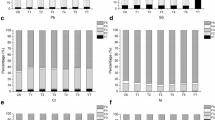
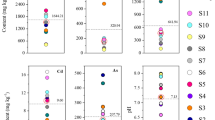
Abstract
Maize fields near Mae Tao Creek in Pha Te Village, Tak Province, Thailand are contaminated with Zn, Cd, and Pb. This research studied the interaction between levels of the metals contaminating the soil and maize development, heavy metal accumulation in the seeds, and the soil bacterial community structure. Our field experiment was carried out in five plots with metal contents that gradually decreased from a high level near the creek to a lower level further into the land: Zn 380–4883 mg kg−1, Cd 6–85 mg kg−1, and Pb 34–154 mg kg−1. Cultivation and isolation on nutrient agar (NA) was utilized to study the culturable bacterial community, and polymerase chain reaction denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE) was utilized for the unculturable bacterial communities. All statistical analyses clearly indicated that rainfall and irrigation were the main factors affecting total Zn concentration and bioavailable Zn, Cd, and Pb in the field. The variation in the contents of the heavy metals was weakly correlated with the culturable bacterial community indices (Shannon-Wiener, evenness and richness), but the contents resulted in a difference in the overall diversity of the bacteria in the soil. The richness, numbers of culturable rhizobacteria, and maize growth stage significantly affected the amount of Zn and Cd that accumulated in the roots. In addition, maize accumulated a high level of Zn in the seeds, while the low contents of Cd and Pb in the seeds were below our limit of detection. The results obtained could be informative for the management of maize cultivation in the area.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkajit P (2015) Review of the current situation of cd contamination in agricultural field in the Mae Sot District, Tak Province, northwestern Thailand. App Envi Res 37:71–82
Baker AJM (1981) Accumulators and excluders-strategies in the response of plants to heavy metals. J Plant Nutr 3:643–654
Barillot CDC, Sarde CO, Bert V, Tarnaud E, Cochet N (2012) A standardized method for the sampling of rhizosphere and rhizoplane soil bacteria associated to a herbaceous root system. Ann Microbiol 63:471–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0491-y
Baudoin E, Benizri E, Guckert A (2002) Impact of growth stage on the bacterial community structure along maize roots, as determined by metabolic and genetic fingerprinting. Appl Soil Ecol 19:135–145
Berendsen RL, Pieterse CMJ, Bakker PAHM (2012) The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci 17:478–486
Bouis HE, Welch RM (2010) Biofortification—a sustainable agricultural strategy for reducing micronutrient malnutrition in the global south. Crop Sci 50:S20–S32
Bray RH, Kurtz LT (1945) Determination of total, organic and available forms of phosphorus in soil. Soil Sci 59:39–45
Brimecombe MJ, de Leij FA, Lynch JM (2001) The effect of root exudates on rhizosphere microbial populations. In: Pinton E, Varanini Z, Nanniperi R (eds) The Rhizosphere: Biochemistry and Organic Substances at Soil-Plant Interface. Springer, Netherlands, pp 95–140
Chaney RL (1989) Toxic element accumulation in soils and crops: protecting soil fertility and agricultural food chains. In: Bar-Yosef B, Barrow NJ, Goldshmid J (eds) Inorganic Contaminants in the Vadose Zone. Springer-Verlag, Germany, pp 140–158
Changsaluk S, Chaikhunpol B, Udomlab N et al (2012) Commercial corn hybrids trial in farmers' field in Tak province in the 3rd phase. In: Proceedings of the 50th Kasetsart University Annual Conference, Kasetsart University, Thailand, pp 207–215
Cheng SF, Huang CY, Lin YC, Lin SC, Chen KL (2015) Phytoremediation of lead using corn in contaminated agricultural land—an in situ study and benefit assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 111:72–77
Chiarini L, Bevivino A, Dalmastri C, Nacamulli C, Tabacchioni S (1998) Influence of plant development, cultivar and soil type on microbial colonization of maize roots. Appl Soil Ecol 8:11–18
Ciampitti IA, Elmore RW, Lauer J (2016) Corn growth and development chart. K-State Research and Extension. http://www.bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF3305.pdf. Accessed 20 July 2017
Da Mota FF, Gomes EA, Marriel IE et al (2008) Bacterial and fungal communities in bulk soil and rhizospheres of aluminum-tolerant and aluminum-sensitive maize (Zea mays L.) lines cultivated in unlimed and limed Cerrado soil. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:805–814
Dandurand LMC, Knudsen GR (2002) Sampling microbes from the rhizosphere and phyllosphere. In: Hurst CJ, Crawford RL, Knudsen GR et al (eds) Manual of environmental microbiology, 2nd edn. ASM Press, Washington, D.C, pp 516–526
Ekasingh B, Gypmantasiri P, Thong-ngam K et al (2004) Maize in Thailand: production systems, constraints, and research priorities. CIMMYT, Mexico
Estefan G, Sommer R, Ryan J (2013) Methods of soil, plant, and water analysis: a manual for the West Asia and North Africa Region, 3rd edn. International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas, Lebanon
Ferguson JE (1990) The heavy elements: chemistry, environmental impact and health effects. Pergamon Press, New York
Figueroa-López AM, Cordero-Ramírez JD, Martínez-Álvarez JC, López-Meyer M, Lizárraga-Sánchez GJ, Félix-Gastélum R, Castro-Martínez C, Maldonado-Mendoza IE (2016) Rhizospheric bacteria of maize with potential for biocontrol of Fusarium verticillioides. SpringerPlus 5:330 1-12
Giller KE, Witter E, Mcgrath SP (1998) Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1389–1414
Gomes NCM, Heuer H, Schönfeld J, Costa R, Mendonça-Hagler L, Smalla K (2001) Bacterial diversity of the rhizosphere of maize (Zea mays) grown in tropical soil studied by temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. Plant Soil 232:167–180
Govindasamy V, Senthilkumar M, Magheshwaran V et al (2010) Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp.: Potential PGPR for sustainable agriculture. In: Maheshwari DK (ed) Plant Growth and Health Promoting Bacteria. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 333–364
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):9
Harley JP, Prescott LM (2002) Laboratory exercises in microbiology, 5th ed. McGraw-Hill Companies, USA
Hazelton P, Murphy B (2007) Interpreting soil test results what do all the number mean?, 2nd ed. CSIRO publishing, Australia
Hill TCJ, Walsh KA, Harris JA, Moffett BF (2003) Using ecological diversity measures with bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43:1–11
Hu Q, Qi HY, Zeng JH et al (2007) Bacterial diversity in soils around a lead and zinc mine. J Environ Sci 19:74–79
Hussein J, Truong P, Ghadiri H et al (2006) Vetiver buffer strips: modelling their effect on sediment and nutrient reduction from surface flow. In: Proceeding of 4th International Vetiver Conference: Vetiver and People, Caracas, Venezuela, pp 1–13
Johnston-Monje D, Lundberg DS, Lazarovits G, Reis VM, Raizada MN (2016) Bacterial populations in juvenile maize rhizospheres originate from both seed and soil. Plant Soil 405:337–355
Jost L (2010) The relation between evenness and diversity. Diversity 2:207–232
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edn. Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton, pp 5–36
Karthik C, Oves M, Thangabalu R, Sharma R, Santhosh SB, Indra Arulselvi P (2016) Cellulosimicrobium funkei-like enhances the growth of Phaseolus vulgaris by modulating oxidative damage under Chromium(VI) toxicity. J Adv Res 7:839–850
Kettler TA, Doran JW, Gilbert TL (2001) Simplified method for soil particle-size determination to accompany soil-quality analyses. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:849–852
Khonsue N, Kittisuwan K, Kumsopa A, Tawinteung N, Prapagdee B (2013) Inoculation of soil with cadmium-resistant bacteria enhances cadmium phytoextraction by Vetiveria nemoralis and Ocimum gratissimum. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1696 1-9
Land Development Department (1998) Soil Analysis. http://www.ldd.go.th/PMQA/2553/Manual/OSD-03.pdf. Accessed 04 July 2017 (in Thai)
Li Z, Xu J, Tang C, Wu J, Muhammad A, Wang H (2006) Application of 16S rDNA PCR amplification and DGGE fingerprinting for detection of shift in microbial community diversity in Cu-, Zn-, and Cd-contaminated paddy soils. Chemosphere 62:1374–1380
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Magurran AE (2004) Measuring biological diversity. Blackwell science Ltd, Hoboken
Marschner P, Crowley D, Yang CH (2004) Development of specific rhizosphere bacterial communities in relation to plant species, nutrition and soil type. Plant Soil 261:199–208
McGrath SP, Cunliffe CH (1985) A simplified method for the extraction of the metals Fe, Zn, Cu, Ni, Cd, Pb, Cr, Co and Mn from soils and sewage sludges. J Sci Food Agric 36:794–798
Mekong Institute (2016) Mekong development report 2016 bringing prosperity from trade to farm, Mekong Institute, Thailand. 71p. http://portal.gms-eoc.org/uploads/resources/2440/attachment/Mekong_Development_Report_r261016.pdf. Accessed 20 July 2017
Miller RO (1998) Nitric-perchloric acid wet digestion in an open vessel. In: Kalra YP (ed) Handbook of reference methods for plant analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 57–62
Mohammadzadeh A, Tavakoli M, Motesharezadeh B, Chaichi MR (2017) Effects of plant growth-promoting bacteria on the phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by sunflower. Arch Agron Soil Sci 63:807–816
Moreira H, Marques APGC, Franco AR, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2014) Phytomanagement of Cd-contaminated soils using maize (Zea mays L.) assisted by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9742–9753
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nihorimbere V, Ongena M, Smargiassi M et al (2011) Beneficial effect of the rhizosphere microbial community for plant growth and health. Biotechnol Agron Soc Environ 15:327–337
Nogueira SF, de Paula AM, Pereira BFF et al (2011) Water type and irrigation time effects on microbial metabolism of a soil cultivated with Bermuda-grass Tifton 85. Braz Arch Biol Technol 54(3):477–486
O’Sullivan LA, Webster G, Fry JC et al (2008) Modified linker-PCR primers facilitate complete sequencing of DGGE DNA fragments. J Microbiol Methods 75:579–581
Palumbo JD, O'Keeffe TL, Abbas HK (2007) Isolation of maize soil and rhizosphere bacteria with antagonistic activity against Aspergillus flavus and Fusarium verticillioides. J Food Prot 70:1615–1621
Piromyou P, Buranabanyat B, Tantasawat P, Tittabutr P, Boonkerd N, Teaumroong N (2011) Effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) inoculation on microbial community structure in rhizosphere of forage corn cultivated in Thailand. Eur J Soil Biol 47:44–54
Prasad MNV, Nakbanpote W (2015) Integrated management of mine waste using biogeotechnologies focusing Thai mines. In: Thangavel P, Sridevi G (eds) Environmental Sustainability: Role of Green Technologies. Springer, India, pp 229–249
Prasad MNV, Nakbanpote W, Sebastian A, Panitlertumpai N, Phadermrod C (2015) Phytomanagement of Padaeng zinc mine waste, Mae Sot District, Tak Province, Thailand. In: Hakeem KR, Sabir M, Ozturk M et al (eds) Soil remediation and plants: prospects and challenges. Elsevier, London, pp 661–687
Qureshi S, Richards BK, Hay AG, Tsai CC, McBride MB, Baveye P, Steenhuis TS (2003) Effect of microbial activity on trace element release from sewage sludge. Environ Sci Technol 37:3361–3366
Rohlf FJ (2009) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system version 2.2. Getting Started Guide. Applied Biostatistics Inc., New York
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold spring harbour laboratory press, New York
Schulte EE, Hopkins BG (1996) Estimation of soil organic matter by weight-loss-on-ignition. In: Magdoff FR et al (eds) Soil Organic Matter: Analysis and Interpretation. Soil Science Society of America, USA, pp 21–23
Sebastian A, Panitlertumpai N, Nakbanpote W et al (2016) Fate of trace elements in rice paddies. In: Rinklebe J, Knox AS, Paller M (eds) Trace elements in waterlogged soils and sediments. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 313–328
Sheoran V, Sheoran AS, Poonia P (2016) Factors affecting phytoextraction: a review. Pedosphere 26:148–166
Simmon K, Deatrick J, Lewis B (2014) Soil sampling. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Science and Ecosystem Support, Division Athens, Georgia
Simmons RW, Pongsakul P, Saiyasitpanich D, Klinphoklap S (2005) Elevated levels of cadmium and zinc in paddy soils and elevated levels of cadmium in rice grain downstream of a zinc mineralized area in Thailand: implications for public health. Environ Geochem Health 27:501–511
Singh JS, Pandey VC, Singh DP (2011) Efficient soil microorganism: a new dimension for sustainable agriculture and environmental development. Agric Ecosyst Environ 140:339–353
Singh M, Awasthi A, Soni SK (2015) Complementarity among plant growth promoting traits in rhizospheric bacterial communities promotes plant growth. Sci Rep 5:15500 1-8
Siripornadulsil S, Siripornadulsil W (2013) Cadmium-tolerant bacteria reduce the uptake of cadmium in rice: potential for microbial bioremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 94:94–103
Sooksamiti P, Totirakul V (2009) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in the creek and sediment around Pha Te Village, Mae Sot District, Tak Province, Thailand. Department of Primary Industries and Mines, Thailand. http://www1.dpim.go.th/dt/pper/000001266808400.pdf. Accessed 21 July 2017 (in Thai)
Sozubek B, Belliturk K, Saglam MT (2014) Cadmium and zinc accumulation in maize influenced by zinc fertilizer in cadmium polluted soil. Turk J Agric Nat Sci 2:1407–1412
Sriprachote A, Kanyawongha P, Ochiai K, Matoh T (2012) Current situation of cadmium-polluted paddy soil, rice and soybean in the Mae Sot District, Tak Province, Thailand. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 58:349–359
Sriprachote A, Pengprecha S, Pengprecha P (2014) Assessment of cadmium and zinc contamination in the soils around Pha Te Village, Mae Sot District, Tak Province, Thailand. App Envi Res 36:67–79
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Thamjedsada T, Chaiwiwatworakul P (2012) Evaluation of cadmium contamination in Mae Tao Creek sediment. Proceeding of International Conference on Sustainable Environmental Technology (ICSET), Century Park Hotel, Bangkok, Thailand
Thewys T, Witters N, Van Slycken S et al (2010) Economic viability of phytoremediation of a cadmium contaminated agricultural area using energy maize. Part I: effect on the farmer's income. Int J Phytoremediation 12:650–662
Treesubsuntorn C, Dhurakit P, Khaksar G et al (2017) Effect of microorganisms on reducing cadmium uptake and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9058-6
Truong PNV, Loch R (2004) Vetiver system for erosion and sediment control. 13th international soil conservation organisation conference, Brisbane, Australia, no. 247, pp 1–6
Unhalekhaka U, Kositanont C (2009) Microbial composition in cadmium contaminated soils around zinc mining area, Thailand. Mod Appl Sci 3:1–8
Vigliotta S, Matrella S, Cicatelli A, Guarino F, Castiglione S (2016) Effects of heavy metals and chelants on phytoremediation capacity and on rhizobacterial communities of maize. J Environ Manag 179:93–102
Wahsha M, Fontana S, Nadimi-Goki M, Bini C (2014) Potentially toxic elements in foodcrops (Triticum aestivum L., Zea mays L.) grown on contaminated soils. J Geochem Explor 147:189–199
Watcharamai T, Saenton S (2013) Leaching of heavy metals from Mae Tao Watershed’s agricultural soils, Mae Sot District, Tak Province. In: Proceeding international graduate research conference 2013, Chiang Mai University, Thailand, ST50–54
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S Ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173(2):697–703
Wenzel WW, Lombi E, Adriano DC (2004) Root and rhizosphere processes in metal hyperaccumulation and phytoremediation technology. In: Prasad MNV (ed) Heavy Metals in Plants: from Biomolecules to Ecosystems. Springer, Berlin, pp 313–344
Wood J, Scott KP, Avgustin G (1998) Estimation of the relative abundance of different bacteroides and Prevotella Ribotypes in gut samples by restriction enzyme profiling of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA gene sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3683–3689
Xie Y, Fan J, Zhu W et al (2016) Effect of heavy metals pollution on soil microbial diversity and bermudagrass genetic variation. Front Plant Sci 7:755
Xue Y, Yue S, Zhang W, Liu D, Cui Z, Chen X, Ye Y, Zou C (2014) Zinc, iron, manganese and copper uptake requirement in response to nitrogen supply and the increased grain yield of summer maize. PLoS One 9:e93895
Yang B, Wang Y, Qian PY (2016) Sensitivity and correlation of hypervariable regions in 16S rRNA genes in phylogenetic analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 17:135 1-8
Zhang Z, Schwartz S, Wagner L (2000) A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol 7:203–214
Zhang L, Zhang L, Song F (2008) Cadmium uptake and distribution by different maize genotypes in maturing stage. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 39:1517–1531
Zhang YQ, Pang LL, Yan P (2013) Zinc fertilizer placement affects zinc content in maize plant. Plant Soil 372:81–92
Acknowledgements
P. Natthawoot gratefully thanks the Junior Science Talent Project and the National Science and Technology Development Agency (NSTDA) for grant no. JSTP-06-54-02E. The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr. Neung Teaumroong, School of Biotechnology, Institute of Agricultural Technology, Suranaree University of Technology for valuable suggestions and support with PCR-DGGE; Dr. Jolyon Dodgson for English proofreading; and the Laboratory Equipment Center, Mahasarakham University; the Faculty of Science and Technology, Rajabhat Mahasarakham University; and Land Development Department Station 5, Khon Kaen Province, Thailand for research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Roberto Terzano
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 410 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panitlertumpai, N., Nakbanpote, W., Sangdee, A. et al. Potentially toxic elements to maize in agricultural soils—microbial approach of rhizospheric and bulk soils and phytoaccumulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 23954–23972 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2427-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2427-y