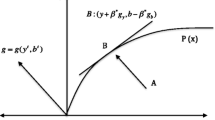
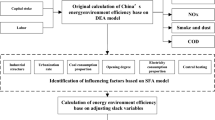
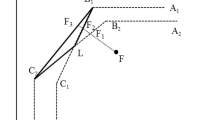
Abstract
To achieve the goal of green development and low-carbon development, the Chinese government has proposed a series of high-quality development and energy efficiency improvement measures. This study constructs two data envelopment analysis (DEA) models using meta-frontier methods to analyze China’s regional and provincial energy efficiency. Compared to traditional DEA models, the proposed models not only integrate technical-level disparities between different regions but also consider integer constraints on variables. The empirical results reveal that there is still great potential for optimization in China’s energy efficiency. There are serious development imbalances in energy efficiency and technology levels in different regions of China. In addition, the efficiency optimization space of each region is discussed from the viewpoints of technology and management. The results show that most provinces need to improve efficiency in terms of management, technology, or both.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigner, D., Lovell, C. K., & Schmidt, P. (1977). Formulation and estimation of stochastic frontier production function models. Journal of econometrics, 6(1), 21–37.
Bi, G. B., Song, W., Zhou, P., & Liang, L. (2014). Does environmental regulation affect energy efficiency in China’s thermal power generation? Empirical evidence from a slacks-based DEA model. Energy Policy, 66, 537–546.
Chambers, R. G., Chung, Y., & Färe, R. (1996). Benefit and distance functions. Journal of Economic Theory, 70(2), 407–419.
Chambers, R. G., Chung, Y., & Färe, R. (1998). Profit, directional distance functions, and nerlovian efficiency. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 98(2), 351–364.
Chang, M. C. (2019). Studying the room for improvement in energy intensity by data envelopment analysis under the meta-frontier framework. Energy Strategy Reviews, 26, 100398.
Chang, M. C., & Hu, J. L. (2019). A long-term meta-frontier analysis of energy and emission efficiencies between G7 and BRICS. Energy Efficiency, 12(4), 879–893.
Chen, Y., Wang, M., Feng, C., Zhou, H., & Wang, K. (2021). Total factor energy efficiency in Chinese manufacturing industry under industry and regional heterogeneities. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 168, 105255.
Cheng, Z., Liu, J., Li, L., & Gu, X. (2020). Research on meta-frontier total-factor energy efficiency and its spatial convergence in Chinese provinces. Energy Economics, 86, 104702.
Chiu, C. R., Liou, J. L., Wu, P. I., & Fang, C. L. (2012). Decomposition of the environmental inefficiency of the meta-frontier with undesirable output. Energy Economics, 34(5), 1392–1399.
Chung, Y. H., Färe, R., & Grosskopf, S. (1997). Productivity and undesirable outputs: A directional distance function approach. Journal of Environmental Management, 51(3), 229–240.
Ding, T., Wu, H., Jia, J., Wei, Y., & Liang, L. (2020). Regional assessment of water-energy nexus in China’s industrial sector: An interactive meta-frontier DEA approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 244, 118797.
Fang, S., Ji, X., Ji, X., & Wu, J. (2018). Sustainable urbanization performance evaluation and benchmarking: An efficiency perspective. Management of Environmental Quality: An International Journal, 29(2), 240–254.
Färe, R., & Grosskopf, S. (2010). Directional distance functions and slacks-based measures of efficiency. European Journal of Operational Research, 200(1), 320–322.
Färe, R., Grosskopf, S., & Pasurka, C. A., Jr. (2007). Environmental production functions and environmental directional distance functions. Energy, 32(7), 1055–1066.
Guo, X., Lu, C. C., Lee, J. H., & Chiu, Y. H. (2017). Applying the dynamic DEA model to evaluate the energy efficiency of OECD countries and China. Energy, 134, 392–399.
Hernández-Sancho, F., Molinos-Senante, M., & Sala-Garrido, R. (2011). Energy efficiency in Spanish wastewater treatment plants: A nonradial DEA approach. Science of the Total Environment, 409(14), 2693–2699.
Lin, B., & Du, K. (2013). Technology gap and China’s regional energy efficiency: A parametric metafrontier approach. Energy Economics, 40, 529–536.
Liu, X., Sun, J., Yang, F., & Wu, J. (2020). How ownership structure affects bank deposits and loan efficiencies: An empirical analysis of Chinese commercial banks. Annals of Operations Research, 290(1), 983–1008.
Long, L. J. (2021). Eco-efficiency and effectiveness evaluation toward sustainable urban development in China: A super-efficiency SBM–DEA with undesirable outputs. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23(10), 14982–14997.
Mohsin, M., Hanif, I., Taghizadeh-Hesary, F., Abbas, Q., & Iqbal, W. (2021). Nexus between energy efficiency and electricity reforms: A DEA-Based way forward for clean power development. Energy Policy, 149, 112052.
O’Donnell, C. J., Rao, D. P., & Battese, G. E. (2008). Metafrontier frameworks for the study of firm-level efficiencies and technology ratios. Empirical Economics, 34(2), 231–255.
Oh, D. H. (2010). A metafrontier approach for measuring an environmentally sensitive productivity growth index. Energy Economics, 32(1), 146–157.
Shi, G. M., Bi, J., & Wang, J. N. (2010). Chinese regional industrial energy efficiency evaluation based on a DEA model of fixing non-energy inputs. Energy Policy, 38(10), 6172–6179.
Song, M., Xie, Q., & Shen, Z. (2021). Impact of green credit on high-efficiency utilization of energy in China considering environmental constraints. Energy Policy, 153, 112267.
Song, M. L., Zhang, L. L., Liu, W., & Fisher, R. (2013). Bootstrap-DEA analysis of BRICS’energy efficiency based on small sample data. Applied Energy, 112, 1049–1055.
Song, M., Zhao, X., & Shang, Y. (2020). The impact of low-carbon city construction on ecological efficiency: Empirical evidence from quasi-natural experiments. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 157, 104777.
Sun, J., Li, G., & Lim, M. K. (2020a). China’s power supply chain sustainability: An analysis of performance and technology gap. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03682-w
Sun, J., Wang, Z., & Zhu, Q. (2020b). Analysis of resource allocation and environmental performance in China’s three major urban agglomerations. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(27), 34289–34299.
Tian, P., & Lin, B. (2018). Regional technology gap in energy utilization in China’s light industry sector: Nonparametric meta-frontier and sequential DEA methods. Journal of Cleaner Production, 178, 880–889.
Wang, N., Chen, J., Yao, S., & Chang, Y. C. (2018). A meta-frontier DEA approach to efficiency comparison of carbon reduction technologies on project level. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 82, 2606–2612.
Wu, A. H., Cao, Y. Y., & Liu, B. (2014). Energy efficiency evaluation for regions in China: An application of DEA and Malmquist indices. Energy Efficiency, 7(3), 429–439.
Wu, J., Zhang, W., & Zhou, Z. (2019). Construction resource allocation for industrial solid waste treatment centers in cities of Anhui Province, China. Management of Environmental Quality: An International Journal, 30(5), 1190–1202.
Xue, L. M., Zheng, Z. X., Meng, S., Li, M., Li, H., & Chen, J. M. (2021). Carbon emission efficiency and spatio-temporal dynamic evolution of the cities in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01751-z
You, Y., Wang, Y., & Li, S. (2021). Effects of eco-policy on Kuwait based upon data envelope analysis. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23(9), 12828–12841.
Zhang, D., Li, M., Ji, X., Wu, J., & Dong, Y. (2019). Revealing potential of energy-saving behind emission reduction: A DEA-based empirical study. Management of Environmental Quality: An International Journal, 30(4), 714–730.
Zhang, N., Zhou, P., & Choi, Y. (2013). Energy efficiency, CO2 emission performance and technology gaps in fossil fuel electricity generation in Korea: A meta-frontier nonradial directional distance function analysis. Energy Policy, 56, 653–662.
Zhou, Z. (2014). Zhixiang. Integer DEA theory, method and application. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China.
Zhou, P., Ang, B. W., & Han, J. Y. (2010). Total factor carbon emission performance: A Malmquist index analysis. Energy Economics, 32(1), 194–201.
Zhou, Z., Xu, G., Wang, C., & Wu, J. (2019). Modeling undesirable output with a DEA approach based on an exponential transformation: An application to measure the energy efficiency of Chinese industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 236, 117717.
Acknowledgements
This research is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Grant Numbers. 72174053, 71871153 and 71971203; Anhui Philosophy and Social Science Foundation under the Grant Number. AHSKY2021D147; the sponsorship of the Collaborative Innovation Center for New Urbanization and Social Governance of Soochow University; the sponsorship of the Tang Scholar of Soochow University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Sun, J. Analysis of China’s regional energy efficiency based on DEA considering integer constraint. Environ Dev Sustain (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02192-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02192-y