Abstract
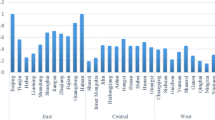
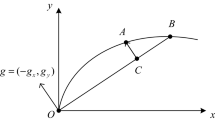
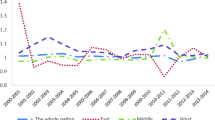
The super-efficiency directional distance function (DDF) with data envelopment analysis (DEA) model (SEDDF-DEA) is more facilitative than to increase traditional method as a rise of energy efficiency in China, which is currently important energy development from Asia-pacific region countries. SEDDF-DEA is promoted as sustained total-factor energy efficiency (TFEE), value added outputs, and Malmquist-Luenberger productivity index (MLPI) to otherwise thorny environmental energy productivity problems with environmental constraint to concrete the means of regression model. This paper assesses the energy efficiency under environmental constraints using panel data covering the years of 2000–2015 in China. Considering the environmental constraints, the results showed that the average TFEE of the whole country followed an upward trend after 2006. The average MLPI score for the whole country increased by 10.57% during 2005–2010, which was mainly due to the progress made in developing and applying environmental technologies. The TFEE of the whole nation was promoted by the accumulation of capital stock, while it was suppressed by excessive production in secondary industries and foreign investment. The primary challenge for the northeast of China is to strengthen industrial transformation and upgrade traditional industries, as well as adjusting the economy and energy structure. The eastern and central regions of the country need to exploit clean- or low-energy industry to improve inefficiencies due to excessive consumption. The western region of China needs to implement renewable energy strategies to promote regional development.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. 2006. IGS, Japan: the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programmer.
References
Andersen P, Petersen NC (1993) A procedure for ranking efficient units in data envelopment analysis. Manag Sci 39:1261–1264
Arabi B, Doraisamy MS, Emrouznejad A, Khoshroo A (2017) Eco-efficiency measurement and material balance principle: an application in power plants Malmquist Luenberger Index. Ann Oper Res 255(1–2):221–239
BP (2017) BP statistical review of world energy, June 2017. Available from: (https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy.html)
Chang Y, Zhang N, Danao D et al (2013) Total energy efficiency analysis of transportation system in China: a non-radial DEA approach. Energy Policy 58(9):277–283
Chang YT, Zhang N, Danao N, Zhang N (2013) Environmental efficiency analysis of transportation system in China: A non-radial DEA approach. Energy Policy 58(9):277–283
Chen L, Liu J, Wang X et al (2014) Analysis on Chinese manufacturing environmental performance based on the direction distance function. J Arid Land Resour Environ 28:17–22
Chen J, Song M, Xu L (2015) Evaluation of total energy efficiency in China using data envelopment analysis. Ecol Indic 52:577–583
Chung Y, Färe R, Grosskopf S (1997) Productivity and undesirable outputs: a directional distance function approach. J Environ Manag 51:29–240
Crossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environmental. Q J Econ CX 2:353–379
Diabat A, Shetty U, Pakkala TPM (2015) Improved efficiency measures through directional distance formulation of data envelopment analysis. Ann Oper Res 229(1):325–346
Du L, Hanley A, Zhang N (2016) Environmental technical efficiency, technology gap and shadow price of coal-fueled power plants in China: a parametric meta-efficiency frontier analysis. Resour Energy Econ 43:15–32
Du J, Chen Y, Huang Y (2017) A modified Malmquist-Luenberger Productivity Index: assessing environmental productivity performance in China. Eur J Oper Res https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2017.01.006
EAPI (2017) Global energy architecture performance index report. World Economic Forum. Available from: (http://reports.weforum.org/global-energy-architecture-performance-index-2017/?doing_wp_cron=1520478806.7356379032135009765625)
Emrouznejad A, Yang GL (2016) A framework for measuring global Malmquiste-Luenberger productivity index with CO2 emissions on Chinese manufacturing industries. Energy 115:840–856
Färe R, Grosskopf SA, Carl A et al (2007) Environmental production functions and environmental directional distance functions. Energy 32:1055–1066
Gang Tian G, Shi J, Sun LC et al (2017) Dynamic changes in the energy–carbon performance of Chinese transportation sector: a meta-frontier non-radial directional distance function approach. Nat Hazards 89(2):585–607
Goto M, Otsuka A, Sueyoshi T (2014) DEA (Data Envelopment Analysis) assessment of operational and environmental efficiencies on Japanese regional industries. Energy 66(4):535–549
Guo W, Sun T, Zhou P (2015) Evaluation of China regional TFEE and its spatial convergence—based on the improved undesirable SBM model. Syst Eng 33:70–80
Halkos GE, Tzereme NG (2009) Exploring the existence of Kuznets curve in countries’ total energy efficiency using DEA window analysis. Ecol Econ 68:2168–2176
Halkos GE, Tzereme NG (2012) The effect of access to improved water sources and sanitation on economic efficiency and growth: The case of Sub-Saharan African countries. South African Journal of Economics 80(2):246–263
Halkos GE, Managi S (2017) Measuring the effect of economic growth on countries’ environmental efficiency: a conditional directional distance function approach. Environ Resour Econ 68:753–775
He W, Liu C, Guo S (2016) Empirical study on evaluation and determinants of atmospheric environmental efficiency of Tianjin. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment 30(1):31–35
Honma S, Hu J (2008) Total-factor energy efficiency of provinces in Japan. Energy Policy 36:821–833
Hu JL, Wang S (2006) Total-factor energy efficiency of provinces in China. Energy Policy 34:3206–3217
Huang Y, Shi Q (2015) Research on total energy efficiency and environmental total factor productivity in China’s regional economies. China Popul Resour Environ 25:25–34
IPCC (2006) IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. Available from: (http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url1/4gcFmt_h2PddckW3nViNAaWYmgFH0xgPKlgysRQgzXtDnAH2e1tg8tMWz3iUkAPv461f7jMcsA3UEfY-BENgdO6fkyyoFKzs6vHrCZ296K1y)
Lee BL, Wilson C, Pasurka CA et al (2017) Sources of airline productivity from carbon emissions: an analysis of operational performance under good and bad outputs. J Prod Anal 47:1–24
Li M, Xie J, Zhang EZ (2014) Convergence of China regional energy efficiency difference—based on China’s provincial data. Economic Science 1:23–38
Li X, Yang J, Liu X (2013) Analysis of Beijing’s total energy efficiency and related factors using a DEA model that considers undesirable outputs. Math Comput Model 58:956–960
Ma HL, Huang DC, Yao HZ (2011) Total-factor energy efficiency analysis of three major economic provinces in China: based on super-DEA and Malmquist. China Popul Resour Environ 21:38–43
Ma X, Liu Y, Wei X et al (2017) Measurement and decomposition of energy efficiency of Northeast China—based on super efficiency DEA model and Malmquist index. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19859–11987
Mai Y, Sun F, Shi L et al (2014) Evaluation of China’s industrial water efficiency based on DEA model. J Arid Land Resour Environ 28:42–47
Meng F, Fan L, Zhou P, Zhou D (2013) Measuring environmental performance in China’s industrial sectors with non-radial DEA. Math Comput Model 58:1047–1056
Munisamy S, Arabi B (2015) Eco-efficiency change in power plants: using a slacks-based measure for the meta-frontier Malmquist-Luenberger productivity index. J Clean Prod 105:218–232
Ramli NA, Munisamy S, Arabi B (2013) Scale directional distance function and its application to the measurement of eco-efficiency in the manufacturing sector. Ann Oper Res 211(1):381–398
Shan HJ (2008) Re-estimating the capital stock of China: 1952-2006. J Quant Tech Econ 10:17–31
Shen M, Cheng Y (2015) China’s industrial water use and pollutants emission efficiency: a study based on provincial data from 2003 to 2012. J China Univ Geosci (Social Sciences Edition) 15:31–40
Sueyoshi T, Yuan Y (2015) China’s regional sustainability and diversified resource allocation: DEA environmental assessment on economic development and air pollution. Energy Econ 49:239–256
Suzuki S, Nijkamp P (2016) An evaluation of energy-environment-economic efficiency for EU, APEC and ASEAN countries: design of a target-oriented DFM model with fixed factors in data envelopment analysis. Energy Policy 88:100–112
Tu ZG, Liu LK (2011) Efficiency evaluation of industrial sectors in China accounting for the energy and environment factors: based on provincial data by a SBM approach. Econ Rev 2:55–65
Vlontzos G, Niavis S, Manos B (2014) A DEA approach for estimating the agricultural energy and environmental efficiency of EU countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 40:91–96
Wang B, Wu Y, Yan P (2010) Total energy efficiency and environmental total factor productivity growth in China’s regional economics. Econ Anal 10:95–109
Wang D, Li S, Sueyoshi T (2014) DEA environmental assessment on U.S. industrial sectors: investment for improvement in operational and environmental performance to attain corporate sustainability. Energy Econ 45:254–267
Wang J, Zhao T, Zhang XH (2016) Energy and environmental unified efficiency of industrial subsectors and its influencing factors in China. Resources Science 38(2):0311–0320
Wang F, Feng GF (2013) Evaluation of China’s regional energy and environmental efficiency based on DEA window model. China Industrial Economics 304(7):56–68
Wang K, Yu S, Zhang W (2013) China’s regional energy and total energy efficiency: A DEA window analysis based dynamic evaluation. Math Comput Model 58:1117–1127
Wang MS, Ji JY (2014) An analysis of energy efficiency and its influential in China—based on SBM-Tobit two stage model. Journal of northeastern university (society Science) 16:584–589
Wang QW, Zhou DQ (2008) An empirical study on the change of total factor energy efficiency in China. Syst Eng 26(7):74–80
Wei C, Shen M (2007) Energy efficiency and energy productivity: a comparison based on the panel data by province. J Quant Tech Econ 9:110–121
Wu F, Fan L, Zhou P et al (2012) Industrial energy efficiency with emissions in China: a nonparametric analysis. Energy Policy 49:164–174
Yagi M, Fujii H, Hoang H, Managi S (2015) Total energy efficiency of energy, materials, and emissions. J Environ Manag 161:206–218
Yang L, Ouyang H, Fang K (2015) Evaluation of regional environmental efficiencies in China based on super-efficiency-DEA. Ecol Indic 51:13–19
Yao X, Zhou H, Zhang A, Li A (2015) Regional energy efficiency, carbon emission performance and technology gaps in China: a meta-frontier non-radial directional distance function analysis. Energy Policy 84:142–154
Yu C, Shi L, Wang Y et al (2016) The eco-efficiency of pulp and paper industry in China: an assessment based on slacks-based measure and Malmquist-Luenberger index. J Clean Prod 127:511–521
Yuan XL, Zhang B, Yang WP (2009) The total factor energy measurement of China based on environmental pollution. China Ind Econ 251:76–86
Zhang W, Wu W (2011) Research on total-factor energy efficiency of metropolitan provinces of Yangtze River Delta based on environmental performance. Econ Res 10:95–109
Zhang W, Zhu Q, Li H (2013) Energy use, carbon emission and China’s total factor carbon emission reduction efficiency. Econ Res 10:138–150
Xiaojun M, Yan L, Xiaoxue W et al (2017) (2017) Measurement and decomposition of energy efficiency of Northeast China—based on super efficiency DEA model and Malmquist index. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19859–11987
Acknowledgements
Furthermore, we are grateful to Prof. Chung-chou Tsai for providing useful advice.
Funding
This study was supported by the Youth Social Society Foundation of School in Jiangsu Province of China (Grant No. Skqn2017002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Xu, Jt. An assessment of energy efficiency based on environmental constraints and its influencing factors in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 16887–16900 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1912-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1912-7