (2011) Adsorption of tetracycline onto goethite in the presence of metal cations and humic substances. J Colloid Interface Sci 361:247–251
Zhao YP, Gu XY, Gao SX, Geng JJ, Wang XR (2012) Adsorption of tetracycline (TC) onto montmorillonite: cations and humic acid effects. Geoderma 183:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.03.004
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 41672224], [grant number 41372259], [grant number 41807457]; the National Key Research and Development Program of China [grant number 2016YFC0400701]; and the Henan Province Transportation Science and Technology Project [grant number 2017 J4-1].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Yang, S., Wang, Y. et al. Adsorption characteristics of oxytetracycline by different fractions of organic matter in sedimentary soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 5668–5679 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4028-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4028-1